Companies lose billions of dollars every year because of software implementations that go wrong, but most of those dollars could have been saved by planning the process in advance.
For example, in mid-2019, fashion brand ASOS revealed to their investors that an implementation issue with their warehouse management software cost the company at least $25 million. They had performed a sizeable overhaul on their software, and massive complications resulted in inventory counting errors and items not included in packages.
No matter the size of your company, software implementation is a challenging task that requires careful planning and execution. Even the best software will fail without proper testing, evaluation, change management, end-user training, and post-implementation evaluation, so it is crucial to have a thorough plan before you begin the process.
What Is Software Implementation?
Software implementation is the process of adopting and integrating a new software application into your company’s systems and workflows. When considering enterprise software implementation plans, we typically think of mission-critical applications that are critical business operations, such as enterprise resource planning (ERP), CRMs, or supply chain software. The implementation process can also apply to software updates or significant upgrades that require development work.
Implementation can be a daunting task that carries risk, but it also has the opportunity and potential to make your company more productive and profitable via more automation and better data moats. It’s worth taking on the challenge since you could be much better off in just one year than you would have been if you hadn’t made any changes.
- Conga Implementation
- Coupa Implementation
- Duck Creek Implementation
- Guidewire Implementation
- Icertis Implementation
- MS Dynamics 365 Implementation
- MS Teams Implementation
- NetSuite CRM Implementation
- Oracle HCM Implementation
- S/4HANA Implementation
- SAP Ariba Implementation
- Salesforce CPQ Implementation
- Salesforce CRM Implementation
- ServiceNow Implementation
- Sharepoint Implementation
- SuccessFactors Implementation
- UKG Pro Implementation
- Workday Implementation
- Zoho CRM Implementation
✓ Thank you, the checklist will be sent to your email
Why Is Successful Software Implementation Critical?
Software implementation is a complex and risky endeavor. A staggering number of companies fail when integrating new software into their systems, and over the last few years, the number of botched implementations has risen dramatically.
Too many companies invest a ton of time and money into purchasing new software. Yet, once they make the purchase, they don’t put any energy into figuring out how to get it up and running or training employees on the new software. As a result, the implementation plan goes awry.

Shortcutting the planning stages can send negative ripples through your entire organization — at best, a rushed implementation will slow everyone down and cause headaches. At worst, shortcuts could contribute to your company’s downfall.
Poor implementation can cause unexpected downtime that costs you extra money in lost revenue and salaries paid out for little to no productivity. For example, if your employees can’t figure out how to use your new software because of a poor configuration or integration, they could develop workarounds that are less accurate or efficient.
In addition to lost revenue, a poor implementation can result in data loss and security vulnerabilities that can be exploited and lead to your systems being compromised.
How to Create a Successful Software Implementation Plan in 6 Steps
Once you’ve selected your software and chosen an implementation team — whether it’s your IT team or a third-party vendor — you’ll need a plan to make sure everything goes smoothly to drive ROI on our software investment. By developing processes ahead of time, you can avoid any surprises, minimize the risk of failure, and create the proper training so your entire company will realize the full benefits of your new software.
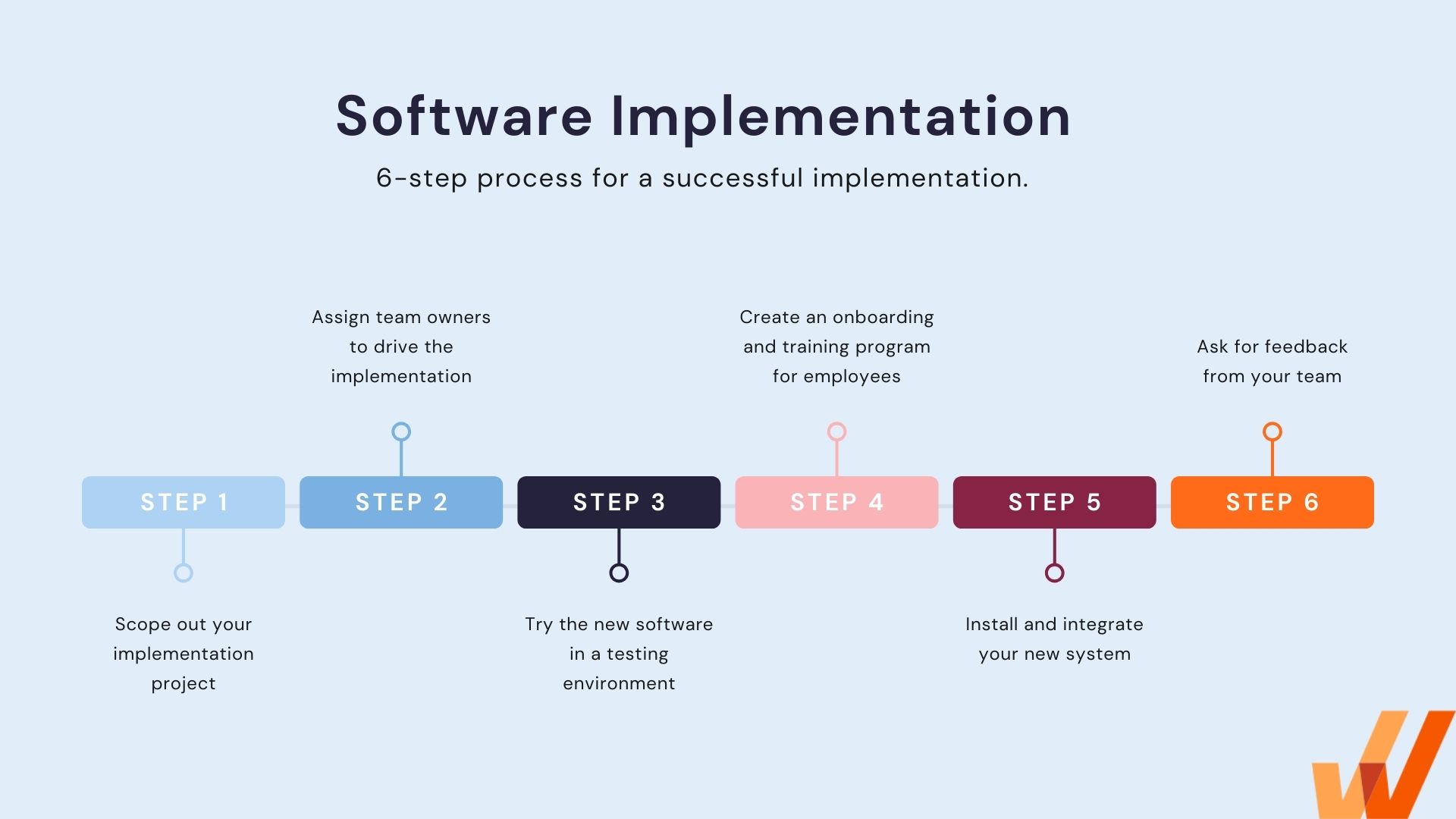
Successful software implementation starts with a clear definition of change success and the accompanying processes. Here are six steps to follow to ensure your software implementation project goes smoothly.
1. Scope out your implementation project
An implementation project scope is a detailed roadmap that outlines all the tasks you need to complete as part of your project. You can also use scopes to manage expectations, plan when each step will occur, and prevent issues by listing possible problems so you can fix them in advance. They can also assist in minimizing scope creep, which can cause confusion and missed deadlines.
You can tailor your project scope statement to the complexity of the software you’re implementing and your systems, but all scopes should include the following information:
- Deliverables — list the name and description of the software you are implementing and the total implementation cost.
- Your timeline — include a start and completion date. If you don’t have exact dates, provide an estimate.
- Prep work — anything that needs to be done with your current systems before implementation can begin.
- Excluded items — tasks that will not be part of the current implementation process but might be on a broader road map.
- Expected outcomes — to align stakeholders, explain what benefits you expect to gain and how your teams will use the new software.
- Potential conflicts or issues that may arise during implementation — this is anything that needs to be fixed or adjusted after your new software is deployed.
- A list of teams or employees that the new software will impact — make sure to include the types of training you’ll be providing.
2. Assign team owners to drive the implementation process
Communication is an essential part of successful software implementation. By assigning team owners, you can identify which responsibilities need to be managed so nothing falls through the cracks. These owners will know the best way to work around possible issues and understand how certain teams will be using the software. They can also think through the whole implementation process and work out any kinks before getting too far down the road with implementation.
You’ll need to determine who will be responsible for each step of the implementation and who should be involved in the planning and post-deployment stages. It’s common to select team owners by matching their expertise with the tasks. You can appoint employees with in-depth knowledge of each part of the process and according to their area of expertise. For instance, an implementation team can include employees from IT, engineering, project management, and learning and development.
The complexity of your company’s systems and your chosen software will determine how many people you need on your team. For instance, larger companies with more complex software may need a bigger team to execute an implementation successfully. On the other hand, smaller organizations can often get by with just a few team owners.
One additional benefit of assigning different team members from across your organization to this process is that it helps provide different teams support from people they trust – helping to alleviate any resistance to change that may occur.
3. Try out new software in a testing environment
To successfully implement a new piece of software into your system, you’ll need to have things in place to make sure your new software is compatible with your current systems and working as intended. The more testing you do, the greater your chance of implementation success.
A testing environment is a virtual space set up exactly like your current system but completely separate from the software you use every day. This testing or staging environment allows you to build, launch, and test new software to make sure it’s compatible and helps highlight bugs or any features that are not working correctly. Your developers will set up a testing environment for you — make sure it’s part of your scope.
A testing environment takes extra time to set up, but it’s needed to protect your live system from malfunctioning. It might be tempting to deploy a seemingly simple piece of software without trying it out in a testing environment first. Still, even simple software can melt down your current systems if there are serious incompatibilities, so don’t risk it.
PRO TIP
With Whatfix Mirror, you can easily and quickly create sandbox IT environments of your web-based enterprise applications for user testing and hands-on IT training. End-users can interact and engage with a replica version of your software applications. This allows you to identify bugs, collect user feedback, and train users before launching new systems without risking live software use.
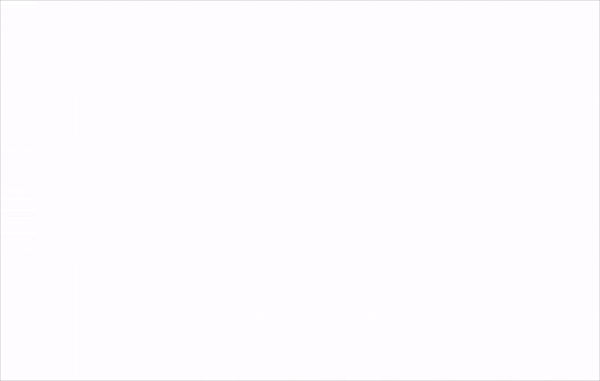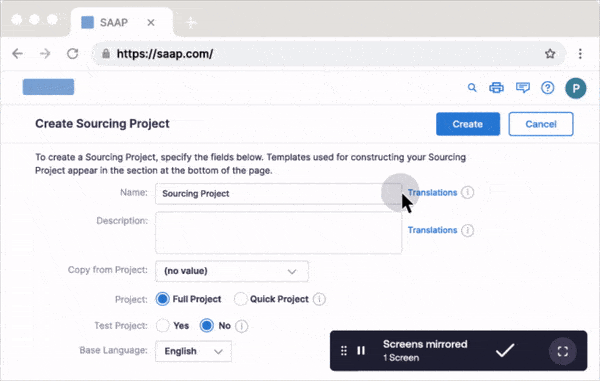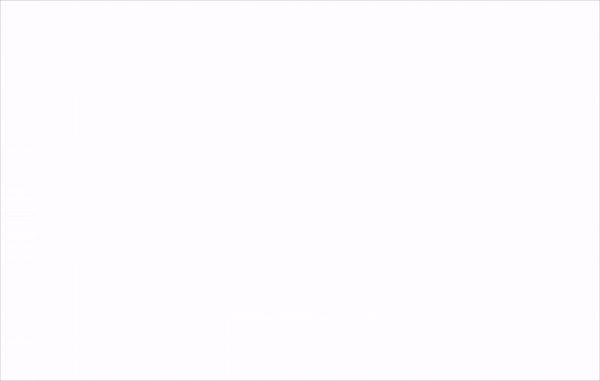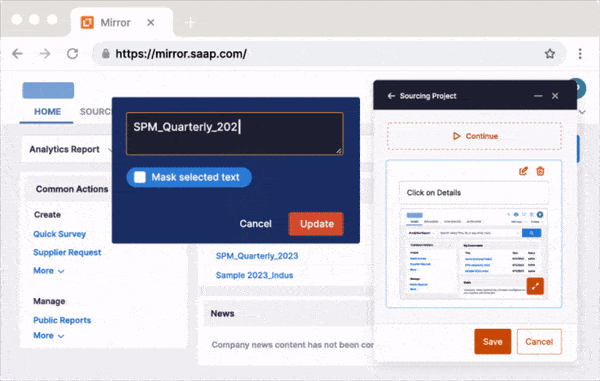
4. Create an onboarding and training program for employees
Software implementation is often only associated with the technical steps, but preparing your team is a critical part of the process. Create your employee onboarding and training programs in parallel with your implementation, so you don’t have any downtime once the software is ready for use.
To make sure everyone who needs to use the software gets trained, roll out your training on a team-by-team basis to make sure each team knows the right way to use the software for their particular application.
Your software implementation onboarding and training program should include:
- An overview of the software’s essential functions
- How to use the software for maximum efficiency in each team’s workflow
- Who to turn to for help
- Ongoing support and a way to provide feedback
- Training on new features as they come up
PRO TIP
With a digital adoption platform like Whatfix DAP, IT teams and application owners can use a no-code editor to create in-app guidance and on-demand user support to guide new and existing users through new software and process updates. With Whatfix, engage your end-users in the flow of work with product tours, interactive walkthroughs, in-app tutorials, onboarding checklists, tooltips, in-app resource centers, and more.
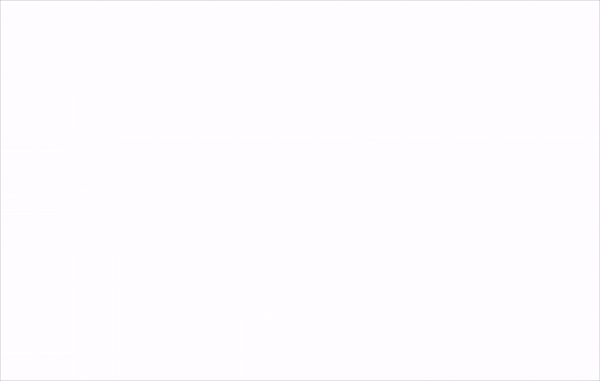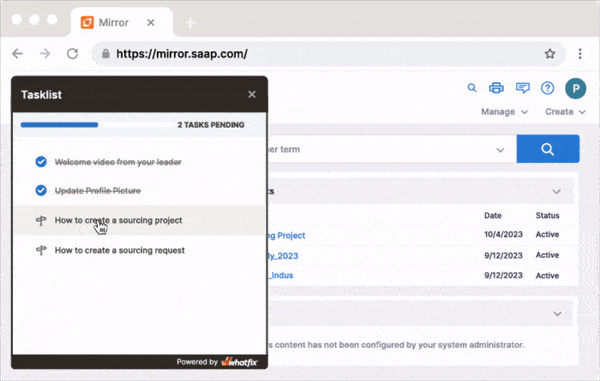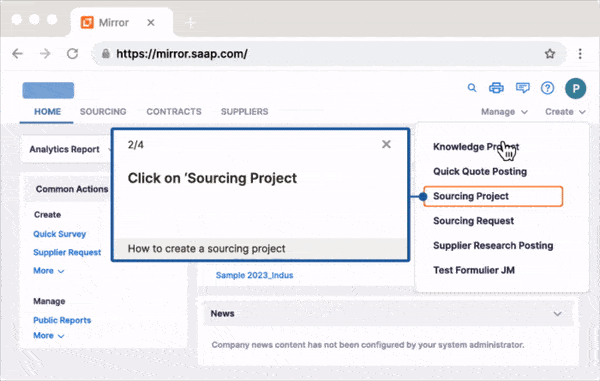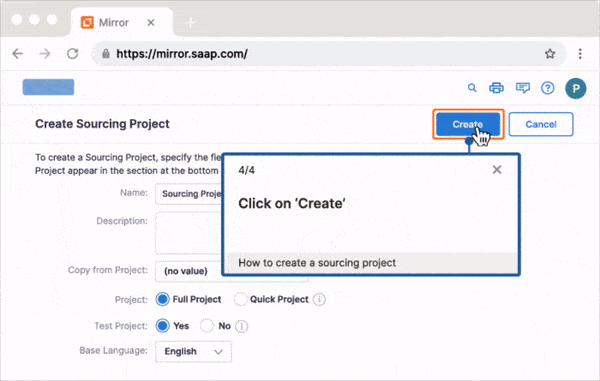
5. Install and integrate your new software tool
Now it’s time to do the installation and integration work. Depending on what you’ve installed, this is the point where your employees will begin using your new software. If your deployment requires shutting down your existing systems, roll out your new software during off-hours when the least amount of employees are logged in, and warn employees in advance.
If your software requires new accounts or logins, make sure to send out account creation and login instructions just before or at the same time the launch occurs. In addition, it’s helpful to send reminders at least a few days before launch to ensure you don’t encounter any surprises.
To encourage digital adoption, seek out internal champions of the new software to improve adoption. These advocates play a vital role in getting more people excited about using your new software by showing employees how it can help them. Tasks that are well suited for internal champions include answering basic questions and showing a new user how to navigate the software.
6. Ask for feedback from your team
It’s essential to design a feedback process as part of your implementation, so you can identify any glitches, bugs, or other issues once the software goes live. Early feedback will let you address issues before they are widespread, so start asking for feedback while employees are training to use the software.
The process of getting feedback from every employee using your new software can seem like a daunting task, but a short email survey is usually enough to highlight common issues. You can ask for feedback by department or on an individual basis and focus on questions that ask how they feel about their experience using the software. To ensure a secure feedback loop, make sure your business has a trusted email hosting service to prevent phishing attacks or compromising critical business information.
Regardless of the method you use to solicit feedback, your implementation team should have an open line of communication with employees to provide support and address any issues that arise.
With Whatfix, organizations are able to gather feedback from employees on their onboarding and training flows – right in the flow of work.

Whatfix also empowers L&D and IT teams to understand how employees are actually using and interacting with their company’s software and technology. By capturing employee behavioral analytics, organizations are able to understand what features are being underutilized, see what types of training have higher rates of engagement, and create more contextual onboarding, training, and support content.
Whatfix provides application owners and IT teams tasked with software implementation projects with a comprehensive no-code platform to enable software users, drive user adoption, and achieve business outcomes with frictionless software experiences. With Whatfix:
Enable application end-users with contextual, in-app onboarding and continuous training – all in flow the flow of work – with role-based Tours, Task Lists, Flows, Smart Tips, and more.
Provide on-demand performance support for application users with Whatfix Self Help. Connect your in-app help center to your knowledge repositories and LMS to provide constant in-app support for employees.
Identify common troubleshooting issues to take a data-driven approach to new user support documentation and in-app guidance with Guidance Analytics.
Build sandbox application environments for simulated hands-on user training and testing with Whatfix Mirror.
Keep application data clean by enabling users with in-app Field Validation.
With Whatfix Surveys, collect feedback from application users to identify additional training needs, gather information on the overall software implementation, identify bugs, and more.
Analyze application end-user behavior to identify areas of user friction and process inefficiencies, map optimal workflows, compare cohorts of users, and analyze user adoption journeys with Whatfix Analytics.
Request a demo to see how Whatfix empowers organizations to improve end-user adoption and provide on-demand customer support
Thank you for subscribing!



