In a digital-first environment, technical issues occur and end-users require support to troubleshoot their problems. Customers experience setup issues, encounter a service error or product bug, or need general help in utilizing an advance product capability. Employees face faulty IT equipment, may become locked out of their accounts, and require assistance on technical application-related tasks and processes.
As organizations continue to evolve their customer-facing support and internal IT service delivery, the role of the help desk has expanded to ensure seamless experiences in increasingly complex environments. By responding quickly to end-user support issues, help desks ensure businesses provide high-levels of customer service and enable their workforce with frictionless IT experiences.
In this article, we’ll explore help desks, including their core functions, outline the types of help desks companies can implement, explore the challenges and benefits of maintaining an effective help desk system, and break down the roles and responsibilities of the IT service agents that make help desks run efficiently.
What Is a Help Desk?
A help desk is a central hub within an organization that provides real-time (usually technical) assistance to customer-facing and internal end-users. It includes the systems and technology platforms that make this end-user support possible, as well as the service agents that provide the technical assistance and support.
Help desk platforms often include self-service portals, ticketing systems, end-user relationship management, escalation procedure workflows, knowledge base integration, and messaging tools. Help desks are typically the first point of contact between your business and your end-user when they encounter issues with your product or service offerings or with your internal IT or enterprise software.
In recent years, AI-driven help desk solutions have emerged, offering automated responses, chatbot support, and advanced data analytics, further streamlining IT service and support operations. While AI help desks can assist in managing routine inquiries and improve response times, they complement rather than replace traditional human service teams.
Help Desk vs. Service Desk
It is not unusual for IT professionals and service teams to use “help desk” and “service desk” interchangeably—if for nothing else, they sound nearly identical—service teams are help teams, right? Therefore, it seems the only difference is semantic. However, this is not entirely correct.
Key differences between these two that affect their approach, responsibilities, and value to organizations, as described below:
- A help desk focuses on providing real-time support and user assistance on technical issues. It’s a point of contact for end-users (mostly customer end-users, but also internal employee end-users for larger organizations) to submit support queries and requests for additional IT-related assistance.
- A service desk can help with these technical issues but also provide a more comprehensive scope. They collect customer feature requests and suggestions, answer FAQs, draft knowledge bases, provide contextual answers to new questions, etc. A service desk is responsible for helping your organization provide end-user support on IT products and services to avoid service disruptions, as well as service-related questions and requests (ie, “How do I do X process?” or “How to add X new service?).
Help Desk
A help desk has a more limited scope of responsibilities around helping companies handle immediate customer support tickets. Help desk tickets can include inquiries regarding billing, software bugs, and questions on how to use a feature or interface. These tickets are time-sensitive because they usually involve customers who require this real-time assistance before they can continue using a product or service as intended. Therefore, help desks have more than enough on their plate just fielding these incoming requests reactively.
Here are additional characteristics of a help desk:
- Approach: Resolves customer issues reactively through support ticket management; critical for fast-paced industries like IT and healthcare.
- Scope: Primarily handles immediate, time-sensitive support requests, like software bugs, billing inquiries, or how-to-use questions.
- Types of Requests: Focuses on incident management—resolving specific customer issues that prevent normal operations.
- ITIL Framework: Utilizes the ITIL framework for incident management, helping teams detect, classify, and resolve issues systematically.
- End-User Experience: Enhances user experience satisfaction through quick, reliable issue and ticket resolution.
- Skills & Training: Help desk agents are trained in technical knowledge of products or services to handle immediate customer issues.
- Collaboration & Integration: Collaborates with other teams on an ad-hoc basis, driven by the immediate need to resolve customer tickets.
Service Desk
A service desk has a broader scope of responsibilities because it manages the entire service lifecycle—from building strategies for service requirements to defining service level agreements (SLAs), creating service documentation, navigating service transitions, and implementing an IT framework to continuously maintain the quality of service operations. Service desks are also an essential point of accountability for giving companies visibility into the causes of recurring issues.
Here are additional characteristics of a service desk:
- Approach: Proactively identifies and prevents issues using data-driven strategies to improve service reliability and deflect service tickets.
- Scope: Manages the entire service lifecycle, from defining service requirements and creating service documentation to continuously monitoring service quality.
- Types of Requests: Handles a broader range of service-centric responsibilities, including incident, problem, change management, and knowledge management.
- ITIL Framework: Adopts a broader ITIL framework for IT service management, ensuring seamless customer relationships beyond resolving incidents.
- End-User Experience: Focuses on creating a consistent, high-quality experiences where users can resolve issues independently or by tackling the root cause of issues.
- Skills & Training: Service desk agents require a more comprehensive skill set, including technical IT management, process management, and customer service.
- Collaboration & Integration: Coordinates closely with IT, engineers, and executives, serving as a central point of accountability for service reliability and performance.
Types of Help Desks
Help desks can be categorized as internal, supporting employees, or external, assisting customers with issues related to the organization’s products or services. The type of help desk your organization needs depends on factors such as company size, customer base—in terms of number and technical proficiency, international presence (with agents across time zones for 24/7 support), and whether your customers are B2C, B2B, or enterprise-level.
Here are the most common types of help desks:
- IT Help Desk: IT help desks resolve technical issues in real time. They maintain support resources like FAQs, knowledge bases, and technical documentation, ensuring users receive timely assistance as products and services evolve.
- Network Help Desk: A network help desk focuses on troubleshooting and managing network-related issues, including connectivity, equipment security—routers, servers—and the configuration of network devices. They are critical in environments where network uptime is crucial.
- Software-Specific Help Desk: This help desk supports specific software applications. For example, organizations like Microsoft have dedicated help desks for each product line—such as Windows, Azure, Power BI, and Office 365—to address the unique needs of each application and provide contextual product support from expert IT agents.
- Web Help Desk: Web help desks assist website or web-based application users in navigating platforms, troubleshooting technical issues, and answering website or web app functionality queries.
- Enterprise Help Desk: Enterprise help desks cater to large organizations—typically 1,000+ employees—with complex support requirements. They manage high volumes of tickets and address technical challenges that could affect the organization’s operations or revenue streams.
- Outsourced Help Desk: An outsourced help desk is managed by a third-party provider. Many large organizations, like Dell and Google, outsource their routine help desk functions to specialized agencies. These agencies provide scalable support for handling customer issues globally.
- HR Help Desk: Operating internally, HR help desks provide centralized HR service delivery support for employee inquiries related to benefits, payroll, onboarding, and other HR operations. They streamline HR communications within organizations and act as an internal knowledge base.
- Cloud-Based Help Desk: Cloud-based help desks operate remotely, allowing organizations to scale support without maintaining physical infrastructure. Platforms like Zendesk and Freshdesk offer these services, enabling global support without needing on-premises servers.
- On-Premises Help Desk: On-premises help desks are hosted on an organization’s physical servers. Popular self-hosted help desk solutions include Helpy, Chatwoot, and Spiceworks. This model offers more control over data and security but requires more maintenance.
- Multi-Level Help Desk: Multi-level help desks categorize tickets into priority levels by complexity and route them to the appropriate technical level. This model ensures that simpler issues are resolved quickly while more complex problems are escalated to experienced agents.
- Specialized Help Desk: Specialized help desks provide targeted support for niche products or services. For instance, a specialized help desk may handle inquiries exclusively about high-tech equipment or industry-specific software.
Components of a Help Desk
A help desk operates efficiently when its core components work together harmoniously. Here are the essential building blocks—or components—of a successful help desk.
1. Effective Help Desk Agent Team
A help desk’s success starts with its team. Agents must possess technical knowledge and strong interpersonal skills, particularly empathy, which is vital in customer service. The team is usually structured with different roles, each contributing to the overall efficiency of the help desk:
- Support Agents: Frontline support staff that handle everyday issues, providing immediate assistance and troubleshooting.
- Tier 2 Specialist: Agents who manage more complex or escalated queries that require specialized technical or product knowledge.
- Technical Support Engineer: Handles highly technical issues, providing in-depth troubleshooting and solutions that frontline agents (and tier 2 specialists) cannot address.
- Help Desk Manager: Oversees the entire operation, ensuring that response times meet SLAs (Service Level Agreements) and managing team performance.
- Knowledge Manager: Maintains and updates the knowledge base, ensuring agents and customers access accurate and comprehensive information, how-to user documentation, and product knowledge.
2. Strong Help Desk Software
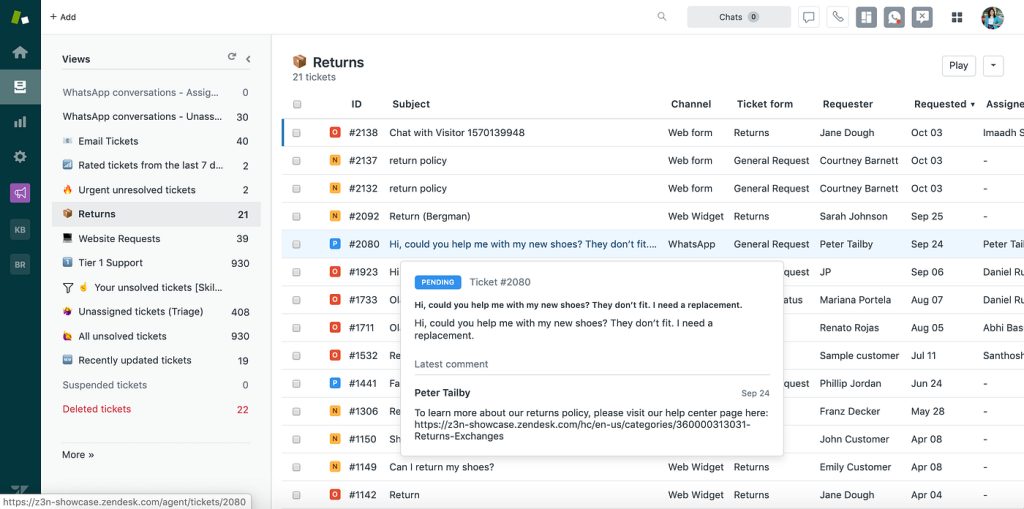
Modern help desk systems like Zendesk, Guru, or Confluence provide the infrastructure that powers service teams, from delivering high-level customer service to supporting internal IT support requests. Help desk software enables service agents with an all-in-one tool to handle incoming tickets, manage customer conversations, route service tickets, and more, improving their efficiency and productivity.
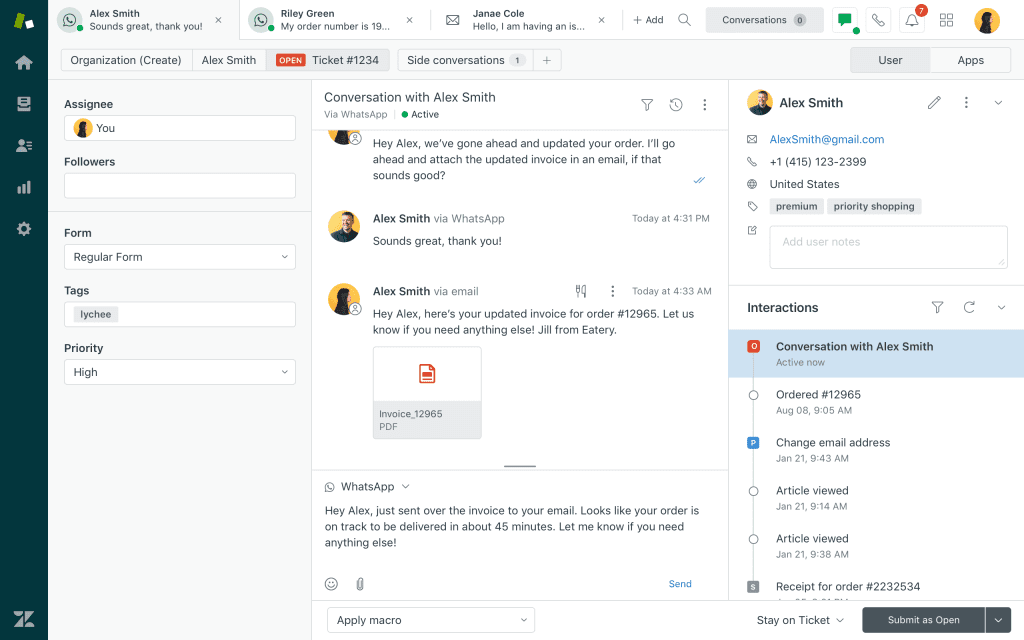
Help desk sofware provides features like ticket creation, real-time tracking, and integrations with tools like CRM and email systems. The software should allow for automated ticket creation and assignment, making it easier for teams to manage inquiries efficiently. Without robust software, teams would struggle to keep track of customer and end-user requests or manage workloads effectively.
Help desk software usually includes several core functionalities:
- Ticket management: The core of any help desk system is its ability to generate “tickets” for each customer issue or inquiry. These help desk tickets are tracked from creation to resolution, ensuring no request is overlooked.
- Omnichannel support: Modern help desks integrate different communication channels—email, live chat, phone, and social media—into a single platform. This allows agents to manage interactions from different platforms without missing important customer communications.
- Self-service portals: Many help desk systems feature knowledge bases and FAQ sections that allow users to resolve common issues independently, reducing the number of incoming support requests.
- Automation: Workflow automation, such as ticket routing and escalation, helps reduce manual work for support teams, allowing them to focus on more complex tasks.
- Reporting and analytics: Help desk software tracks key help desk metrics like response time, resolution time, and customer satisfaction scores to provide actionable insights that improve overall service performance.
- SLA tracking: Meeting service level agreements (SLAs) is crucial to maintaining—and improving—customer satisfaction. Help desk software should be able to track SLA compliance, send alerts for approaching deadlines, and flag tickets at risk of breaching the SLA. Customizable SLA policies for different customer channels ensure that tickets are handled in order of urgency and priority, preventing customer dissatisfaction.
- User feedback: Many help desk systems include built-in customer feedback capabilities, such as customer satisfaction (CSAT) surveys or Net Promoter Scores (NPS) survey templates, allowing customers to rate their support experience. Analyzing this feedback helps support teams improve their processes and ensure customers leave a positive experience.
- Integrations: Seamless integrations with other business platforms and support channels—such as CRM systems, live chat, communication platforms, and social media networks—are maximizing help desk software ROI. Integration with CRMs like Salesforce or HubSpot ensures that agents can view customer histories directly from the help desk interface, helping them provide more personalized service.
- Customization and scalability: A help desk solution must adapt to your service team’s evolving needs. Customizable workflows, ticket forms, and reporting dashboards are critical for businesses with unique requirements. As a company grows, the software should scale alongside it, allowing more agents, customers, and ticket volume to be managed without system overload or performance degradation.
3. Frictionless Support Ticket Workflows
Even with the best software, support teams need optimized workflows to handle tickets without delays. Frictionless workflows prioritize tickets based on urgency, flag VIP customers, and provide clear escalation paths for unresolved issues. By streamlining these processes, help desks can minimize bottlenecks, ensuring agents can focus on resolving customer issues efficiently rather than managing the flow of tickets.
4. Self-Serviceability
Empowering customers to find solutions independently is an increasingly vital component of modern help desks. A well-maintained employee or customer self-service portal with an updated knowledge base, FAQs, and how-to user guides can significantly reduce ticket volume. In addition, integrating AI-powered chatbots allows for automated responses to common questions, providing instant help to users and freeing agents to focus on more complex queries. This self-service model not only enhances user satisfaction but also boosts overall efficiency.
5. Analytics & Reporting
Data is the foundation of continuous improvement in help desk operations. Effective help desks leverage analytics and reporting tools to track key performance metrics such as ticket resolution times, customer satisfaction scores, and agent productivity. Performance dashboards give teams a clear view of their core help desk metrics how well they meet SLAs, while customer feedback helps pinpoint areas for further improvement. By analyzing this data, help desks can make informed decisions about refining processes and optimizing support.
6. Automation and Integrations with Internal Tools
Automation is a powerful tool that reduces the manual burden on agents. Automating repetitive tasks such as ticket assignment and follow-up, help desks can streamline operations and respond to customer queries more quickly.
Integrating with internal tools such as messaging apps like Slack and Microsoft Teams, CRM platforms like HubSpot and Salesforce, project management tools like Asana, and email systems ensures that the help desk operates as part of a unified support system. These integrations allow for seamless team collaboration and ensure that customer interactions are consistent and well-coordinated.
Organizations can integrate their help desk with other knowledge management tools, like knowledge bases and chatbots, to fully integrate knowledge-related services. With a digital adoption platform like Whatfix, organizations can enable service agents with in-app help desk guidance on resolving issues and support end-users with just-in-time support that deflects help desk issues.
Help Desk Policies and Procedures
To ensure consistent and effective support, every help desk must operate under clearly defined policies and procedures. These guidelines standardize how agents handle customer queries, manage workflows, and escalate issues. Well-crafted policies also help improve response times, ensure compliance with service-level agreements, and create a more streamlined support experience for both agents and customers.
- Ticket Categorization and Prioritization: Every help desk should have a clear policy for categorizing and prioritizing tickets based on urgency and complexity. For instance, technical issues affecting many users or high-priority customers should be escalated immediately, while general inquiries can follow standard workflows. This ensures critical issues receive immediate attention.
- Escalation Procedures: Agents need clear escalation protocols when they cannot resolve an issue. Escalation policies should define when and how tickets should be passed to higher-level support teams or specialized departments. This procedure ensures that the appropriate experts handle complex issues and prevents unresolved tickets from languishing in the queue.
- Response Time and SLAs: A help desk’s response time is often measured against SLAs (service-level agreements) that dictate how quickly agents must acknowledge and resolve customer issues. Establishing clear response time guidelines helps teams stay on track and meet customer expectations. SLAs should be communicated to all agents and measured consistently to maintain accountability.
- Documentation and Knowledge Management: Maintaining a well-organized knowledge base is essential for streamlining support. Agents should document their resolutions and unique solutions for future reference into process documentation. This ensures the help desk has a library of documented procedures that agents and customers can access when needed, reducing the time spent on recurring issues.
- User Communication and Feedback: Clear communication is critical throughout the support process. Help desks should have policies that guide agents in interacting with customers, including providing regular updates and seeking feedback post-resolution. Encouraging customers to share their experiences helps improve the help desk and strengthens user satisfaction.
- Incident Reporting and Tracking: Incident tracking assists help desks in analyzing patterns in recurring issues and developing preventative solutions. Policies should ensure that every large or small issue is documented and tracked. This makes it easier for teams to identify recurring problems and implement long-term fixes.
- Data Privacy: Help desks often deal with sensitive customer data, which requires strict adherence to privacy regulations and internal data security policies. Help desk agents must follow specific procedures when handling customer information, including encryption, secure storage, and limited access to personal details. This protects customer data, fostering trust and compliance with relevant laws.
Benefits of a Help Desk
An effective help desk is more than just a tool for customer support—it’s a strategic asset that can directly impact a company’s success. According to Zendesk’s 202o CX Trends report, nearly three out of five buyers report that good customer service is critical to brand loyalty. Moreover, a report by Bain and Company found that a 5% increase in customer retention can increase profits by over 25%.
These metrics show that a high-performing help desk cultivates brand loyalty, boosts revenue, and improves overall customer retention.
1. Centralized Customer Support Management
A help desk serves as a single source of truth for all customer support interactions. From managing customer conversations across various channels—like SMS, social platforms, live chat, and email—to handling ticketing and tracking customer satisfaction, help desks simplify support processes. This centralization reduces chaos, enabling businesses to provide consistent, world-class support.
Every interaction with a customer is logged and documented, creating a detailed conversation trail that ensures continuity in support. This allows agents to quickly reference past interactions, providing context and eliminating the need for customers to repeat information. This digital conversation trail increases agent efficiency—and improves the customer experience—by ensuring no important details are missed.
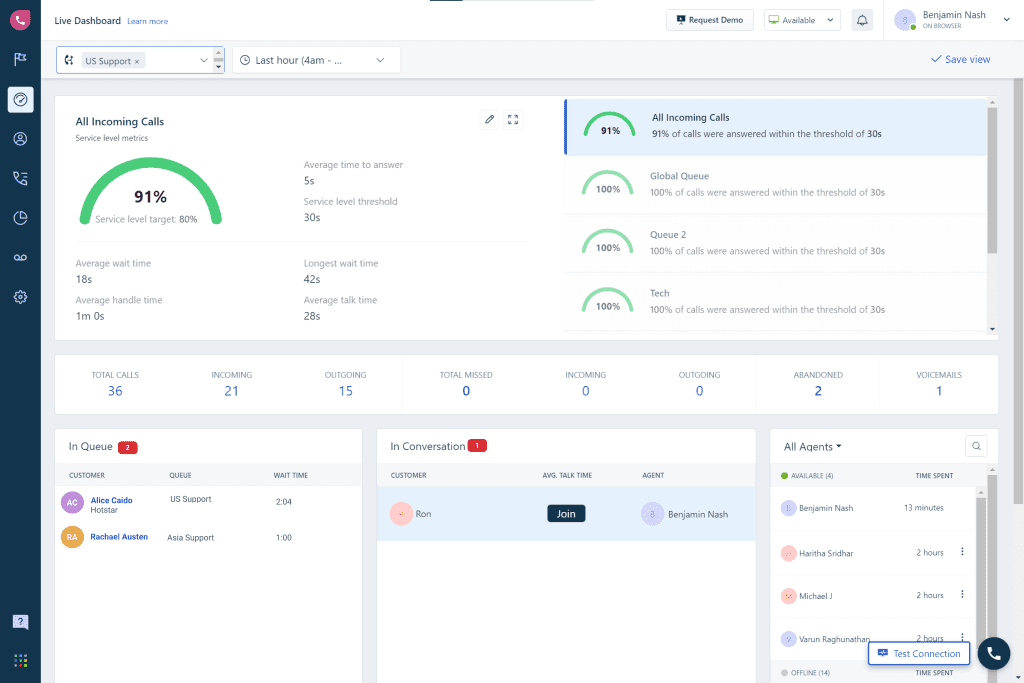
2. Streamlined Ticketing and Issue Resolution
Help desks consolidate all customer conversations, issues, and feature requests into one place, making managing and resolving support tickets easier. Support teams can reassign conversations, track resolutions, and ensure no ticket is overlooked by maintaining a unified record of when and how issues are handled.
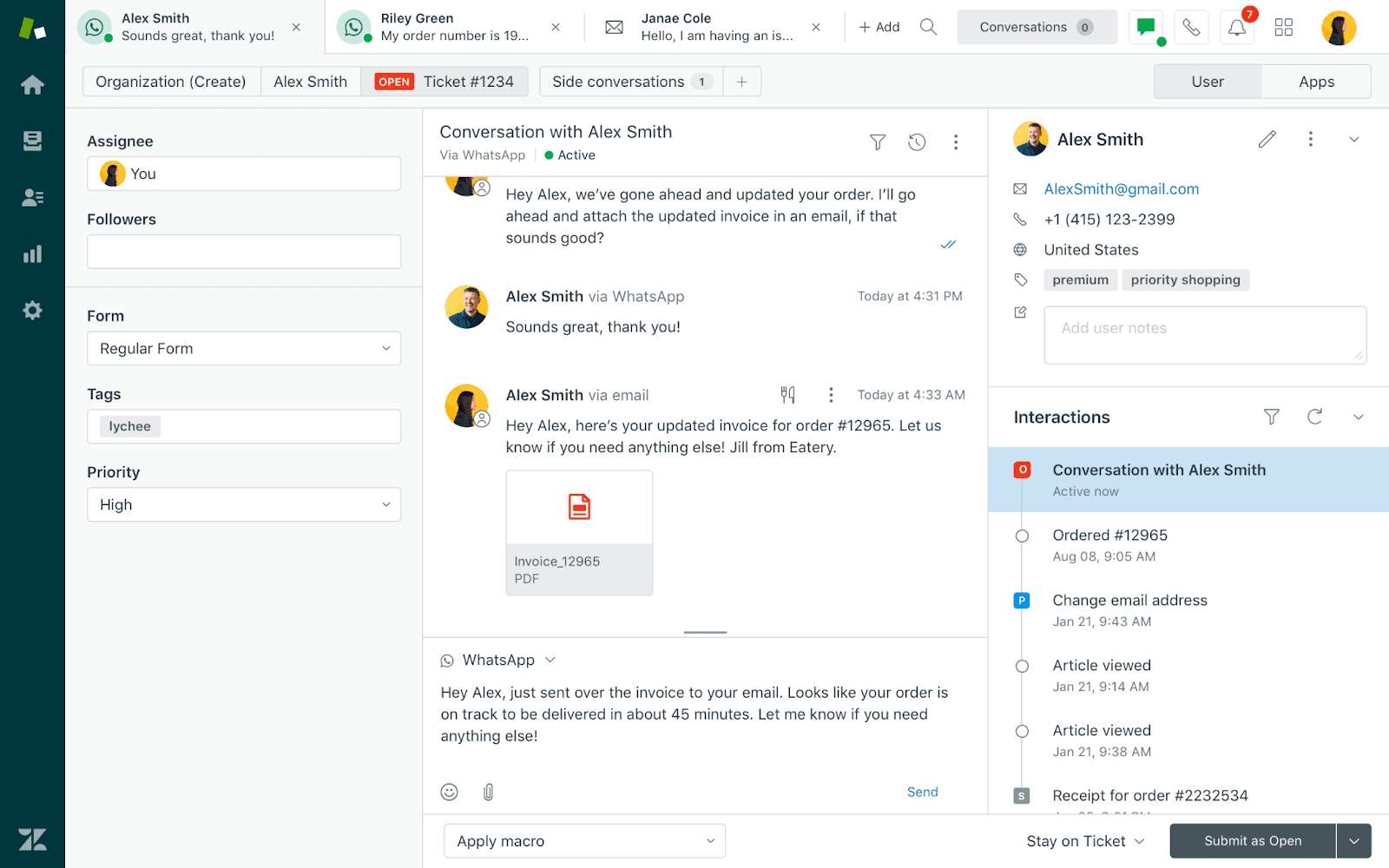
3. Improved Customer Experience and Higher Satisfaction
Modern help desk applications focus on improving customer experience. These systems simplify the process of users reaching out to support teams. By providing full visibility into every aspect of support operations, teams can track key metrics such as response times and customer satisfaction in real time. This visibility allows for quicker issue resolution and helps identify areas for improvement, ultimately resulting in improved customer experiences.
4. Improved agent efficiency and productivity
Beyond automation, help desk software enhances team collaboration and reduces bottlenecks in agent workflows. Features like internal notes, task assignment, and collaborative ticketing enable agents to work seamlessly on complex issues. These tools streamline communication within the team, preventing duplicated efforts and ensuring the right person handles the right tasks. Additionally, agents can quickly reference past conversations or shared documentation, reducing the time spent seeking information.
5. Scalability to Handle Increasing Customer Queries
As companies grow, their support needs expand as well. A well-designed help desk scales with the organization, enabling teams to onboard new agents and continually enhance self-help resources like FAQs and knowledge bases. By refining and expanding these resources over time, help desks can handle a growing volume of queries without compromising service quality.
6. Enhanced Communication and Collaboration
Many help desk platforms include features like a shared inbox that allows agents to reassign tickets to subject matter experts or teams seamlessly. With integrations to third-party tools like CRM, ERP, or project management platforms, agents can collaborate more effectively and manage support workflows without leaving the help desk.
7. Data-Driven Insights on Support Performance
Help desks track vital metrics like first response time (FRT), customer satisfaction scores (CSAT), and Net Promotor Score (NPS). These insights allow teams to monitor their performance and identify opportunities for improving customer support quality.
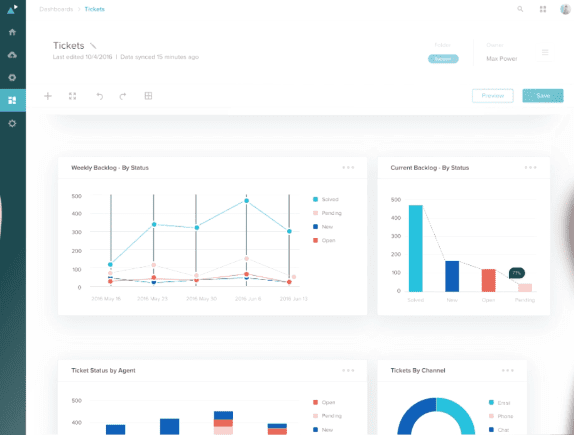
8. Reduced Response and Resolution Times
With all customer issues funneled into a single inbox, help desks make it nearly impossible for inquiries to slip through the cracks. Self-service resources like product documentation and AI-driven chatbots can also handle simple queries immediately, further reducing customer wait times.
9. Knowledge Base Creation and Management
Help desks often come with integrated content management solutions that allow teams to author, edit, and share self-help resources like FAQs, how-to guides, and video tutorials. By maintaining an up-to-date knowledge base, help desks reduce the workload for agents and empower customers to resolve issues independently.
Challenges Facing Help Desk Teams
A help desk—comprising both the software and the human team—can significantly improve customer support operations, but it is not without its challenges. From managing increasing ticket volumes to keeping up with technological changes, help desks face several obstacles that can impact their effectiveness, including:
- High volume of tickets: Support teams often experience spikes in ticket volumes after launching new products or features, making significant changes to existing services, or encountering widespread technical issues. During these periods, it can be challenging to scale the team up quickly enough or update self-help resources in time to meet demand. Managing these short-term spikes while maintaining quality service can challenge existing help desk resources.
- Integrating with your enterprise software: While many help desk platforms include easy integrations with popular SaaS tools, challenges arise when integrating with custom-built systems or on-premises software. Establishing smooth communication between a help desk platform and other business-critical systems often requires custom configurations, which can slow down operations and introduce inefficiencies.
- Maintaining technology infrastructure: Help desks that rely on in-house or on-premises solutions might struggle to keep up with technological advancements. Regular updates, including security patches, bug fixes, and new feature implementations, are critical to ensure the help desk continues to function efficiently. Falling behind on these updates can lead to outdated tools that hinder the support process.
- Balancing customer expectations: While exceeding customer expectations is a goal, balancing these expectations with available resources can be challenging. Communicating realistic timelines and managing expectations regarding response times is critical to maintaining customer satisfaction without overwhelming the team.
- Maintaining data security and privacy: Help desks often handle a significant amount of sensitive customer information, making data security a top concern. Protecting PII (Personally Identifiable Information) from breaches is vital to maintaining trust and complying with data privacy regulations. This challenge requires continuous investments in cybersecurity measures and ensuring all help desk processes align with regulatory standards.
Help Desk Best Practices
With rising customer expectations and increased contact volumes, the role of help desks in customer retention has never been more vital. A report by McKinsey (titled “The State of Customer Care in 2022”) found that 61% of customer care leaders reported a surge in call volumes, primarily driven by more complex queries. Simultaneously, organizations face talent shortages, with nearly 50% of customer care managers experiencing higher attrition rates, further straining the capacity to deliver quality service.
Therefore, a well-managed help desk becomes indispensable. Statistics show that 73% of customers will switch to a competitor if they experience bad customer service, underscoring the imperative of delivering consistent, positive interactions. By offering prompt resolutions and seamless support, help desks play a critical role in fostering customer loyalty. They help resolve issues swiftly and ensure customers remain satisfied—driving retention and generating organic growth through word-of-mouth recommendations.
When you’ve chosen a help desk stack and built your support team, the next step is ensuring you provide the best support experience possible. You can maintain efficiency, improve customer satisfaction, and drive long-term customer loyalty by implementing key best practices.
1. Implement a User-Friendly Ticketing System
A user-friendly ticketing system is customers’ first point of contact when they report issues or make inquiries. This help desk system should:
- Minimize friction with an intuitive interface that is easy to navigate.
- Simplify the process with self-service options and a streamlined ticket submission form.
- Support multiple communication channels (email, web forms, chat, or social media) to meet users where they are.
- Offer clear and timely updates on ticket status via email or SMS.
- Ensure that support resources are easily accessible across both mobile and desktop platforms.
2. Prioritize and Categorize Tickets
To ensure efficient support, help desks should adopt a grading system to categorize tickets by issue type, severity, or customer priority. This system ensures the team is always focused on the most critical issues at any given time. However, this doesn’t mean ignoring smaller issues—it is about balancing properties using an organized framework for ticket classification.
3. Provide Multi-Channel Support Options
As of July 2024, 65.67% of the world’s 5.19 billion Internet users connect via mobile devices; Facebook alone has over 3 billion monthly active users, and 4.37 billion people across the globe use email. Offering multi-channel support gives your help desk wider coverage, ensuring you can assist users via their preferred platforms. Moreover, you can reduce ticket volume by leveraging self-service tools and in-app support, allowing customers to find solutions independently.
4. Maintain a Regularly Updated Knowledge Base
Always update your product documentation and knowledge base before shipping any product updates. This allows users to find relevant information without needing direct support. Also, consider adding a suggestion widget to your help articles to allow users to contribute feedback or suggest improvements.
5. Train Help Desk Staff Regularly
Your help desk agents’ skills are critical to your support system’s overall performance. Investing in regular service agent training—via webinars, 1:1 sessions, or cohort-based courses—ensures agents can de-escalate issues, resolve problems quickly, and show empathy to customers. Continuous skill development will keep your team agile and responsive.
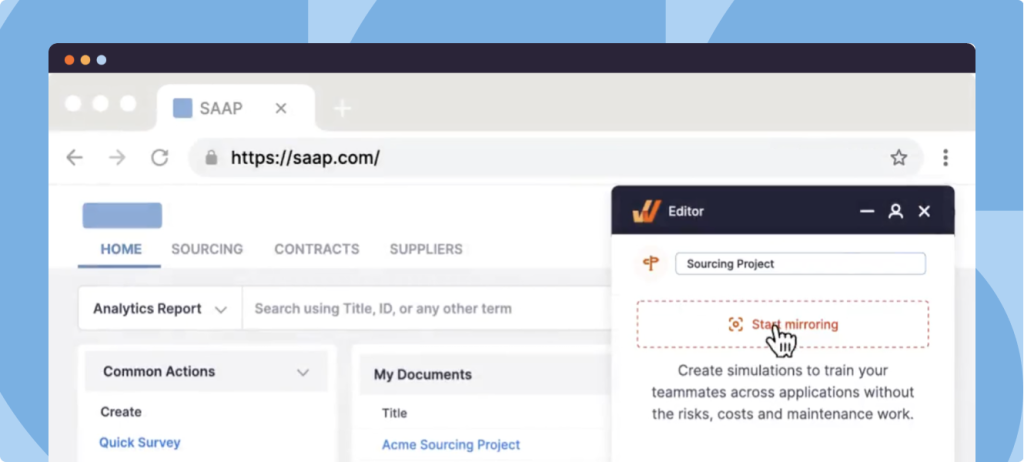
With a tool like Whatfix Mirror, organizations can create replica sandbox environments of their products and services to train service agents on how to use them and how to overcome service requests. Help desk teams can also replicate their help desk system and its processes and tasks, allowing service agents to interact with simulated scenarios and hands-on training without risking live help desk usage with real customers.
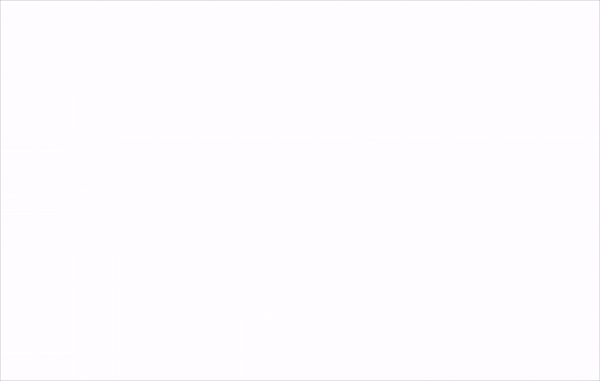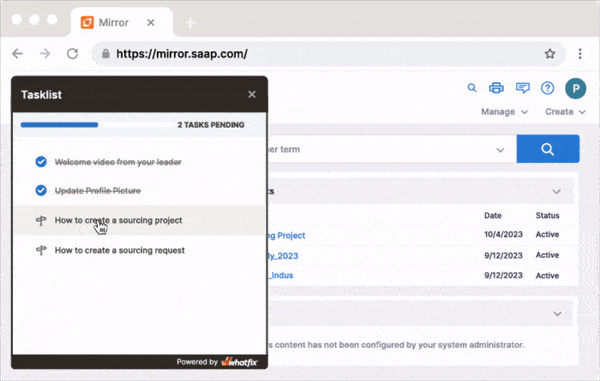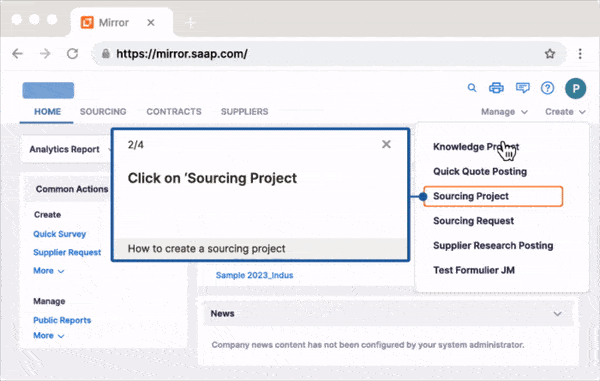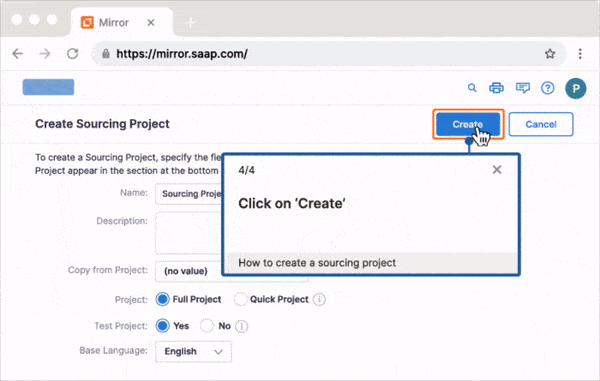
6. Establish Clear Escalation Procedures
Every help desk needs a well-defined escalation process for complex or unresolved tickets. If an issue remains resolved or falls outside the agent’s expertise, having clear procedures for escalating to higher-level support or specialists ensures quick and effective resolutions. This avoids bottlenecks and reduces frustration for both customers and agents.
Examples of Help Desks
Real-world examples of effective help desks highlight how different organizations manage customer support, streamline workflows, and enhance the user experience.
Below are a few examples from leading companies that have successfully implemented help desks, incorporating artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance customer service and efficiency:
1. LATAM Airlines’ help desk for its customers
LATAM Airlines, a leading airline in Latin America, uses Zendesk to streamline customer support across 22 countries. The airline serves 62 million passengers annually.
As a cloud-based platform, Zendesk powers both its external customer service and internal HR processes. Externally, Zendesk helps manage high volumes of customer inquiries regarding passenger refunds, flight cancellations, and more. Internally, the airline’s HR team leverages Zendesk’s self-service features, creating over 3,000 knowledge base articles for 30,000 employees.
By implementing Zendesk’s AI-driven Answer Bot, LATAM Airlines improved customer inquiry resolution times, improving customer satisfaction. Furthermore, it also empowers employees to access answers without human intervention, enhancing employee satisfaction metrics.
2. Mercedes-Benz India’s help desk for its dealerships
Mercedes-Benz India implemented Zoho Desk to handle communications between its 89 dealerships across 41 cities. Zoho Desk’s customizable interface integrates seamlessly into its organizational structure, allowing the organization to efficiently track, respond to, and resolve issues raised by dealerships.
By leveraging Zoho Desk’s customized dashboards and reporting creatures, Mercedes-Benz monitors the issue resolution times to ensure high customer satisfaction. This effective communication and issue management system plays a key role in maintaining the company’s stellar reputation across its dealer network.
3. Databricks’ multi-level help desk example
Databricks, a fast-growing software company, adopted Freshdesk to streamline both IT ticket resolution and enterprise service management across multiple departments. Initially focused on IT support, Freshdesk’s AI-powered automation, including Freddy AI, helped Databricks achieve a 23% deflection rate through self-service tools.
As a multi-level help desk, Freshdesk enables Databricks to manage tickets across different levels of complexity, escalating more challenging issues when needed. Due to its success, Databricks expanded Freshdesk’s use across eight other departments, including HR, legal, and security, to streamline (and simplify) operations for over 7,000 employees.
Freshdesk’s user-friendly interface, workflow automation, and platform integration helped reduce IT costs and improve overall efficiency.
4. Valley Driving School’s help desk for its student drivers
Valley Driving School reduced ticket resolution times by 40% after implementing HelpDesk by LiveChat. HelpDesk integrates AI-driven features that help small and mid-sized businesses handle tickets more efficiently. The school handles over 100 tickets within four hours using HelpDesk’s prioritization and tagging features, automating much of the workload.
In addition to AI, HelpDesk includes a customizable ticketing system, multichannel support (email, chat, in-app), and automated workflows that assign and prioritize tickets based on predefined rules. Its collaboration tools allow teams to manage tickets together, while its reporting features provide valuable insights into team performance and customer satisfaction.
HelpDesk also integrates with knowledge base software for self-service and popular tools like Slack for enhanced workflow management.
Best Help Desk Software
The help desk software landscape is crowded, making it difficult for businesses to choose the right solution. To help you navigate the options, we’ve identified top-rated help desk systems for 2024.
These platforms were selected for their robust features and ability to streamline customer service processes. From automation to omnichannel support, these help desks offer various tools to enhance your team’s efficiency and increase customer satisfaction.
- Zendesk
- Zoho Desk
- Freshdesk
- HubSpot Service Hub
- Salesforce Service Cloud
- Jira Service Desk
- HappyFox
- JitBit Helpdesk
- Gorgias
- TeamSupport
1. Zendesk
- G2 Rating: 4.4 out of 5
- Pricing: Simple ticketing starts at $19/agent/month, Zendesk Suite starts at $55/agent/month, Support Enterprise at $115/agent/month., Add-ons like AI and Workforce Management start at $25/agent/month.
Zendesk for Service is an AI-powered customer support platform designed for businesses of all sizes. Offering omnichannel communication, advanced ticketing, and self-service options, Zendesk improves customer satisfaction while scaling up to meet your growing business needs. Its AI-driven automation features help streamline workflows, allowing support teams to focus on delivering exceptional service experiences.
Key Features:
- Omnichannel Support: Manage customer interactions across email, social media, live chat, and phone from one unified interface.
- Workflow Automation: Automate repetitive tasks like ticket routing, prioritization, and follow-ups to ensure efficiency and faster resolution times.
- AI-Driven Insights: Automatically categorize and prioritize tickets, enabling faster issue identification and resolution.
- Custom Dashboards: Visualize customer data and team performance with customizable dashboards.
2. Zoho Desk
- G2 Rating: 4.4 out of 5
- Pricing: $19-$40 per agent/month (Free trial available)
Zoho Desk is an omnichannel help desk application designed to enhance agent productivity by managing queries across multiple channels, like email, chat, phone, and social media. Features like workflow automation and AI-powered ticket categorization streamline customer support and improve efficiency.
Key Features:
- Omnichannel Support: Manage interactions from multiple platforms.
- Workflow Automation: Automate ticket management for efficiency.
- AI-Driven Insights: Prioritize and categorize tickets automatically.
- Custom Dashboards: Visualize data with customizable reporting.
3. Freshdesk
- G2 Rating: 4.4 out of 5
- Pricing: Starts at $19 per agent/month (Free trial available).
Freshdesk is an intelligent AI-powered customer service platform designed for businesses of all sizes. It offers robust ticketing, automation, and omnichannel support, helping businesses streamline workflows. Freshdesk’s built-in AI, Freddy AI, increases efficiency by automating tasks and assisting agents with resolving customer queries quickly.
Key features:
- Omnichannel Support: Manage interactions across email, chat, phone, and social media from one interface.
- Self-Service Portals: Customers can access help articles through the knowledge base.
- Extensive Integrations: Seamlessly integrates with over 1,000 apps, including Slack, Salesforce, and Shopify.
4. HubSpot Service Hub
- G2 Rating: 4.4 out of 5
- Pricing: Free- $0/month (up to 2 users), Starter- $15/month per seat, Professional- $90/month per seat.
HubSpot Service Hub is an AI-powered customer service platform that enhances customer relationships through unified insights and streamlined support. It features omnichannel messaging, automated ticketing, and robust self-service tools. Integrating with HubSpot’s marketing and sales tools, it provides 360-degree insights to improve customer retention and satisfaction.
Key Features:
- Omnichannel Messaging: Manage customer interactions across various channels seamlessly.
- AI-Powered Automation: Automate ticketing and workflows to improve support efficiency.
- Customer Success Workspace: A centralized hub for tracking customer health and performance metrics.
- Extensive Integrations: Connect with over 1,500 third-party apps to enhance workflows.
5. Salesforce Service Cloud
- G2 Rating: 4.4 out of 5
- Pricing: Starter Suite: $25/user/month. Pro Suite- $100/user/month, Enterprise- $165/user/month, Unlimited- $330/user/month.
Salesforce Service Cloud is an AI-powered customer service platform designed to enhance agent productivity and deliver enhanced customer experiences. It features an integrated workspace that simplifies case management and incident resolution while supporting field service operations. Agents can access real-time customer data by consolidating information from multiple channels—such as phone, social media, email, and chat—allowing for informed decision-making and faster response times. This holistic approach improves service quality, driving customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Key Features:
- Omnichannel Routing: Manage customer interactions from multiple platforms in real time.
- Knowledge Management: Access to quick, relevant solutions for resolving issues.
- Slack Integration: Streamline collaboration across teams.
- AI-powered insights: Automate workflows and predict case priority.
6. Jira Service Desk
- G2 Rating: 4.2 out of 5
- Pricing: Free Plan- For up to 3 agents., Standard- $17, 400 per year (51-100 agents), Premium- $44,000 per year (51-100 agents), Enterprise- Custom pricing for 201+ agents.
Jira Service Desk was rebranded as Jira Service Management in 2020, integrating enhanced ITSM capabilities and features beyond Atlassian’s original offering. Therefore, it is now an IT service management platform that provides teams with tools to streamline requests, incidents, and changes. It supports high-velocity operations across IT, development, and business teams, making managing customer service and internal requests easier.
Key Features:
- SLA Management: Monitor and ensure timely resolution of service requests.
- Multi-Channel Support: Manage requests via customer portals, email, and chat.
- Incident and Problem Management: Automatically prioritize, track, and resolve incidents.
- Asset and Configuration Management: Track and manage hardware and software assets.
- Knowledge Base Integration: Provide self-service solutions with an embedded knowledge base.
7. HappyFox
- G2 Rating: 4.5 out of 5
- Pricing: Basic– $29/month/agent (5-agent limit), Team- $69/month/agent, Pro: $89/month/agent, Enterprise PRO- Custom pricing.
HappyFox Helpdesk is an advanced help desk platform designed for omnichannel support, offering seamless ticket management for customer inquiries across email, phone, chat, and social media. With features like a self-service knowledge base, automation rules, and reporting tools, it streamlines workflows and enhances team productivity. Furthermore, HappyFox integrates with numerous third-party apps and suits IT teams, HR, and customer service departments.
Key Features:
- Omnichannel Ticketing: Consolidates tickets from multiple channels.
- Automation Engine: Automates repetitive tasks and workflows.
- Customizable Knowledge Base: Build internal and external knowledge bases.
- Task Management: Break down complex issues into manageable tasks.
- Proactive Agent Collision: Prevent duplicate ticket handling.
8. JitBit Helpdesk
- G2 Rating: 4.2 out of 5
- Pricing: Freelancer Plan- $29/month (1 agent), Startup Plan- $69/month (4 agents), Company Plan- $129/month (7 agents), Enterprise Plan- $249/month (9 agents, $29/agent/additional agent).
Jitbit Helpdesk is a versatile issue tracker for customer support and internal IT teams. Its core focus is email-based ticketing, allowing users to track and manage customer inquiries seamlessly. With features like a live chat widget, a built-in knowledge base, a report builder, and asset management, Jitbit provides a comprehensive solution for handling support requests. It also includes an automation engine for streamlining workflows and 500+ integrations with third-party apps like Jira, Slack, and GitHub. Available as both a cloud-based SaaS and an on-premises version, Jitbit is highly customizable and developer-friendly.
Key Features:
- Two-Way Email Integration: Converts emails into tickets for seamless inbox management.
- Automation Rules: Automate repetitive tasks and streamline ticket assignments.
- Mobile App Support: Handles tickets on the go via iOS and Android apps.
- Knowledge Base: Build self-service portals for recurring issues.
- Real-Time Updates: Provides live ticket and status updates without refreshing.
9. Gorgias
- G2 Rating: 4.6 out of 5
- Pricing: Starter- From $10/month (based on the average monthly support tickets), Pro- From $300/month (based on the average monthly support tickets).
Gorgias is a help desk platform specifically designed for eCommerce businesses. It offers omnichannel support, automation, and integrations with popular eCommerce tools like Shopify and BigCommerce. With over 13,000 merchants using Gorgias, it is built to enhance customer service efficiency, boost revenue, and drive growth.
Key Features:
- Omnichannel support across email, chat, and social media.
- AI automation to handle repetitive tasks.
- Integrations with 100+ eCommerce tools.
10. Team Support
- G2 Rating: 4.4 out of 5
- Pricing: Chat Support: $29/agent/month, Essential Support: $35/agent/month, Professional Support: $49/agent/month, Enterprise Support: Custom pricing available.
TeamSupport is a customer service software solution that simplifies complex ticket management while offering omnichannel support. Its customizable features, including automated ticketing, life chat, and analytics, provide seamless collaboration and proactive customer care. Integrations with tools like Slack, Salesforce, and HubSpot help teams improve workflow efficiency and deliver timely support.
Key Features:
- Omnichannel Ticketing: Centralized management of queries from multiple channels in one place.
- Data Analytics: Real-time insights into customer behavior and team performance.
- AI-Assisted Support: Automates processes and improves ticket resolution speed.
How to Build a Help Desk Stack
Selecting the right help desk software is vital for streamlining your support operations and delivering a seamless, responsive, and customer-centric experience. By leveraging the appropriate tools, you can ensure faster response times, more efficient workflows, and higher customer satisfaction. Below are the key categories for help desk software that play an essential role in achieving these goals:
1. Help Desk Software
At the heart of any support operation is the help desk software itself, which manages inquiries, organizes tickets, and tracks resolutions. Platforms like Zendesk, Freshdesk, and Zoho Desk provide comprehensive ticket management systems that handle queries from multiple channels, including email, chat, phone, and social media.
With powerful automation features, these tools can automatically route and prioritize tickets. Real-time monitoring offers valuable insights into metrics like response time and customer satisfaction. Integrating seamlessly with CRM platforms and other business tools, these solutions help teams maintain a high level of customer support.
2. Knowledge Base Platforms
A well-maintained knowledge base is essential to reducing incoming support tickets, and knowledge base software like Confluence, Guru, and Notion make it easy for teams to create, organize, and share a library of support resources. By offering FAQs, how-to guides, and troubleshooting documents, these tools empower customers to resolve common help desk tickets and issues independently. When integrated with help desk software, agents can quickly access and share relevant information, ensuring consistent and timely responses.
3. Live Chat Software
To meet customers where they are, live chat tools enable real-time communication on websites and apps. Solutions like Intercom, LiveChat, and Olark seamlessly integrate with help desk platforms, allowing agents to manage customer conversations while tracking other support activities. With AI-driven chatbots, these systems can automate initial responses to FAQs, ensuring faster resolution for routine inquiries while freeing up agents for more complex tasks.
4. Remote Support Tools
Remote support software is indispensable for technical support teams. Tools like TeamViewer, AnyDesk, and LogMein enable agents to access and control a customer’s device remotely, helping troubleshoot technical problems more effectively. Features such as screen sharing, file transfers, and session recording simplify the process, allowing support teams to resolve complex issues without being physically present.
5. Analytics and Reporting Tools
Analytics and reporting tools are imperative to improve support operations continuously. Platforms like Zoho Analytics, HappyFox BI, and Power BI provide detailed insights into help desk performance, tracking key metrics such as first response time (FRT), customer satisfaction scores (CSAT), and average resolution times. These insights allow support teams to identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions that increase customer satisfaction.
6. Digital Adoption Platforms
Digital adoption platforms (DAP) allow customers to find solutions independently, reducing overall ticket volumes and improving the user experience. They also guide service agents through common tickets and support requests, helping them with real-time support to overcome end-user issues. Tools like Whatfix, WalkMe, and Pendo integrate directly into applications, offering features like embedded search, contextual tooltips, and guided walkthroughs.
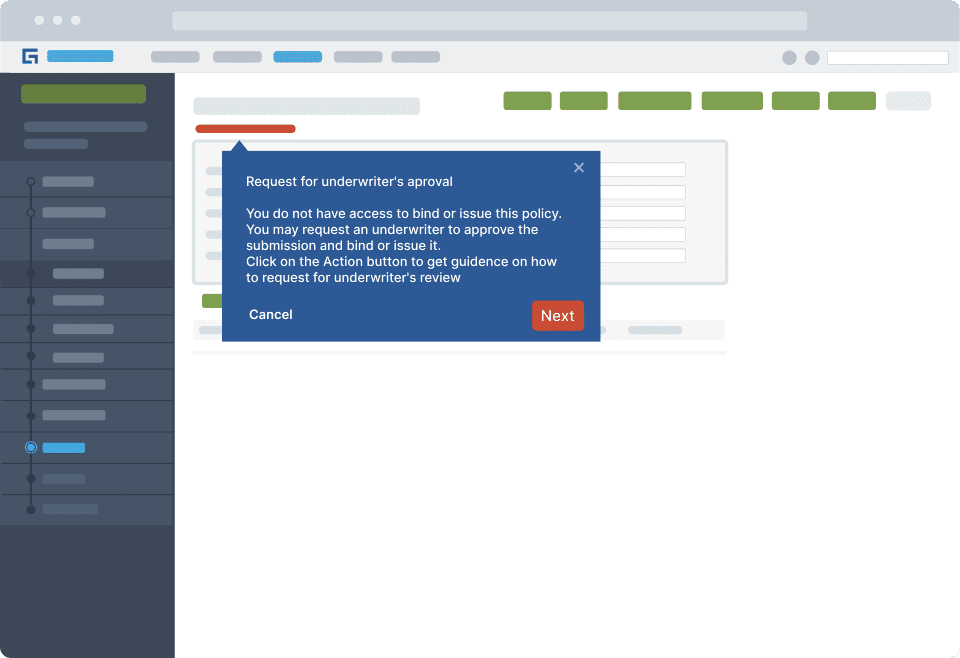

Whatfix’s Self-Help overlays onto any web application, desktop application, mobile app, or website. It provides contextual help to users and integrates seamlessly with FAQs, support centers, Learning Management Systems (LMS), user documentation, and more.



Users are provided with help content tailored to the specific tasks they are performing within the application. If they need more information, they can use a search feature to find detailed help articles or tutorials. In addition, help support cards offer step-by-step guidance directly in the app, walking users through specific workflows or tasks they need assistance with, ensuring they can complete processes smoothly and without challenges.
These solutions enable users to resolve issues independently, providing instant answers and reducing the workload on support teams. Moreover, they empower users to navigate applications effectively without relying on direct agent intervention.
Help Desks Click Better With Whatfix
Whatfix’s self-help support solution integrates seamlessly with leading help desk platforms like Zendesk, Freshdesk, Zoho Desk, and others, allowing your help desk to deliver more efficient, contextual, and user-friendly experiences.
By providing in-app guidance, real-time support, and user insights, Whatfix enhances the user experience, empowers users to resolve issues independently, guides agents through common service request resolution flows, and provides just-in-time training to both end-users and service agents.
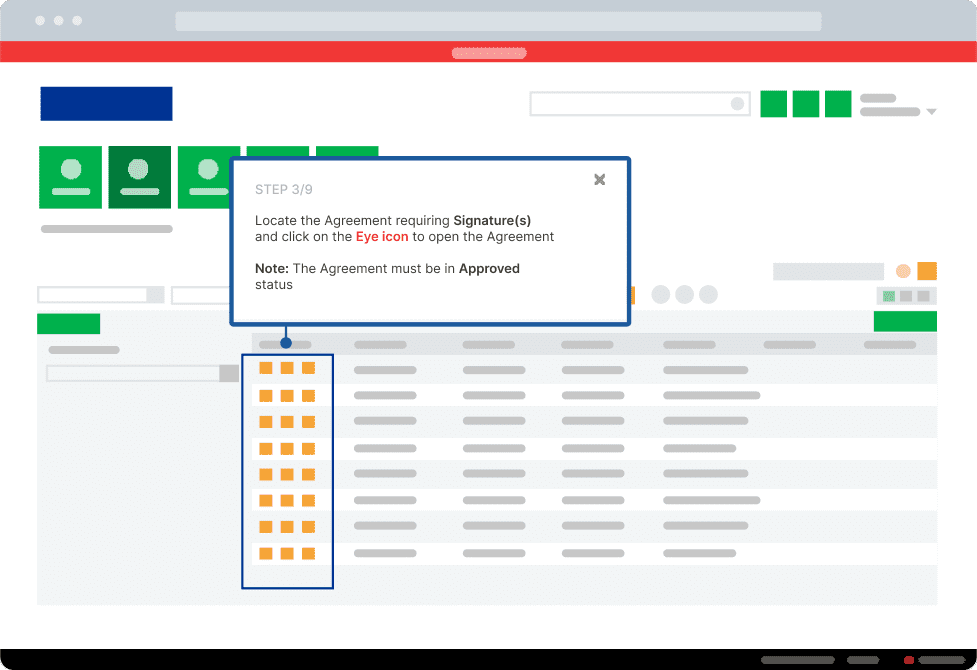
1. In-App Guidance with Whatfix Flows
With step-by-step in-app guidance, Whatfix Flows helps users navigate help desk systems and resolve issues in real-time. Whether troubleshooting, ticket creation, or navigating self-service portals, these flows turn complex workflows into intuitive, task-driven processes. This reduces errors, speeds up issue resolution, and boosts customer satisfaction.

2. Task Lists for Practical Application
Whatfix Task Lists break down complex workflows into actionable steps that help users stay on track with their tasks. For help desks, this can mean guiding agents through ticket resolution processes or helping users with common troubleshooting steps. By providing clear, step-by-step instructions, Task Lists ensure that even complex queries are handled efficiently, reducing the time spent on each ticket and improving overall productivity.
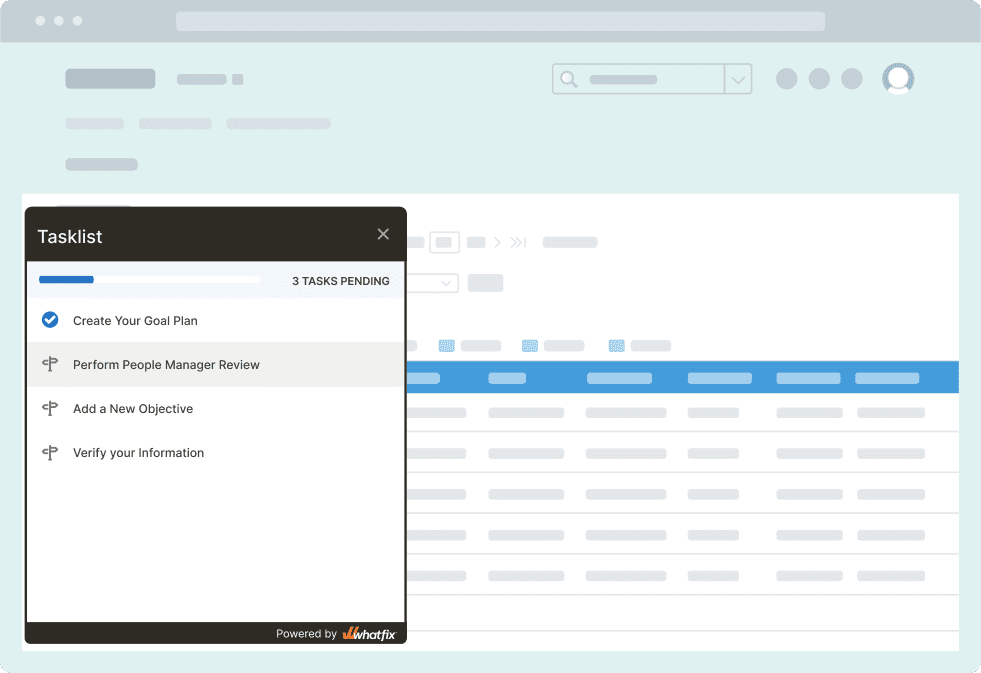

3. Interactive Walkthroughs for Support Tasks
Create interactive walkthroughs with Whatfix to provide real-time, immersive learning for users and agents alike within the help desk interface. Instead of simply reading instructions or watching demos, users are guided through tasks like creating a support ticket, navigating self-service portals, or resolving basic troubleshooting issues directly within the help desk interface. This hands-on engagement improves learning retention and makes the support process faster and smoother, reducing the need for agent intervention in routine tasks.
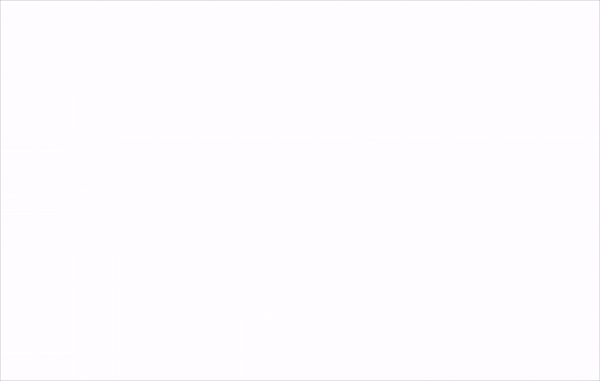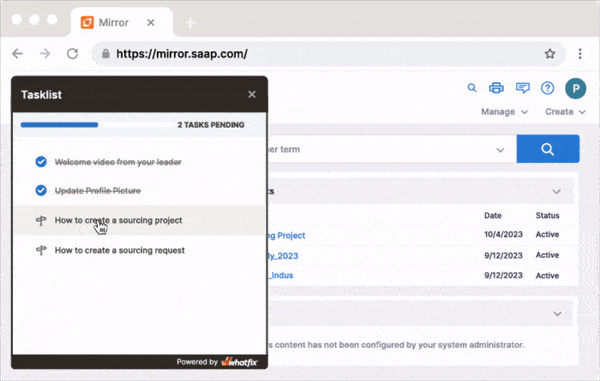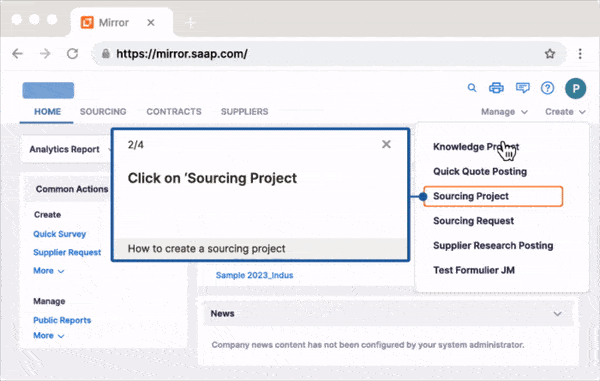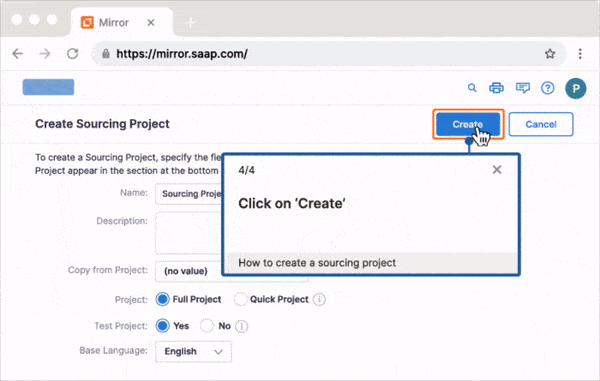
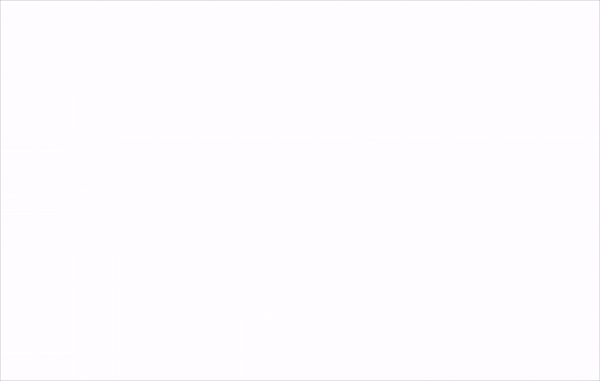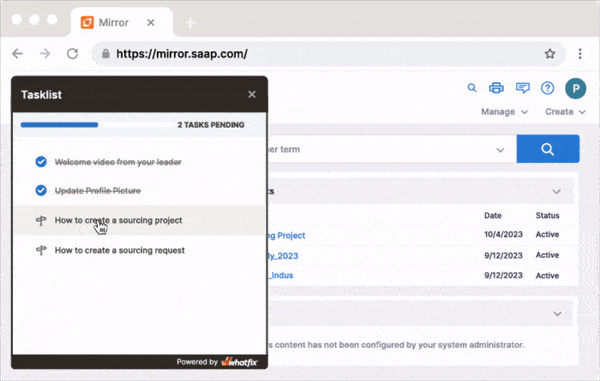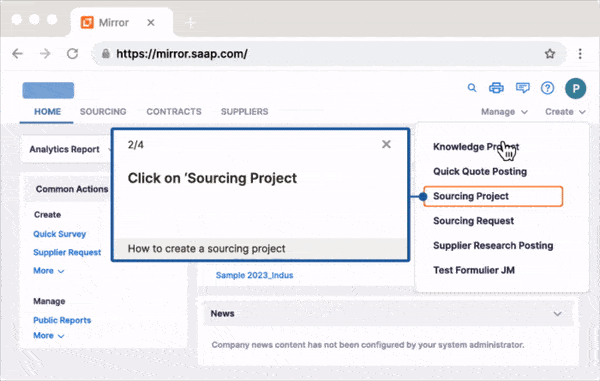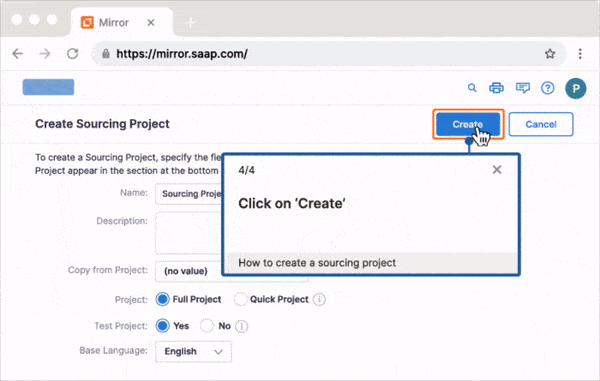
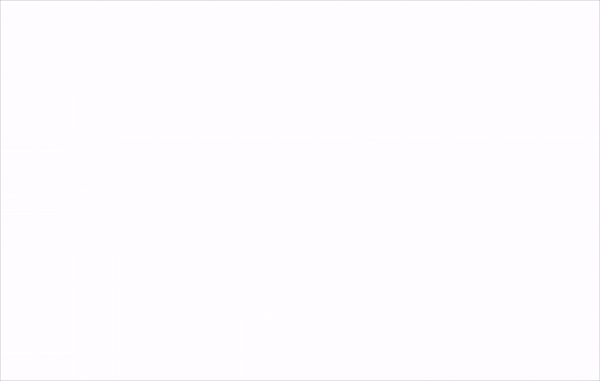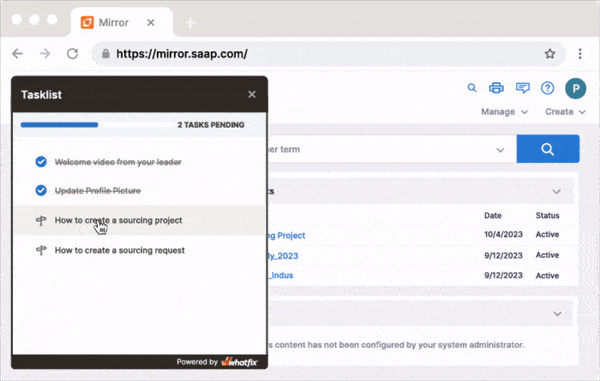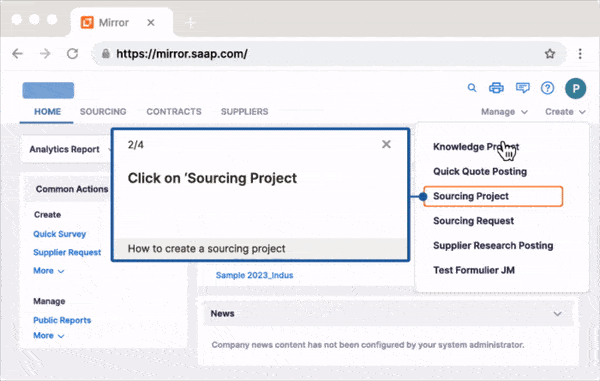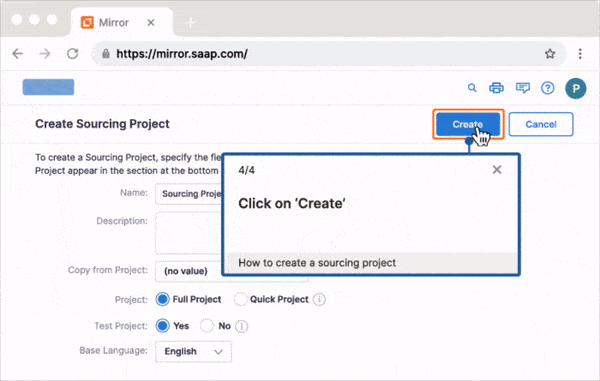
4. Smart Tips for Contextual Guidance
Smart Tips offer real-time, contextual guidance for help desk users, offering additional information when and where needed. These tips can appear as users fill out forms or navigate the help desk platform, reminding them of important details or helping them avoid common mistakes. For example, when submitting a ticket, Smart Tips might guide users on correctly filling in their information or offer solutions before a ticket is even submitted, reducing ticket volume and ensuring high-quality submissions.
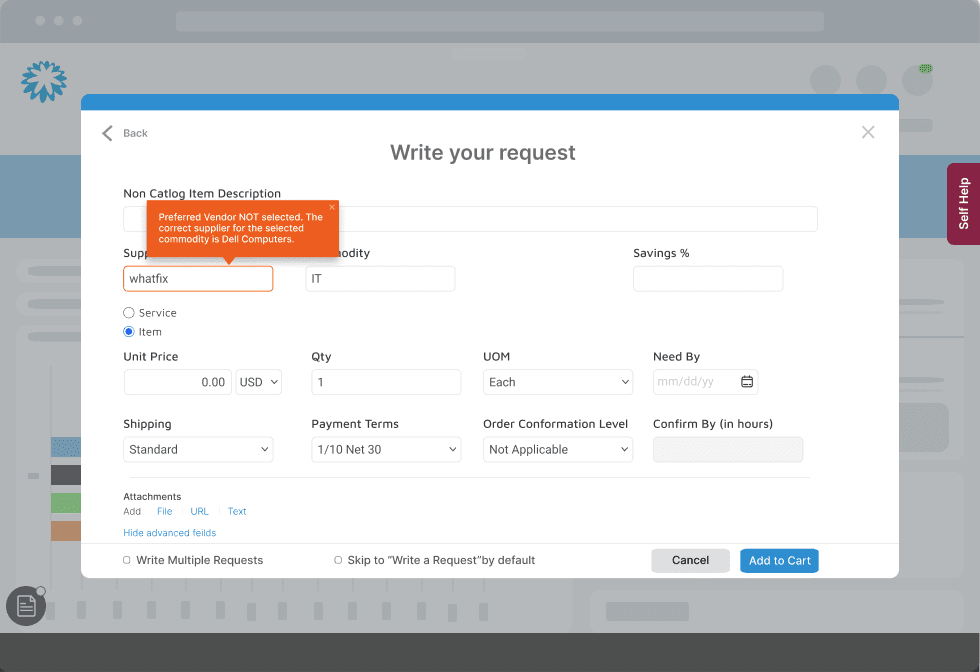

5. Beacons for Highlighting New Features
Beacons in Whatfix are visual indicators that highlight important updates or features within the help desk interface. For instance, they can alert users to newly available self-service options or guide them to key resources like FAQs or knowledge base articles. By driving users toward the most relevant parts of the help desk, Beacons enhance engagement and ensure that users can quickly find the information they need without overloading agents with routine inquiries.
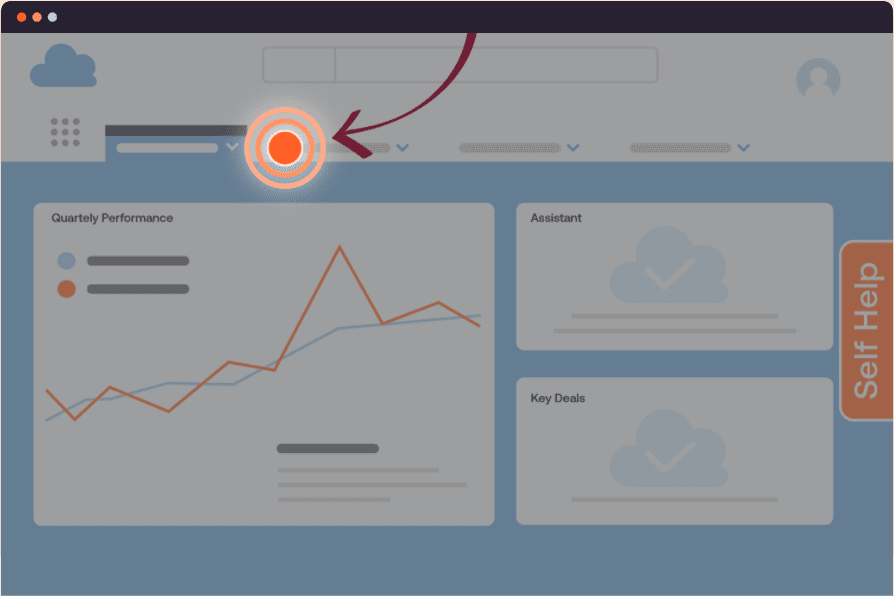

6. Self Help for On-Demand Assistance
Whatfix’s Self-Help Widgets are invaluable for help desks because they provide on-demand, context-specific support right within the platform. These widgets pull in relevant guides, articles, and FAQs based on the user’s current task, allowing users to resolve issues on their own without needing to submit a ticket. This feature reduces the workload on help desk agents and empowers users to solve common issues independently, improving both user satisfaction and the overall efficiency of the help desk.