Organizational change is a necessary component of company growth and adaptation, yet it often encounters significant obstacles that hinder progress. Despite the best intentions, many change initiatives falter due to a variety of barriers within the workplace.
These change management obstacles stem from resistance to change, poor communication, inadequate training, or lack of leadership support. Understanding these barriers is crucial for any organization striving to implement successful change.
This article explores the common challenges organizations face when outperforming their competitors and provides insights into overcoming these hurdles to ensure smoother change transitions and sustainable growth.
What Are the Most Common Barriers to Change Projects?
11 Top Barriers to Successful Change Initiatives for Organizations
Although the barriers to change might be different for every organization, we have identified the top barriers to change leading to failure of the change initiative.

1. Lack of clarity
Lack of clarity is a significant barrier to organizational change as it creates confusion and uncertainty among employees and stakeholders, undermining the effectiveness of the change initiative.
When a change’s goals, purpose, and processes are not communicated, employees may need help understanding why the change is happening, what is expected of them, and how the change will impact their roles and the organization.
Key impacts of lack of clarity include:
- Confusion and misalignment: Employees may interpret the change differently without clear guidance, leading to misalignment in actions and efforts.
- Reduced engagement: Employees who do not understand the change or see its relevance are less likely to be engaged or motivated to participate.
- Increased resistance: When employees are unclear about how the change will affect their jobs, responsibilities, or future within the company, it can lead to fear and resistance.
- Inefficient execution: Without a clear plan, employees and managers may spend unnecessary time and resources trying to figure out what needs to be done. This inefficiency slows down the change process, creates bottlenecks, and leads to mistakes that could have been avoided with better clarity.
On the other hand, if you come prepared with a clear project scope and a compelling narrative, it will lead to a smoother change transition. For clarity before change implementation, you must address the preliminary questions such as:
- Why is the change needed?
- How will it affect our current state?
- How do you expect to get there?
2. Ineffective change communication
Ineffective change communication is a major hindrance to the success of change initiatives within an organization, as it directly impacts employees’ understanding, acceptance, and engagement with the change process.
Statistically, only 68% of managers know the actual reason for organizational change. This number declines from 53% to 40% for mid-level managers and frontline supervisors. Gartner suggests that due to poor change communication, 73% of employees experience moderate to high-stress levels, and the affected employees perform 5% less than an average employee.
Key impacts of ineffective change communication:
- Confusion and misinformation: When communication is unclear, incomplete, or inconsistent, employees are left to fill in the gaps with their assumptions or rely on rumors. This can lead to widespread confusion about the change’s goals, process, and benefits, causing employees to misunderstand what is expected of them.
- Increased resistance: Poor communication often leads to a lack of understanding and trust, fueling resistance to change.
- Delays and inefficiency: Without clear and timely communication, employees may not know how to proceed with their tasks during the change process, leading to delays and inefficiencies.
- Loss of trust in leadership: If leaders fail to communicate effectively, employees may begin to question their competence, intentions, or commitment to the change initiative.
To overcome the barrier of ineffective change communication, organizations must focus on developing and implementing a robust communication strategy, including clear, consistent messaging and open dialogue between leadership and employees.
3. Strategic shortcomings
Strategic shortcoming refers to the lack of a robust and well-defined strategy guiding an organizational change initiative. This barrier occurs when the change effort is not adequately aligned with the overall business objectives or the strategy is poorly conceived, lacking the necessary depth, foresight, or flexibility.
Without a solid strategic foundation, change initiatives can quickly falter, leading to wasted resources, missed opportunities, and, ultimately, failure to achieve the desired outcomes.
Key impacts of strategic shortcomings include:
- Lack of direction and focus: When the strategy guiding the change is vague or poorly articulated, employees and managers may need help understanding the goals and priorities. This results in fragmented efforts, with different departments or teams pursuing conflicting objectives or duplicating efforts.
- Misalignment with business goals: If the change initiative is not aligned with business goals, it can lead to actions that, while seemingly productive, do not contribute to the long-term success of the organization.
- Ineffective resource allocation: Without a clear understanding of the priorities and expected outcomes, organizations may invest time, money, and effort in areas that do not yield significant returns.
To overcome the barrier of strategic shortcomings, organizations must focus on developing a robust, well-aligned strategy that clearly defines the purpose, goals, and execution plan for the change initiative.
4. Change resistant culture
The longer a current process has been in the organization, the more invested employees are. The status quo always feels comfortable, creating a lot of inertia in the organization. During change implementation, other cultural issues like internal politics, poor behavior control, and personal agendas start surfacing, contributing to a change-resistant culture. In such an environment, employees are likely to be skeptical about the benefits of change, leading to low engagement and even active opposition.
Key impacts of a change-resistant culture include:
- Widespread resistance and pushback: When an organization’s culture resists change, any attempt to introduce new initiatives will likely be met with significant pushback.
- Lack of innovation and adaptability: A culture that resists change often stifles innovation and adaptability. In such cultures, employees may be discouraged from proposing new ideas or experimenting with different approaches, leading to a stagnant organization that cannot respond effectively to market shifts, technological advancements, or competitive pressures.
To overcome the barrier of a change-resistant culture, organizations must take deliberate steps such as demonstrating their commitment to change, addressing the reasons for resistance, etc., to shift the cultural mindset and create an environment that is more open to change.
5. Lack of organizational buy-in
For a successful change initiative, you must earn buy-in from top management and entry-level employees. Top management buy-in is essential to add legitimacy to the change initiative.
Their job is more than just sponsoring the initiative; it is to take the onus of the change and lead by example. However, mid- and entry-level employees must be on board to implement the change at the ground level.
When employees understand and believe in the necessity and value of the change, they are more likely to be motivated, engaged, and cooperative, making the transition smoother and more effective.
Key impact of lack of organizational buy-in include:
- Reduced engagement and participation: When stakeholders do not buy into the change, they are less likely to engage with the process. This disengagement can result in minimal participation in change-related activities, such as training programs, meetings, or implementation efforts.
- Increased resistance to change: Lack of buy-in often translates into overt or covert resistance. Employees who do not believe in the shift may openly challenge it, spread negative sentiments, or undermine the process.
- Inconsistent implementation: When there is a lack of buy-in, different parts of the organization may implement the change unevenly or not at all. Some teams or departments may fully embrace the change, while others may ignore or reject it.
To overcome the lack of organizational buy-in barrier, organizations must focus on building support and commitment across all levels by engaging key stakeholders early in the planning and decision-making process and clearly articulating the benefits of change to all employees.
6. Change fatigue
Organizations often have multiple change projects in the implementation stage at one time. When change occurs in an organization simultaneously, it overwhelms the employees, resulting in change fatigue.
Key impacts of change fatigue include:
- Decreased employee engagement: When employees are repeatedly asked to adapt to new changes without sufficient time to adjust, they can become disengaged. This disengagement manifests as a lack of enthusiasm, reduced motivation, and a minimal effort approach to the change initiatives.
- Increased resistance to change: Constant exposure can push your employees to resist these initiatives in the long run.
- Lowered productivity and quality: As employees become fatigued by continuous change, their productivity and the quality of their work may decline. The mental and emotional strain of adapting to multiple changes can result in mistakes, oversights, and a general decline in output quality.
- Failure to sustain change initiatives: Change fatigue can prevent even well-conceived and strategically essential initiatives from taking hold. If employees are too exhausted or disillusioned to engage with a change properly, it may not be fully implemented or sustained over time.
To overcome the barrier of change fatigue, organizations must carefully plan and prioritize changes, ensuring that employees are able to handle the many initiatives at a time.
7. Lack of governance
Lack of governance reflects the absence of a clear structure, oversight, and accountability in managing the change process. Governance in the context of change management refers to the framework of policies, roles, responsibilities, and processes that guide and control the implementation of change initiatives. Without effective governance, change efforts can become disorganized, misaligned, and ultimately unsuccessful.
Key impacts of lack of governance include:
- Lack of clear roles: With proper governance, there is often clarity about who is responsible for various aspects of the change initiative. Essential tasks may be neglected, duplicated, or poorly executed when roles and responsibilities are not clearly defined.
- Inconsistent decision-making: Governance provides a structured approach to decision-making, ensuring that decisions are made consistently and aligned with the organization’s strategic goals. Without governance, decisions may be made in an ad-hoc or inconsistent manner, leading to confusion and misalignment.
- Inadequate risk management: Effective governance includes mechanisms for identifying, assessing, and mitigating change-associated risks. Without governance, organizations may fail to anticipate or manage risks effectively, leading to unexpected challenges that could have been avoided or mitigated.
- Poor communication and coordination: Governance structures typically include processes for ensuring effective communication and coordination across the organization. Without these processes, communication can become fragmented, with different teams or departments operating in silos.
To overcome the barrier of lack of governance, organizations must establish a robust governance framework that provides clear structure, oversight, and accountability for the change initiative.
8. Inadequate training and support
Inadequate training and support leaves employees unprepared to adapt effectively to new systems, processes, or roles. When employees receive the proper end-user training and support they need, they may be able to understand and implement the changes, leading to frustration, resistance, and decreased productivity.
This lack of preparation can severely hinder the success of the change initiative, as it prevents employees from fully engaging with and embracing the organization’s new direction.
Key impacts of inadequate training and support include:
- Lack of competence and confidence: When employees are not adequately trained, they may lack the necessary skills and knowledge to perform their jobs effectively under the new system or process. This incompetence can lead to mistakes, reduced efficiency, and a general lack of confidence.
- Lowered productivity and efficiency: Without proper training, employees may take longer to perform tasks, make more errors, and struggle to meet productivity standards.
- Frustration and decreased morale: When employees are not given the tools and support they need to succeed, frustration can quickly set in. This frustration can lead to decreased morale, as employees may feel supported or valued by the organization.
- Failure to realize the benefits of change: If employees are not adequately trained and supported, the organization may fail to realize these benefits fully. Instead of driving improvement, the change may result in a disjointed, inefficient operation where the potential gains are overshadowed by ongoing struggles to adapt.
With a digital adoption platform (DAP), organizations can enable employees through times of change with in-app guidance and on-demand support in the flow of work. With Whatfix DAP, change leaders and application owners can create:
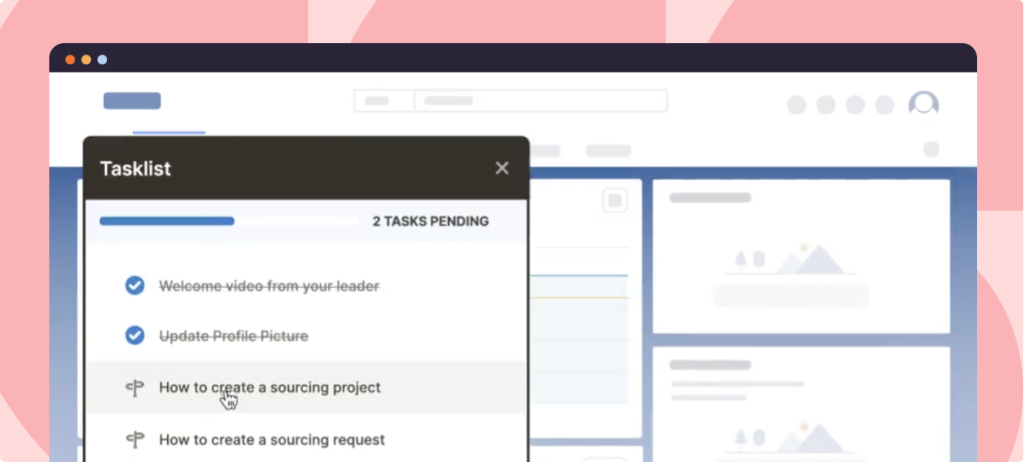
- Tours and Task Lists to accelerate time-to-proficiency for new users or when implementing a new technology.
- Flows to guide users through complex processes or infrequently done tasks.
- Smart Tips to nudge users to take specific action or provide additional information at key friction points.
- Self Help provides employees an on-demand, in-app resource center that integrates with your knowledge repositories.
- Pop-Ups to alert employees of process changes, remind them of upcoming deadlines, communicate company news, and drive awareness of new training.
9. Unrealistic expectations or timelines
Ambitious goals, while inspiring, can often lead to undue pressure on teams, resulting in rushed and substandard implementation efforts. When timelines are too tight, there is insufficient time for adequate planning, training, and adjustment, all crucial elements for a smooth transition.
This can lead to employee burnout, lower morale, and resistance to change, as employees feel overwhelmed by the pace of the expected transformations.
Key impact setting of unrealistic expectations include:
- Increased stress and burnout: Unrealistic timelines often force employees to work at an unsustainable pace, leading to increased stress and burnout. This can result in higher absenteeism, decreased morale, and ultimately, higher turnover rates as employees struggle to cope with their demands.
- Lowered quality of work: When timelines are too tight, employees may rush through tasks to meet deadlines, decreasing the quality of work.
To overcome this barrier, organizations must break down the change initiative into smaller, manageable milestones with realistic deadlines. These milestones should be clearly defined and achievable, allowing employees to focus on one step at a time rather than feeling overwhelmed by the entire change process.
10. Insufficient resources
For larger organizational change projects, additional resources are needed to improve the ability to plan, implement, and sustain change initiatives effectively. Resources in this context refer to the financial, human, technological, and time-related assets required to execute a change process. When these resources are lacking, the change initiative will likely encounter delays, poor execution, and, ultimately, failure to achieve its intended outcomes.
Key impacts of insufficient resources include:
- Delays and inefficiencies: Insufficient resources often lead to delays in implementing change initiatives. For example, the change process can be slowed down if there are not enough financial resources to invest in necessary technology or training programs.
- Overburdened employees: A lack of human resources means the existing workforce may be stretched too thin, taking on additional responsibilities without the necessary support. This overburdening can lead to burnout, decreased productivity, and higher turnover rates.
- Compromised quality and scope of change: When resources are limited, organizations may be forced to scale back the scope of the change or compromise on quality. For instance, a change initiative initially aimed to overhaul an entire department may be reduced to only minor adjustments due to budget constraints.
- Failure to sustain change: Ongoing maintenance, support, and refinement are often necessary to ensure the change continues delivering its intended benefits. With adequate resources, the organization may be able to maintain the change, leading to a gradual return to old habits and processes, effectively nullifying the efforts made.
To overcome the barrier of insufficient resources, organizations must take a proactive approach to resource planning and allocation which includes strategically prioritizing the most critical aspects of the change initiative or exploring alternative options, such as partnerships, grants, or shared services.
11. Lack of leadership support
Leadership is central to guiding, influencing, and driving the change process. When leaders are not fully committed to or actively involved in a change initiative, they undermine the entire effort, leading to confusion, resistance, and, ultimately, failure to achieve the desired outcomes.
Key impacts of lack of leadership support include:
- Lack of clear vision and direction: Without leadership support, the change initiative may lack a clear purpose or strategic alignment with the organization’s goals. This absence of vision can lead to confusion among employees, who may not understand why the change is necessary or how it fits into the broader organizational strategy.
- Weak communication: Leaders need to actively support the change to ensure communication efforts are maintained, resulting in a lack of engagement and buy-in from employees.
- Loss of trust and credibility: If employees perceive that leaders are not genuinely committed to the change, it can erode confidence in leadership and the organization. This loss of trust can have long-lasting effects, reducing employee morale, engagement, and willingness to support future change efforts.
To overcome the barrier of lack of leadership support, organizations must ensure that leaders are fully engaged and committed to the change initiative from start to finish.
Starting a change initiative?
Download our pack of six change management templates to kick-start your change project.
How to Overcome Change Management Barriers
Now that you have identified the barrier to your organization’s change management success, let’s find an answer to another important question: How do you overcome these barriers to change?
The following tips will help you in implementing change better.
1. Strategize with the ADKAR Model
The ADKAR Model is an outcome-oriented change management method that aims to limit resistance to organizational change. It breaks down the change process into five sequential steps: Awareness, Desire, Knowledge, Ability, and Reinforcement.
Here is what each step of the model means.
- Awareness about the need for change, which helps in understanding its rationale.
- Desire among employees to support and participate in the change, which is crucial for overcoming resistance.
- Knowledge, involves providing the necessary training and information to implement the change.
- Ability ensures that employees have the skills and resources to make the change happen effectively.
- Reinforcement solidifies the change by embedding new practices and behaviors, preventing regression to old ways.
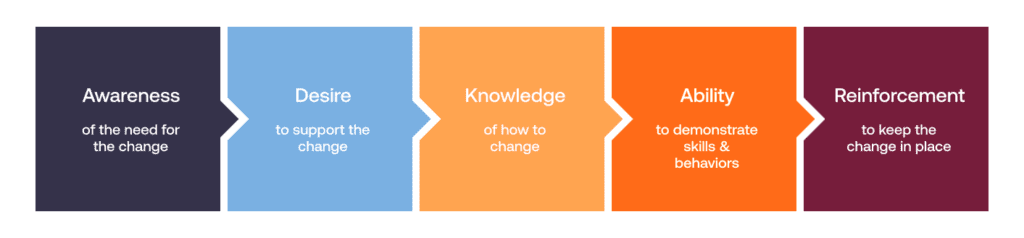

By addressing these areas, the ADKAR model ensures a comprehensive and structured approach to change management, increasing the likelihood of its acceptance and long-term sustainability.
2. Create a communication plan
Creating a comprehensive change announcement plan is a critical enabler of successful change initiatives, as it ensures that all stakeholders are informed, engaged, and aligned with the change process.
Since change is personal, you must address change management communication with consideration and empathy. By tailoring the communication to meet the needs and preferences of different audience segments, the plan ensures that the message is not only delivered but also understood and embraced. Answer the simple questions like ‘what’s in it for me?’. You can avoid ambiguity by documenting the process, the critical milestones, and the steps needed to get there.
3. Involve those most impacted by the change early in the planning process
Employees are the catalyst of change. You must involve them early instead of expecting them to accept the new processes. This involvement can range from participating in planning and decision-making processes to providing feedback on proposed changes.
It encourages open communication, builds trust, and helps identify potential issues early on, allowing for a more collaborative and inclusive approach to managing change.
If a new platform is rolled out that only a core group of staff is aware of, the initiative will fail miserably. You need to check the pulse of the team and, gauge how employees feel about the change project, and act upon the received feedback.
4. Provide contextual onboarding and training for new processes or software
Providing contextual onboarding and hands-on training when implementing new software or processes is critical in facilitating successful user adoption and reducing transitional issues. Contextual onboarding, tailored to the user’s specific role and tasks, significantly enhances understanding and retention of new information.
This approach helps bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application, ensuring that employees are aware of the new processes or software and competent in using them effectively. Contextual onboarding reduces the learning curve and accelerates the adoption of new systems, thereby minimizing disruption to workflows and enhancing overall productivity during the transition phase.
With a digital adoption platform like Whatfix, organizations can enable their end-users with in-app guidance and support in the flow of work. This facilitates change by providing employees with contextual onboarding and in-app training that guides technology end-users through complex processes and software – enabling them to learn by doing.
Whatfix DAP overlays on any software application, offering real-time, in-app guidance and support tailored to the user’s specific tasks and needs. Employees receive step-by-step assistance as they navigate the new software right within the application, which helps them learn by doing.
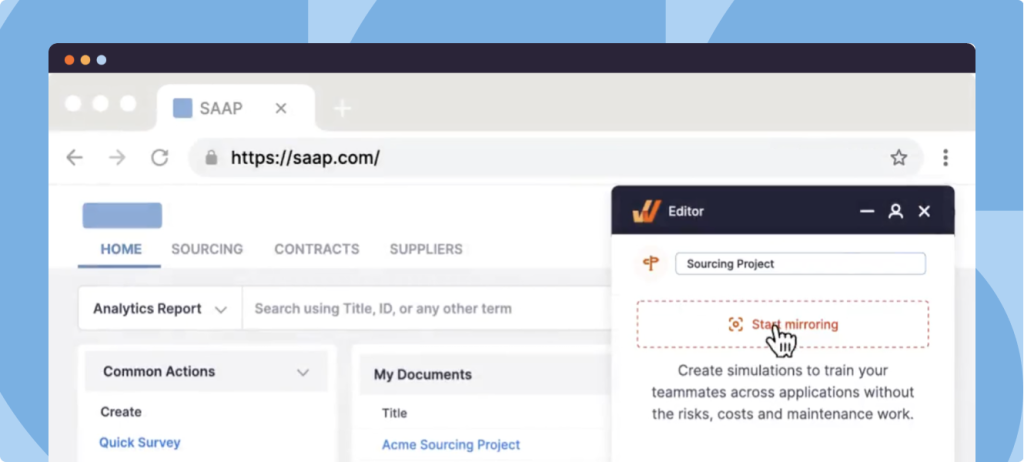
Furthermore, tools like Whatfix Mirror enable you to create replica sandbox environments of enterprise software applications without technical support. This creates an interactive, duplicate application environment for your end-users to learn with hands-on experiences on your real workflows without impacting your company data and performance.
5. Prioritize change by opportunity
Effective prioritization involves identifying which change aspects will deliver the most significant benefits and aligning them with the organization’s strategic objectives.
This clarity ensures that the change initiative does not become overwhelming or diluted by trying to address too many elements simultaneously. It allows for a more structured and manageable approach, where resources such as time, budget, and personnel can be allocated efficiently to areas with the highest return on investment or the most critical needs.
This approach helps maintain momentum, keeps the workforce aligned and motivated, and ensures that the initiative stays on track toward achieving its intended outcomes.
6. Assess and mitigate resistance
Assessing resistance allows leaders to proactively identify potential sources of opposition and address them before they can derail the initiative. By understanding the concerns and fears that drive resistance, organizations can tailor their communication strategies, provide targeted support, and engage employees in the change process, thereby reducing uncertainty and building trust.
This approach minimizes disruptions and fosters a more inclusive and supportive environment where employees feel heard and valued, ultimately increasing the likelihood of a successful and sustainable change implementation.
7. Involve your employees
Employee involvement leads to a greater understanding and acceptance of the change, giving them a sense of ownership and empowerment.
When employees are actively engaged, they can provide valuable insights and feedback based on their experience and expertise, which can enhance the quality and applicability of the change. This approach also helps identify potential challenges and resistance, allowing for more effective strategies to address them early.
Furthermore, involving employees from the beginning in your change initiative fosters a collaborative environment where the change is viewed as a collective effort rather than a top-down imposition. This significantly increases commitment and reduces resistance, as employees feel valued and acknowledged in shaping the change that affects their work and environment.
8. Enable employees with moment-of-need performance support
Enabling employees with moment-of-need performance support involves providing them with the necessary tools, resources, and assistance when needed. Constant support encourages self-sufficiency, reduces the learning curve, and enhances employees’ ability to adapt to new processes or technologies.
Whatfix DAP is an effective tool for providing moment-of-need performance support. The platform integrates directly into your software applications, offering real-time guidance and assistance to users.
The guidance is provided via interactive, step-by-step walkthroughs, contextual tooltips, and on-screen self-help menus available to users as they navigate through new or complex tasks within the application.
Additionally, Whatfix’s personalized support can be tailored to the role and level of the user, ensuring that the assistance is relevant and practical.
9.Leadership development and support
Leadership development and support are crucial to overcoming the barriers of organizational change because they equip leaders with the skills, knowledge, and confidence needed to guide their teams through the complexities of transformation.
Effective leadership ensures clear communication, alignment with strategic goals, and the ability to address resistance and challenges as they arise. By investing in leadership development, organizations create leaders who are not only champions of change but also capable of fostering a positive, resilient culture that embraces and sustains change. This strong leadership foundation is essential for navigating change uncertainties and driving successful outcomes.
10. Monitor and measure success
Monitoring and measuring success is a crucial step in enabling and sustaining change initiatives within an organization. This process involves setting clear, measurable goals and regularly tracking progress against these objectives.
By monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs), leadership can gauge the effectiveness of the change, identify areas where the initiative is performing well, and recognize aspects that may need adjustment. This ongoing evaluation helps ensure that the change goals stay aligned with the organization’s strategic objectives and deliver the intended benefits.
Change Clicks Better With Whatfix
Make it easier to navigate through changes with Whatfix. Whatfix‘s comprehensive suite of end-user analytics, contextual in-app guidance, and moment-of-need support emerges as a powerful enabler of effective enterprise change management. By leveraging these capabilities, organizations can not only navigate the complexities of change smoothly but also ensure that their workforce is adequately supported throughout the transition.
Explore what Whatfix can do for your change management efforts by scheduling a free demo with us today!