Employee performance management is a core responsibility of workplace supervisors and HR leaders. This practice is multifaceted and involves performance monitoring, goal setting, and establishing systems of rewards and consequences based on performance. Accurate measurement of employee performance is essential to manage this process effectively, but it is challenging to achieve without a structured approach.
Using a standardized tool or structure is critical to ensuring consistency and reliability in performance assessments. One widely used tool for assessing performance is the 9-box grid, a framework that helps business leaders assess employees based on their current performance and future potential.
In this article, we will explore the 9-box grid, outline its benefits and limitations, and provide guidance on creating one for your business. We will also provide several common alternative approaches to employee performance assessment.
What Is the 9-Box Grid?
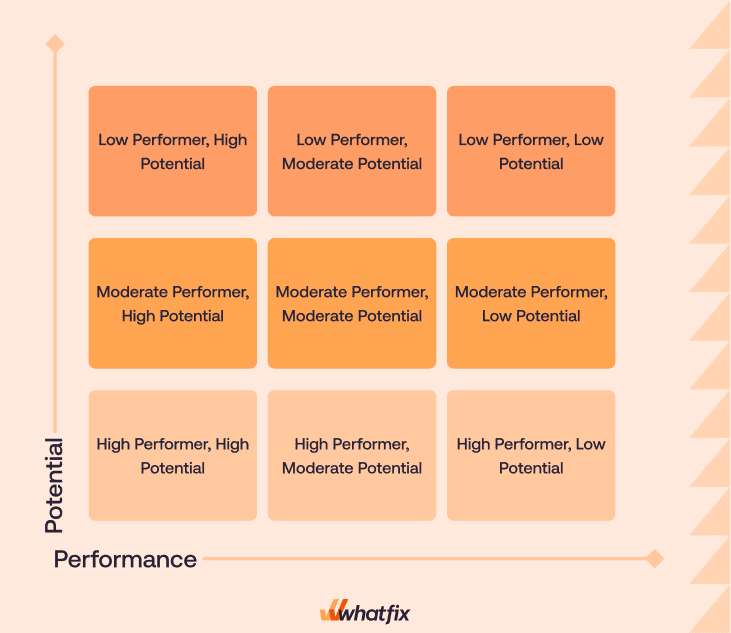
The 9-box grid is an employee talent management tool for conducting performance assessments. This 3×3 grid comprises nine categories into which employees are grouped based on their current performance and potential for future growth. The horizontal axis of this grid represents an employee’s current performance, ranging from low to high. The vertical axis, on the other hand, represents their potential, also ranging from low to high.
When it all comes together, each box of this grid represents the combination of performance and potential an employee exhibits in their role or for a given competency. These boxes can be additionally labeled with unique titles, such as “high performer,” “high risk,” or “key player,” or with broad categories of action to be taken, such as “improvement required” or “consider for leadership.”
These categories and suggestions can vary depending on the evaluation’s purpose. Still, the grid itself serves as a roadmap that can help managers and other business leaders understand their teams and make decisions for the future. Ultimately, the 9-box grid provides a visual and structured framework for facilitating employee development and succession planning.
What Is the Purpose of the 9-Box Grid?
A 9-box grid enables department and organizational leaders to evaluate and manage talent. Underlying this broader goal there are many specific reasons to use the 9-box grid as part of employee development processes. Here are some of its key purposes:
1. Identifying high performers and high-potential employees
One main purpose of the 9-box grid is to help managers single out employees who consistently exceed expectations and exhibit strong potential for future growth. These employees are placed in the top-right box of the 9-box grid, representing high-performance and high-potential employees who make good candidates for promotions or additional responsibilities.
2. Informing succession planning and career development
The 9-box grid allows managers to group members according to their performance and potential, creating pools of employees with similar readiness levels for future promotion, upskilling needs, and leadership identification. These categories are a starting point from which managers and other leaders can begin succession planning and create curated employee development plans for individual team members.
For example, suppose the categories toward the bottom-left corner of the 9-box grid contain many more employees than those toward the upper-right corner. In that case, managers should take this as a sign to revisit the team’s training efforts.
3. Highlighting training and support needs
The 9-box grid also allows managers to address shortcomings, skill gaps, and other training needs. It allows managers to make better decisions about where to focus development efforts.
For instance, employees exhibiting low performance but high potential may be able to move up to the top-right corner of the grid if equipped with the appropriate training or resources. Alternatively, employees grouped into the high-performance, low-potential category may benefit from one-on-one discussions with a supervisor to determine what might be causing friction. Over time, thoughtful use of this tool ensures more targeted development efforts and more efficient use of training resources.
4. Facilitating talent discussions and resource allocation
Because this tool provides a standardized way to evaluate employees, the 9-box grid can be used in talent discussions to eliminate biases stemming from personal opinions or relationships. It helps leaders make more informed decisions about talent development resource allocations. Sometimes, it might make more sense to devote resources to improving specific employee development areas rather than investing in broad mentoring and coaching programs.
5. Aligning employee development with organizational goals
By facilitating talent evaluations, the 9-box grid empowers business leaders to build a talent pipeline for future leadership needs, target skill gaps that align with organizational priorities, and strategically build a workforce well-equipped to serve critical business functions. Depending on organizational priorities, managers may choose to intervene in different ways.
For example, if an organization prioritizes sales growth, managers may provide sales or customer relationship management training to employees that fall into all categories for high potential.
How to Create and Use a 9-Box Grid
A 9-box grid is a relatively simple tool, but there are a few essential steps to follow to maximize its use for employee talent evaluation:
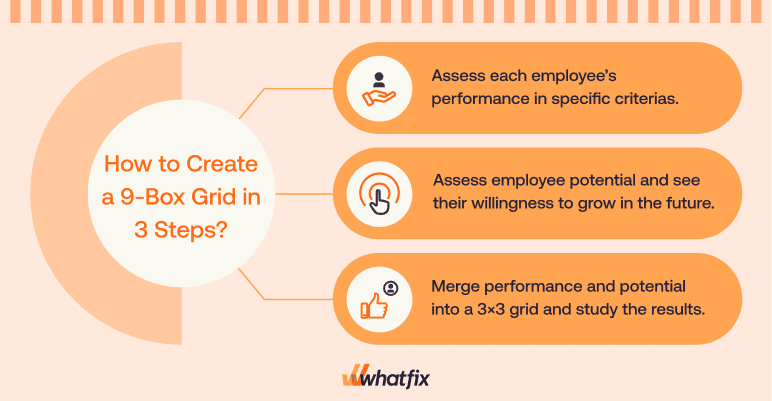
1. Identify valuable talent
Start by assessing each employee’s performance based on established job requirements and competency frameworks. Establish criteria for rating employee performance according to these required attributes.
In general, each employee will fit into one of these three groups:
- Low performance: Employees who must meet job requirements and achieve their targets and goals. They demonstrate a lack of motivation and alignment with the organization’s vision.
- Moderate performance: Employees who partially match their job requirements, individual targets, and goals.
- High performance: Team members who fully meet their job requirements and individual targets and consistently perform all tasks.
2. Assess employee potential
Next, evaluate the potential of each employee. Potential is defined by how much team members are expected to grow in the future, their willingness to learn, and their ability to apply their knowledge to routine tasks. Because potential is an intangible, more subjective concept, this process can be more complex than assessing performance. When you boil things down, potential can be considered an employee’s expected future behavior.
When measuring potential, employees can be grouped into the following categories:
- Low Potential: Employees who have reached their maximum capacity or are not motivated to grow further.
- Moderate Potential: Employees with room to further develop performance or expertise in their current role.
- High Potential: Team members who perform beyond expectations and responsibilities. They naturally and enthusiastically take on leadership opportunities and are always prepared for new challenges.
Employees may fall on different ends of the performance scale versus the potential scale. For example, an employee with low potential might already be working at the maximum capacity required for their current position, making them unsuitable choices for future leadership roles and heightened responsibilities.
On the other hand, employees who exhibit moderate performance and high potential may be better considerations for upcoming leadership roles, assuming managers provide them with effective training programs.
3. Merge performance and potential into a 3×3 grid
After evaluating employees according to their performance and potential, the final step is to place them in the corresponding box on the 9-box grid. For example, employees performing at a high level, but showing moderate potential may land in the top-center box, while an employee exhibiting low performance but showing high potential would be placed in the bottom-right box.
By creating a visual map of employee performance and potential, the 9-box grid can give managers and HR a clear view of where each employee stands and help inform them about the condition of their teams as a unit.
Breaking Down the 9-Box Grid Quadrants
HR and managers work together to assign each employee to relevant boxes on the 9-box grid based on the x-axis, which represents an employee’s current performance, and the y-axis, which represents their future potential.
These quadrants guide managers in creating an action plan for each employee based on their performance and potential.
1. Low Performance/Low Potential
Employees who fall into box 1 perform below expectations and do not demonstrate qualities that indicate potential for future growth. These team members may require individual coaching, but they may be simply ill-fitted for their current roles, potentially requiring reassignment or termination.
2. Low Performance/Medium Potential
This box includes employees who show some growth potential but are presently underperforming. These employees may begin performing at higher levels if provided support or training.
3. Low Performance/High Potential
Employees placed in box 3 are not meeting current expectations but demonstrate strong potential. These team members may begin performing higher if provided with a development plan or paired with a mentor who shares similar experiences.
4. Medium Performance/Low Potential
Employees landing in box 4 meet some or many of their role responsibilities but need indicators of potential. These team members may be fit to remain in their roles but are not the best candidates for promotions or additional responsibilities.
5. Medium Performance/Medium Potential
Employees in box 5 fall right in the middle of both scales. They are adequate performers and show some growth potential, but need a push in both areas. These employees are good candidates for future leadership roles but require training or mentoring to reach their full potential.
6. Medium Performance/High Potential
This box contains employees who perform moderately but show exceptional growth potential. These team members might benefit from the support in leadership development programs or special projects to help them reach the next level.
7. High Performance/Low Potential
Employees in box 7 are high performers who show little motivation or potential for future growth within an organization. These employees may be well-suited and happy to remain in their current roles for the long run.
8. High Performance/Medium Potential
Box 8 contains employees who exceed expectations but show limited potential for leadership roles or special responsibilities. These team members may be good fits for middle management positions or lateral moves rather than senior management.
9. High Performance/High Potential
This is the top-right box of the 9-box grid, representing employees who excel and show great growth potential. These team members are prime candidates for strategic projects and leadership development. If they remain engaged and supported, these employees could move into the highest levels of leadership.
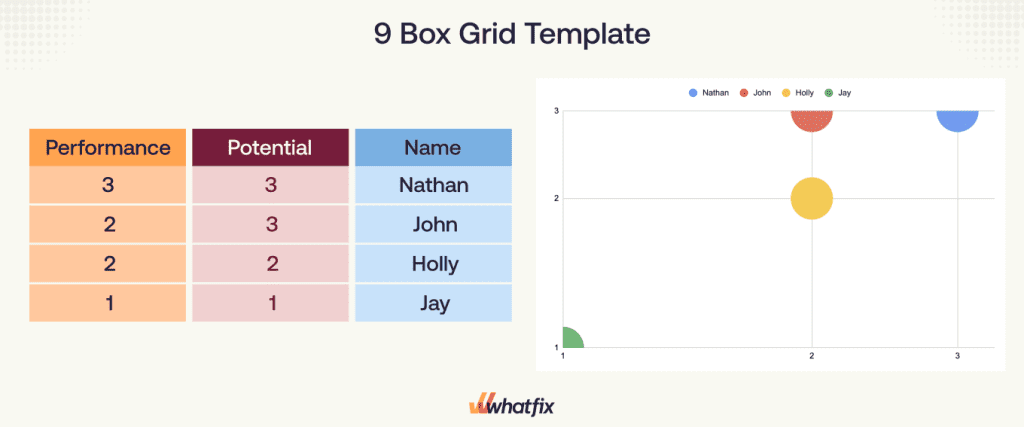
9-Box Grid Template
Are you looking to use a 9-box grid for your team? Download this free 9-box grid template to measure your team’s performance and create development plans for your employees:
Pros and Cons of the 9-Box Grid Exercise
Like all HR exercises for people evaluation, there are pros and cons of the 9-box grid. Let’s break down both below:
What are the benefits of using a 9-box grid?
The benefits of using a 9-box grid include:
- Easy and accurate identification of high performers and high-potential employees.
- Facilitates leadership succession planning and leadership development.
- Highlights of specific training and development needs for focused and efficient employee growth.
- Provides a structured approach for talent discussions among managers and leaders.
- Facilitates resource allocation decisions and development efforts to maximize business outcomes.
What are the limitations of using a 9-box grid?
Although the 9-box grid provides numerous benefits, it also has certain limitations:
- Employee evaluations may be subjective and influenced by manager biases
- Assessments are based on a static view of employees, not accounting for changes in performance or potential over time.
- Categorization reduces complex individual performance and potential into a simple matrix, potentially overlooking nuances.
- Accurate and fair evaluations require significant time and effort.
- Poor rankings can lead to lower morale and limit perceived growth potential if not framed correctly.
9-Box Grid Alternatives
Although the 9-box grid is primarily considered an effective method for succession planning and performance management, many alternative exercises and tools can help managers evaluate the talent of their teams. Here are some of the top alternatives to the 9-box grid:
1. Talent review meetings
Talent review meetings are structured discussions in which leaders and managers evaluate employees’ performance and potential. These meetings help managers identify high-potential employees, address development needs, and plan for succession.
Benefits:
- Facilitates comprehensive, qualitative discussions about employees.
- Encourages collaboration among leaders to ensure fair and holistic evaluations.
- Helps identify organizational talent trends and gaps.
Drawbacks:
- Can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
- May be subject to biases if not structured properly.
2. Performance-potential matrix
The performance-potential matrix is similar to the 9-box grid, but it can be customized with different dimensions and criteria. This tool maps employees based on their current performance and potential, typically resulting in more than nine boxes.
Benefits:
- Allows for more nuanced and flexible evaluations.
- Can be tailored to specific organizational needs and criteria.
- Encourages a deeper understanding of employee strengths and areas for development.
Drawbacks:
- May become complex and more challenging to manage with more dimensions.
- Requires consistent and objective data to be effective.
3. Competency models
Competency models define the skills, behaviors, and attributes necessary for success in specific organizational roles. Employees are assessed against these competencies to identify strengths and development needs.
Benefits:
- Provides clear expectations and standards for performance.
- Helps align employee development with organizational goals.
- Facilitates targeted training and development programs.
Drawbacks:
- Developing and maintaining competency models can be resource-intensive.
- May require regular updates to stay relevant with evolving business needs.
4. Individual development plans (IDPs)
IDPs are personalized action plans that outline an employee’s career goals and the steps needed to achieve them. These plans are co-created by the employee and their manager and focus on development opportunities, training, and experiences.
Benefits:
- Empower employees to take ownership of their career development.
- Provides a structured approach to personal and professional growth.
- Enhances employee engagement and retention.
Drawbacks:
- Requires commitment from both employees and managers to be effective.
- Can be challenging to track progress and ensure accountability.
5. Succession planning software
Succession planning software automates identifying and developing future leaders within the organization. This software helps manage talent pipelines, track employee development, and ensure readiness for critical roles.
Benefits:
- Streamlines and automates the succession planning process.
- Provides data-driven insights and analytics for better decision-making.
- Enhances transparency and consistency in talent management.
Drawbacks:
- Can be expensive to implement and maintain.
- Requires accurate and up-to-date data to be effective.
- May need integration with other HR systems for comprehensive functionality.
Upskilling Clicks Better With Whatfix
The 9-box grid is a powerful tool for evaluating workforce potential and identifying appropriate measures for maximizing individual potential across teams. By categorizing employees based on their performance and potential, this tool helps manager make better talent development decisions.
For managers, a digital adoption platform like Whatfix enables employees to learn in the flow of work with on-demand performance support – driving productivity and maximizing technology investments.
Here’s how Whatfix enables employee training:
- Whatfix’s no-code content creation allows for seamless and rapid development of training materials without the need for extensive technical knowledge.
- Whatfix Mirror offers hands-on training on mission-critical software applications, ensuring employees gain practical experience and confidence.
- Smart Tips provides contextual reminders and nudges at critical moments, helping employees stay on track and avoid common pitfalls.
- The Self Help feature offers on-demand access to contextual knowledge, documentation, and process assistance, empowering employees to resolve issues independently.
- Guidance Analytics provides insights into end-users engaging with in-app experiences and learning flows, enabling continuous improvement of training materials.
- In-app surveys facilitate post-training feedback, employee net promoter score (eNPS), and feedback on changes, ensuring that training programs continuously align with employee needs and organizational goals.
To learn more about Whatfix, schedule a demo today.