Large organizations understand the need for a dedicated L&D strategy that develops leaders from within, upskills employees to become influential team members, and utilizes various learning methods and training techniques to drive skill acquisition.
This article explores different training methods, including traditional instruction-led learning, eLearning experiences, and hands-on training, to identify the more effective employee training methods for corporate learning.
By uncovering each method’s strengths, limitations, and applications, we aim to provide insights that empower organizations to design training programs that foster continuous learning, skill enhancement, and adaptability in an ever-changing professional landscape.
What are the most effective employee training methods?
- eLearning
- On-the-Job training
- Instructor-led learning
- Role-playing learning
- Coaching
- Simulation training
- Collaborative training
- Video training
- Cross-training
- Job shadowing
- Case studies
- Peer-to-peer learning
- Spaced learning
- Gamification
- Mobile learning
- Blended learning
- Microlearning
- Adaptive learning
What Is an Employee Training Method?
Employee training methods refer to the various approaches and techniques used to develop employees’ skills, knowledge, and competencies. These methods are designed to enhance performance, improve efficiency, and promote career growth within the organization.
Employee training methods encompass a range of L&D strategies, from traditional classroom-based training to modern technology-driven approaches. The choice of training methods depends on factors such as the nature of the content, the learning objectives, the target audience, available resources, and the organization’s goals.
18 Best Employee Training Methods & Techniques
Here’s a list of the most common employee training methods that organizations can choose from depending on their requirements and goals.
1. eLearning
As the corporate world embraced hybrid work environments, eLearning became the most recognized employee training method for organizations. eLearning (also known as online learning) refers to delivering educational content through online platforms. It often involves multimedia elements like videos, quizzes, interactive modules, and downloadable resources. Learners can access the material at any time, which promotes self-paced learning.
Modern organizations leverage corporate learning management systems (LMS) to create online training courses, manage learning content, distribute training, and assess performance. eLearning is ideal for managing mandatory compliance training, onboarding new employees, and knowledge-based training where consistent content delivery is essential.
Advantages of eLearning
- Scalability: Organizations can deliver training to many employees across different locations simultaneously.
- Consistency: All learners receive the same content and experience.
- Flexibility: Employees can learn at their own pace, anytime, anywhere.
- Cost-Effective: Reduces the costs associated with travel, printed materials, and classroom facilities.
Disadvantages of eLearning
- Lack of Engagement: Learners may lose interest if the content isn’t interactive or compelling.
- Technological Barriers: Employees may face issues with internet connectivity or access to devices.
- Self Motivation: Employees must be self-disciplined to complete the courses without direct supervision.
2. On-the-Job training
On-the-job training enables employees’ active participation by allowing them to learn on the hob or in the flow of work. The end goal of on-the-job training is faster task mastery or accelerated time-to-proficiency through learning by doing exercises and real-life scenarios.
On-the-job training embraces the 70-20-10 rule of learning, which states:
- 70% of learning comes from real experiences.
- 20% from social interaction.
- 10% from traditional learning sessions, like instructor-led or classroom-style learning.
On-the-job training is ideal for sales teams, manufacturing jobs, technical roles, call centers, and customer service positions. On-the-job training may include mentorships, job coaching or shadowing, and hands-on training exercises.
Advantages of on-the-job learning
-
Immediate Application: Employees apply new skills in real-time, accelerating learning.
-
Low Cost: Minimal formal resources are required since the training happens on-site.
-
Feedback: Learners receive direct feedback from supervisors, allowing for real-time adjustments.
-
Learning in the Flow of Work: Employees learn new skills without disrupting their daily routines and productivity.
-
Personalization: Facilitates personalized training by allowing employees to focus on the skills most relevant to their job.
Disadvantages of on-the-job training
-
Inconsistent Learning: The quality of training can vary depending on the mentor’s skills or time availability.
-
Mistakes in a Real-World Environment: Errors can lead to costly consequences or safety issues in high-risk industries.
-
Limited Scope: Training may be limited to immediate tasks without broader context or theoretical knowledge.
-
Lack of Interaction: This can be less productive for employees who prefer face-to-face interaction or guidance.
PRO TIP
With Whatfix Mirror, IT teams and L&D leaders can quickly create replicate sandbox environments of any web application to provide hands-on training to new employees. Create in-app guided experiences like Flows and Task Lists that walk new end-users through your application’s workflows and their contextual tasks to drive proficiency, knowledge acquisition, and task mastery.
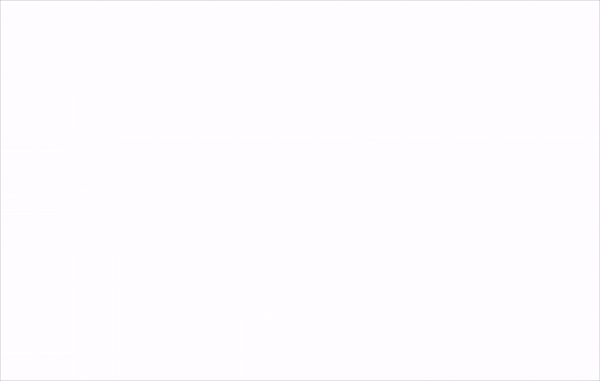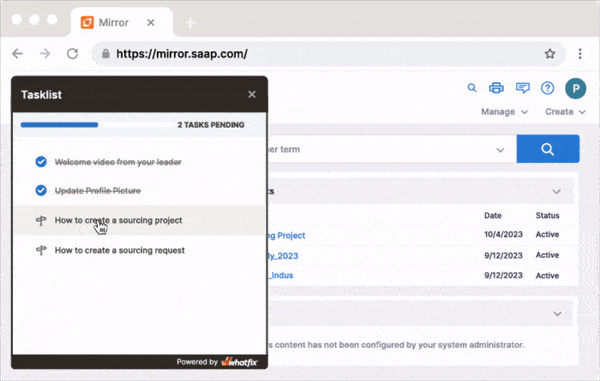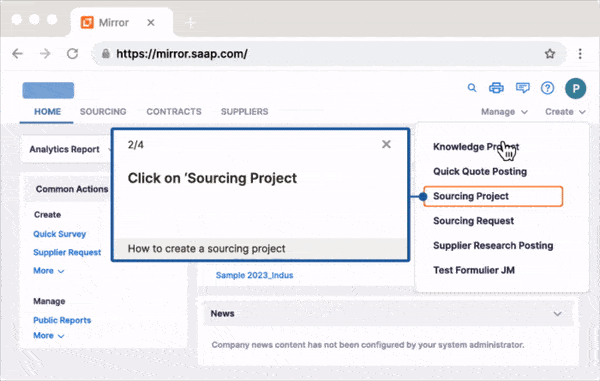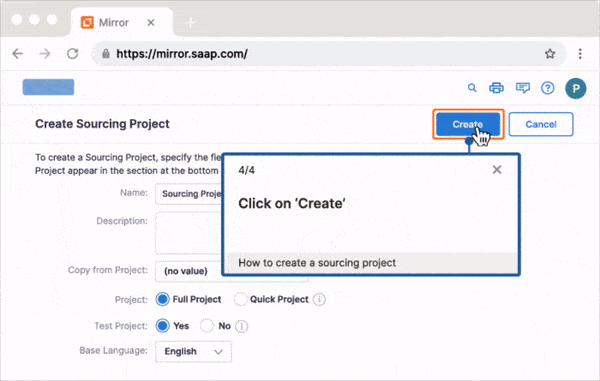
3. Instructor-led learning
Instructor-led training is a traditional type of training where an instructor or subject matter expert leads a group of employees through the training content in person or virtually. Instructor-led training (ILT) can be delivered in face-to-face learning experiences like classrooms or workshops, or via online experiences like webinars. It allows interaction, discussions, and immediate responses to questions. Instructor-led learning is ideal for leadership training, regulatory compliance, technical skills training, and team-building exercises.
Advantages of instructor-led training
- Interactive: Allows for discussions, questions, and personalized guidance.
- Immediate Feedback: Instructors can clarify doubts and adjust teaching methods in real-time.
- Structured Learning: Follows a planned syllabus, ensuring comprehensive topic coverage.
Disadvantages of instructor-led training
- Time consuming: Requires scheduling sessions, which can interrupt work routines.
- Resource Intensive: High costs for training facilitators, venues, and materials, especially for large groups.
- Geographical Constraints: In-person training may be difficult for remote or distributed teams.
4. Role-playing learning
Role-playing is a highly interactive training technique where employees act out scenarios they might encounter. It focuses on developing soft skills such as communication, conflict resolution, and decision-making by placing employees in real-world situations to practice responses. Role-playing is ideal for sales, customer service training, call center training, leadership training, conflict resolution, negotiation, and teamwork skills.
Advantages of role-playing
- Builds Confidence: Employees can practice new skills in a low-risk environment.
- Improves Communication: Participants learn how to communicate and collaborate in real-time.
- Problem Solving: Promotes critical thinking by making participants solve complex situations.
Disadvantages of role-playing
- Engagement: Not everyone is comfortable with role-playing scenarios; this can affect performance.
- Limited Realism: Scenarios may not fully replicate actual job challenges, limiting the realism of the training.
- Time Consuming: Role-playing exercises can be time-intensive and challenging to scale for large teams.
5. Coaching
Job coaching involves an experienced professional, like a supervisor, mentor, or experienced team member, coaching an employee on specific job tasks and responsibilities. This on-the-job learning method can be implemented in person or virtually using coaching software, making it ideal for both in-office and remote workforces. Coaching is also ideal for leadership development, employee development, performance improvement, and succession planning.
Advantages of job coaching
- Personalized: Tailored to the individual needs of each employee.
- Ongoing Feedback: Continuous feedback and adjustments ensure long-term growth.
- Goal Oriented: Focuses on achieving specific, measurable outcomes.
Disadvantages of job coaching
- Resource Intensive: Requires dedicated time and attention from both coaches and trainees.
- Coach Skill Levels: The effectiveness of coaching depends on the coach’s skill and expertise, which can vary.
- Scalability: Difficult to implement across large organizations due to the personalized nature of the method.
6. Simulation training
Simulation training is an effective training method that involves realistic, immersive replications of real-life work processes or scenarios. This hands-on, experiential technique allows individuals to learn or practice different skills and decision-making procedures in a zero-risk environment before applying them in real life. Simulation training is ideal for aviation, healthcare, emergency response, customer service, and technical operations.
Advantages of simulated training
- Problem-Solving Skills: Builds problem-solving and critical thinking skills under pressure.
- Risk-Free Environment: Employees can make mistakes and learn from them without real-world consequences.
- Enhanced Retention: Hands-on simulation leads to better retention of knowledge and skills.
- Real-World Application: Simulates complex situations where employees can practice their responses.
Disadvantages of simulated training
- High Costs: Developing and maintaining simulation environments can be expensive.
- Technology Barriers: Some employees may need help to adapt to simulation tools or VR technology.
- Limited Access: Simulations might only be available for some job roles, especially those with limited tech-based aspects.
7. Collaborative training
Collaborative training involves learning through teamwork and shared experiences. Employees work together to solve problems, complete tasks, or discuss ideas. The collaborative learning approach encourages knowledge sharing and mutual learning. Collaborative training is ideal for team-building exercises, innovation workshops, problem-solving, and brainstorming sessions.
Advantages of collaborative training
- Reduced Costs: When training is conducted in groups, it reduces time investment and costs.
- Team Building: Fosters collaboration and teamwork.
- Diverse Perspectives: Employees learn from each other’s experiences.
- Engagement: Interactive and engaging, promoting higher retention rates.
- Knowledge Retention: When employees discuss concepts with each other, they solidify their understanding and are more likely to remember the information.
Disadvantages of collaborative training
- Group Dynamics: Ineffective collaboration due to group conflicts or uneven contributions can reduce effectiveness.
- Time-Consuming: Requires significant coordination and time to complete group activities.
- Difficult to Manage: Training outcomes vary widely based on group chemistry and dynamics.
8. Video training
Video training delivers educational content through video, either live or pre-recorded. It includes tutorials, explainer videos, or recorded webinars that employees can watch at their convenience. Creating training videos enables employees to digest information in an easy-to-understand format that is easier to retain and that employees can go back and watch at any time. Video training is ideal for product training and tutorials, compliance training, employee onboarding, and soft skills development.
Advantages of video training
- ROI: Video training is a one-time cost associated with video production that can be used until your processes become outdated.
- Retention: Videos provide better knowledge retention, employee engagement, and learner attention than basic text documents or traditional classroom seminars.
- Visual Learning: Great for visual learners and those who prefer multimedia content.
- Scalable: Easily accessible to employees across different locations.
- Engaging: High-quality visuals and sound can make content more engaging than text-based materials.
- Measure Effectiveness: Your video hosting providers give you access to different training metrics to track and measure training effectiveness.
Disadvantages of video training
- Passive Learning: This may not encourage active engagement or critical thinking.
- Limited Customization: Pre-recorded content cannot be tailored to individual needs or questions.
- Technical Issues: Requires reliable internet and devices for smooth viewing.
9. Cross-training
Cross-training is a training method in which an employee learns how to perform another employee’s role while performing the role they were hired for. This concept aims to help employees boost their existing skills and become more flexible resources for the organization.
Not only does this create a more skilled employee, but it also encourages your workforce to explore other opportunities throughout the organization, driving internal mobility. Cross-training is ideal for manufacturing, retail, customer service, and team-based environments.
Advantages of cross-training
- Increases Flexibility: Employees can step into various roles, reducing operational disruptions.
- Enhances Employee Skills: Helps employees develop broader skills and knowledge.
- Improves Collaboration: Employees better understand their colleagues’ roles, improving teamwork.
Disadvantages of cross-training
- Risk of Overburdening: Employees may become overwhelmed if expected to take on too many additional responsibilities.
- Shallow Learning: Employees may not gain deep expertise in any one area, leading to competence gaps.
- Resistance: Employees may resist learning tasks outside of their core job functions.
10. Job shadowing
Job shadowing allows employees to follow and observe other professionals working in different job functions to gain insight into their work area. It is also implemented to allow less experienced individuals to work alongside experienced professionals to sharpen their skills from those who have already mastered them. Job shadowing is ideal for career development, leadership training, and role transitions.
Advantages of job shadowing
- Relationship building: This approach builds strong relationships between new hires and tenured employees.
- Real-World Experience: Provides firsthand insight into specific roles or responsibilities.
- Career Development: Helps employees prepare for promotions or role changes.
- Low-Cost: Minimal resources are required since learning happens in real time.
Disadvantages of job shadowing
- Limited Interaction: Learning is passive, as the employee observes rather than does.
- Not Always Scalable: Difficult to implement across many roles simultaneously.
- Dependence on Mentor Availability: Scheduling can be challenging depending on mentor availability.
11. Case studies
With the case study method, employees are presented with a real or fictional complex situation to analyze and use as a reference for their solutions. While cases vary in complexity and detail, trainees must be given enough data and information to analyze the situation and devise solutions. Case studies are ideal for leadership training, strategy development, and problem-solving exercises.
Advantages of case studies
-
Critical thinking: Encourages analysis and problem-solving in real-world contexts.
-
Collaborative Learning: Promotes teamwork and sharing of different perspectives.
-
Real-World Relevance: Ties theory to practical, applicable situations.
Disadvantages of case studies
-
Time-Consuming: Case studies require significant time to prepare and discuss.
-
Subjective Outcomes: May lead to different solutions that could be difficult to evaluate equally.
-
Not Suitable for all Learners: Some employees may struggle to relate case studies to their specific roles.
12. Peer-to-peer learning
Peer-to-peer learning is a mutual learning strategy that involves participants of the same level engaging in collaborative learning. This type of learning allows employees to work through new concepts and share ideas with their peers working on the same project.
The opportunity to teach and be taught by one another is an effective way for organizations to grow stronger employees who work together productively. Peer-to-peer learning is ideal for knowledge transfer, team building, and improving communication.
Advantages of peer-to-peer learning
-
Cost-Effective: Utilizes internal resources without requiring external trainers.
-
Engaging: Encourages active participation and collaboration among employees.
-
Knowledge Sharing: Enhances the transfer of knowledge across departments and teams.
Disadvantages of peer-to-peer learning
-
Varying Expertise: The quality of learning depends on the expertise of the peers, which can vary widely.
-
Lack of Structure: There may be a need for formal structure, making it difficult to track outcomes.
-
Not Scalable: More challenging to implement in large organizations with limited peer-to-peer opportunities.
13. Spaced learning
Spaced learning breaks down extended team member training programs into several sessions or modules of shorter durations, with spaced intervals in between. Parts of these sessions are reintroduced multiple times over the next few days or weeks for learners to recall information, driving long-term knowledge retention. Spaced learning is ideal for skill-building, compliance training, and technical knowledge.
Advantages of spaced learning
- Improved Retention: Reinforces learning through repetition over time.
- Low Cognitive Load: Breaking content into small chunks makes it easier to digest.
- Efficient: Short sessions make it easier for busy employees to participate.
Disadvantages of spaced learning
- Longer Timeframe: Requires a longer commitment as learning is spaced out over time.
- Coordination Required: Scheduling and organizing repeated sessions can be logistically challenging.
- Disengagement Between Sessions: Learners may lose engagement or forget content between spaced sessions.
14. Gamification
Gamification is a training method that incorporates gaming elements such as points and badges into training courses. By leveraging psychology, gamified training engages learners and makes them more willing to take on repetitive tasks despite the risk of failure. Gamification of training has been shown to increase employee performance and the adoption of new software. The gamification approach is ideal for sales training, compliance training, onboarding, and skill development.
Advantages of gamified training
- Motivates Engagement: Using rewards, badges, and points boosts employee involvement.
- Increases Retention: Active participation through challenges leads to higher retention.
- Encourages Competition: Healthy competition can drive employee performance and learning outcomes.
Disadvantages of gamified training
- Cost of Development: Gamified training content can be expensive and time-consuming.
- Risk of Distraction: Overemphasis on the game elements can distract from learning objectives.
- Not Suitable for All: Some employees may respond poorly to competitive or game-like environments.
15. Mobile learning
Mobile learning (or mLearning) refers to online learning via a personal mobile device such as a smartphone, tablet, or laptop. This training method empowers learning on the go, enabling users to access content whenever and wherever they want. Mobile learning is ideal for remote teams, field workers, sales teams, and employees requiring on-the-go learning.
Advantages of mobile learning
- Accessible Anywhere: Ideal for remote employees or those frequently on the go.
- Convenient: Employees can complete training at their convenience, promoting flexibility.
- Engaging: Using multimedia (videos, quizzes, etc.) enhances the learning experience.
Disadvantages of mobile learning
- Screen Size Limitations: Mobile devices may not be ideal for content-heavy or detailed materials.
- Distractions: Learners may be easily distracted when using mobile devices for training.
- Connectivity Issues: Requires stable internet or mobile data, which may only sometimes be available.
16. Blended learning
Blended learning combines traditional face-to-face and eLearning to create a more holistic, effective training system. It leverages the best in-person learning experiences (like social learning and subject-matter-expert-led training lessons) with online learning (via LMS courses, hands-on training experiences, etc.) to provide a comprehensive, multi-method approach to learning and development. Blended learning is ideal for leadership development, technical training, complex skills development, and employee onboarding.
Advantages of blended learning
- Best of Both Worlds: Combines eLearning’s flexibility with instructor-led training’s interactivity.
- Customization: Allows for tailoring of content based on individual needs and learning preferences.
- Flexible Scheduling: Employees can complete digital components at their own pace, with in-person sessions complementing the learning.
Disadvantages of blended learning
- Coordination Required: Organizing both online and in-person components can be logistically complex.
- Varied Engagement Levels: Employees may engage more with one format than the other, affecting overall effectiveness.
- Resource-Intensive: Requires both digital platforms and live instructors, which can increase costs.
17. Microlearning
Microlearning is an approach to learning new knowledge that breaks learning content into small, bite-sized information modules. Smaller learning sessions provide all the information necessary for learners to quickly achieve a specific training objective, making microlearning valuable in business contexts. Microlearning is ideal for product knowledge, compliance training, skill reinforcement, and time-sensitive learning.
Advantages of microlearning
- Easy to Digest: Short lessons ensure learners are not overwhelmed with too much information.
- Just-in-Time Learning: Employees can access training as needed, ensuring timely application.
- High Retention: Microlearning’s minor, focused nature improves retention and recall.
- Convenient: Fits nicely into busy schedules, allowing learners to access content quickly during spare moments.
- Interactive: Accommodates various learning styles through multimedia elements and interactive formats.
Disadvantages of microlearning
- Lack of Depth: Microlearning may not be suitable for complex topics that require in-depth exploration.
- Fragmentation: Learners may need help to connect fragmented lessons into a cohesive whole.
- Frequent Updates: Content needs to be regularly updated to ensure relevance and accuracy.
18. Adaptive learning
Adaptive learning uses AI and data analytics to deliver personalized learning experiences. The system adjusts the content, difficulty, and learning pace based on the individual’s performance, learning style, and progress. Adaptive learning is ideal for continuous professional development, technical training, compliance, and personalized learning needs.
Advantages of adaptive learning
-
Personalized Learning: Tailors content to the learner’s specific needs and pace, optimizing learning efficiency.
-
Scalable: Adaptive learning platforms can cater to large groups while delivering individualized experiences.
-
Increased Engagement: Customized content keeps learners more engaged and invested in their progress.
Disadvantages of adaptive learning
-
High Initial Costs: Developing or purchasing adaptive learning platforms can be expensive.
-
Data Privacy Concerns: Collecting personal performance data requires stringent privacy and security measures.
-
Limited Availability: Adaptive learning tools are still developing and may not be widely accessible across all industries.
Factors to Consider While Choosing the Right Training Method
Here are a few factors to consider while choosing the best employee training method for your learning use case:
- Learning objectives: Identify the specific goals of the training. Are you focusing on technical skills, soft skills, compliance, or leadership development? Different training methods suit different learning objectives (e.g., technical skills simulations, leadership development coaching, etc.).
- Learner preferences: Consider your learners’ demographics and preferences. For example, younger employees may prefer digital or mobile learning, while others may benefit more from in-person or instructor-led training. Use the VARK method to match training methods with preferred learning styles for different employees.
- Accessibility and availability: Consider the training logistics, including where and when it will occur. Also, ensure that the training method is accessible to all employees. This may include providing subtitles for video training, ensuring mobile content is screen-reader compatible, or offering alternative learning formats.
- Costs and resources: Different training methods have varying costs. Some methods, like eLearning or mobile learning, might require technology and content development investments. Others, like instructor-led training, might involve hiring trainers and renting physical spaces. Assess your organization’s budget and resource availability to choose a method that aligns with your financial capabilities.
- Time constraints: Assess the amount of time available for training. Methods like microlearning or spaced learning work well for employees with limited time, while more involved methods like job shadowing or simulations may require longer, dedicated sessions.
Training Clicks Better With Whatfix
In an era defined by rapid technological advancements and the ever-growing need for skill agility, the integration of digital adoption platforms (DAPs) marks a transformative shift in the landscape of employee training.
As organizations strive to empower their workforce with the skills and knowledge required to navigate complex digital environments, DAPs emerged as catalysts of success.
With no-code platforms like Whatfix DAP, organizations can create in-app guided training and performance support that overlays employee workflows and tasks. This guidance enables employees to learn in the flow of work, which is more effective than traditional classroom-style learning techniques. According to the 70-20-10 learning model, 70% of all skill acquisition and institutional knowledge comes from hands-on experiences.
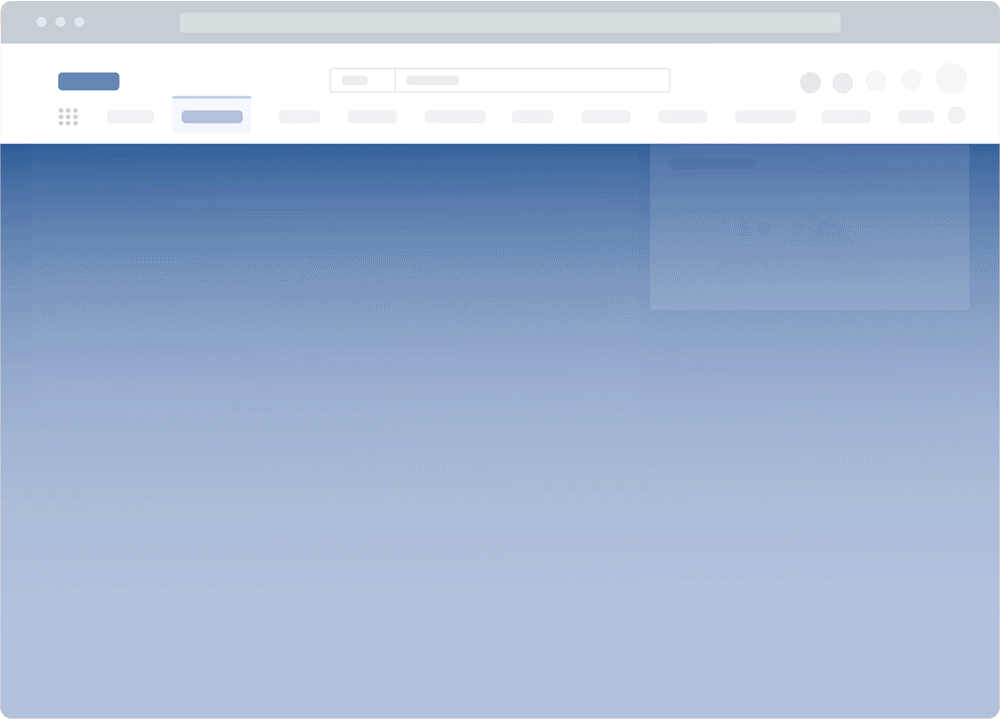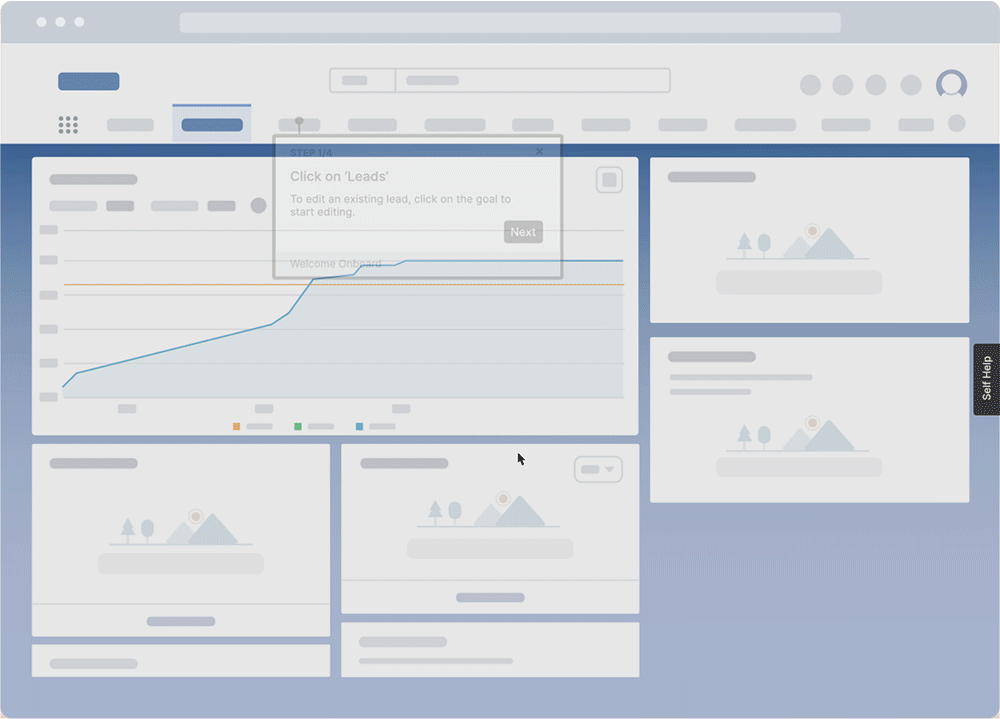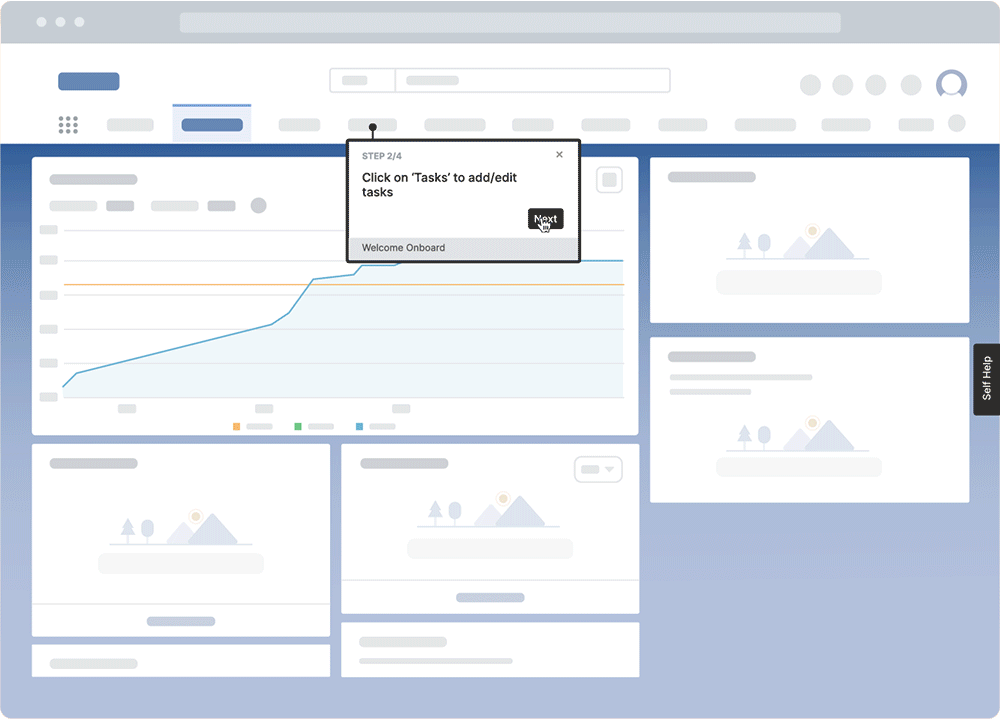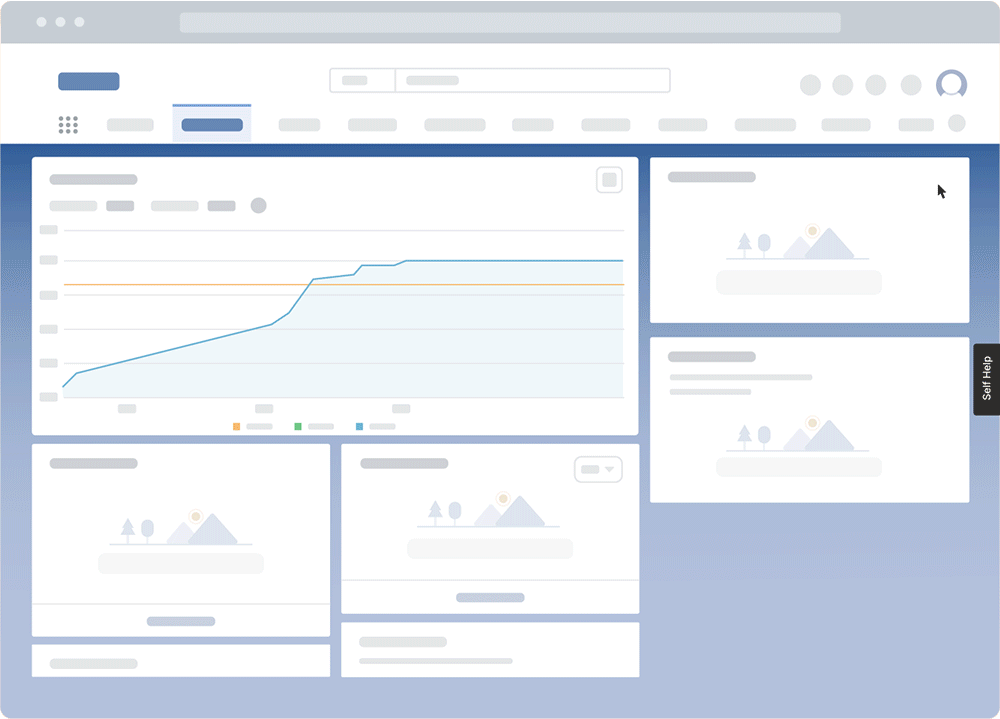
DAPs seemingly guide employees through software applications, offering contextual, role-based learning experiences and performance support and providing insight into how users engage with applications and in-app training. DAPs enable employees with user-friendly guidance that drives productivity and maximizes digital application ROI.

This “learning by doing” mentality fosters a culture of continuous learning and growth, all without sacrificing employee output.
Ready to learn more? Request a Whatfix demo today!






