Organizations across all sectors recognize the importance of efficient knowledge management. Companies, from tech startups to large corporations, are racing to strengthen their knowledge-based operations and end-user services to enable customer end-users and internal employees.
Knowledge bases enable organizations to establish a centralized, searchable repository that allows end-users to find information. Knowledge base software provides organizations the tools and infrastructure to create a centralized information hub.
What Is a Knowledge Base?
Knowledge base software is a knowledge management platform for creating, storing, organizing, and sharing knowledge and information in a self-service hub for customers or employees. It enables organizations to establish a centralized repository that end-users can easily access, navigate, and search to find contextual how-to articles, technical help, documentation, and other user support information.
Organizations can use a knowledge base to store a variety of content. For customer-facing knowledge bases, this includes FAQs, technical setup, product documentation, how-to guides, changelogs, new feature updates, and video tutorials. For employee-facing internal knowledge bases, this includes SOPs, methods of procedures, process documentation, IT help support, company policies, HR services, training materials, and more.
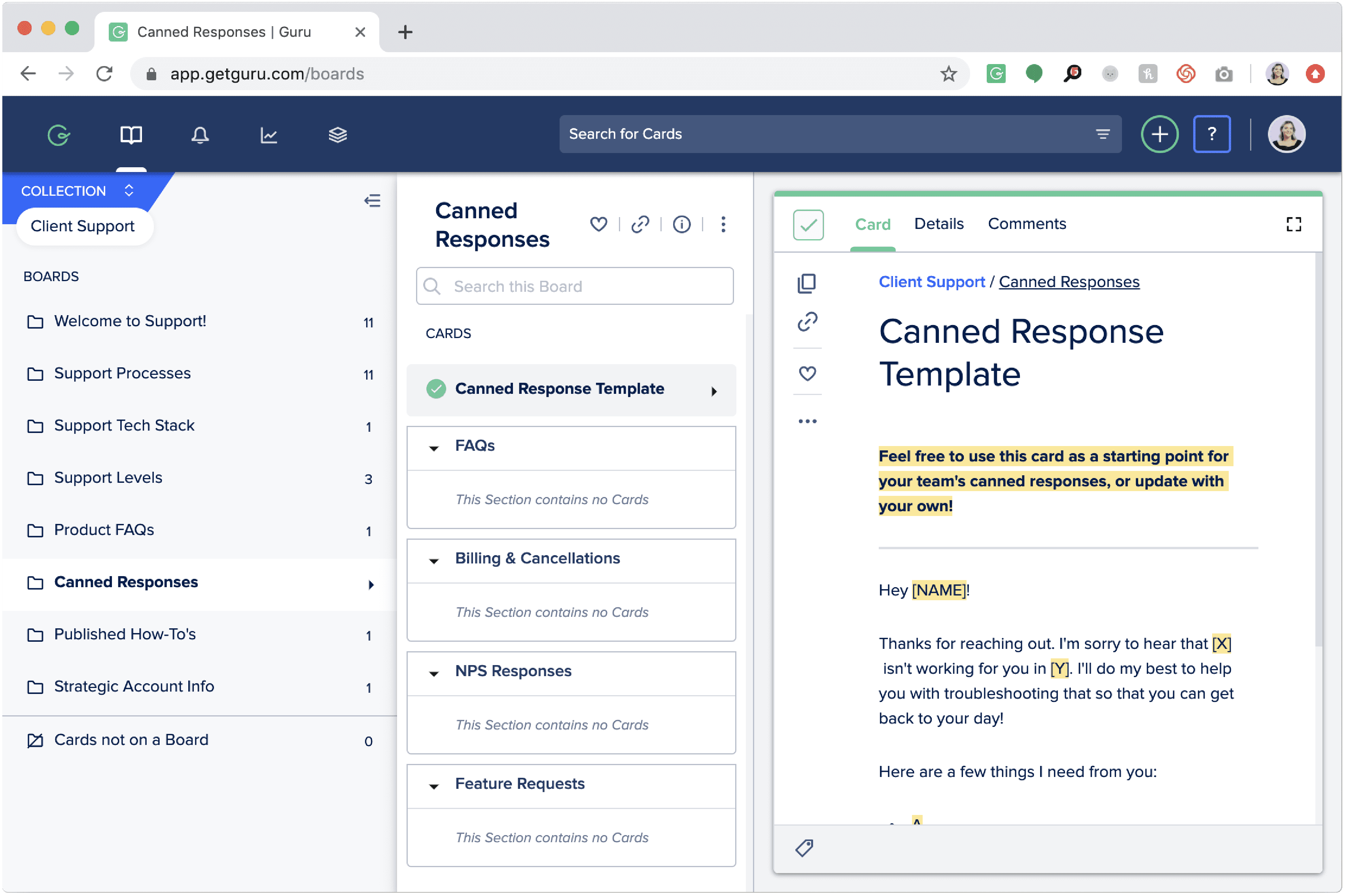
Above, you can see an example of Guru’s dashboard, where an organization can write, store, document, and share knowledge and processes from across the organization. This software can help organizations enhance employee experience and boost information accessibility. The goal is to create a user-friendly knowledge ecosystem. This should adapt to your needs and support productivity.
Knowledge bases enable organizations with:
- Centralized information: A knowledge base is a single source of truth for an organization’s collective knowledge.
- Searchability: Advanced search functionalities allow users to quickly find the exact information they need.
- Content Creation and Maintenance: Knowledge bases typically offer intuitive content creation and updates interfaces.
- Customization: Organizations can customize their knowledge base to match their branding via no-code, drag-and-drop editors.
Components of a Knowledge Base
A knowledge base will enable organizations with capabilities, components, and features that enhance their functionality and drive knowledge-related business outcomes.
- Editor for content creation and management: Features for creating and organizing content. Using this feature, all information remains current and accessible.
- Self-service portal: A platform for users to navigate to find help content and documentation to resolve support-related issues.
- Knowledge center customization: Features allowing organizations to tailor the look and feel of their knowledge base. This helps maintain brand consistency.
- Search functionality: This empowers users to find resources quickly.
- Taxonomy governance: This allows admins to group content together based on tags and categories, providing guardrails to organization knowledge that allows users to navigate and find information quickly. This allows provides SEO support for customer-facing knowledge bases to become indexed on Google, allowing users to find knowledge base articles organically from search engines.
- Version control: System for tracking changes to documents over time. Version control supports accuracy and accountability.
- Built-in reports: Tools to track metrics like failed searches and content performance. Reports can help you maintain a relevant and effective knowledge base.
- Feedback and analytics: Tools to understand how customers use your product. These features help improve knowledge base content over time.
- Multilingual capabilities: This feature caters to global workforces and customer bases. It ensures information is accessible to all users.
- Third-party integrations: Connections with popular tools. These integrations streamline workflows by connecting different systems.
- User access controls: Manage who can view or edit specific content, helping govern knowledge updates and protect sensitive information.
Types of Knowledge Bases
Organizations can use a knowledge base to store a variety of content. There are two primary use cases for knowledge bases: customer and internal knowledge bases.
- Customer knowledge base: Helps customers find answers to their questions. For customer-facing knowledge bases, this includes FAQs, technical setup, product documentation, how-to guides, changelogs, new feature updates, and video tutorials.
- Internal knowledge base: Information for employees in an organization. For employee-facing internal knowledge bases, this includes SOPs, methods of procedures, process documentation, IT help support, company policies, HR services, training materials, and more.
What to Include in Your Knowledge Base
A knowledge base enables customer care and IT teams to create centralized information hubs in various forms, each serving the different needs of an organization’s knowledge services. These can include:
- Product Documentation Guides: Explains how to use a product or software. These include feature explanations and best practices. They serve as a reference for customers and internal teams.
- Help Center: Includes step-by-step instructions and how-to articles for using a product or service. They may include annotated screenshots and interactive elements, as well as more in-deth user guides.
- FAQs: Frequently asked questions and the answers. FAQ pages provide quick solutions. They may be the first stop when users need help.
- SOPs: Detailed instructions for routine operations in an organization. Having SOPs helps with training new employees and maintaining operational efficiency.
- Employee handbook: A guide to an organization’s procedures and expectations. It typically covers topics like code of conduct and benefits.
- Intranet: A private network for an organization’s staff. Intranets may include different types of knowledge bases or internal wiki. They’re a hub for communication and collaboration.
Benefits of Knowledge Bases
Knowledge bases can provide benefits and drive business outcomes tailored to different business needs – however, here are the core benefits of customer-facing knowledge bases and internal knowledge bases:
Benefits of customer knowledge base
- Enhanced customer experience: Provides customer self-service support that enable end-users to resolve issues independently, right when they need help.
- Deflection of support tickets: Directs customers automatically to the right tutorial or guide. This reduces inquiries to support teams and provides a better customer experience.
- Reduced average resolution times: Support tickets can be connected to the right answers. That allows agents to handle more requests efficiently.
- 24/7 support: Offers users information when and where they want it, even during holidays and off-hours.
- Increased user satisfaction: Access to knowledge and round-the-clock support reduce wait times, leading to higher customer satisfaction.
Benefits of internal knowledge base
- Increased productivity: Knowledge workers can find answers to questions on their own, from product knowledge, company policies, operating procedures, and more.
- Consistent information and better knowledge sharing: Ensures all team members have access to up-to-date information, regardless of your department. This reduces confusion and helps to align workforces.
- Improved employee onboarding and training: Employees can document processes that new employees can find and learn from asynchronously.
- Enhanced collaboration: Knowledge sharing across departments and locations becomes easier with the right tools.
How to Create a Knowledge Base
While creating a knowledge base may seem daunting, many companies already have most of the resources on hand. Using a knowledge base software will help you compile most of these already-existing resources into a knowledge management tool ready for your employees or customers to use.
1. Brainstorm FAQs and How-To Topics
Take the time to identify common challenges and knowledge gaps your users face. Have customers been missing out on a useful feature of your platform? Are employees constantly asking where to log their vacation days?
Make a note of these common queries and include these resources in your knowledge base. Then, to ensure a thorough knowledge base, survey both employees and customers to see what they would like to know.
2. Create, Collect, Curate, and Organize Your Content
Not only does this phase require finding updated resources, but it also means creating more based on your pain points. Think about your current content format and if changing it up may contribute to user success.
For example, if all processes and support information is in document form, consider repurposing text-based documents into how-to videos and webinars, as well as creating infographics and diagrams.
3. Determine Your Writing Process
Writing knowledge base articles is almost the same as writing an informative blog content. In both cases, you want to engage readers, give helpful instructions or knowledge, and allow them to walk away with new information or ideas.
Here are a few general guidelines for writing knowledge base articles:
- Write a strong and clear headline
- Be descriptive
- Avoid typos
- Link to helpful resources
- Focus on readability
- Add the most frequently asked questions in your support ticket auto-responder or chatbot.
- Avoid being redundant
- Make content easy to skim
4. Choose a Knowledge Base Software
Now that you know the basics of how to create a knowledge base, it’s time to choose the right tool to get the job done. Upgrade your knowledge management by using a program designed specially to help your users learn more effectively.
The best knowledge base software will allow you to:
- Create a searchable hub that contains your various company knowledge and policies
- Connect with both internal and external users
- Easily incorporate new changes and processes
- Track user activity
- Provide contextual and immediate support
- Ask for feedback
5. Make Your Knowledge Base Content Easily Accessible
Once you have created your knowledge base, users must know exactly how and where to utilize it. Actively promote your content during onboarding, announcements, and marketing campaigns to ensure customers and/or employees know it’s available.
When choosing software, ensure it integrates directly into your app or website for easy access and empowering your organization to create omnichannel customer experiences.
With Whatfix’s native knowledge base integrations, organizations can embed their knowledge directly into their digital apps for internal employees, as well as customers and end-users. This provides on-demand, self-help support in the moment of need for employees and customers.

6. Continuous add new knowledge articles
Never consider your knowledge base “complete.” To provide the most relevant and helpful content for your users, continue creating and editing certain documents as your business evolves.
For instance, if your organization updates its policies in any way, you’ll want to reflect these changes in your existing knowledge base.
Additionally, knowledge base software provide detailed analytics on what users are searching for. Augment that data with user feedback and help desk ticket trends to identify new support articles to create. With Whatfix Guidance Analytics, understand what queries users are searching for the most to easily spot new knowledge base articles to create.



How to Write Knowledge Base Articles
A well-crafted knowledge base consists of dozens to hundreds of how-to articles that empower customers and employees with the knowledge and guidance to resolve issues independently, access knowledge, and achieve outcomes.
Your knowledge base articles should be easy to find and formatted in a clear and concise way. Here are eight tips to help you write effective knowledge base articles:
- Curate your articles to your audience: Knowing your audience is the key to developing helpful knowledge base articles. Learning your audience’s technical understanding or preferred learning form allows you to cater to their needs. For example, marketers may prefer embedded videos, while developers prefer mark-up annotations.
- Don’t make assumptions: Remember, most of your customers do not know the product as well as your internal stakeholders do. New employees may not be familiar with internal company language. Do not use complex language, technical jargon, or internal lingo in your article. Assume that most of the users are starting from square one and we recommend over-communicating even “simple” instructions.
- Use headers and subheaders: Organizing your knowledge base articles enables users to quickly skim articles and find what they are looking for. Include a table of contents to make it easier for users to navigate directly to the details they’re looking for. Don’t forget to keep your headers and subheaders simple. Conduct keyword research to ideate header copy targeting long-tail keywords from search engines like Google.
- Use anchor links: Anchor links are web page elements that allow users to jump to another location on the same page. They guide your users to the desired information and significantly improve the user experience by helping them navigate through knowledge base articles.
- Create easy-to-read, skimmable articles: Knowledge base articles are usually quite long to begin with, but it’s essential to ensure that you don’t intimidate readers with a wall of text. Introduce bullets, tables, and various formatting elements to ensure your articles are skimmable and easy to read.
- Use multimedia like videos, annotated screenshots, and GIFs: Include multimedia content such as videos, images, GIFs, infographics, and animations. No matter how ‘good’ your writing is, it will most likely be overlooked without visuals.
- Write straightforward titles: Simple titles help you summarize what your article is actually about. Refrain from getting too creative with the title, instead write simple search-optimized titles. This will help direct readers to the answers they’re searching for – and will help your content appear in search results, providing more visibility for those searching for answers.
- Use SEO tools to create search-optimized articles: Leveraging keyword research tools such Ahrefs and Semrush to keep your knowledge base content SEO-friendly. These tools will give you insights into what your customers and users are searching for in relation to your support questions. It will also help you understand what types of queries are most commonly searched, allowing you to plan new knowledge base articles.
Best Practices for Maintaining a Knowledge Base
Now that you know how to create a knowledge base, it’s crucial to understand how to make this resource as successful as possible for your company.
1. Keep Your Knowledge Base Well Maintained
Keeping your knowledge base up-to-date is crucial to its success. Users will utilize the resource as long as they can trust the information. How frequently depends on how often there are changes within your company. Make sure to refresh it as soon as you announce a new company update or process so users can reference the information without delay.
Finding an intuitive software that requires zero-coding experience and applies changes automatically to all formats will make it easy to maintain your knowledge base.
Below you can see an example of Cirrus HR Service Desk using Atlassian to easily manage and maintain its knowledge bases.
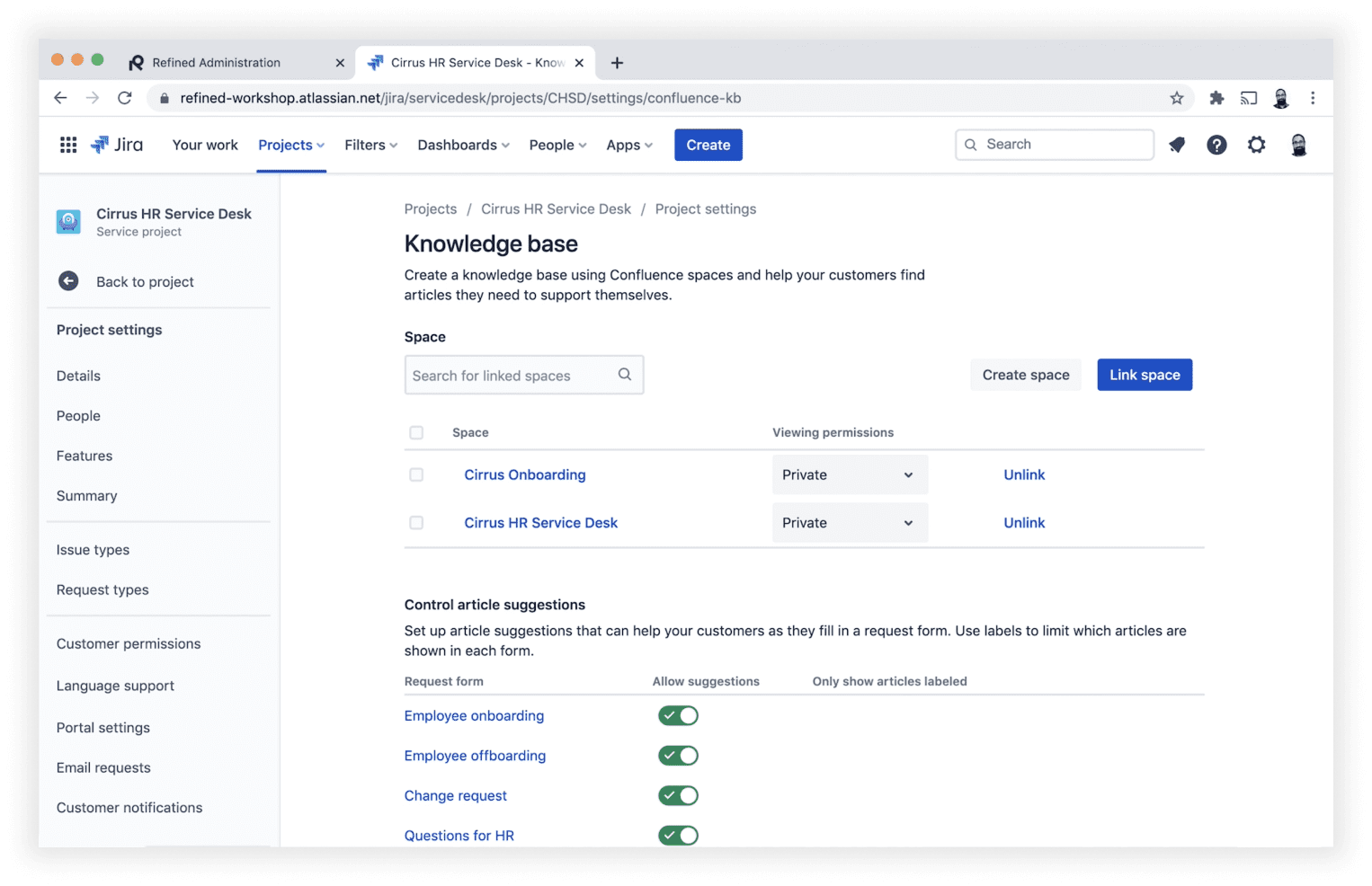

2. Stay True to Your Brand
Keeping your brand consistent is especially important for an external knowledge base. Your knowledge base is an extension of your product and should represent it. Not only should it include your logo and brand colors, but the way you speak to users should also remain consistent. Users may get confused by discrepancies in things like messaging and aesthetics.
Below you can see a great example of how Airtable uses its branding throughout its knowledge base:

3. Use Interactive Content Types
Because 90% of what humans process is visual, people will process your information better in interactive and graphic formats. Including video tutorials, webinars on the topic, infographics, or even screenshots will increase user interaction.
For example, Buffer uses video tutorials in its knowledge base to make its content more digestable.

4. Know Your Audience
To create effective knowledge bases, reference your customer information to understand how to write and position your knowledge base articles. It is critical to craft the tone and style of your knowledge base depending on the audience because if fail to understand the content, they’ll reach out to the customer service team — which defeats the purpose of proactively providing a knowledge base in the first place.
5. Track How Your Knowledge Base Is Being Used
By choosing a knowledge base software with analytics and feedback capabilities, you will understand how users engage with your product. Don’t forget to check these metrics and utilize surveys to see how users respond to certain aspects of your program and to continuously work on improving your company’s KM strategy.
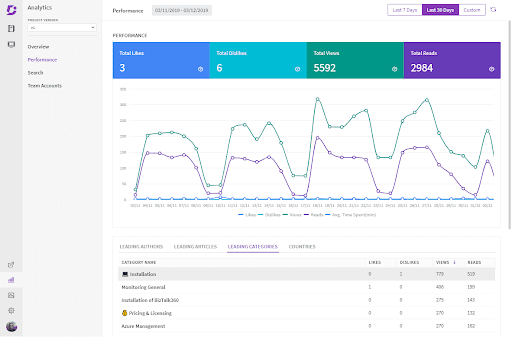

Above you can see how organizations can track how their knowledge base is being used with back-end analytics and reporting tools with Document360’s knowledge base platform.
Enable end-users by integrating Self Help into your application’s UI with Whatfix
While many brands have a robust knowledge base, it can be challenging to get users to find the contextual knowledge base article they need to overcome their specific support issue.
With Whatfix DAP, enable users with in-app support via Selp Help, which integrates with your knowledge repositories (knowledge base, help center, training resources, customer LMS, changelog, onboarding resources, help desk, etc.), aggregating your help documentation into a searchable help center that overlays your application UI.
Users are presented with contextual support entries and help content based on their application location, persona, and user role. Users can also search for any contextual issue using Self Help’s search bar. Whatfix AI also learns from your help content, providing conversational answers based on your knowledge repositories to answer user questions.
With Whatfix, your knowledge base becomes more than a static help center – you empower your customers with on-demand, in-app, AI-powered Self Help that acts as your users’ assistant, supporting them when and where they need it.
Ready to get started? Request your Whatfix demo today!