What Is a 9-Box Grid? (+Template)
- Published:
- Updated: October 9, 2024


To assess employee performance and understand an employee’s growth potential, HR and people managers must consider two dimensions: an employee’s current contribution and future potential.
Understanding the impact and success an employee has had in achieving their goals is an obvious tactic for measuring employee performance and allows companies and teams to recognition and reward strong team members.
On the other hand, assessing future potential allows organizations to identify individuals who have been (or are capable of being) high performers and possess the potential to become future leaders or individual contributors with expert subject matter knowledge with the right upskilling.
The 9-box grid is a commonly used employee performance assessment that groups employees into nine different quadrants, allowing each quadrant’s employees to receive equal training and support to help them advance to a higher quadrant that ultimately improves employee performance and identifies future leaders.
What Is the 9-Box Grid?
The 9-box grid provides a framework for assessing employee performance and enabling succession planning. The exercise’s grid maps employees against two axes: current performance and future potential.
The vertical (y) axis indicates growth potential, referring to an individual’s potential to grow into leadership roles. The horizontal axis (x) represents an employees’ current performance, identifying whether they are below, meeting, or exceeding performance expectations. The 9 boxes in the grid result from the relationship between their ‘potential’ and ‘performance’.
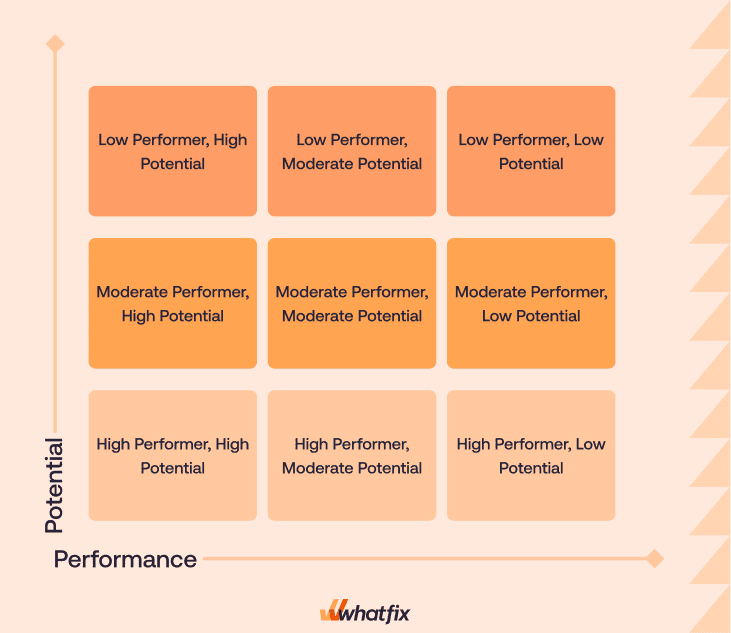
How to Create a 9-Box Grid
There are three steps to creating a 9-box grid for evaluating your employees:
1. Identify valuable talent
During the first step, the performance level of each employee is assessed. The exact criteria to score performance varies depending on the needs of an organization. In general, each employee must be categorized into one of these three groups:
- Low performance – Employees do not match their job requirements and fail to achieve their targets and goals. They demonstrate a lack of motivation and alignment with the organization’s vision.
- Moderate performance – Employees partially match their job requirements, individual targets, and goals.
- High performance -The team member fully meets their job requirements and individual targets and consistently perform all tasks.
2. Assess employee potential
As the next step, the potential of each employee is assessed. An employee’s potential is defined by how much they are expected to grow in the future, their willingness to learn new things, and their ability to apply their knowledge in routine tasks.
As discussed in one of the challenges, evaluating employee potential is less familiar for organizations than assessing employee performance.
To bring both concepts down to the most straightforward terms, they can be distinguished as performance being the past behavior and potential being the expected future behavior. Potential often falls into the following categories:
- Low potential – The employee has reached their maximum capacity or is not motivated to grow further.
- Moderate potential – The employee can further develop performance or expertise in their current role.
- High potential – The team member performs beyond the expectations of their position and responsibilities. They naturally and enthusiastically take on leadership opportunities and are always prepared for new challenges.
Assessing potential differs from assessing performance even if the process seems the same. For example, an employee with low potential might already be working at the maximum capacity required for the current position, making them unsuitable for becoming future leaders.
On the other hand, if an employee is low or moderate on the performance scale but has high potential, they can be considered for leadership roles in the next two to three years, given that they undergo effective training programs.
3. Merge performance and potential into a 3×3 grid
Once all employees have been scored as low, moderate, or high on both performance and potential, the final step is to plot them on a 3×3 grid, resulting in your 9-box grid. The grid gives managers and HR a clear view of where each employee stands.
Tom Sullivan
President and CEO, ProGrowth Associates LLC
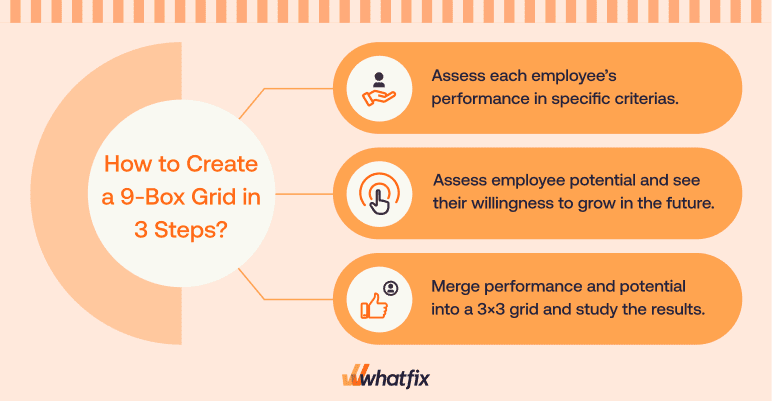
Breaking Down the 9-Box Grid Quadrants
HR and managers work together to assign each employee to relevant boxes on the 9-box grid based on the x-axis, which represents an employee’s current performance, and the y-axis, which represents their future potential.
These quadrants guide managers to create an action plan for each employee based on their performance and potential.
1. Low Performance/Low Potential
Characteristics:
- Consistently underperforms with limited growth potential.
- May need more skills, motivation, or both.
- Requires significant support to improve.
Action plan
- Implement a performance improvement plan.
- Provide close supervision and frequent feedback.
- Consider reassignment of duties.
- If there is no valid reason for low performance and no other suitable job role, create an exit plan for the individual.
2. Low Performance/Medium Potential
Characteristics:
- Moderate potential but underperforming in current role.
- Fails to identify or implement creative solutions when necessary.
- May need skill development or better role alignment.
- Shows sporadic signs of potential.
- Needs the proper discipline.
Action plan:
- Conduct a skills gap analysis and provide relevant employee training.
- Offer regular feedback and support.
- Reevaluate role suitability and consider reassignment.
3. Low Performance/High Potential
Characteristics:
- Demonstrates strong potential but currently underperforms.
- May need more motivation or direction.
- Operates in the best interest of the company.
- Potential to excel with proper guidance.
Action plan:
- Provide targeted coaching and mentoring.
- Identify and remove obstacles hindering performance.
- Set clear performance goals and track progress.
4. Medium Performance/Low Potential
Characteristics:
- Reliable performer with limited growth potential.
- May excel in current role but not suited for higher responsibilities.
- Consistent and dependable.
Action plan:
- Recognize and reward consistent performance.
- Provide opportunities to enhance efficiency in current role.
- Manage expectations regarding career progression.
5. Medium Performance/Medium Potential
Characteristics:
- Consistent and reliable performance.
- Moderate potential for future growth.
- Steady, dependable contributor.
Action plan:
- Provide opportunities for incremental skill development.
- Communicate expectations and role requirements.
- Encourage cross-training to broaden skills.
- Provide classroom training and on-the-job learning opportunities to overcome any skill gaps that hold them back.
- Regularly review performance and potential for growth.
- Consistently praise accomplishments and good performance to motivate.
6. Medium Performance/High Potential
Characteristics:
- Solid performance with clear signs of high potential.
- Capable of handling more responsibility.
- May need opportunities to showcase potential.
Action plan:
- Assign challenging projects to stretch abilities.
- Provide leadership development opportunities.
- Offer mentoring from high-performing leaders.
7. High Performance/Low Potential
Characteristics:
- High current performance with limited potential for future growth.
- Maybe at the peak of career performance.
- Highly skilled and knowledgeable in current role.
Action plan:
- Continue to provide challenging work to maintain engagement.
- Recognize and reward sustained high performance.
- Offer opportunities to mentor others and share expertise.
- Can be considered for pay raise and mid-level management.
8. High Performance/Medium Potential
Characteristics:
- Excellent performance with moderate potential for advancement.
- Strong contributor and critical team member.
- May excel in specialized roles rather than broad leadership.
Action plan:
- Recognize and reward outstanding performance.
- Offer specialized training and development opportunities.
- Explore opportunities for lateral moves to enhance skill set.
9. High Performance/High Potential
Characteristics:
- Outstanding performance with high potential for future leadership.
- Highly motivated and skilled.
- Key candidate for succession planning.
Action plan:
- Fast-track development programs and leadership training.
- Pay and reimburse for all personal learning and development courses and training.
- Provide significant challenges and opportunities for growth.
- Engage in succession planning and retention strategies.
- Check-in regularly to ensure they are happy in their current role, if there are any signs of dissatisfaction, and to identify potential burnout.
9-Box Grid Template
To help you perform a 9-box grid exercise to help measure employee performance and create development plans for employees, we’ve created a free 9-box grid template for you to download below:
✓ Thank you, the template will be sent to your email
What Is the Purpose of the 9-Box Grid?
Here are some reasons to consider implementing the 9-box grid method for people management in your organization.
1. Identifying high performers and high potentials
The 9-box grid helps organizations identify employees who consistently perform excellently and exhibit strong potential for future growth. Companies can recognize their top talent by categorizing employees based on their performance and potential and creating tailored employee development plans.
2. Informing succession planning and career development
The grid provides valuable insights into which employees are ready to move into higher roles or take on greater responsibilities. This information is crucial for succession planning, ensuring the organization has a pipeline of capable leaders. It also aids in career development planning by identifying which employees must be prepared for future roles.
3. Highlighting training and support needs
The 9-box grid assesses employees’ performance and potential. It highlights areas where individuals may need additional training, support, or resources to improve or realize their potential. This ensures targeted development efforts and efficient use of training resources.
4. Facilitating talent discussions and resource allocation
The grid is a common framework for managers and leaders to discuss and evaluate organizational talent. It helps make informed decisions about where to allocate resources, such as specific employee development areas or mentoring and coaching programs to maximize employee growth and organizational effectiveness.
5. Aligning employee development with organizational goals
The 9-box grid aligns individual employee development plans with the organization’s broader strategic goals. By systematically assessing and developing talent, companies can ensure that their workforce capabilities align with their long-term objectives, fostering organizational growth and success.
9-Box Grid Alternatives
Although the 9-box grid is considered to be the best method for succession planning and performance management, here are some alternatives in case you do not have the time or resources to build it.
1. Talent review meetings
Talent review meetings are structured discussions in which leaders and managers evaluate employees’ performance and potential. These meetings aim to identify high-potential employees, address development needs, and plan for succession.
Benefits:
- Facilitates comprehensive, qualitative discussions about employees.
- Encourages collaboration among leaders to ensure fair and holistic evaluations.
- Helps identify organizational talent trends and gaps.
Drawbacks:
- Can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
- May be subject to biases if not structured properly.
2. Performance-potential matrix
The performance-potential matrix is similar to the 9-box grid, but it can be customized to different dimensions and criteria. It maps employees based on their current performance and potential, typically using more than nine boxes.
Benefits:
- Allows for more nuanced and flexible evaluations.
- Can be tailored to specific organizational needs and criteria.
- Encourages a deeper understanding of employee strengths and areas for development.
Drawbacks:
- May become complex and more challenging to manage with more dimensions.
- Requires consistent and objective data to be effective.
3. Competency models
Competency models define the skills, behaviors, and attributes necessary for success in specific organizational roles. Employees are assessed against these competencies to identify strengths and development needs.
Benefits:
- Provides clear expectations and standards for performance.
- Helps align employee development with organizational goals.
- Facilitates targeted training and development programs.
Drawbacks:
- Developing and maintaining competency models can be resource-intensive.
- May require regular updates to stay relevant with evolving business needs.
4. Individual development plans (IDPs)
IDPs are personalized action plans that outline an employee’s career goals and the steps needed to achieve them. These plans are co-created by the employee and their manager and focus on development opportunities, training, and experiences.
Benefits:
- Empower employees to take ownership of their career development.
- Provides a structured approach to personal and professional growth.
- Enhances employee engagement and retention.
Drawbacks:
- Requires commitment from both employees and managers to be effective.
- Can be challenging to track progress and ensure accountability.
5. Succession planning software
Succession planning software automates identifying and developing future leaders within the organization. It helps manage talent pipelines, track employee development, and ensure readiness for critical roles.
Benefits:
- Streamlines and automates the succession planning process.
- Provides data-driven insights and analytics for better decision-making.
- Enhances transparency and consistency in talent management.
Drawbacks
- Can be expensive to implement and maintain.
- Requires accurate and up-to-date data to be effective.
- May need integration with other HR systems for comprehensive functionality.
The 9-box grid model helps manage employees with different levels of performance and potential in your organization.
Remember, the actual value of the 9-box grid is not about putting specific labels on employees. It is instead implemented to evaluate an employee’s success and ensure that the organization invests in the proper development programs for the right employee.
With a digital adoption platform like Whatfix, enable your employees to learn in the flow of work with on-demand performance support – driving productivity and maximizing technology investments. Here’s how Whatfix enables employee training:
- Whatfix’s no-code content creation allows for seamless and rapid development of training materials without the need for extensive technical knowledge.
- Whatfix Mirror offers hands-on training on mission-critical software applications, ensuring employees gain practical experience and confidence.
- Smart Tips provides contextual reminders and nudges at critical moments, helping employees stay on track and avoid common pitfalls.
- The Self Help feature offers on-demand access to contextual knowledge, documentation, and process assistance, empowering employees to resolve issues independently.
- Guidance Analytics provides insights into end-users engaging with in-app experiences and learning flows, enabling continuous improvement of training materials.
- In-app surveys facilitate post-training feedback, employee net promoter score (eNPS), and feedback on changes, ensuring that training programs continuously align with employee needs and organizational goals.
To learn more about Whatfix, schedule a free demo with us today.
The 9-Box Grid FAQs
What are the benefits of using a 9-box grid?
The benefits of using a 9-box grid include:
- Identifying high performers and high-potential employees.
- Planning leadership succession and developing future leaders.
- Highlighting specific training and development needs, allowing for focused and efficient employee growth.
- Creating a structured approach for talent discussions among managers and leaders.
- Assisting in making informed decisions about where to allocate resources and development efforts to maximize organizational effectiveness.
What are the limitations of using a 9-box grid?
While the 9-box grid is a useful tool, it has certain limitations:
- The assessment of performance and potential can be subjective and may lead to biases.
- It provides a static view of employees at a single point in time, not accounting for changes in performance or potential.
- Reduces complex individual performance and potential into a simple matrix, potentially oversimplifying nuances.
- Requires significant time and effort to ensure accurate and fair evaluations.
- May lead to labeling employees in a way that affects their morale and limits their perceived potential for growth.
Request a demo to see how Whatfix empowers organizations to improve end-user adoption and provide on-demand customer support