What is a Digital Ecosystem, and How Can It Help Your Business?


More and more, businesses are recognizing the benefits of partnerships and connectivity. Six out of the top seven companies in the world have a digital ecosystem in place. They build networks of connected products and partner with other companies, sharing resources and expertise throughout their ecosystem.
You don’t need to be one of the world’s top companies to benefit from creating this type of connected network. Even partnering with one other company will help increase your customer base, brand reach, access to resources, like software infrastructure, and more.
We’ll show you how a healthy digital ecosystem empowers businesses to achieve digital transformation and digital innovation, allowing organizations to be more agile, lower costs, and roll out new products more quickly.
What Is a Digital Ecosystem?
A digital ecosystem is a network of inter-connected companies or products. In some cases, digital ecosystems consist of two or more companies partnering together to offer a wider range of products or services than they could on their own. In other cases, a single company creates an ecosystem of connected products in a suite offering.
Example of a Thriving Digital Ecosystem
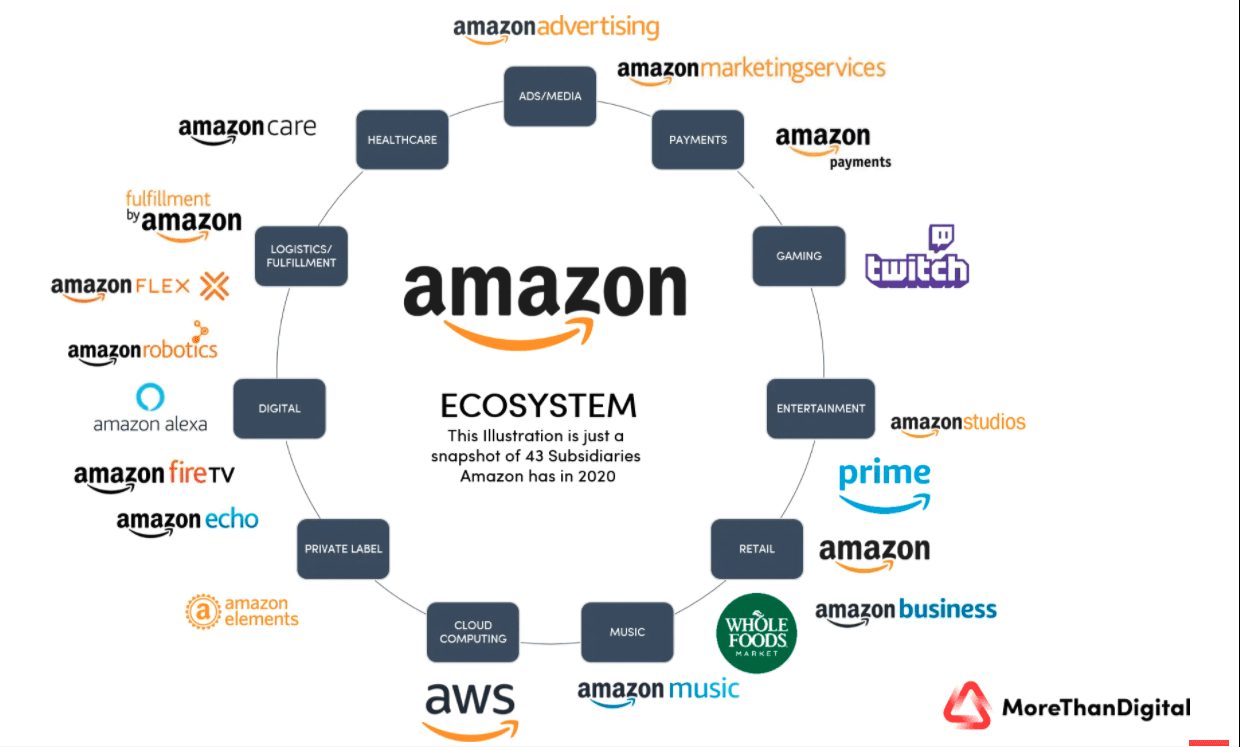
Amazon is one of the world’s top seven companies and a well-known example of a robust digital ecosystem. It has a variety of in-house products and platforms, as well as a network of partnerships with other companies.
One example of Amazon’s ecosystem at work is the new Alexa-integrated Buick. Amazon’s partnership with Buick means Buick gets a value-add for its customers in the form of the built-in virtual assistant. Amazon gets another platform for its voice-activated shopping and search features.
Common Types of Digital Ecosystems
In the example above, Amazon is an “all-encompassing” digital ecosystem, mixing a suite of interconnected products with multi-company partnerships.
However, businesses typically either focus on in-house ecosystems or partnership-based ecosystems. Both approaches have their advantages, but they require different strategies and resource allocation, which is why companies often choose one or the other.
1. In-House Ecosystem
One type of digital ecosystem is when a single company offers a suite of interconnected products. Together, these products address a variety of consumer needs. Often the pieces of the suite work together so that a customer can access extra features or improved functionality if they use more than one.
An example is Microsoft, which offers a range of business products, including a cloud platform, productivity tools, and devices to host all of that software. It is easy for a customer to buy a tablet that already has Microsoft software installed, eliminating the need to go to Microsoft’s competitors for productivity solutions.
2. Multi-Company Partnership
The other primary type of digital ecosystem is when two or more companies partner to offer collaborative products or services. This is not a merger or acquisition—all participating companies contribute to and benefit from the network.
These ecosystems come in many sizes. They might be made up of just two companies or a huge number. Amazon, for example, has a core network of 67 partners.
Bright Pattern, a contact center software company, created a small ecosystem when it partnered with Visual Contact, a customer experience (CX) solutions provider. Bright Pattern and Visual Contact have different specialties: one builds software, and the other provides CX solutions. By working together, they can now offer full-service software and improved CX without hiring or training new teams.
4 Benefits of Building a Digital Ecosystem
Either type of network can have far-reaching benefits for your company. A healthy ecosystem can make your company more agile, help lower costs, and open up new revenue sources.
1. Better prepared for economic change or global issues
A robust set of partnerships or products can help your company adapt to rapid economic changes. If demand drops for one product, you can change your strategy to focus on another without having to start from scratch. Or you can lean on your partner companies. With combined resources, you might be able to pivot more quickly to meet changes in demand.
You can see this in action by looking at how companies with robust ecosystems could adapt to economic changes brought on by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Uber’s in-house ecosystem consists of ride-sharing services and other transportation-based services, such as its food delivery program Uber Eats.
The pandemic caused ride bookings to drop by 75%. But at the same time, demand for Uber Eats more than doubled. Having a strong internal ecosystem enabled the company to withstand what could have been a devastating economic event.
2. Build customer loyalty with a ‘family’ of products
Encourage people to buy from you by offering a suite of interconnected products. It’s more convenient for customers if they can get everything they need in one place. Incentivize them even further by providing package discounts if they buy multiple products at once.
For software companies, offer a single sign-on process. This way users don’t need to make multiple logins for each of your products. This added convenience further encourages them to buy everything from you.
Apple has one of the most complete product families of any company. It sells a full range of products that work together in a user-friendly manner but aren’t easy to pair with non-Apple devices. Apple laptops, tablets, and smartphones all come equipped with Safari (Apple’s browser), iCloud (Apple’s cloud platform), and the Apple App Store. As an added brand-loyalty incentive, Apple offers discounted product packages.

Once a customer has an Apple product, there’s no reason for them to look elsewhere for related devices or services—the company offers just about everything you need. On top of that, Apple products work very well with each other, but they don’t integrate well with products from other companies – meaning easy integration with your existing products and services.
This benefit will continue to grow as consumers and businesses alike adopt IoT-powered smart devices. For example, Google offers smart-powered lights, blinds, home security systems, door locks, and more – all interconnected in a digital ecosystem.
3. Quickly create new revenue streams
Partnering with companies that already have the infrastructure in place allows you to roll out new products or services in a shorter time. In some cases, it can shorten your time-to-product by months. This is the case for companies that partner with Bond, a fintech startup.
Bond connects with companies that want to offer branded banking products, like credit or debit cards. It can take upwards of 18 months for companies to build these products on their own. Partnering with Bond shortens this time considerably because Bond already has all of the software and infrastructure in place.
Another example comes from Alipay, an online payment platform. Alipay worked with partners to expand its lifestyle platform in response to COVID-19. Within three weeks of the onset of the pandemic, the company rolled out multiple new features, including:
- Online consultations with doctors
- Live infection-tracking map
- Insurance offerings for frontline workers
- Food delivery services

In both of these examples, creating a digital ecosystem enabled the business to build new products or features in a much shorter time frame than they could have otherwise achieved.
4. Lower customer acquisition costs
One other way a digital ecosystem can benefit your company is by making it less expensive to acquire new customers. Multi-company ecosystems give you access to an expanded customer base without spending additional money on advertising or other customer acquisition costs (CAC). According to a McKinsey study, banks with robust ecosystems see 10-20% savings on CAC.
In part, this is because of the new features or products you have access to, thanks to the partnership. You can offer these features as a value-add for new customers without the cost of creating them from scratch.
You also lower your CAC costs by adding your partners’ customer base to yours. You can see this in Citibank’s partnerships with PayPal. The company instantly expanded its potential client base to include PayPal’s 300 million customers.
Citibank’s network of partnerships also includes Google. The connection helps Citibank attract younger, more digitally minded customers, and it gives the company access to Google’s data analytics capabilities. Since Google already has analytics tools in place, this is less expensive and time-consuming than if Citibank had to build its own.
Time and budget are both potential barriers to implementing new technology. But partnering with digitally innovative companies can jump-start your digital transformation. Building a digital ecosystem can give you access to customer analytics and data, as well as new digital features or products that would be time-consuming and expensive to try and build in-house.
Request a demo to see how Whatfix empowers organizations to improve end-user adoption and provide on-demand customer support
Thank you for subscribing!


