IT Strategic Planning: Examples, Tools, Free Templates (2024)
- Published:
- Updated: January 29, 2024


IDC research suggests organizations will spend $7.4 trillion on digital transformation by the end of 2023.
With disruptive technologies driving enterprise innovation, IT departments can no longer exist solely as a reactive cost center to supplement office requirements. IT leaders must come to the foreground with a strategic IT plan to help sustain digital transformation and ITIL change management initiatives.
In this blog, we explore strategic IT planning and its phases, as well as software tools to facilitate IT innovation and modernization while delivering on their promise to reduce costs and drive strategic outcomes.
What is an IT Strategic Plan?
An IT strategic plan is a detailed document encapsulating an IT roadmap for a 3-5 year time span. The plan outlines the overall goals, required strategies, and tactics to support those IT goals in alignment with the organization’s overall business objectives.
IT Strategic Plan vs IT Strategy
Although a strategic IT plan and IT strategy are similar-sounding, there is a difference. IT strategy guides an organization to focus on how the IT department will help the business succeed, while an IT strategic plan is a long-term roadmap to help the organization implement those strategies.
The Need for Strategic IT Planning
During uncertainties such as COVID-19, technological disruption has experienced rapid acceleration in recent years. Remote work and digital selling have become a norm, and many organizations struggled to keep up with these changes. However, organizations with a well-established IT strategic planning process were able to quickly adapt to change and manage new IT changes better and more efficiently.
Given the criticality of a strategic IT plan, Gartner reports that only 29% of CIOs rated their IT strategy and planning as effective. However, the Fortune 500 organizations that have prioritized IT strategic planning have reported returns as high as 700%.
When executed correctly, as a continuous and iterative process, IT strategic planning enables an organization to:
- Be responsive to change
- Focus on high-value programs
- Reduce operational costs by funding the best-suited technology for digital transformation
- Communicate better and collaborate cross-functionally
- Improve data security and privacy
- Understand changing customer demands, market landscape, and digital innovation driving the businesses
- Align their technology roadmap with organizational goals
For example, when employees began working remotely across geographies, organizations relied on IT departments to take charge of investment priorities, security policies, and the adoption of new virtual technologies to keep businesses afloat, all of which required intensive strategic IT planning.
Key Components of an IT Strategic Plan
Every organization will have a different IT strategy suited to its business needs and requirements. Here are the core components that form the foundation of a successful IT strategic plan:
1. Alignment of IT with business goals
An IT strategic plan must be aligned with the overall business goals. Any IT infrastructure requests, digital transformation projects, and organizational change management strategies should be discussed well in advance to decide on investment priorities for the considered time frame.
2. Technological roadmap
The technology roadmap includes the long-term IT initiatives, requirements, and impact of technology implementation, followed by a detailed technology adoption plan.
For example, many organizations have migrated to cloud services such as AWS and Microsoft Azure from legacy (and outdated) on-premise data centers. This cloud transformation required a contextual change management plan for a successful transition focused on development, migration, setup, security, and adoption.
3. Change communication plan
Employees often undergo denial, anger, and resistance phases that make up the change curve before they can adapt to change completely. With a transparent and detailed change communication plan, you can onboard your team members and help them embrace change better – driving the adoption of new IT technologies.
4. IT services
For effective IT strategic planning, IT leaders must standardize the IT services offered within an organization and bridge the gap between the existing and required services. IT frameworks or operating models can be helpful here.
5. IT governance
IT governance is a subset of corporate compliance and ensures efficient and effective use of IT within the organization. IT includes policies related to cyber security and data protection. With the rise of hybrid and remote work with employees distributed across the globe, the need for an IT governance strategy has never been more critical.
6. IT best practices
IT organizations establish these best practices over a long period, and adherence to them ensures lower risks, reduced costs, and improved SLAs. Deciding on these best practices is a continuous process and must be updated regularly for relevance and improvement.
7. IT goals and metrics
IT leaders must clearly define the goals and KPIs in their IT strategic plan for the IT team to deliver timely. Well-structured IT metrics, KPIs, and goals will allow your team members to better plan for ad-hoc requests.
IT Strategy Plan Example
Based on the varying scopes of IT strategies across different organizations, the format of strategic IT plans differs. Here are three examples of IT plans for you to consider:
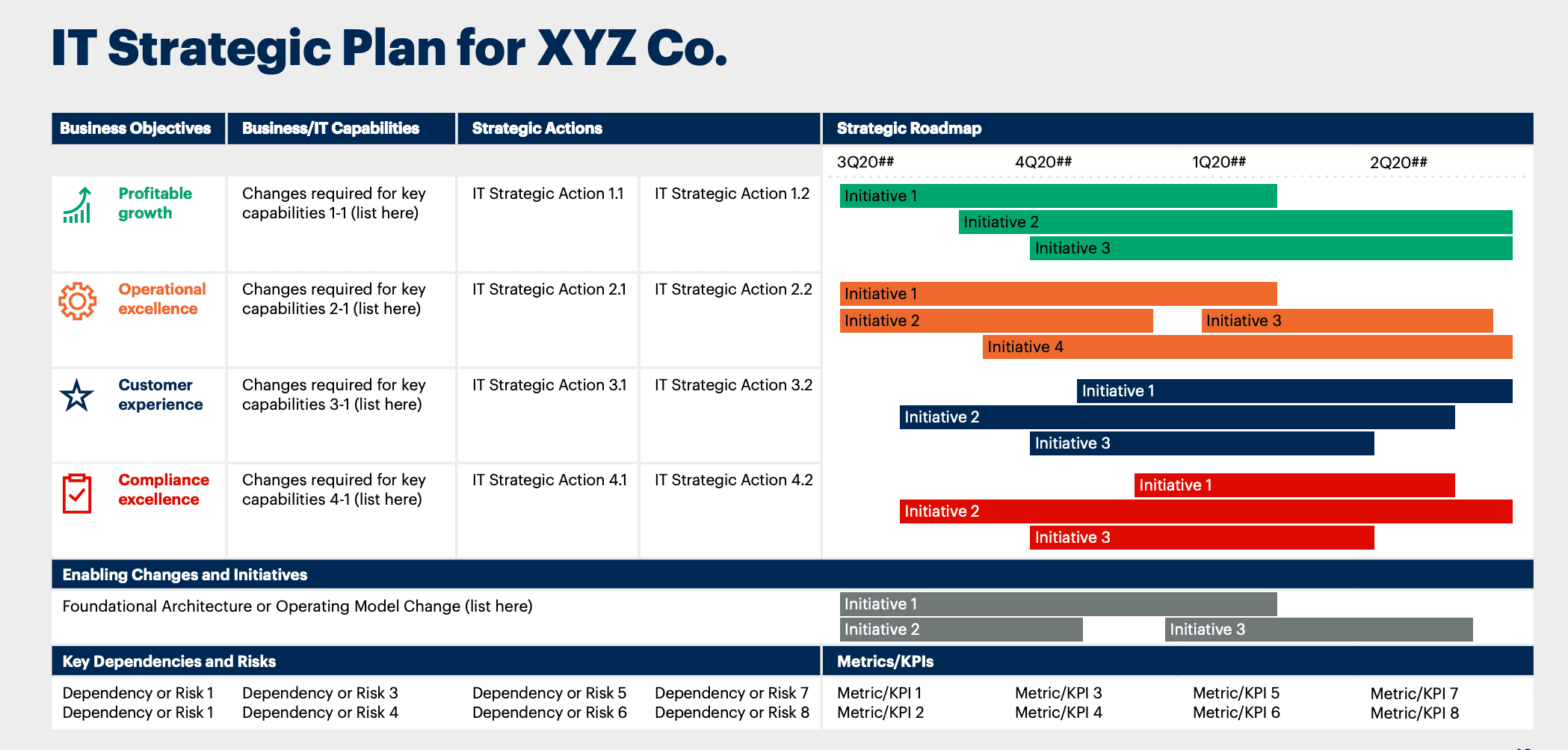
Gartner IT strategy plan example
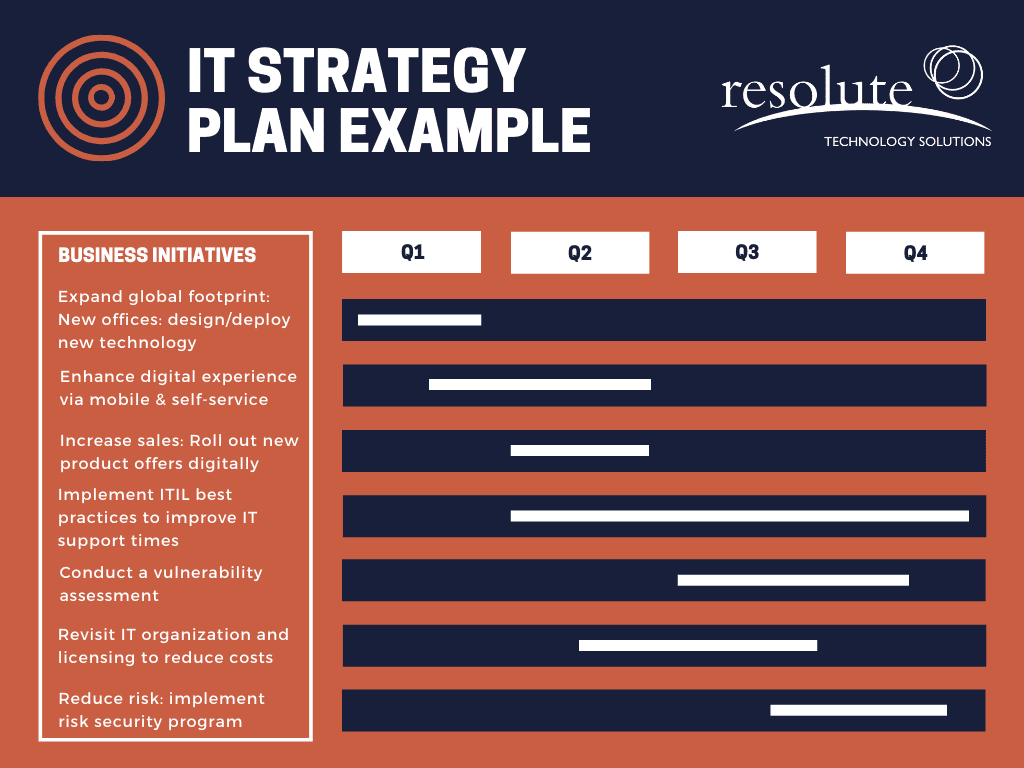
Resolute technology services IT strategy plan example
Whatfix IT strategy plan example
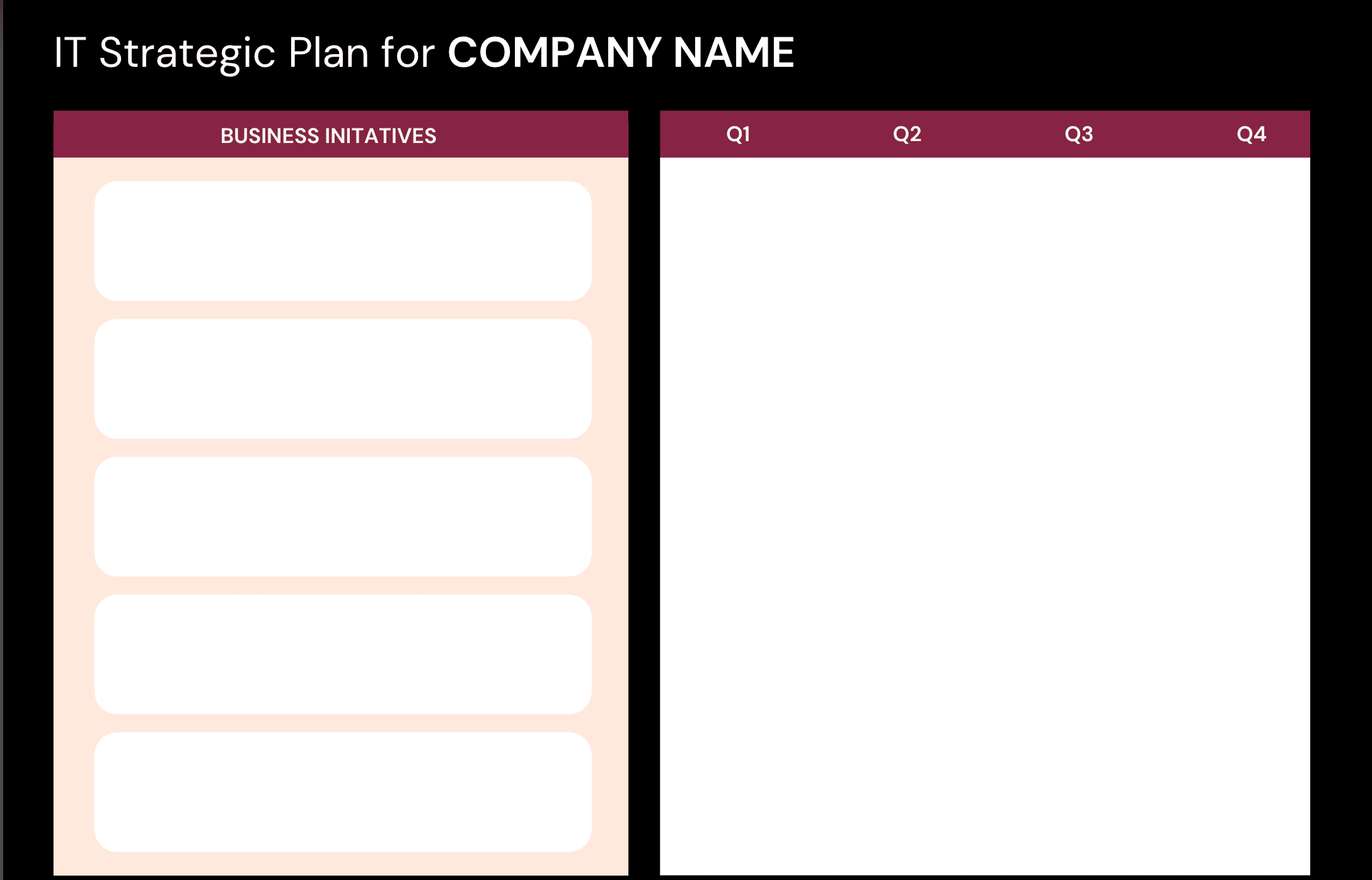
Here’s an editable version of the above strategic IT plan to get you started:
✓ Thank you, the template will be sent to your email
5 Phases of the IT Strategic Planning Process
IT strategic planning mainly occurs in the following five phases:
1. Discovery and analysis
In the first phase, IT leaders must analyze the inefficiencies of their business processes. The project manager facilitates stakeholder feedback via employee surveys, focus groups, and stakeholder interviews to assess the challenges and opportunities. Data can also be collected from external agencies, customers, and industry best practices to provide actionable insights.
2. Stakeholder buy-in
Any significant change implementation, such as software implementation, shouldn’t be completed without stakeholder buy-in. The easiest way to achieve this is to involve them in the planning process and show them that the project has support from leadership. Organizations may also hire external change management consultants to bring in the required expertise and objectivity based on a project’s scope.
3. Assigning roles and responsibilities
Create a detailed project charter outlining the project scope along with roles and responsibilities in this phase. You may use the RACI matrix to clearly define roles and increase employee accountability.

4. Implementation
In the implementation phase, the budget, deliverables, and timelines are clearly outlined. Since external factors may sway the timelines, it is crucial to highlight and prioritize long-term and medium-term IT goals and objectives. This allows you to create a plan with a strategic roadmap, connecting strategy with outcomes.
5. Review and documentation
All implementations will not be successful in one cycle, and much can change over 3-5 years. Therefore, it is essential to regularly track the progress of your IT change plan project and document it for future reference.

5 Strategic IT Plan Use Cases
McKinsey’s research found that 87% of leaders find “the complexity of existing infrastructure as an obstacle to implementing next-generation services.” As a result, CIOs need IT strategic planning to simplify and streamline legacy environments.
Here are a few additional use cases for IT strategic planning:
1. Digital innovation
IT strategic planning helps enterprises focus on digital innovation by allowing internal and external stakeholders to collaborate on future technology and investment decision-making. Businesses focus on developing high-value strategies for digital innovation initiatives such as:
- Switching from offline to digital processes
- Implementation of new software and platforms
- Development of a new technology
- Automation, IoT connectivity, and big-data analytics
2. Managing existing IT portfolio
IT strategic planning enables IT leaders to evaluate their current IT dependencies and associated risk assessments by obtaining regular feedback. This ensures enterprise cost optimization by conducting a cost-benefit analysis and redirecting funds to high-priority projects.
3. Digital transformation
Strategic IT planning helps an organization progress from a nascent or emerging stage to a digitally mature stage on the digital maturity index, empowering them to become more adaptive to digital transformation.
Deloitte’s report on Digital Maturity Index indicates a 38.5% increase in revenue and a 16.2 % upliftment in EBIT numbers when organizations become digitally mature and can optimize both the operational and strategic indices through digitalization.
4. Cloud migration
Creating a strategic IT plan can help organizations develop a plan for migrating to the cloud, including identifying the most suitable cloud solutions and developing a migration roadmap. By migrating to the cloud, organizations can improve their agility and responsiveness to changing business needs, as well as access a range of cloud-based services and tools that can enhance their operations.
Cloud migration can also help organizations reduce their IT infrastructure costs by eliminating the need for on-premises hardware and reducing maintenance and support requirements.
5. IT risk management
IT risk management enables organizations to identify, assess, and mitigate IT risks that may pose a threat to their operations. Organizations can enhance their cybersecurity and ensure business continuity in the face of potential disruptions by developing strategies for mitigating IT risks.
By taking a proactive approach to IT risk management, organizations can protect their critical assets, maintain compliance with industry regulations, and maintain the trust of their customers and stakeholders
7 Best IT Strategic Planning Software
Digital tools help IT teams manage their IT strategy plans. Here are seven of the best software tools to plan, execute, and manage IT strategy planning in 2024:

1. Cascade Strategy
G2 Rating: 4.8 out of 5 stars
Pricing: $57 per month per feature
Cascade Strategy is a one-stop solution for planning, execution, reporting, and people management to enhance business performance through IT planning. The solution allows you to create customized strategic plans, manage IT goals and KPIs, track project performance with dashboards, and manage human capital. Users also benefit from features such as single sign-on(SSO), data encryption, and strong integration capabilities.
2. Workboard
G2 Rating: 4.7 out of 5 stars
Pricing: Custom pricing
WorkBoard is the pioneer of enterprise strategy and result management solutions. It increases collaboration and accountability by clearly defining the goals in terms of OKRs. You can track the status of a project and initiate feedback if required.

3. entomo
G2 Rating: 4.7 out of 5 stars
Pricing: Employee Performance Management – $15 per user per month
entomo is a business-performance management software that helps organizations align goals to manage remote and distributed teams by offering skill gap analysis, task management, learning recommendations, succession planning, lead management, and augmented analytics.

4. ApptioOne
G2 Rating: 4.4 out of 5 stars
Pricing: Custom pricing
ApptioOne helps create a unified model by combining financial and operational data based on the industry-standard taxonomy of cost categorization. This software assists in implementing a structured view of IT expenses, lowering IT expenditure, and accelerating forecasting cycles.

5. Jira Align
G2 Rating: 4.1 out of 5 stars
Pricing: Contact for pricing
Jira Align is an enterprise agile planning platform that helps organizations align their IT initiatives with business strategy. It provides a range of features for agile planning, portfolio management, and reporting, including agile boards, roadmaps, and dashboards.

6. Planview
G2 Rating: 4.2 out of 5 stars
Pricing: Contact for pricing
Planview provides comprehensive project and portfolio management capabilities, which can help IT teams align their activities with business strategy. It allows users to create and manage project timelines, budgets, and resources and provides visibility into project progress and status.

7. Hive
G2 Rating: 4.6 out of 5 stars
Pricing: Contact for pricing
Hive is a project management tool that can help IT teams collaborate on strategic planning by providing a centralized workspace with task management, project tracking, and communication features. Hive can streamline the planning process, monitor progress, and ensure everyone is aligned with the strategic goals, improving communication, collaboration, and visibility.
With digital transformation on the rise, organizations must focus on the right implementation partners to support IT modernization and IT change management. You can make your IT strategy more bulletproof by leveraging a digital adoption platform such as Whatfix.
Whatfix helps organizations drive IT change, and modernization projects with an adoption strategy powered by in-app guidance, embedded self-help support wikis, and change management features such as beacons and task lists.
Schedule a demo with our experts to discover how Whatfix can help you roll changes effortlessly.
Request a demo to see how Whatfix empowers organizations to improve end-user adoption and provide on-demand customer support
Thank you for subscribing!