What Is Procurement? Types, Best Practices, Metrics
- Published:
- Updated: July 19, 2024

To maintain profitability, businesses must think strategically about selecting and purchasing their goods and services.
What happens to an organization that can’t ensure a timely supply of goods and services critical for business operations? It inevitably lags behind the competition. The solution? An effective procurement process.
By implementing digital procurement strategies, companies can reduce their operational costs, enhance the quality of their software, streamline their business processes, and promote transparency across all levels of the organization. These efforts can help drive growth, increase profitability, and improve competitiveness.
In this article, we’ll explore what procurement means for your business, how to implement it successfully, challenges to anticipate, and leading software solutions to consider.
What Is Procurement?
Procurement is the act of sourcing and obtaining goods and services necessary for maintaining business processes. It’s the overall process of purchase planning, specification determination, research, sourcing, pricing negotiations, purchasing decisions, and further supply control.
The ultimate goal of procurement is investing in high-quality, cost-effective supplies that deliver the highest possible value for the business.
Procurement vs. purchasing
Are procurement and purchasing the same? They seem similar but are different.
Procurement involves multiple steps, from identifying the need to keeping the records. Purchasing focuses on transactions and is a part of the procurement process.
Let’s look at the key differences between procurement and purchasing:
| Procurement | Purchasing |
| Long-term, strategic approach | Short-term, transaction-focused |
| Starts long before the purchase decision and continues after the transaction happens | Limited to the purchasing process |
| Aims at getting the highest value out of the solution | Aims at identifying the solution with the best price |
| Builds long-lasting relationships with vendors | Doesn’t involve vendor relationship management |
| Proactive approach: identifies the need | Reactive approach: fulfills the need that’s been identified previously |
Simply put, when investing in a new CRM software, you’ll be involved in procurement management since you’re looking for a vendor to supply you with a CRM.
Buying a new piece of equipment, like a new monitor or desk, would be considered purchasing. This could become procurement once you find a vendor supplying you with those new monitors or desks to scale and streamline that purchasing process.
Procurement vs. strategic sourcing
If you dig deeper into procurement management, you’ll notice it often goes hand in hand with strategic sourcing. Instead of comparing the two, it’s best to consider strategic sourcing as a part of procurement in a broader sense.
Strategic sourcing is the process of developing and maintaining a supply chain infrastructure to optimize a business’s supply base and ensure the lowest possible costs. On the other hand, procurement leverages the existing supply chains to ensure a steady flow of supplies.
Sourcing uses insights from procurement for managing supplier relationships, while procurement builds on that foundation to obtain requisitions.
One example of strategic sourcing is negotiating a longer contract with a software vendor at a lower monthly rate. In this way, strategic sourcing can be considered an extension of the procurement process.
Types of Procurement
Procurement is multifaceted, and businesses can undertake four fundamental types: direct, indirect, goods, and services.
Understanding the nuances of each type of procurement is essential for organizations to optimize their purchasing strategies. Organizations can streamline their processes, reduce costs, and improve overall efficiency by identifying which type of procurement is required for each purchase. Here’s a definition of each type of procurement:
- Direct Procurement: Direct procurement is the process of obtaining goods or services that directly impact the company’s bottom line. For example, direct procurement for a smartphone manufacturer would involve acquiring resources like chips, processors, and screens essential to the product offering.
- Indirect Procurement: Indirect procurement involves sourcing supplies for daily business operations. It improves profitability by optimizing processes and reducing production costs. One example of indirect procurement is investing in CRM software to streamline sales and customer management. Your company can still deliver products or services without this software, but it won’t be as effective as using a sophisticated CRM.
- Goods Procurement: Goods procurement involves purchasing physical products a company needs to operate. This can be basic, like office supplies for traditional workplaces, or core to business operations, like a restaurant acquiring food and ingredients or a manufacturing plant sourcing raw materials.
- Services Procurement: Services procurement, or strategic sourcing, involves hiring contractors or agencies to meet specific organizational needs, like optimizing processes, developing end products, or achieving other project-based goals. An example of services procurement includes signing a contract with a marketing consultant who will help you set up paid advertising campaigns.
What Is the Procurement Life Cycle?
Procurement and the procurement life cycle are closely related concepts in supply chain management, but they refer to different aspects of the process.
While procurement refers to the overall process of obtaining goods and services from external sources, the procurement life cycle, also known as the procurement process, refers to the specific stages that make up the procurement process. It’s a subset of the broader procurement concept and details the step-by-step stages of the procurement of goods or services. The procurement life cycle approach emphasizes long-term strategic procurement management, including optimizing procurement activities and relationships over time.
8 Steps in the Procurement Lifecycle Flow
The procure-to-pay process flow can be split into eight steps:
- Need identification: Begin by recognizing the necessity for a specific good or service to prevent future disruptions.
- Purchase requisition: Document the specifications, budget, objectives, and timeline, and conduct preliminary vendor research.
- Review of request: The requisition is reviewed and either approved or denied based on budget alignment and specifications.
- Vendor assessment: Evaluate potential suppliers to determine who best meets the procurement criteria.
- Quotation request: Request detailed proposals from shortlisted vendors to compare and select the best offer.
- Negotiation and contract: Discuss and finalize contractual terms with the chosen supplier to ensure the best deal.
- Receiving supply: Inspect the delivered goods or services to confirm they meet the required specifications.
- Supplier relationship management: Maintain and enhance the relationship through regular communication and feedback.
✓ Thank you, the checklist will be sent to your email
What Is Procurement Management?
Procurement management is the strategic approach to managing and optimizing an organization’s procurement activities. It involves planning, implementing, and controlling the processes used to purchase goods and services from external sources. The goal of procurement management is to ensure that these items are acquired in a cost-effective way, while meeting the company’s standards of quality, quantity, time, and location.
At its core, procurement management includes selecting suppliers, negotiating terms and prices, ensuring compliance with contracts and regulations, and managing ongoing relationships with vendors. This function is crucial to an organization’s overall financial health, directly affecting the cost of goods sold and the quality of products or services delivered. Effective procurement management helps organizations avoid unnecessary costs, enhances profit margins, and supports operational efficiency.
The role of procurement management extends beyond transactional activities to involve strategic duties such as risk assessment, market analysis, and the integration of new technologies. These strategic components help organizations adapt to market changes, anticipate risks, and leverage opportunities in the supply chain to remain competitive and maintain operational sustainability.
Benefits of Procurement Management
To fully experience the benefits of procurement, companies hire procurement managers or even build dedicated teams. What makes them do it? Why should your company bother procurement management?
Here’s why you should prioritize procurement in your organization:
1. Increases cost savings
The procurement process lets you identify and source the most cost-efficient resources possible. But beyond that, establishing an effective procurement process involves developing a centralized approach to supply sourcing, cost management, e-invoicing, and tracking. A resulting central database provides all the tools for receiving timely reports, tracking vendors, and, most importantly, identifying cost-reduction opportunities in the long term.
2. Improves supplier relationship management
Supplier relationship management (SRM) allows you to not only get more lucrative deals, but also maintain an uninterrupted supply of goods and services critical to organizational functioning.
Procurement builds a foundation for successful supplier relationship management by setting clear expectations with suppliers. The strategic approach focuses on fostering mutually beneficial relationships with vendors, ensuring both sides are interested and invested in the continuous partnership.
3. Boosts process efficiency and automation
Procurement technology is a powerful driver of organizational efficiency. It automates and streamlines strategic sourcing processes, reduces supply chain risks, and optimizes repetitive tasks like research and reporting.
4. Standardizes contract lifecycle
An established procurement process creates a standardized contract lifecycle management procedure. The contract lifecycle management includes all the key stages, from contract creation to termination or renewal. Without a standardized process, contract lifecycle management can become another costly expenditure for your organization.
Procurement drives the standardization of the contract lifecycle by developing contract templates, using predefined language, and storing all the data that can be retrieved and/or reused in a centralized system.
Procurement KPIs & Metrics to Monitor
Measuring the effectiveness of the procurement efforts is the crucial step toward building a solid process. Here are essential procurement metrics to track, analyze, and optimize your source-to-pay activities and processes:
- Purchase order cycle time: The average time it takes to process requisitions and transmit purchase orders to vendors.
- Supplier lead time: The average time between sending a purchase order and receiving supplies.
- Supplier defect rate: The number of procured products or services that don’t meet quality specifications out of the total number of supplies.
- Supplier Onboarding Time: Measures the time taken to onboard a new supplier, including due diligence, contract negotiation, and system integration. Shorter onboarding times speed up the procurement process.
- Fulfillment accuracy: Measures the number of accurately fulfilled orders out of the total number of orders.
- Spend Under Management: Indicates the percentage of total procurement spend that is managed through formal procurement processes. Higher percentages suggest better control and oversight of spending.
- Order-to-Cash Cycle Time: Tracks the time from placing an order with a supplier to receiving the payment. Reducing this time improves cash flow and operational efficiency.
- First-Time Match Rate: The percentage of invoices that match the purchase order and goods receipt the first time without discrepancies. Higher match rates reduce the need for manual intervention and rework.
- Touchless Invoice Processing Rate: The percentage of invoices processed without manual intervention. High rates of touchless processing signify effective automation and streamlined workflows.
- Contract Approval Cycle Time: Tracks the time taken to review, approve, and finalize contracts. Reducing this cycle time accelerates the procurement process and enhances agility.
Procurement Process Accuracy: The rate of errors in procurement processes, such as incorrect orders or payments. Higher accuracy minimizes costly rework and disruptions.
5 Best Practices to Optimize the Procurement Process
So how do you drive procurement successfully? We’ve highlighted the five best practices for optimizing the procurement process:
1. Risk identification and mitigation
Be mindful of the risks involved in making a purchase decision and implement risk management processes to predict and prevent possible issues. Price fluctuations, inaccurate forecasting, and supply disruptions can impact your supplier relationships and put your organization at risk. To mitigate those risks, develop a response strategy that involves diversifying suppliers, implementing supply chain management software, and defining clear terms for terminating contracts.
2. Inventory optimization
Inventory optimization involves managing a business’s inventory levels to ensure they remain appropriate for both present and future needs. This process involves maintaining a delicate balance between preventing stock shortages and simultaneously avoiding the problems associated with overstocking.
3. Strengthen vendor management practices
To establish long-term relationships with vendors, it’s important to have a vendor management strategy in place. This involves simplifying the processes of invoice processing, communication, and vendor monitoring. By creating a single system for managing vendor relationships, you can ensure open communication and accountability on both sides.
4. Establish a custom workflow
There’s no one-size-fits-all strategy. You need to develop a workflow that works for your specific needs. With a structured procurement workflow in place, you’ll be able to spend less time managing the process and more time researching the information necessary to make informed decisions.
5. Automate the procurement process with eProcurement solutions
Performing the procurement process manually is time-consuming and prone to errors. Automation allows you to optimize supply chains, relieve staff of routine tasks, and free up time for more important processes, like improving vendor relationships or finding more cost-effective supplies.
Common Procurement Process Challenges
As procurement evolves, organizations face challenges that significantly impact efficiency, cost management, and overall operational effectiveness. Each challenge presents unique complications that demand specific strategies and tools for effective management.
Here are some of the most common procurement challenges that organizations encounter today:
1. Risk management
Risk management involves foreseeing and mitigating potential threats that disrupt the supply chain or impact the financial stability of an organization. These risks range from supplier insolvency and geopolitical instability to unpredictable market dynamics and natural disasters. Effective risk management is critical because it helps organizations maintain operational continuity and safeguard their reputation.
The challenge intensifies as organizations expand globally, with each market introducing its unique set of risks. Without a comprehensive risk management strategy, companies may face significant disruptions, unexpected costs, and potential legal or regulatory penalties. The dynamic nature of risks necessitates an agile and proactive approach to risk identification, assessment, and response.
Leveraging digital transformation tools like Whatfix can significantly enhance your organization’s risk management capabilities. Whatfix can integrate seamlessly with your procurement tools to facilitate real-time risk monitoring and reporting, offering guided analytics and insights that help predict and mitigate risks before they escalate. This approach not only streamlines the risk management process, but also enhances its effectiveness by making critical data easily accessible and actionable.
2 Supplier management
Supplier management is a cornerstone of effective procurement. It focuses on establishing and nurturing supplier relationships to ensure reliable and cost-effective access to goods and services. The challenge involves more than just selecting suppliers—it encompasses ongoing performance monitoring, quality assurance, and contract management to ensure suppliers meet agreed-upon standards and deadlines.
The complexity of supplier management grows with the scale of operations. Companies have to balance multiple relationships, often across different regions with varying legal and cultural environments. Mismanagement in this area can lead to supply chain inefficiencies and quality issues, damage business relationships, or lead to legal disputes.
3. Inaccurate data
Accurate data is the backbone of effective procurement decision-making. Inaccurate data can arise from manual data entry errors, outdated information, or incomplete data collection. These inaccuracies can lead to poor supplier choices, incorrect stock levels, and even financial losses.
The challenge is not only in collecting accurate data, but also in maintaining its accuracy over time. Data may become outdated quickly in fast-moving markets, making it hard to align procurement decisions with current realities.
Whatfix can help mitigate issues of inaccurate data by ensuring that procurement systems are used correctly and efficiently. Whatfix guides can lead users through complex data entry processes, reduce errors, and help maintain the integrity of procurement data through interactive, real-time support.
4. Lack of stakeholder engagement
Stakeholder engagement in procurement is crucial because it ensures that the requirements and expectations of various departments are met. Lack of engagement can lead to resistance to change and misaligned goals, resulting in procurement decisions that don’t adequately support the overall business strategy or meet operational needs.
5. Supply chain disruptions
Supply chain disruptions can significantly impact procurement by causing delays, increasing costs, and reducing the overall quality of goods and services. These disruptions may result from various factors, like natural disasters, geopolitical tensions, or pandemics. Managing these disruptions effectively is critical to maintaining steady business operations and meeting customer expectations.
The challenge is not just in responding to disruptions when they occur, but also in anticipating and mitigating potential risks proactively. This requires robust planning and a deep understanding of the entire supply chain to identify vulnerabilities before they lead to critical issues.
6. Contract management
Contract management involves negotiating the contract terms and conditions and ensuring compliance with those terms during the agreement’s period. Effective contract management ensures that both parties fulfill their expected obligations, which helps maintain a good relationship and avoid legal disputes.
One challenge in contract management is the volume of contracts that a company may enter into, as well as the detail and variability of these contracts. Another difficulty is ensuring that contracts are up-to-date with current laws and regulations, which can frequently change.
Companies can streamline the contract lifecycle process by integrating Whatfix with their contract management systems. Whatfix guides help users navigate complex contract management tools, ensuring that all steps from creation and approval to renewal and archiving are handled efficiently and in compliance with current standards.
7. Inefficient processes
Inefficient procurement processes can lead to significant time and resource wastage. These inefficiencies often stem from outdated procedures, manual handling of tasks, or a lack of integration between different procurement systems. Streamlining these processes is crucial for reducing costs and improving the speed and quality of procurement activities.
Automating routine tasks and improving the flow of information between different procurement stages can boost efficiency tenfold. But the challenge lies in identifying the specific areas of inefficiency and implementing the appropriate technological solutions without disrupting existing operations.
Whatfix can help to address these inefficiencies by providing step-by-step guidance on using procurement automation tools. This not only helps reduce the learning curve associated with adopting new technologies, but also ensures that improvements are implemented consistently and effectively across an organization.
8. Invisible spend
Invisible spending refers to any spending that occurs outside of the controlled procurement processes, often leading to unreported or misclassified expenditures. This can create a significant gap in financial planning and analysis, making it difficult for organizations to accurately track and manage their overall spending.
The primary challenge in managing invisible spend is gaining visibility into all company transactions and ensuring they adhere to procurement policies. Without visibility, budget overruns and non-compliant purchases can occur, which can impact an organization’s financial health.
9. Inflation
Inflation affects procurement by increasing the costs of goods and services. This presents a significant challenge as it can quickly erode profit margins and disrupt budget allocations. Companies have to navigate these increases while maintaining quality and service without passing on excessive costs to customers. Inflation can be unpredictable and varies by region and sector, requiring a flexible and responsive approach to procurement strategy.
Managing inflation effectively involves long-term contracts to lock in prices, diversifying supplier bases to mitigate risks from any geographic location, and constantly monitoring market trends for better procurement decisions. But maintaining operations effectively under inflationary pressure also means adjusting quickly to cost changes, which can be hard without agile processes in place.
10. Fraud risk
Fraud risk in procurement includes bribery, corruption, or kickbacks, and it poses a serious threat to an organization’s financial and ethical standing. Detecting and preventing fraud is essential for maintaining trust and integrity. Fraud can be sophisticated and hidden, often involving collusion between insiders and external parties.
Organizations need to implement stringent controls, regular audits, and transparent processes to combat fraud effectively. Educating employees about ethical practices and setting up a secure whistleblowing framework are also crucial measures. Continuous monitoring and reporting can help identify and address fraudulent activities early, protecting an organization from potential financial and reputational damage.
Example of Enterprise Procurement
The World Bank introduced a procurement framework promoting tailored procurement approaches that emphasize choice, quality, and adaptation. The goal was to determine the best value for the money invested.
The framework consists of four points:
- A Project Procurement Strategy for Development (PPSD) assesses a project’s requirements and risks, revealing the most effective ways for an organization to interact with potential suppliers.
- All procurements funded by the World Bank are guided by the principle of obtaining the best value for money. This means that the focus is not solely on selecting the lowest-cost suppliers, but on choosing those that offer the best overall cost and value in the long run.
- Any concerns during the procurement process are resolved before the contract is signed.
- The World Bank assists in contract management of high-value and high-risk procurements to resolve possible problems quickly and ensure the best business outcomes.
5 Best Procurement Software Tools in 2024
Streamlining and automating the procurement management process is only possible with technology. These are some of the best procurement software tools that will help you build a more effective procurement flow:

1. Coupa
- G2 Rating: 4.1 out of 5 stars
- Pricing: Feature-based pricing
As a procurement management solution, Coupa aims to simplify purchase requisition and order processes for all users. Inside a central repository, procurement managers can easily store and manage contracts, mass update terms, and terminate contracts in bulk. You can learn more from our post on Coupa implementation.
2. SAP Ariba
- G2 Rating: 3.9 out of 5 stars
- Pricing: Custom-pricing
SAP Ariba provides procurement and supply chain solutions enabling more effective collaboration on contract management, control of suppliers, invoicing, etc. It’s a sophisticated solution for large companies and enterprises willing to automate the entire procurement lifecycle.

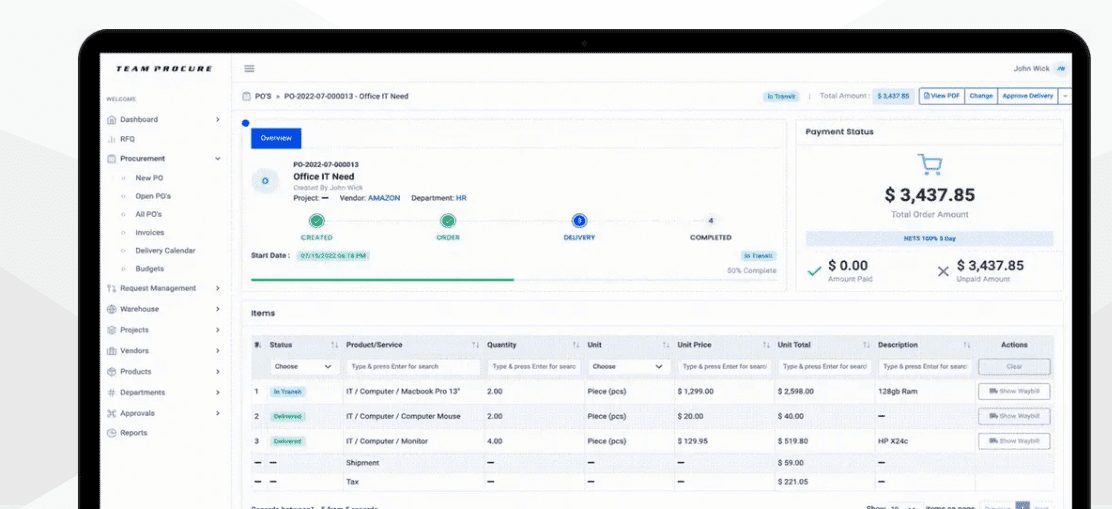
3. Team Procure
- G2 Rating: 6 out of 5 stars
- Pricing: Starts at $250 per month for 3 users, contact for enterprise pricing.
Team Procure is a cloud procurement platform that covers everything from purchase requests and orders to supplier and warehouse management. It offers platforms and tools for every size business and has custom API integrations to meet your unique needs.

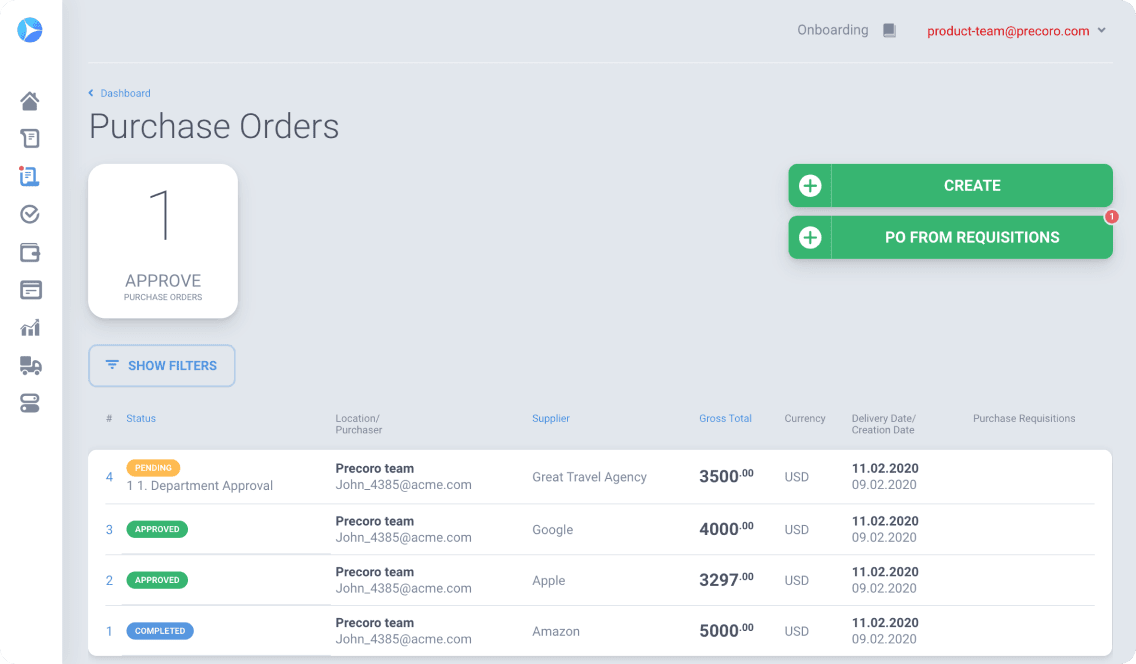
4. Precoro
- G2 Rating: 4.8 out of 5 stars
- Pricing: $35 for less than 20 users
Precoro is a procurement software tool that helps small and midsized businesses manage orders, automate approval workflows, control spending, and receive real-time data in one place.

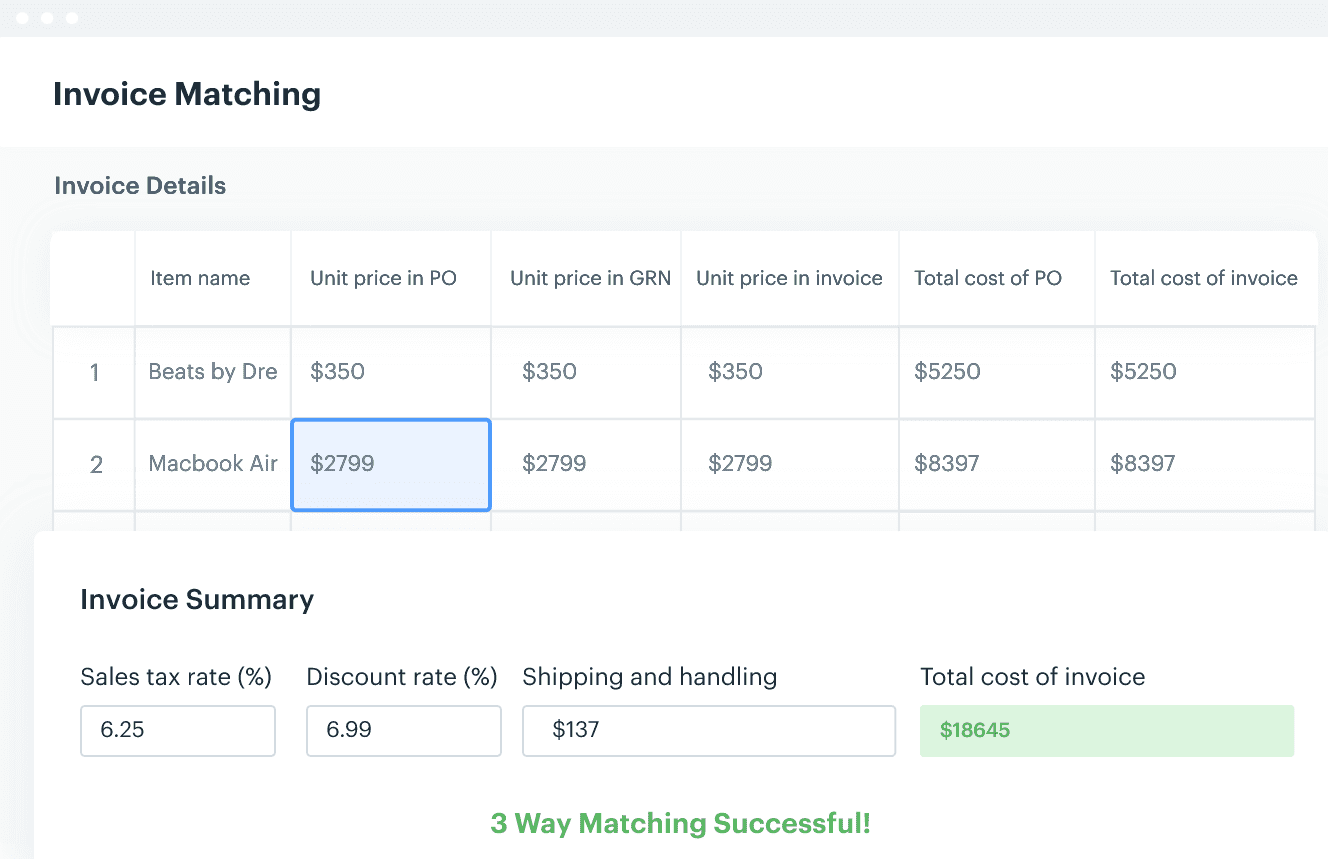
5. Kissflow Procurement Cloud
- G2 Rating: 4.8 out of 5 stars
- Pricing: Custom-pricing
Kissflow Procurement Cloud is a flexible procurement software for mid-sized companies. The platform streamlines all the key procurement flows from purchase requisitions to invoicing.
The procurement process is a complex but vital aspect of any business’s operations. Understanding the nuances between procurement, purchasing, and strategic sourcing is the first step in optimizing your organization’s approach to acquiring goods and services. By recognizing the different types of procurement and the steps involved in the procurement process flow, companies can better position themselves to enhance operational efficiency and drive business success.
The impact of procurement on a business is profound, affecting everything from cost savings and operational efficiency to supplier relationships and quality control. To navigate this landscape effectively, it’s essential to monitor key KPIs and metrics. These indicators help businesses identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions that enhance procurement strategies. Adopting best practices and understanding potential challenges are also crucial in ensuring a smooth, efficient procurement process.
For those looking to streamline and elevate their procurement operations, Whatfix can be your partner in this journey. Our platform offers intuitive, scalable solutions designed to simplify complex processes and empower your team. With Whatfix, you can enhance user adoption of procurement tools, ensure compliance with your procurement policies, and provide real-time support and guidance to your staff. By partnering with Whatfix, you’re not just investing in software; you’re enhancing your team’s capabilities and contributing to your organization’s overall success.
Learn more about how Whatfix can transform your procurement process and turn procurement into a strategic asset for your company.

Thank you for subscribing!