14 Best Process Improvement Methodologies (2024)
- Published:
- Updated: July 2, 2024

Every business has a set of standard processes & practices to help accomplish objectives efficiently and effectively. However, business processes often lose relevance over time, resulting in project delays and increased costs. As a result, you need to go through process improvement exercises regularly.
For example, COVID-19 acted as the digital accelerant of the decade. It disrupted business processes across the globe, and digital transformation became critical for corporate survival.
However, few organizations were ready to handle the changing business dynamics with its user-friendly interface, easy availability of supplies, customer self-service, and no-contact delivery options amidst the lockdown. For example, Amazon increased its market capitalization by over $700 billion because of its continuous investment in improving business processes.
Organizations must invest in continuous process improvement methodologies to adapt their workflows to customer demands, market changes, and digital advancements.
In this article, we will explore the concept process improvement and breakdown the most common process improvement methodologies for businesses to create a continuous improvement cycle culture.
What are the common methodology types for process improvement?
What Is Process Improvement?
Process improvement, also called business process improvement (BPI) or continuous improvement process (CIP), is the practice of optimizing existing business processes to meet the current industry standards and improve customer experience.
Process improvement aims at identifying, analyzing, and improving workflows. Processes can either be modified or complemented with sub-processes, or even eliminated for the ultimate goal of improvement (i.e., minimizing errors, reducing waste, improving productivity, and streamlining efficiency).
Process Improvement vs. Business Process Management
Process improvement and business process management (BPM) are closely related concepts in organizational development and efficiency. While both aim to enhance business processes’ performance and efficiency, they focus on different aspects and have distinct approaches.
Aspect | Process Improvement | Business Process Management (BPM) |
Definition | A systematic approach to enhance a company’s processes by reducing inefficiencies, improving quality, and optimizing productivity. | A holistic management approach that focuses on aligning all aspects of an organization with the wants and needs of clients. |
Focus | Targeted improvements on specific processes to eliminate waste, reduce costs, or improve output. | Comprehensive management of all processes within an organization to achieve operational excellence. |
Scope | Often project-based, focusing on specific, identified processes for improvement. | Ongoing, organization-wide process management focuses on continuous improvement and strategic alignment. |
Methodologies | Utilizes methodologies like Six Sigma, Lean, or Kaizen for specific process enhancements. | Involves using BPM software and tools for process modeling, analysis, automation, and optimization. |
Tools and Techniques | Process mapping, root cause analysis, improvement cycles (e.g., PDCA cycle), and specific tools related to methodologies like DMAIC for Six Sigma. | Process modeling, workflow automation, business rules management, performance monitoring, and improvement software. |
✓ Thank you, the checklist will be sent to your email
14 Best Process Improvement Methodologies & Techniques in 2024
Here are 14 of the most popular frameworks and methodologies for process improvement to invest in:

1. Agile methodology
Agile is a flexible and iterative approach to project management and software development that promotes adaptive planning, evolutionary development, early delivery, and continual improvement. It encourages rapid and flexible responses to change through collaborative effort.
Best For: Organizations working on complex projects with the potential for frequent changes in scope or requirements, especially in software development and project management.
2. Six sigma
Six Sigma is a data-driven approach and methodology for eliminating defects in any process. It focuses on identifying and removing the causes of defects and minimizing variability in manufacturing and business processes using quality management methods. This is done through the five stages of process improvement: define, measure, analyze, improve, and control, or DMAIC.
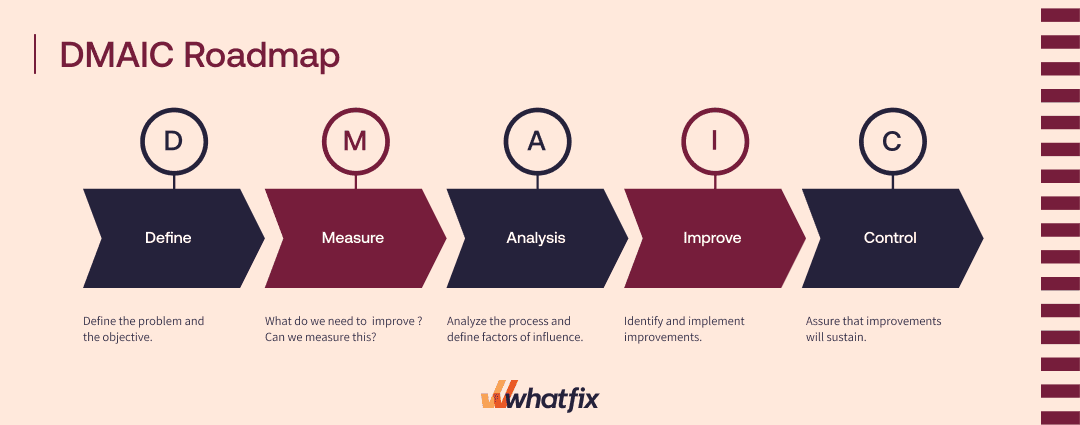
Best For: Companies seeking to improve the quality of their products and processes by identifying and removing the causes of errors and minimizing variability in manufacturing and business operations.
3. Lean manufacturing
Lean manufacturing aims to reduce costs by eliminating waste. Although the name suggests that this methodology is specific to the manufacturing industry, its core principle can also be applied to other sectors. To use this technique effectively, the process improvement team needs to map the value stream to understand buyer perception, allowing teams to successfully eliminate waste and redundancy from business processes.
For example, Intel adopted the lean manufacturing technique to provide higher-quality processors within a reduced time frame. By implementing quality control factors and waste reduction techniques, Intel reduced the time to bring a microchip to the factory from more than three months to less than ten days.
Best For: Manufacturing sectors and other businesses looking to improve efficiency by systematically reducing waste and streamlining processes.
4. Total quality management
TQM aims to improve customer satisfaction by getting the entire organization on board with continuous process improvement. This improvement methodology empowers employees by fostering a culture of change where employees aren’t afraid to experiment and have a shared business goal.
TQM implementation can vary across industries, but organizations using TQM generally follow these principles:
- Organizations should follow a systematic and strategic approach to achieve their business goals, sometimes including QMS implementation.
- Customers determine the level of quality.
- Effective communication and employee training techniques to ensure that employees understand the definition of quality and strive to achieve it.
- Organizations should define the process framework and monitor performance to detect any deviations.
Best For: Organizations aiming to embed quality in every aspect of their processes and products, involving every employee in the effort.
5. Just-in-time
Just-in-time manufacturing, also known as the Toyota Production System, aims to minimize inventory costs and increase efficiency by producing goods as required. Toyota executives invented this concept with a vision to adapt quickly and efficiently to changes in demand for models and reduce losses by keeping inventory that was immediately needed in-store.
It promotes a ‘pull’ strategy instead of a ‘push’ strategy. It is often implemented with the Kanban methodology to avoid overcapacity of work and requires accurate forecasting along with steady production for success.
Best For: Manufacturing processes looking to reduce inventory costs, increase efficiency, and decrease waste.
6. Theory of constraints
The theory of constraints methodology is a highly focused technique for creating rapid improvement. It identifies any process bottlenecks and improves that bottleneck or constraint until it is eliminated. Here are the five steps that can help you attain your goal:
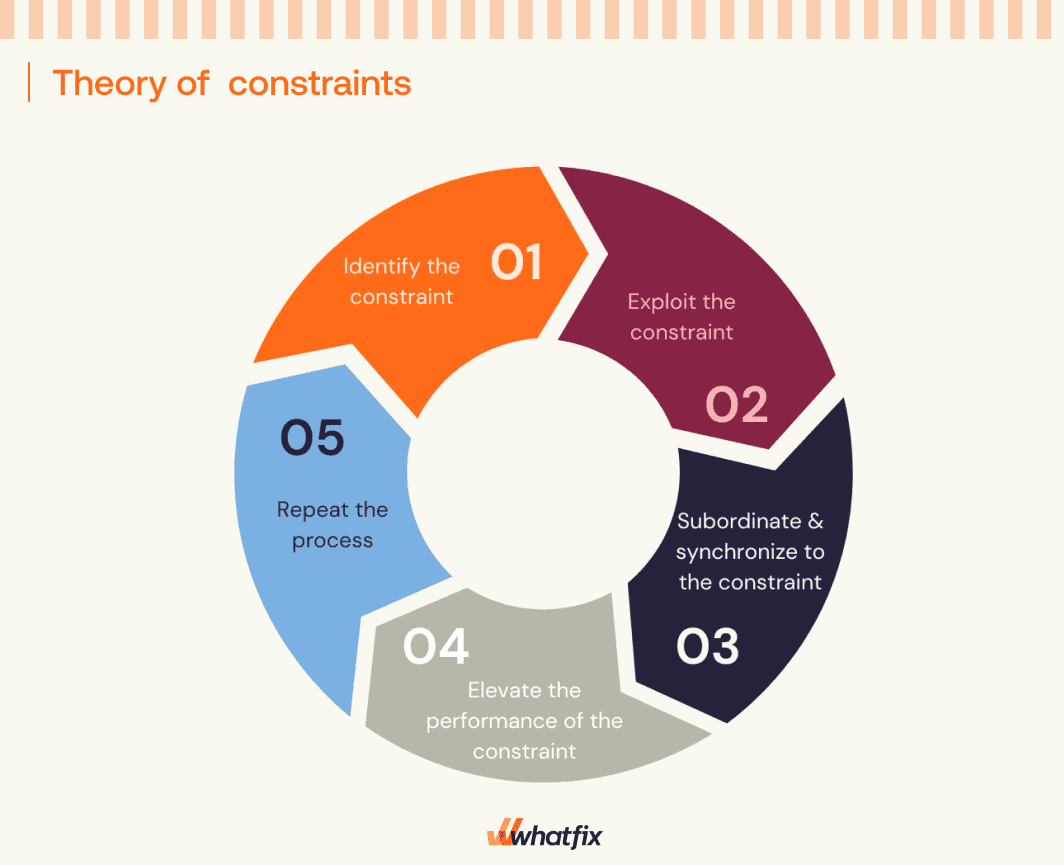
Best For: Businesses interested in systemic change to improve their profitability or operational efficiency by identifying and addressing their most significant constraints.
7. Kaizen
Kaizen emphasizes lean and agile practices to improve the quality and productivity of processes through slight shifts in work and corporate culture. For example, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries America(MHIA) initially created tailor-made(design-to-order) chemical & environmental plant designs.
However, after incorporating the principles of Kaizen methodology, it made small, continuous changes to its design process to establish a standardized module package. It decreased errors in the design phase and reduced cost to the customer by 5-10%.
Best For: Organizations of all sizes seeking to cultivate a culture where everyone is actively involved in suggesting and implementing improvements.
8. PDCA
The PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) Cycle is an iterative, four-stage approach for continuously improving processes and products. It is a fundamental model for problem-solving and quality improvement.
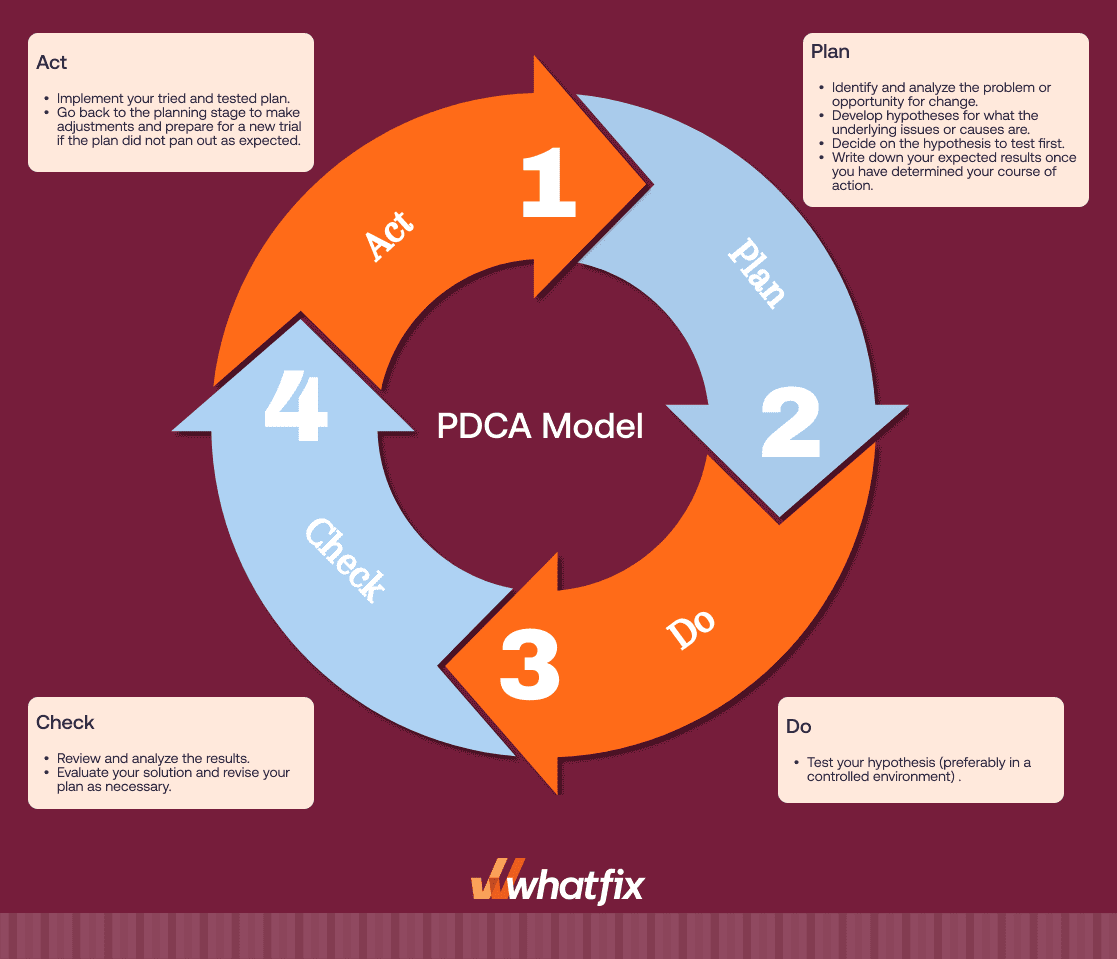
Best For: Any organization or team aiming to implement continuous improvements systematically.
9. Process mapping
Process mapping is a workflow visualization technique that helps companies map out a plan from start to finish for process improvement. The visualization can be a process flowchart, a functional flowchart, or a process model. Using process mapping tools, you can create process maps specific to roles or business goals to analyze your organization’s activities to improve productivity.
Best For: Businesses looking to get a clearer understanding of their processes to identify inefficiencies and areas for improvement.
10. Kanban
Kanban is a visual workflow technique used to identify problems, eliminate bottlenecks, improve efficiencies, and track the progress of your process improvement initiative.
For example, the fashion retail giant Zara uses Kanban boards at store levels to identify the kind of clothes that need to be produced and in what quantity. Store managers send a biweekly order to headquarters, based on their sales data and anecdotal evidence of what loyal customers want to see sold on the shop floor. Trending clothing styles are added to the order, which arrives in the store in two days. Zara’s adoption of lean production techniques has resulted in Inditex (Zara’s parent company) becoming the largest clothing retailer in the world.
Best For: Teams and organizations that want to enhance flow, reduce cycle time, and ensure continuous delivery with a visual management tool.
11. The people, process, technology framework
The people, process, technology (PPT) framework looks at every workplace business process, change, or transformation initiative through the lens of three interacting components:
- The People: The people within an organization directly impacted by a change or are in charge of driving the change.
- The Process: The processes that drive the success of a new implementation or transformation effort.
- The Technology: The tools, systems, and performance support enable your team members to accomplish these processes.
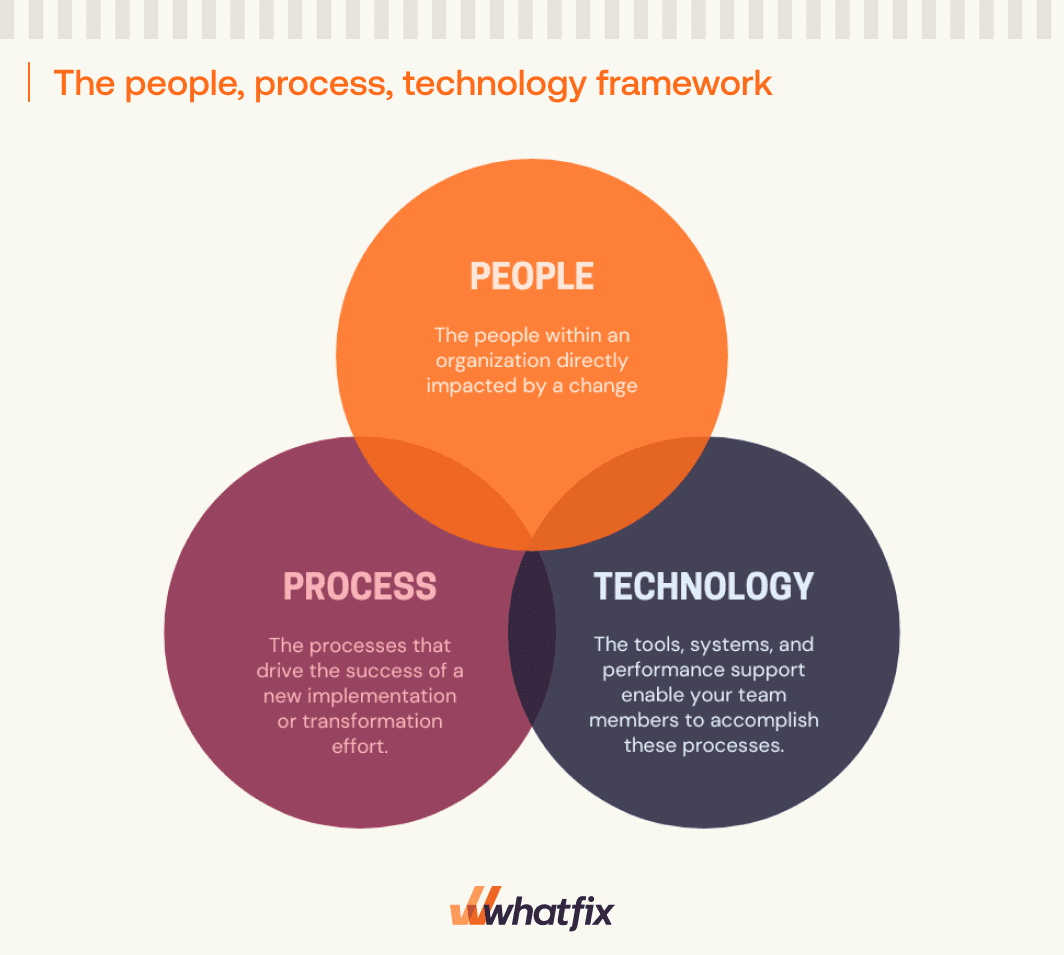
Best For: Organizations transforming, seeking to align their workforce, optimize processes, and leverage technology effectively.
12. 5S method
The 5S method is a systematic approach to workplace organization and standardization. Originating from Japanese manufacturing practices, it consists of five principles: Sort (Seiri), Set in order (Seiton), Shine (Seiso), Standardize (Seiketsu), and Sustain (Shitsuke). The goal is to create a clean, orderly, and efficient environment that enhances productivity and safety.
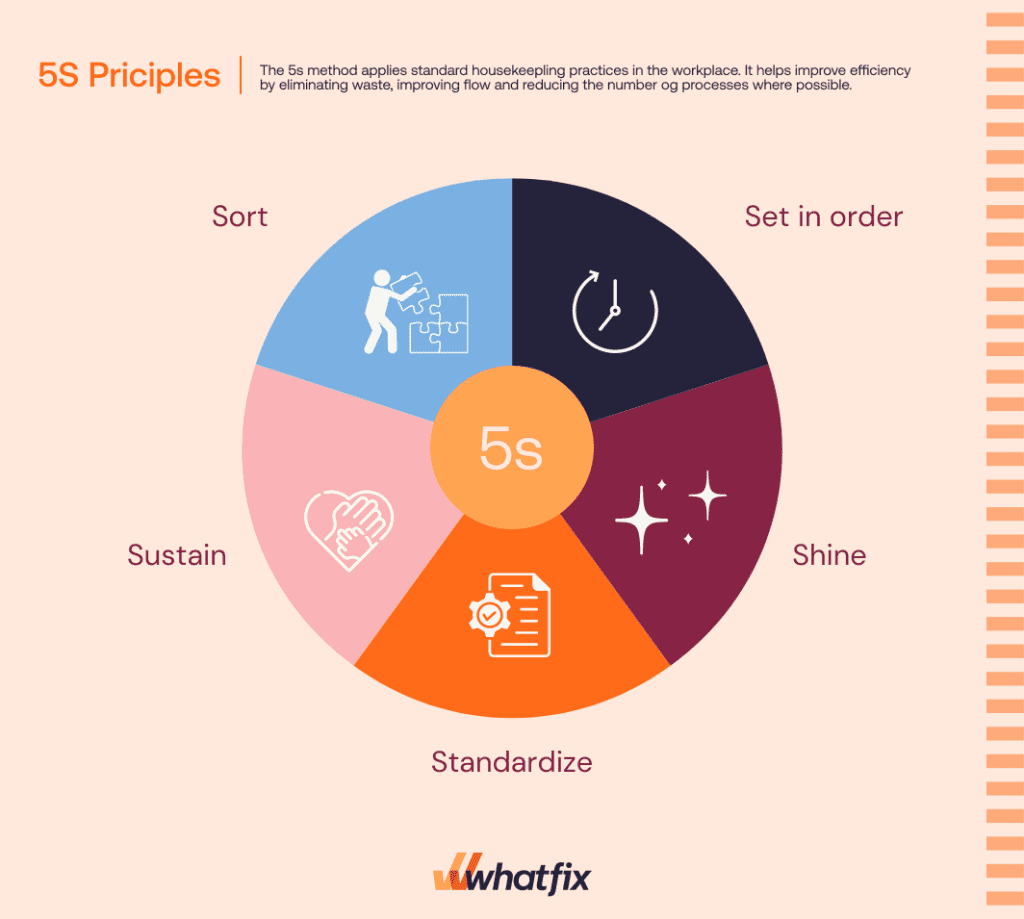
Best For: The 5S method is best suited for manufacturing, warehousing, and other physical workspaces where efficiency, safety, and quality are directly influenced by the organization and cleanliness of the physical environment. It’s also effectively applied in office settings to streamline workflows and reduce clutter.
13. SIPOC analysis
SIPOC is an acronym for Suppliers, Inputs, Process, Outputs, and Customers, representing a high-level view of a process. It is a tool used to identify all relevant elements of a process improvement project before work begins.
By mapping out these five components, teams can ensure a comprehensive understanding of the process and its context, helping to identify potential improvements. Let’s take the example of a simplified SIPOC analysis for a coffee shop that wants to improve its coffee-making process.
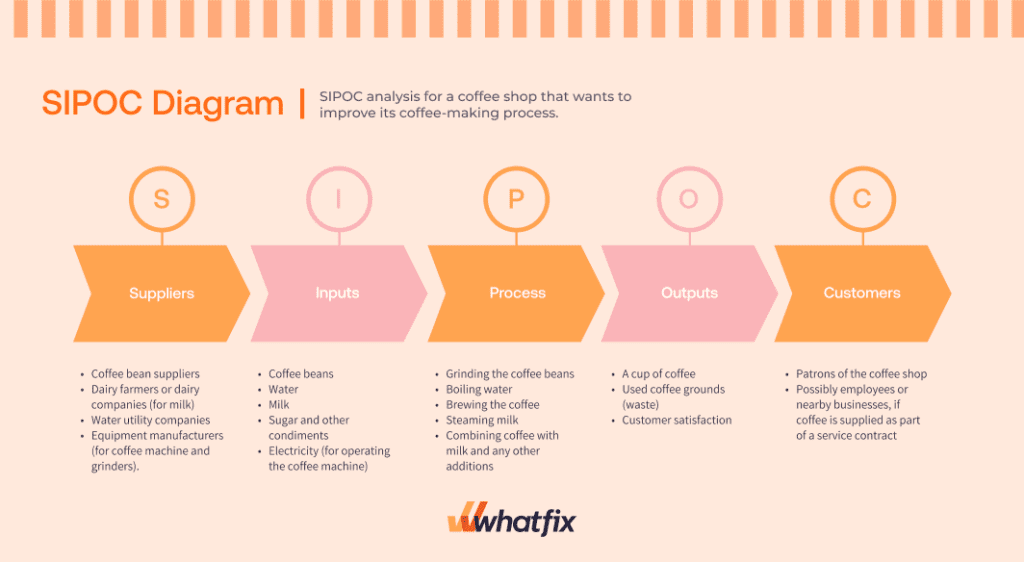
Best For: SIPOC analysis is best for the initial stages of process improvement projects, particularly in complex or cross-functional processes where understanding the relationships between different components is critical. It’s applicable across various industries and departments, from manufacturing to service delivery and administration.
14. Value stream analysis
Value Stream Mapping is a lean-management method for analyzing the current state and designing a future state for the series of events that take a product or service from its beginning through to the customer. VSM helps identify waste and streamline the production process by visualizing the flow of materials and information.
Best For: VSM is best for organizations looking to improve manufacturing, logistics, or service processes by reducing waste, improving flow, and enhancing value to the customer. It is beneficial in manufacturing but can also be applied in healthcare, software development, and other sectors where process efficiency impacts performance and customer satisfaction.
How Improved Processes Drive Business Outcomes
Here are a few of the benefits of process improvement that directly impact your business:
1. Improved productivity
Streamlining processes eliminates unnecessary steps, reduces duplication of efforts, and enables employees to focus on value-added activities. Automation of repetitive tasks further enhances efficiency, allowing teams to accomplish more in less time.
2. Cost reduction
Process improvements often focus on eliminating waste—whether in time, resources, or materials. By identifying inefficiencies and optimizing workflows, businesses can reduce overheads, minimize error rates and rework, and better use materials and assets.
3. Compliance
Documenting and standardizing processes make adhering to industry regulations and standards easier. By incorporating compliance requirements into the process design, organizations can ensure that they consistently meet legal and quality standards.
4. Reduced cycle times
Process optimization often involves reducing bottlenecks, streamlining decision-making, and improving the flow of information and materials. This can significantly reduce the time it takes to complete key business activities, from product development to order fulfillment.
8 Steps To Implementing a Process Improvement Method
Implementing a process improvement method is a strategic initiative that requires careful planning, execution, and monitoring to ensure success. Here are the eight steps to effectively implement such a method within an organization.
1. Gain executive buy-in
Executive buy-in is crucial for securing the resources, support, and visibility needed for the process improvement initiative. Leadership’s endorsement can also help overcome resistance to change within the organization.
To gain executive buy-in, present a compelling business case outlining the process improvement initiative’s benefits, costs, and expected ROI. Highlight how it aligns with the organization’s strategic goals.
2. Establish a cross functional team
A cross-functional team brings diverse perspectives and expertise, ensuring a holistic approach to identifying and solving process inefficiencies.
Select team members from different departments and levels within the organization who have a stake in improving processes. Ensure the team has clear roles, responsibilities, and the authority to implement changes.
3. Define objectives
Clearly defined objectives provide a focused direction for the process improvement initiative and criteria for measuring its success. Set specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) objectives based on the overall goals of the organization and the specific areas of improvement identified.
4. Map current processes
Understanding the current state of your processes is essential for identifying inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and areas for improvement. Use process mapping tools to visually document the steps, inputs, outputs, and flows of the processes. This helps in identifying and understanding the current process landscape.
5. Identify improvement opportunities
Not all processes need improvement, and not all upgrades deliver the same level of impact. Identifying critical opportunities for improvement focuses efforts on areas with the highest potential return. Analyze the process maps to identify inefficiencies, waste, and bottlenecks. Use data and feedback from stakeholders to prioritize improvement opportunities.
6. Select and tailor methodologies
The proper methodology provides a structured approach to implementing process improvements, but it needs to fit your organization’s specific context and needs.
Choose a process improvement methodology (e.g., Lean, Six Sigma, Agile) that aligns with your objectives and organizational culture. Tailor the methodology to suit the specific requirements and constraints of your organization.
7. Implement changes
The actual implementation of changes is where improvements are realized. This step requires careful planning, communication, and execution.
Develop a detailed implementation plan, communicate the changes to all stakeholders, provide necessary training, and execute the plan. Use change management principles to manage resistance and ensure a smooth transition.
8. Monitor, measure, and adjust
Continuous monitoring and measurement allow the organization to assess the impact of the changes and make necessary adjustments to ensure objectives are met.
Use the defined objectives and KPIs to track progress. Regularly review the impact of the implemented changes and adjust the approach as needed to achieve the desired outcomes.
The Whatfix digital adoption platform empowers organizations with the tools for analyzing, building, and delivering better business processes. With its robust features, such as process analytics and process automation, Whatfix empowers organizations to gain deep insights into their existing processes, identify bottlenecks, and implement improvements swiftly.
It facilitates the creation of guided workflows, enabling seamless onboarding and employee training. Moreover, by providing real-time, in-app guidance and performance analytics, Whatfix ensures users can navigate complex processes effortlessly. In the era of constant change and digital transformation, harnessing the power of a digital adoption platform can be the key to achieving operational excellence and staying ahead in the competitive business landscape.
To learn more about Whatfix, schedule a free demo with us today!

Thank you for subscribing!