What Is Vendor Management? (+Challenges, Process, Tools)


Vendor management is the various business processes that organizations go through when working with multiple suppliers and vendors to control costs, reduce risk, and offer excellent service. It empowers companies to optimize costs, reduces potential risks, and ensures high-quality service deliverability – all while managing relationships with dozens of vendors and suppliers.
In this guide, we’ll cover the types of vendor management, break down the entire process into actionable steps, highlight the challenges you should be prepared for, and highlight the best vendor management system (or VMS) to help manage your supplier relationships.
What Is Vendor Management?
Vendor management is a set of practices that businesses follow to find the right vendors and build mutually beneficial relationships with them to control overall cost, reduce risk, and continue to offer excellent servce. It involves vendor analysis, sourcing, contract management, performance reviews, and all the other interactions that you might have with your suppliers.
Often, companies only create processes to manage the first few stages of vendor management – the stages where they source the most cost-effective solution and sign a contract. However, creating an effective vendor management framework offers benefits far beyond just agreeing to a relationship.
Types of Vendor Management
There are nine types of vendor management every company deals with regularly when managing their supplier relationships:
1. Procurement
Procurement is the practice of researching and obtaining products or services critical for performing organization operations.
It’s the first and probably most important stage of vendor management. If you manage to find the right supplier, the rest of the journey shouldn’t be a problem.
Procurement includes the following steps:
- Identifying the need
- Requesting the purchase
- Reviewing the request
- Assessing vendors
- Requesting quotations
- Negotiating and signing a contract
- Receiving supply
2. Vendor onboarding
The other aspect of vendor management is vendor onboarding. It’s the process of providing vendors with all the necessary information, tools, and permissions to activate new suppliers successfully. A solid onboarding process builds the ground for strong buyer-supplier relationships.
During the vendor onboarding process, you’ll:
- Complete risk assessments
- Establish clear expectations and requirements
- Verify vendors’ documents
- Develop an exit strategy
- Implement a communication system
- Provide invoicing details

3. Vendor relationship management
Vendor relationship management (VRM) refers to the process of deepening your relationships with suppliers by ensuring the proper investment into the alliance. The objective of vendor relationship management is to get the maximum possible value from a contractual arrangement.
Here are some of the VRM activities:
- Tracking and documenting disputes
- Collaborating with suppliers
- Running regular performance check-ins
- Inviting vendors to company workshops
- Building a sound contract management strategy
4. Vendor risk management
Vendor risk management, also known as VRM, is a set of activities aimed at reducing the likelihood of suppliers causing business disruptions or taking fraudulent actions.
83% of companies faced a third-party-related incident driving negative consequences for business in the last three years. 59% of respondents confirm that their organizations experienced a data breach caused by one of their suppliers. To mitigate these risks, you’d better perform the assessment process for each of your potential and existing vendors.
There are many risks associated with vendor management, including:
- Cybersecurity risk: possible cyber-attacks or data breach
- Operational risk: business operations disruptions
- Legal and compliance risk: failure to comply with local legislation
- Reputational risk: a negative impact of the partnership on the organization’s image
- Financial risk: revenue loss
5. Performance management
This type of vendor management aims at monitoring and evaluating vendor performance. In other words, it’s a practice of finding out how good your vendors are. To have metrics to compare your vendors’ performance against, you need to set KPIs for service providers and clear standards for product suppliers.
Vendor performance management spots issues with outsourced products or services and provides you with an opportunity to notify vendors about arising problems.
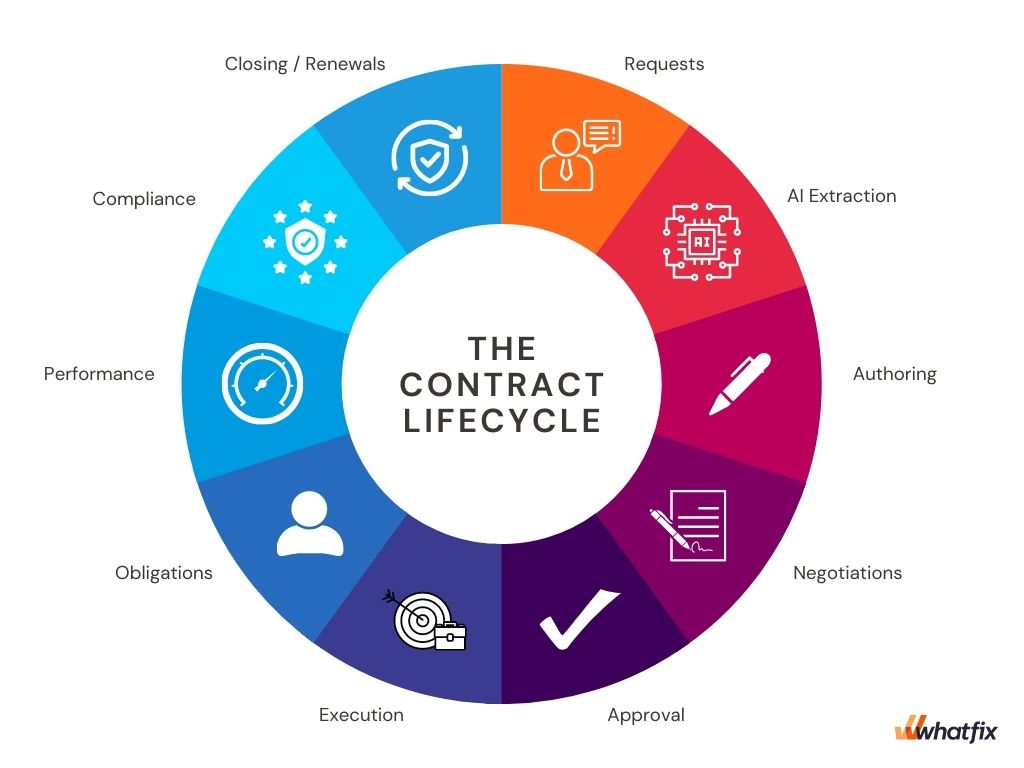
6. Contract management
Vendor contract management is the process of creating and executing vendor contracts to maximize the operational and financial outcomes of the partnership, all while reducing financial risk.
Managing vendor contracts can be a headache for your legal team or procurement managers. You can facilitate it by building a contract management plan and implementing contract lifecycle management (CLM) software or leveraging procurement software. A clear plan will draft the key workflows for the entire contract lifecycle, and software will help you automate the processes and store everything in one place.
7. Compliance management
Vendor compliance refers to requirements that a buyer sets for their vendors in order to regulate the buyer-vendor relationships.
Compliance management is the strategy aimed at assisting both buyers and suppliers to ensure vendors’ compliance with buyers’ statutory, legal, and technical requirements. The key to successful vendor compliance management is drafting a policy that sets clear expectations and provides unambiguous guidelines. When it’s in place, all you need to do is to communicate it to your vendors and keep an eye on their performance.
8. SLA management
Service-level agreements (SLAs) are a contract between a buyer and a vendor that sets the expectations between both parties. It outlines particular aspects of the supply being provided such as how and when the product or service should be delivered, which party is responsible for reporting faults, etc.
SLA management is the practice of keeping track of these contracts and making sure vendors meet the terms outlined there. As a part of SLA management, buyers may also lay out the metrics by which the service or product is measured, as well as the penalties applied if the outlined requirements are not fulfilled.
Benefits of Vendor Management
We’ve already touched upon vendor management benefits such as cost savings and reduced risks. Let’s see the full list of perks coming with a proper vendor management strategy:
1. Better vendor selection
A comprehensive vendor management plan supports the selection of the right strategic vendor partners. By identifying business needs and setting clear expectations, a business can find and invest in high-quality supplies that pay off in the long run.
2. Streamlined processes
When the responsibilities of both a buyer and vendor are outlined, it’s easier to establish smooth workflows. Delivery, compliance, and payments are managed according to a pre-defined scenario, making it easier to guarantee predictable outcomes and an overall more effective procure-to-pay process.
3. More efficient vendor onboarding
Onboarding new vendors and getting them up to speed might take a lot of time and resources. With a vendor management system, new vendors follow a tried and tested path which allows them to navigate through the onboarding process faster.
4. Reduced risk of disruption to supply chain
Vendor management gives you better control over your supply chain and eliminates the risk of disruptions. Having a handle on vendor relationships allows you to obtain critical vendor information promptly and oversee possible issues.
5. Better relationships with vendors
You can’t eliminate the human factor from your vendor relationships. Effective supplier management strengthens loyalty and encourages your vendors to maintain the quality of provided products or services.
6. Reduced costs with more overall efficiency and better vendor rates
As a result of strong vendor relationships, you can achieve better rates and negotiate lucrative deals for your company. Also, having a grasp on your supply chain, you see the hidden costs and gain higher control over your expenses.
Stages of the Vendor Management Process
Here are the six stages involved in the supplier and vendor management process:
1. Discovery, research, and selecting vendors
Vendor management starts with proper research. You need to find a vendor best suited for your needs based on a set of criteria:
- Industry-related experience
- Business management and operations
- Rates
- Associated risks
- Economies of scale
- Social proof
- Terms and conditions
- Legal considerations
When you have all the data at hand, you can make an informed decision and choose the best vendor.
2. Contract negotiations
To set the foundation for long-lasting vendor relationships, you should reach mutually beneficial contract terms in the first place. The negotiation process includes:
- Outlining risks
- Setting security expectations
- Getting visibility into a vendor’s subcontractors
- Agreeing upon KPIs for performance monitoring
- Defining financial terms
It’s good to research your vendor’s business model at this stage and try to understand their objectives. This way, you’ll manage to negotiate the best terms without sacrificing the supply quality.
3. Vendor onboarding
Once the vendor is approved, they’re onboarded into your company’s system. To set them up for success, you’ll need to introduce them to the relevant procedures, establish standards, and set efficient lines of communication.
The vendor onboarding process involves collecting the documentation, sharing permissions, and other activities aimed at integrating a new vendor into the supply chain.
4. Monitoring performance and managing risk
You can’t always be sure that your vendors will keep to the standards set in your contract. That’s why you should be continuously monitoring supplier performance until the contract is terminated.
To make it easy to assess the performance of your vendors, you’d better set KPIs when negotiating contract terms. These might include:
- Order completion time
- Shipping time
- Product or service quality
- Compliance
- Customer service quality
Keep track of these performance metrics and keep open communication with your suppliers to have full control over your supply chain.
5. Payment collection and processing
Strong vendor relationships are based on mutual respect. The best way to show your respect to vendors is by making payments on time, in accordance with the terms outlined in the contract. Vendor management entails building a standardized procedure for processing invoices and making payments, eliminating unnecessary friction from the processes.
6. Feedback from vendors
You aren’t the only party that can share their feedback. It’s important that your vendors also feel encouraged to provide their views of this collaboration. Collecting feedback from vendors will help you get a 360-degree view of the state of things and make more informed decisions.
Challenges of Vendor Management
On your way to a strong vendor management program, you need to overcome certain challenges.
1. Organizing all vendors into one centralized view
You work with dozens of vendors – from coffee capsule suppliers to employee engagement software providers. Organizing and managing them effectively is impossible without suitable processes and tools.
2. Personalizing vendor onboarding and continuous support
You can’t standardize the entire onboarding process when you deal with vendors in completely different sectors. You must find a way to personalize onboarding while delivering a consistent experience.
3. Relying too heavily on certain vendors
With strong buyer-vendor relationships comes the danger of supplier overreliance. What if you lose them? Your business operations will inevitably be disrupted unless you have a supply chain backup plan.
4. Keeping your vendor data clean and compliant
With a vendor management system, your employees that are vendor and supplier-facing will be required to update order and vendor forms. However, companies will have various processes for different vendors and unique workflows for contextual situations.
With a tool like Whatfix, you can provide real-time performance support that helps employees know what data needs to be updated, what is required for each vendor, and in what format it is required – all right inside your vendor management application with smart tips.
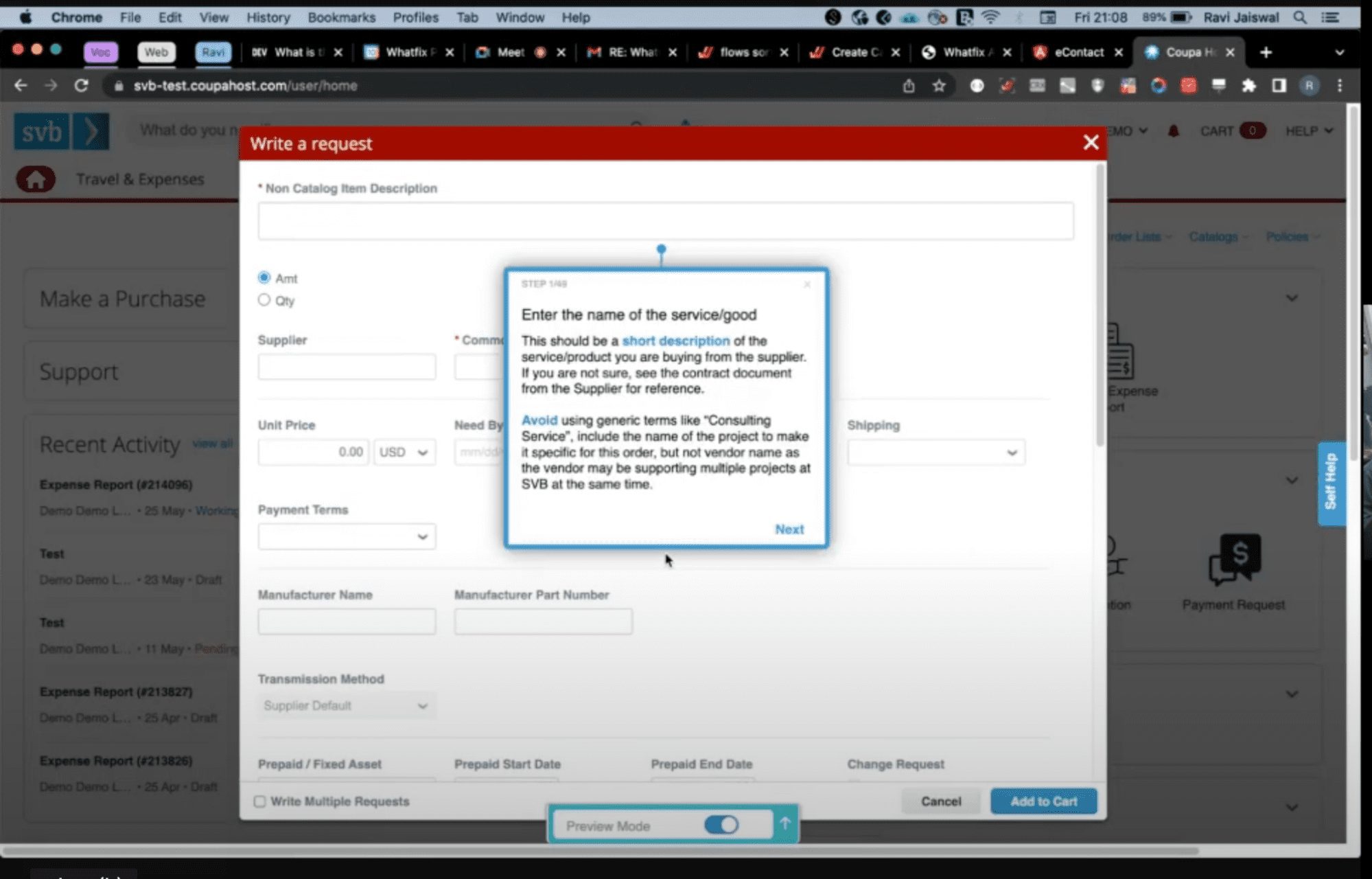
4 Best Vendor Management Software in 2024
The following vendor management systems will help you address supplier and vendor challenges and build streamlined processes.

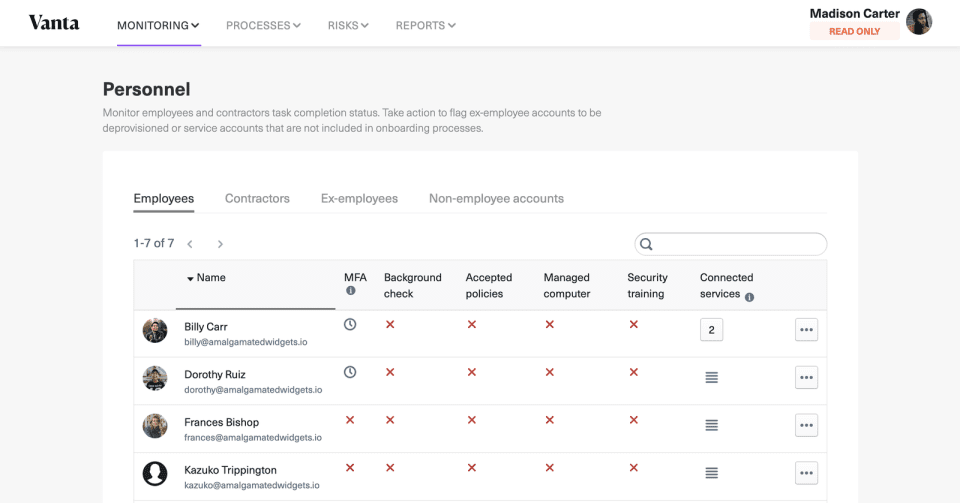
1. Vanta
Vanta is a platform automating the processes of compliance certification for vendors. It makes it easy to craft policies and establish processes to achieve SOC 2, ISO 27001, HIPAA, PCI, and GDPR compliance painless.

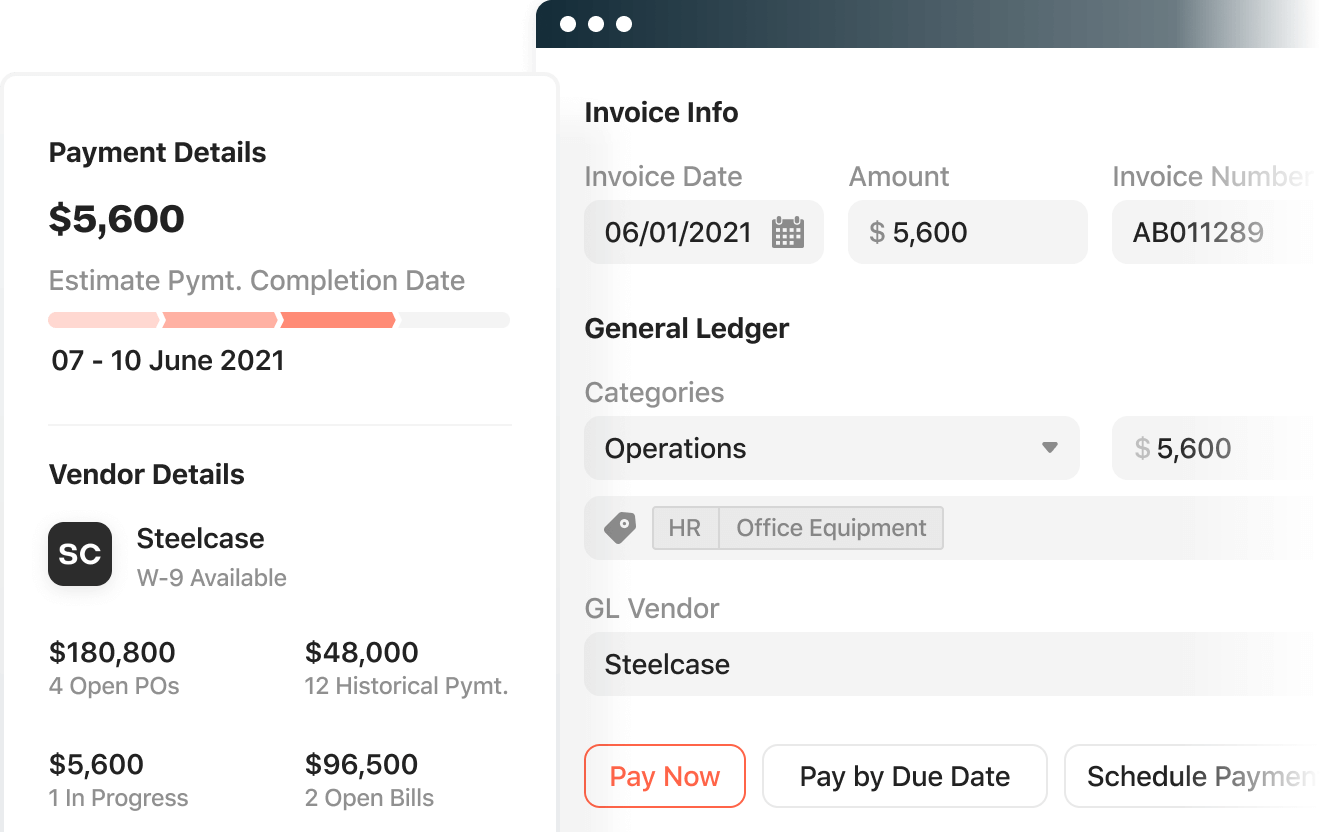
2. Airbase
A spend management platform, Airbase allows companies to take full control of their spending through one interface. It serves as a centralized command and control center that stores vendor details, creates bills from invoices, and supports international vendor payments. With Airbase, users can manage any types of payments such as cards, checks, ACH, vendor credits, and international transfers.

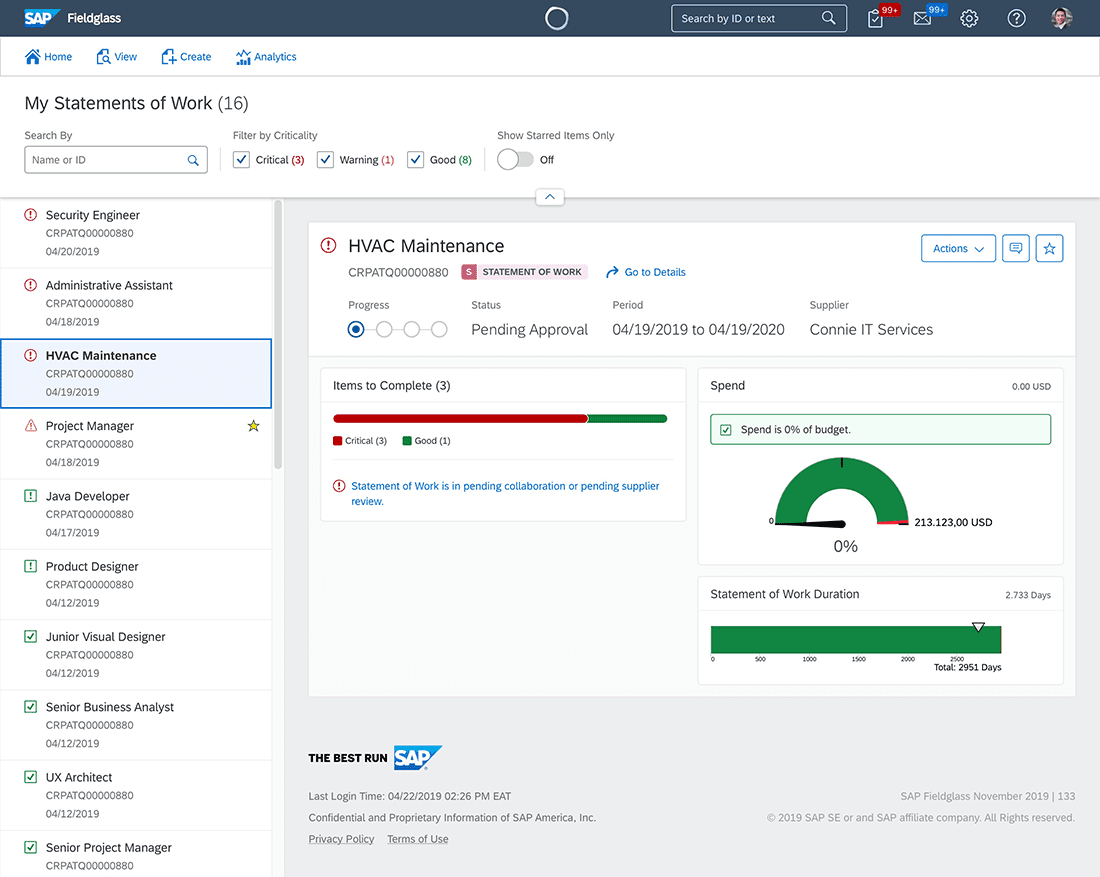
3. SAP Fieldglass
SAP Fieldglass is a comprehensive vendor management system (VMS) that enables organizations to organize, monitor, engage, and pay their vendors from a single app. The platform is best suited for enterprises for its advanced functionality.

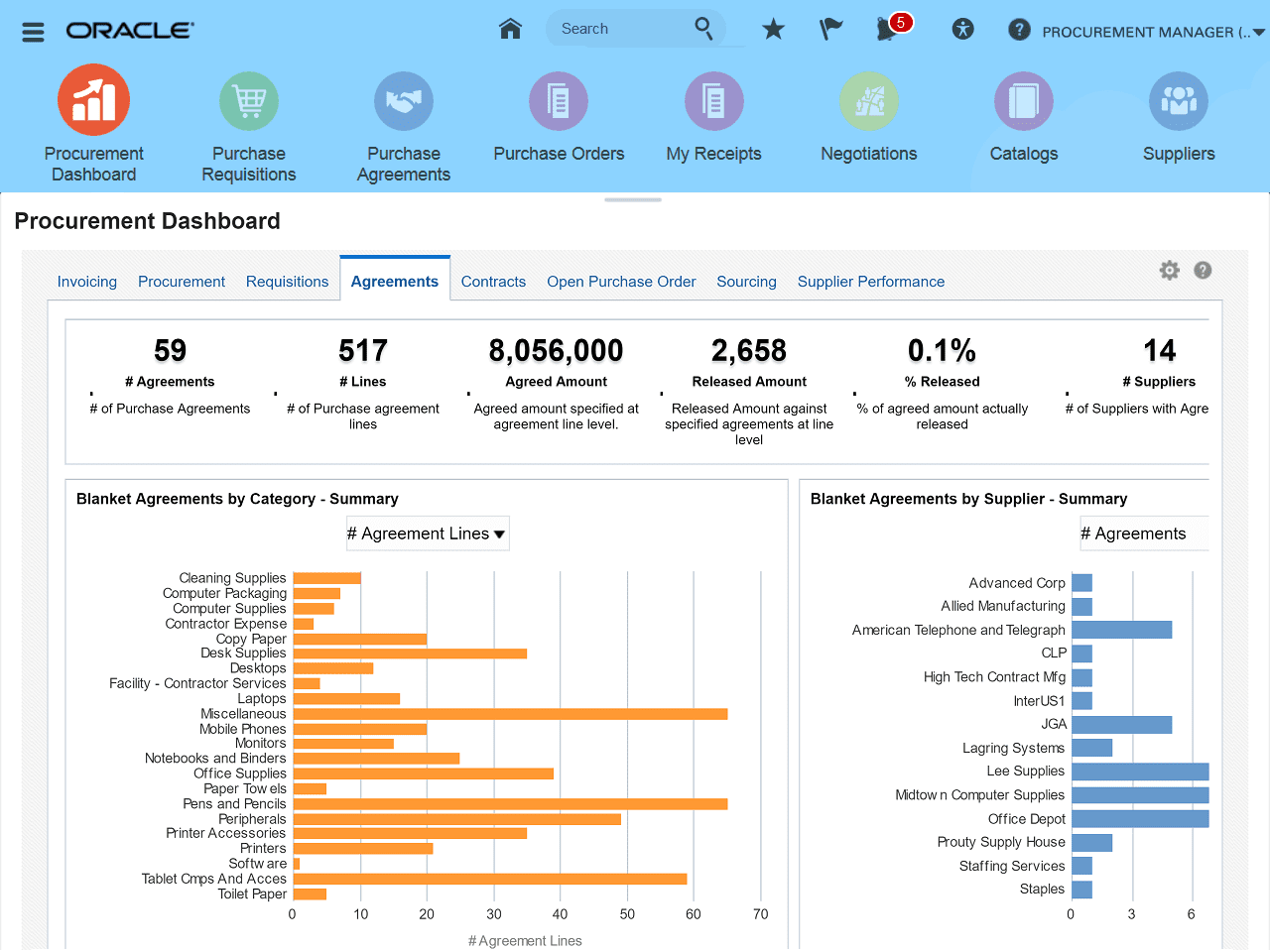
4. Oracle Procurement Cloud
Oracle Procurement presents a tool suite for automating procurement, strategic sourcing, and supplier management processes. Its tools facilitate shopping, order creation, vendor monitoring, payments, reporting, and other processes involved in vendor management.
With Whatfix, drive adoption of your source-to-pay, procurement, and vendor management applications across your suppliers, vendors, procurement teams, and more with contextual in-app guidance.
With Whatfix, you’re empowered to create in-app content such as:
- Interactive walkthroughs
- Step-by-step guides
- Smart tips
- Onboarding task lists
- Embedded knowledge bases
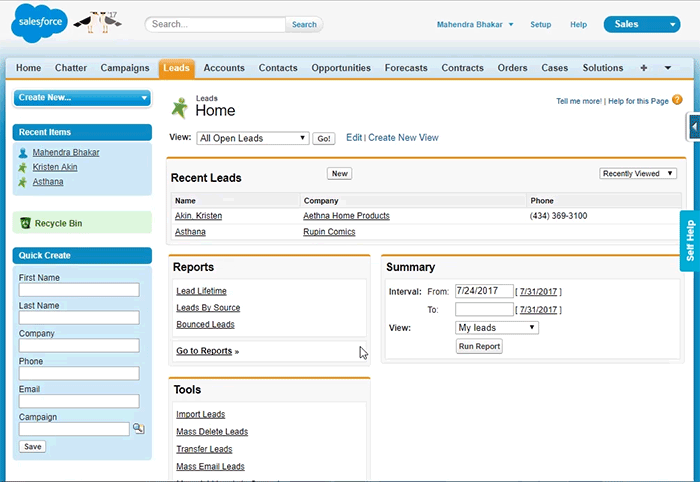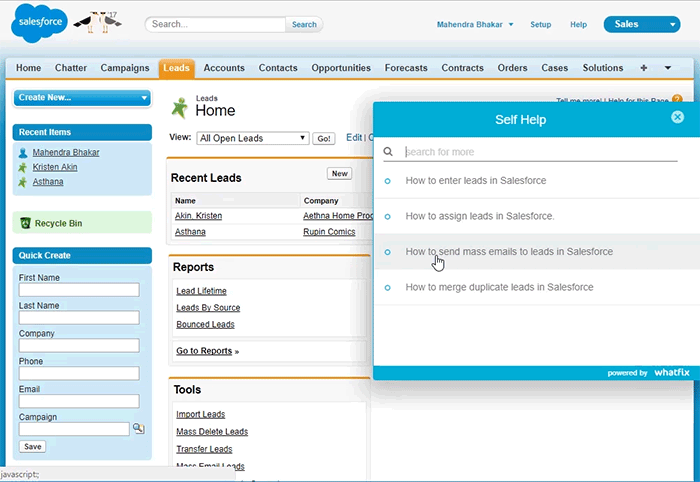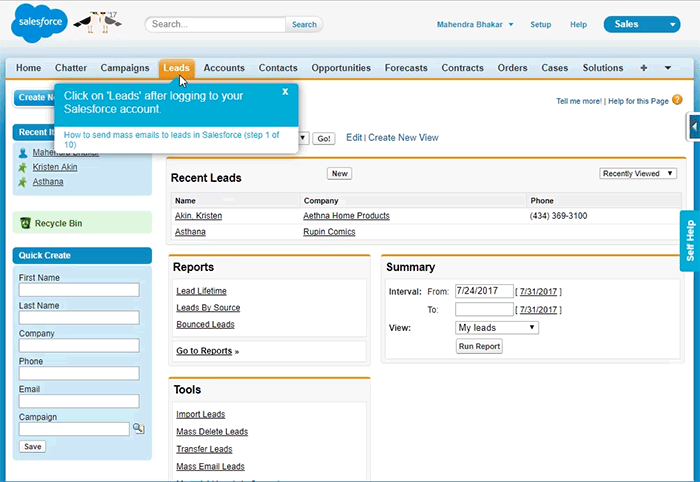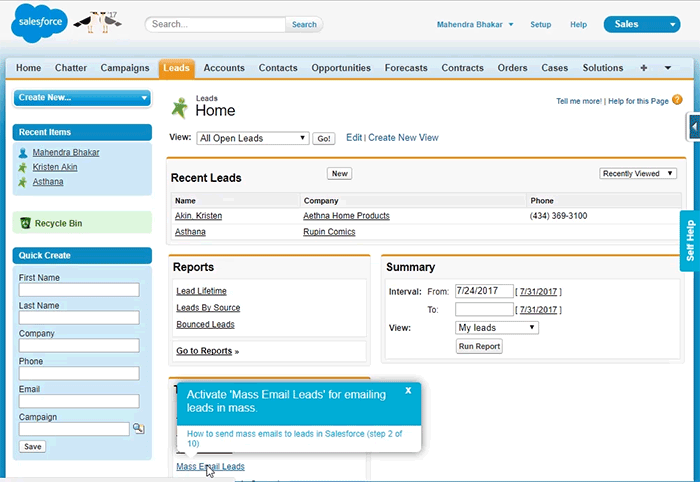
Whatfix lays on top of all modern S2P applications SAP Ariba, Jaggaer, Coupa, iValua, and more – as well as CLM software, procurement tools, CRM systems, and more.
Whatfix is also a fantastic solution for providing personalized, guided onboarding and on-demand self-support for your vendors.
Learn more about Whatfix for S2P applications and vendor management now!
Request a demo to see how Whatfix empowers organizations to improve end-user S2P application adoption, create effective vendor onboarding experiences, and provide on-demand vendor and customer self-support
Thank you for subscribing!