
Priyanka Malik


Organizational change is a complex undertaking. These change projects often coincide with other large organizational projects and may spiral out of control without a tracking process system.
However, with a change control process in place, change leaders are empowered to easily manage all incoming change requests, analyze potential blockers, and drive successful implementation.
In this blog, we explore the change control process, its stages, and how you can leverage one to create an effective change management strategy.
Change control refers to the systematic process of managing any modifications or adjustments made to a project, system, product, or service. This ensures that all proposed changes undergo a structured evaluation, approval, implementation, and documentation process.
Change control aims to maintain the integrity and consistency of a system or project by ensuring that changes are introduced in a controlled and coordinated way, minimizing potential risks and unintended negative consequences. It ensures that every change is justified, beneficial, and aligned with the overarching objectives and requirements.
The change control process should consider the scale and complexity of change for streamlining purposes. For example, change initiatives at scale – such as digital transformation – requires the support of multiple departments and team members, and have higher associated risks. Such initiatives require formalized and extensive control processes.
Although change control and change management are related terminologies, the two have significant differences.
Change control is part of the overall change management process. It’s the “how” of managing and implementing change.
While the change control process is essential for streamlining a change initiative and includes formal documentation of the change, change management is an overarching plan that considers all the various project aspects, from budgeting, to communication, to implementation and more. It’s more about the “why” and “what” – the reasoning behind instituting changes, the strategies used to implement them, and the tools and techniques used to support the process.
During a change implementation project, the change control process provides several crucial benefits, including:
Research suggests that an average employee is only productive for three working hours a day. One of the major reasons for this behavior is unclear deliverables or a poorly managed execution process. Change control often rectifies this issue by reducing employee confusion on project deliverables, helping to improve overall employee productivity.
The change control process streamlines the implementation by documenting all the project details in a centralized location. It also helps provide clear team communication, allowing cross-functional teams to collaborate seamlessly on a change initiative.
Transparency in change management communication is critical to prepare your workforce for an upcoming change and to accept that change at both an individual & company-wide level. Effective change communication will allow you to deal head-on with various barriers to change and reduce internal resistance.
The change control process effectively reduces risks associated with a change initiative and minimizes the risk of change failure. The streamlined approach results in resource optimization and decreased project costs.
Especially relevant in more regulated industries, a change control process ensures that all changes adhere to certain standards and guidelines. By documenting each step of the process, organizations have a clear audit trail. This not only helps in demonstrating compliance during audits, but also provides a historical reference for future change initiatives.
Especially relevant in more regulated industries, a change control process ensures that all changes adhere to certain standards and guidelines. By documenting each step of the process, organizations have a clear audit trail. This not only helps in demonstrating compliance during audits, but also provides a historical reference for future change initiatives.
An effective change control process involves assessing and mitigating risks. Companies can avoid unwanted and unintended consequences by anticipating potential challenges and developing plans to address them. This proactive approach promotes business continuity and ensures that changes have a positive impact instead of causing disruption.
One of the most significant benefits of a change control process is its cyclical nature. After changes are implemented, change feedback is gathered and analyzed to ensure organizations are always evolving, refining, and improving their processes, systems, and strategies.
With a digital adoption platform like Whatfix, enable your employees with in-app guidance and contextual self-help IT support to accelerate the adoption of new software implementations, employee onboarding, change initiates, and more. Whatfix’s no-code editor enables IT teams with a no-code editor to create product tours, interactive walkthroughs, task lists, smart tips, pop-ups, self-help wikis, and more. Analyze and measure user engagement and software usage to identify friction points, measure digital adoption, and improve employee digital experiences.
Whether driven by tech advancements, market shifts, internal improvements, or regulatory compliance, change is inevitable and can significantly impact an organization’s operations. The change control process serves as a systematic approach to manage these transitions, ensuring that changes are beneficial, aligned with business goals, and introduced with minimal disruption.
But when is it the right time to employ this structured method?
Understanding the scenarios that warrant implementing a change control process is crucial, ensuring that organizations harness change as a tool for growth.
When a change project fails, it can expose an organization to risks and incur costs at both the organizational and project levels. Here is a five-stage framework to establish a successful change control process:
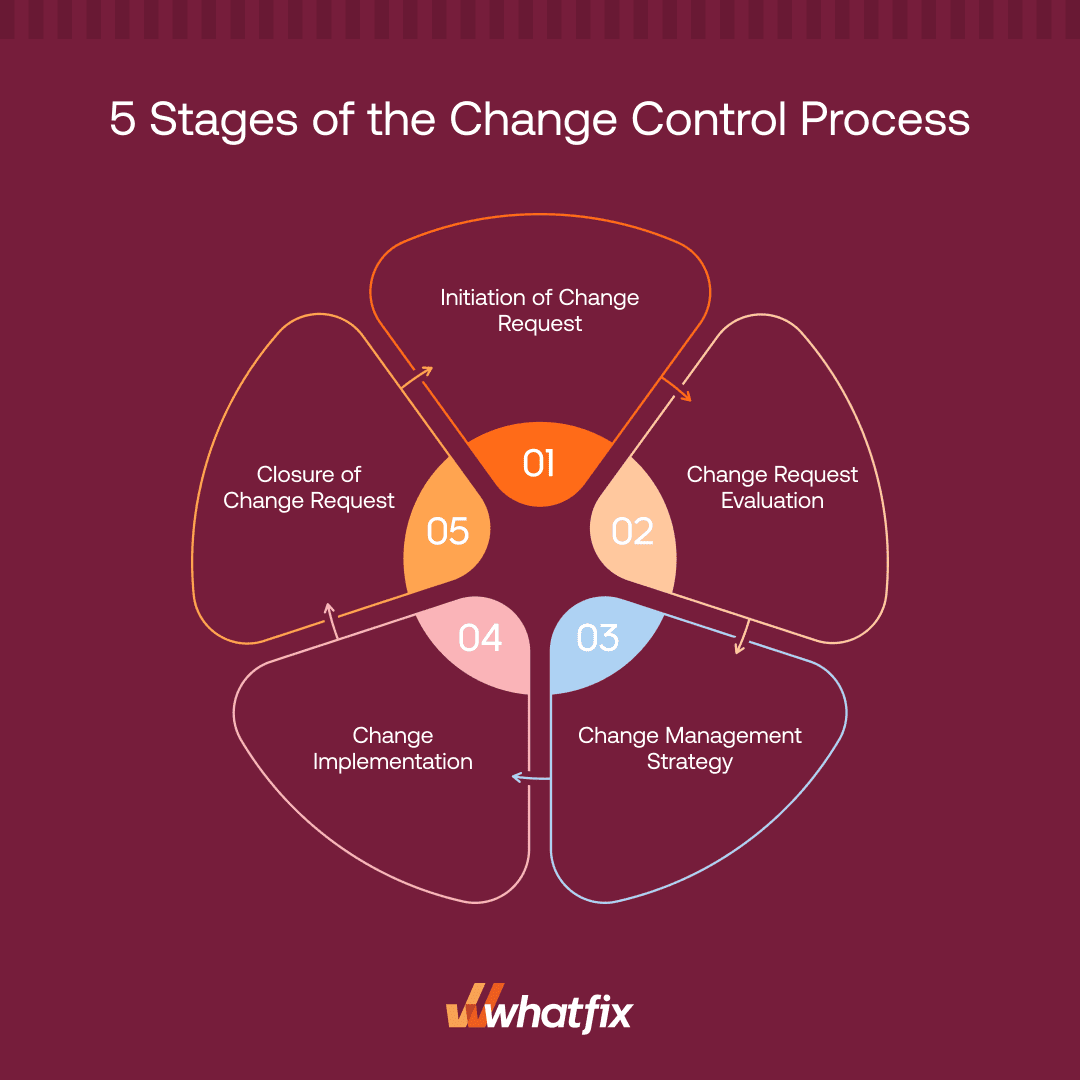
In this stage, there is a clear need for change due to business process inefficiencies, technological advancements, and evolving customer needs. These types of change requests come from various areas of an organization – a project team member, leadership, or a customer.
This requires organizations to have open communication channels to hear the voice of the customer (VoC) and insights from various team members and departments. There must be a detailed change proposal describing the change and how it would benefit the company to initiate a change request. The initiator must outline the reasons for the change on the change request form, which is further added to the changelog.
Here are some examples of what to include in your change request:
In the second phase, the change request is assessed to evaluate the resource requirement, budgeting, and impact on the company. This step also comprises risk evaluation and any behavioral modifications required for the change to succeed. Finally, the process moves to the next step if the change is approved. If rejected, the reasons are documented and communicated to the stakeholders and client.
The third stage includes detailed planning for a change initiative. Change leaders build a clear & concise strategy, including timelines, resources, pilot testing, and how to minimize the impact of change. Here are a few action items for a successful organizational change:
In this step of the change control process, a company begins to disrupt the status quo and initiates the change action plan. It’s crucial to ensure that the change implementation occurs in phases and not at once.
Review the implemented change to mark it as a success or failure. Once the change initiator signs off the document for closure, the process is finalized and closed for future reference.
Implementing an effective change control process can be a game-changer for organizations, driving efficiency and ensuring that changes are well-executed and aligned with business objectives. However, the journey to successful implementation comes with challenges.
To navigate these complexities and ensure a smooth transition, consider the following tips that have proven beneficial for many organizations embarking on this path.
Stakeholder engagement is the cornerstone of any change initiative. Involving those directly or indirectly affected by a change ensures that multiple perspectives are considered. This engagement fosters a sense of ownership and inclusion, which is critical to the success of the change control process.
Stakeholders also often provide valuable insights that might otherwise be overlooked. Their feedback can identify frustrating roadblocks, enhance the efficiency of the process, and drive a more unified approach to implementing changes.
Having a comprehensive documentation system serves as a historical record of all changes made, which ensures transparency, clarity, and traceability. This documentation becomes an essential resource for any team member who needs to understand the rationale, methodology, and outcomes of previous changes.
Well-maintained process documentation also provides a framework for future changes, ensuring consistency and reducing the likelihood of errors. It facilitates knowledge sharing, making it easier for new team members to get up to speed and contribute to ongoing change initiatives.
A change control board (CCB) is responsible for overseeing the change control process. By bringing together a diverse group of experts and decision-makers, the CCB ensures that changes are evaluated holistically, taking into account various organizational perspectives.
The CCB has a dual role of ensuring that changes align with the organizational objectives while also acting as a gatekeeper to allow only well-planned and essential changes to proceed. This centralized decision-making structure ensures that changes are strategic, beneficial, and well-coordinated.
It’s not uncommon for organizations to have limited resources, making it crucial to prioritize changes based on urgency, impact, and feasibility. By ranking changes, organizations ensure that the most critical and beneficial changes are addressed first.
A structured prioritization process also fosters better decision-making and reduces the risk of changes that might not yield significant benefits. It clarifies the change control process and ensures alignment with broader organizational goals.
Standardized procedures bring consistency and predictability to the change control process. They outline a clear roadmap for initiating, evaluating, and implementing changes, ensuring that all team members have a common understanding of the steps involved.
Having standard operating procedures (SOPs) in place also reduces the risk of errors and oversights. They act as a safety net, ensuring that all changes—regardless of their size or complexity—are handled with the same level of diligence and care.
Change control is most effective when everyone involved understands its intricacies. Change management training sessions empower stakeholders with the knowledge and tools they need to navigate the change control process efficiently, ensuring they play an active, informed role.
Alongside training, raising awareness about the reasons for and benefits of changes ensures buy-in from the organization. A well-informed team is more likely to support, advocate for, and effectively implement changes, making the overall process smoother and more successful.
Communication connects all elements of a change control process. Organizations can foster transparency and trust by keeping stakeholders updated about the status of changes.
Regular communication also provides an opportunity for feedback, allowing for real-time adjustments and refinements. It ensures everyone is aligned and working towards a common goal, making the entire change control process more cohesive and collaborative.
Change is inherently unpredictable. Even with the best plans in place, unforeseen circumstances and challenges can arise. That’s why flexibility with the change control process is crucial—it ensures a structured approach to managing change and room to adapt when necessary.
Being rigid can lead to inefficiencies, missed opportunities, or even failures in implementation. Flexibility allows for better responsiveness to a project’s evolving needs and realities, ensuring that the change control process remains effective and relevant.
Every change, no matter how well-planned, comes with potential risks. Organizations can identify, evaluate, and mitigate potential threats associated with proposed changes by incorporating a risk assessment stage within the change control process.
A thorough risk assessment not only safeguards against potential pitfalls, but also instills confidence in stakeholders. Knowing that risks have been considered and planned for ensures a more streamlined implementation, reducing uncertainties and enhancing the overall robustness of the change control process.
Feedback is a vital aspect of continuous improvement. Establishing a mechanism where employees can share their observations, experiences, and suggestions ensures that the change control process is dynamic and improves over time.
Constructive feedback, when acted upon, can lead to refinements that make processes more efficient, user-friendly, and effective. It fosters a culture of open communication where employees feel valued and heard, promoting greater engagement and collaboration throughout the change control journey.
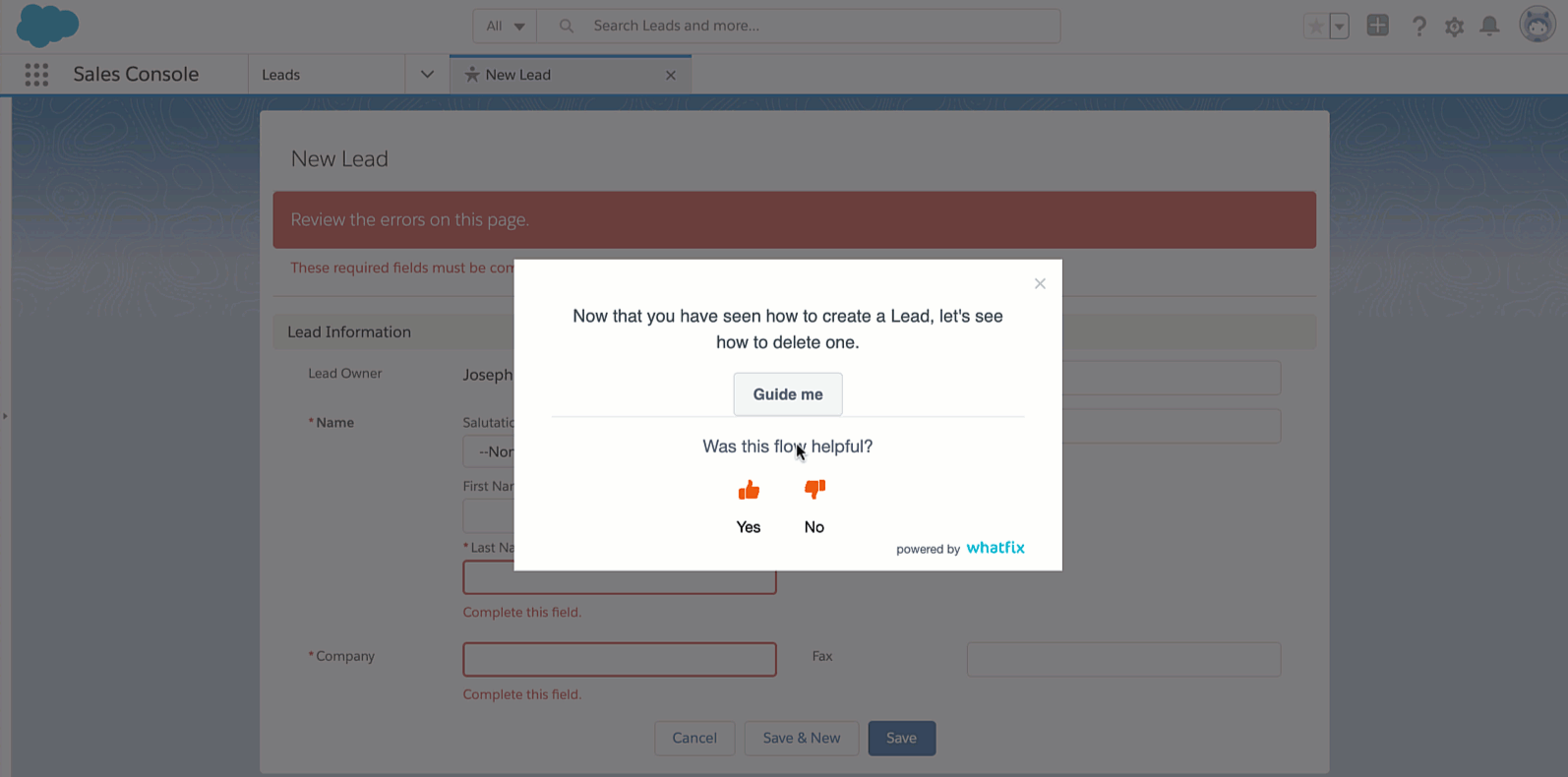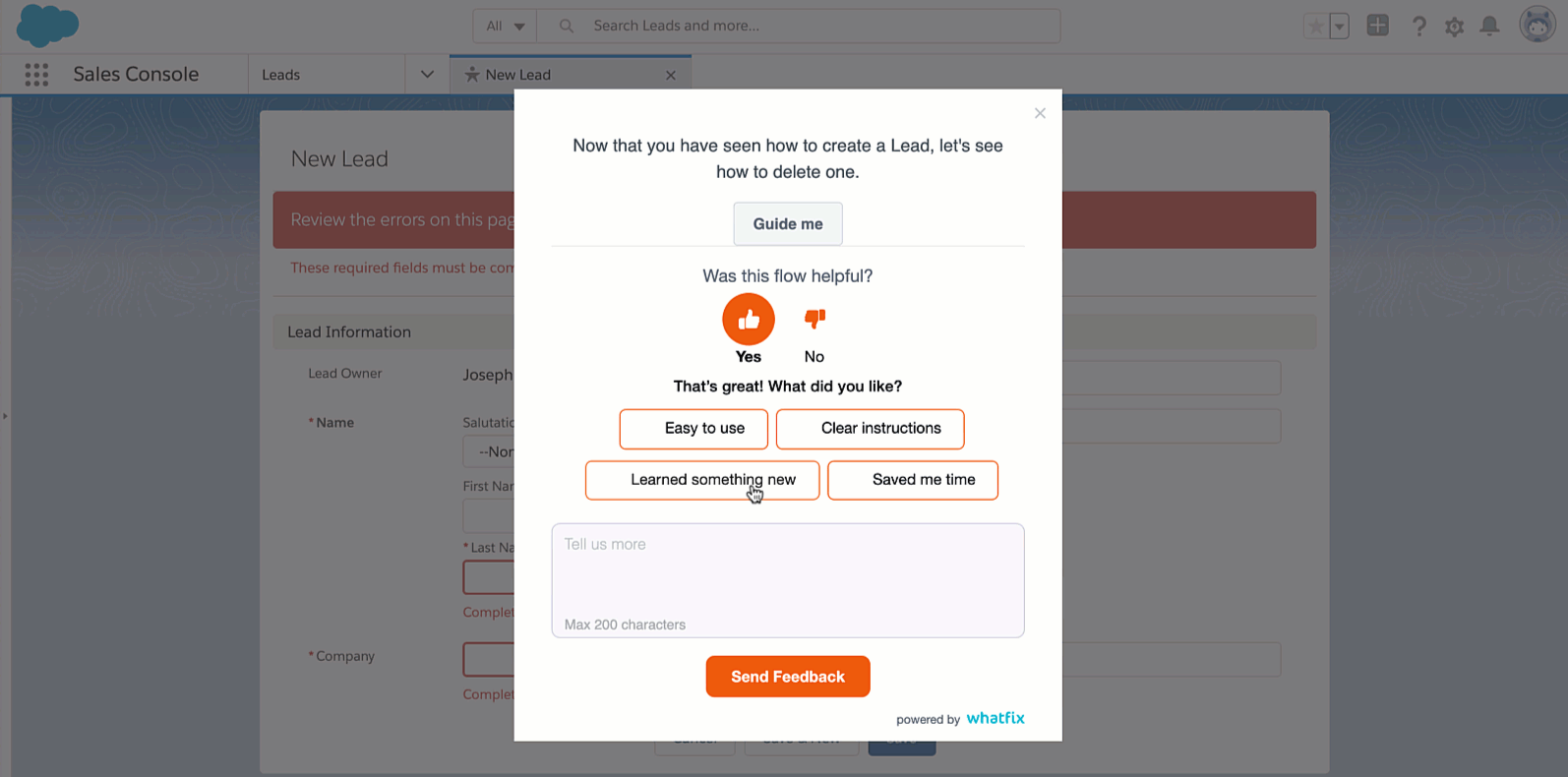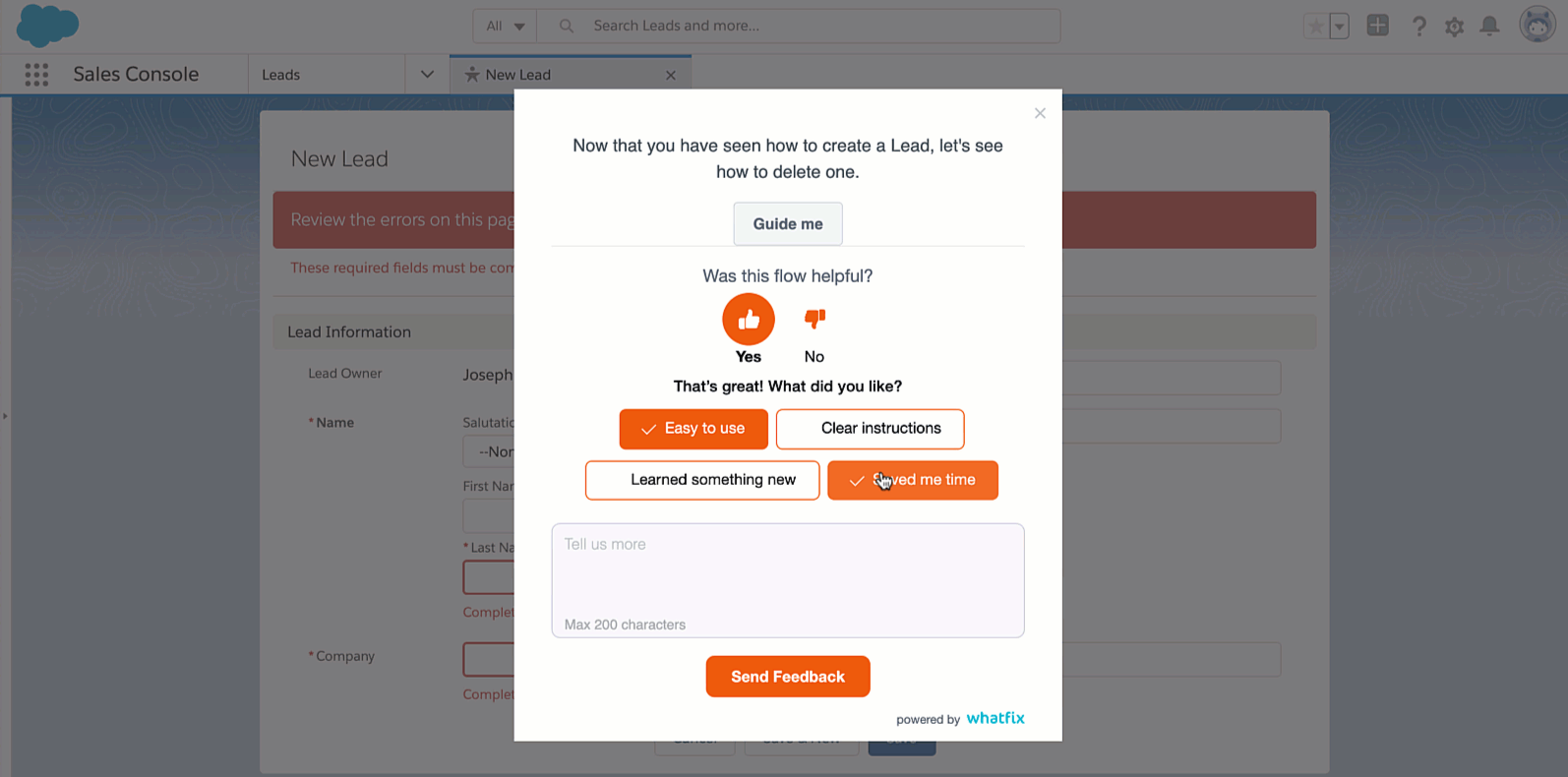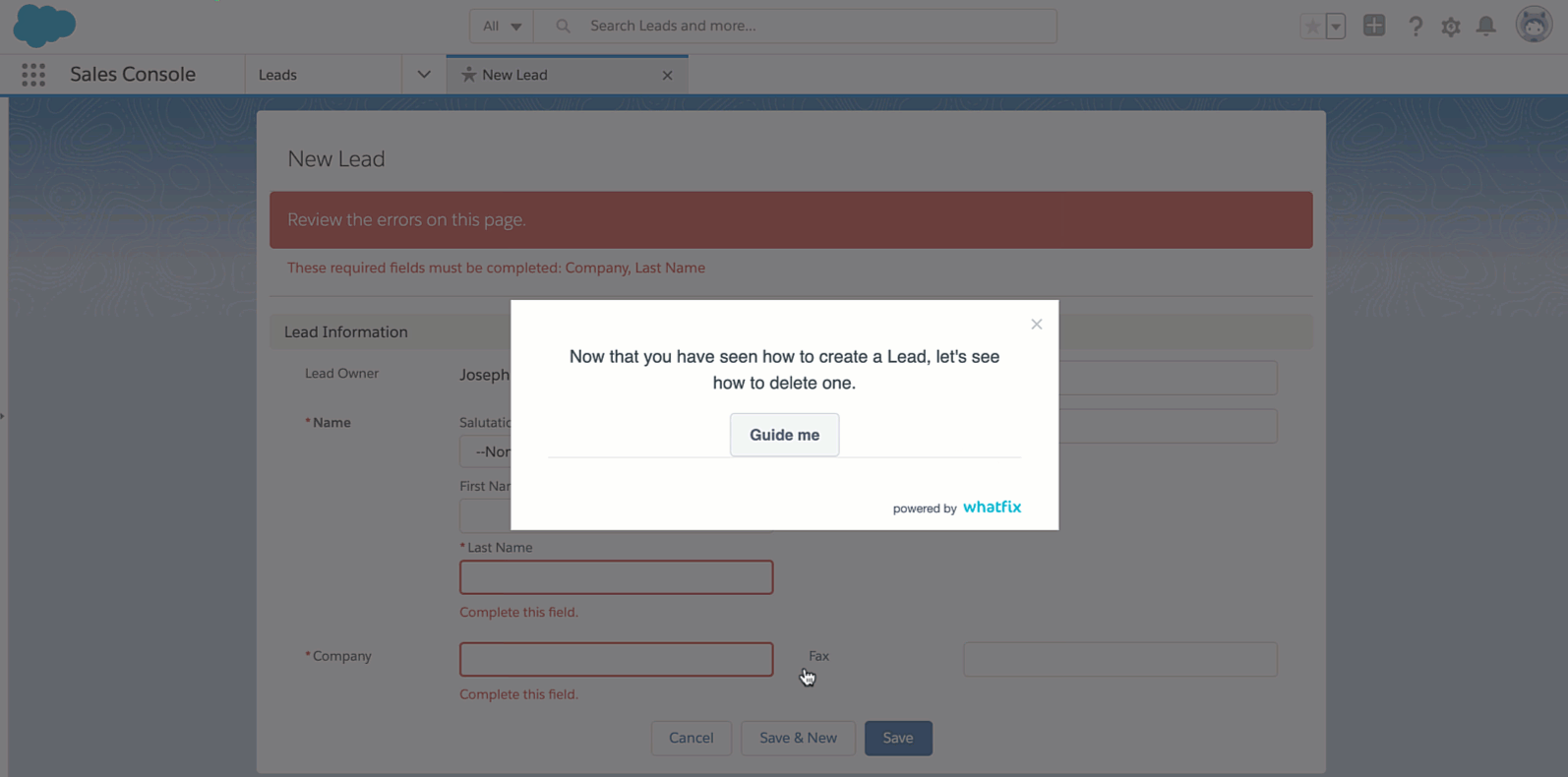
In today’s fast-paced business environment, leveraging technology can enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of the change control process. Tools and platforms can automate various stages, provide real-time tracking, and ensure seamless stakeholder communication.
Technology also ensures that data is stored, accessed, and analyzed systematically. This not only brings speed and accuracy to the process, but also provides valuable insights through data analytics, enabling better decision-making and fostering a more data-driven approach.
Once a change has been implemented, it’s crucial to evaluate its effectiveness and the overall efficiency of the change control process. Conducting post-implementation reviews allows organizations to assess what went well and where there might be room for improvement.
These reviews are not just backward-looking; they also provide essential learnings for future change initiatives. Organizations can refine their approach by understanding the successes and challenges of a recently completed change and ensure that subsequent changes are even more successful.
Change control processes, like all organizational procedures, benefit from regular audits. These audits dive deep into the workings of the process, ensuring that it’s being followed correctly and identifying areas where it could be improved.
An audit isn’t just about compliance; it’s about continuous improvement. By regularly examining the change control process, organizations can stay ahead of potential issues, ensure alignment with industry best practices, and maintain the process’s effectiveness.
The business environment is in a constant state of flux, and what works today might not necessarily be the best approach tomorrow. That’s why committing to continuous improvement ensures that the change control process remains relevant, efficient, and aligned with an organization’s goals.
Embracing a mindset of continuous process improvement means regularly evaluating and refining the process. This approach ensures that the change control process not only responds to current needs, but also anticipates future challenges and opportunities, keeping the organization agile and ahead of the curve.
Navigating the complexities of organizational change demands more than just strategic planning; it requires robust technological support. The tools that enable, track, and enhance every stage are essential for the success of this methodical approach.
Here are some of the best change management software and project management tools that aid in the change control process:

G2 Rating: 4.3 out of 4 stars
Price: Starts at $10/user/month
Originally designed for software bug tracking, Atlassian’s Jira has evolved into a versatile tool that supports change management processes. Its customizable workflows make it adaptable to a variety of change control scenarios.
Key features:

G2 Rating: 4.4 out of 5 stars
Price: Contact for pricing
ServiceNow offers an IT Service Management (ITSM) suite that includes change management functionalities. Its platform allows users to automate change processes, track changes, and integrate with other ITSM practices.
Key features:

G2 Rating:4.1 out of 5 stars
Price: Starts at $7/user/month
As a comprehensive project management tool, Microsoft Project can be adapted to track and manage changes, particularly when they’re part of larger projects.
Key features:

G2 Rating: 4.4 out of 5 stars
Price: Free version available, price determined by tier
Trello‘s card-based system can be used to represent change requests. Its simplicity and visual nature can be useful for teams that want a straightforward way to track and manage changes.
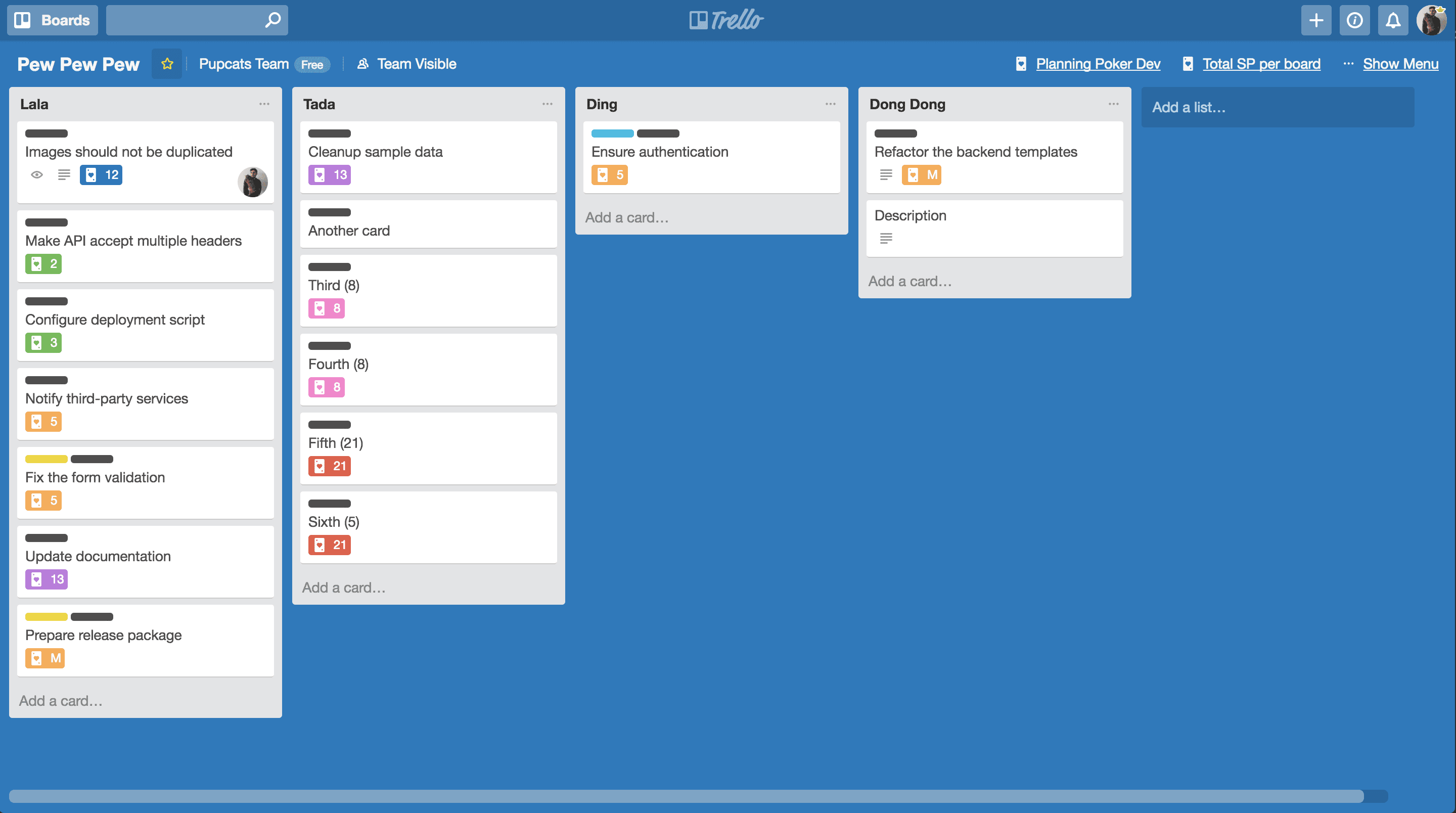
Key features:
G2 Rating: 4.3 out of 5 stars
Price: Free version available
As a task and project management tool, Asana can be customized to handle change requests, prioritize them, and assign them to appropriate team members.
Key features:

G2 Rating: 4.1 out of 5 stars
Price: Starts at $10/month
Another product from Atlassian, Confluence is a collaborative documentation tool. It can document change requests, maintain change logs, and store related documentation.
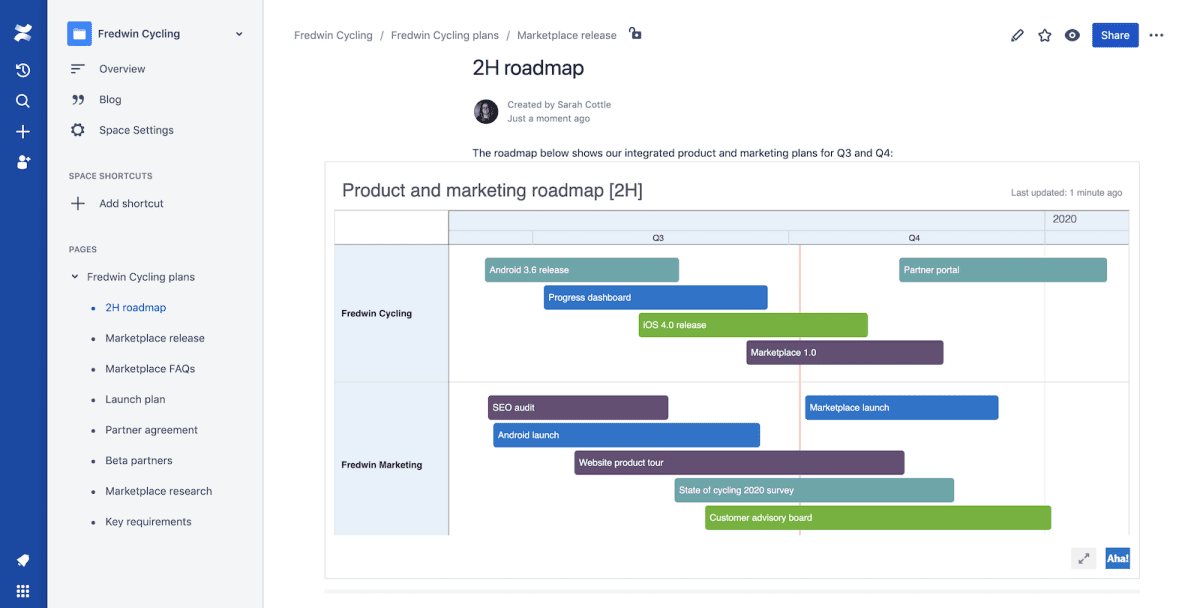
Key features:

G2 Rating: 4.7 out of 5 stars
Price: Starts at $8/4 seats/month
Monday.com is a work operating system that empowers teams to run projects and workflows with confidence. Its visual project management and team collaboration software is popular for change control and other uses.
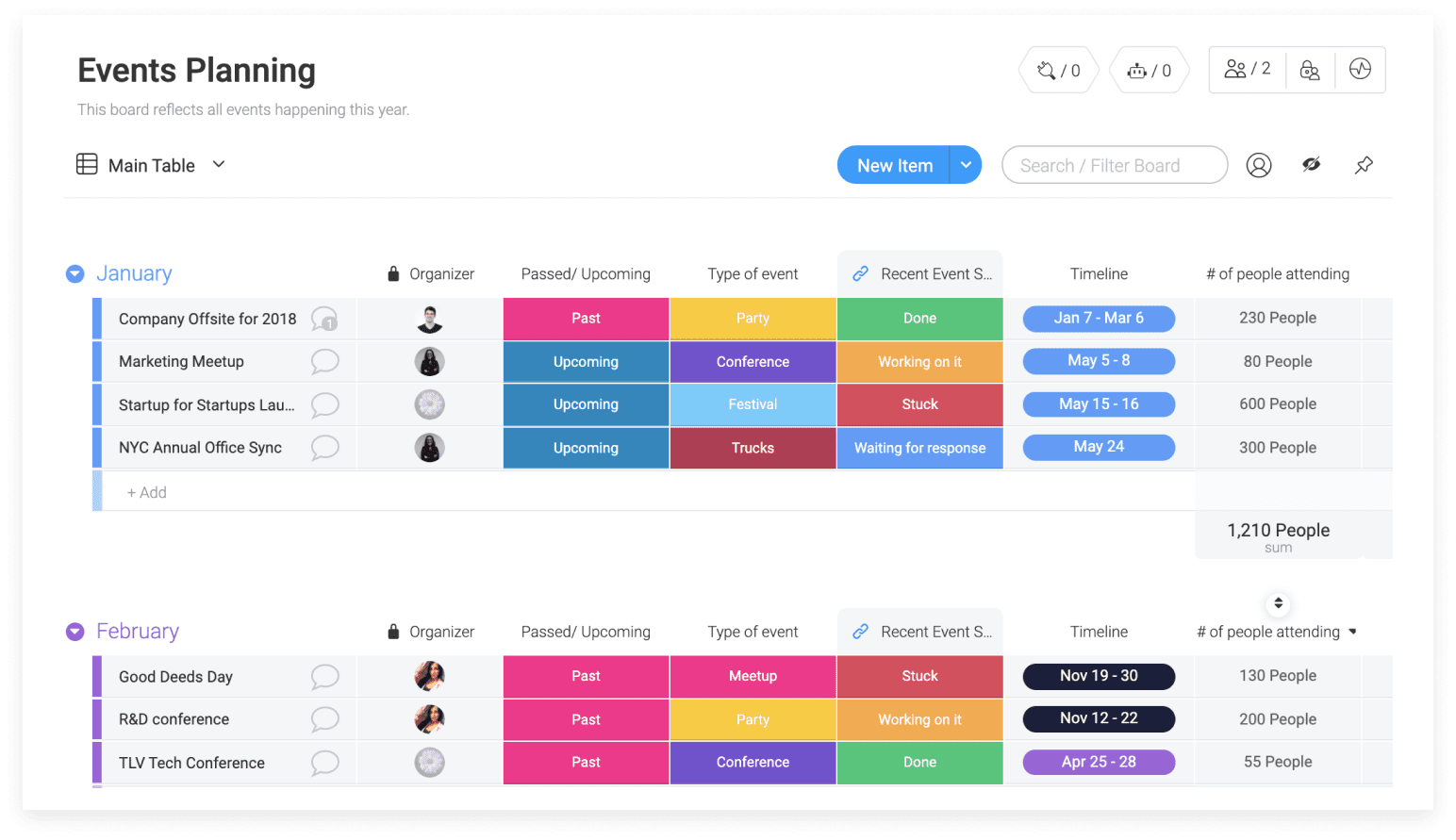
Key features:
Change control is used across industries to act as a check on an entire project. Let’s consider an example from IT change management – software implementation.
Software implementation is a risky and complex task, and to avoid any implementation failures, every organization must consider the following action items:
Change control requires quite a lot of documentation and manual work. Change control templates come in handy to help minimize these administrative tasks.
Here are a few common templates for you to get started with a change control process:
✓ Thank you, the checklist will be sent to your email
In an evolving business landscape, understanding and implementing a change control process is more crucial than ever. Change control not only streamlines modifications within a project or system, but also ensures that every alteration is beneficial, efficient, and in line with an organization’s objectives. From deciding when to employ a change control process to utilizing free templates, the journey can be extensive. However, the heart of successful change lies in its adoption.
Change processes, while foundational, can be daunting. The intricacies of change management require robust tools to ensure effective transition and, above all, a high adoption rate. One of the most significant challenges any organization faces is resistance to change. More often than not, this resistance stems from a lack of understanding or the overwhelming nature of new processes. Enter Whatfix—a game-changer in the realm of digital adoption.
By leveraging a digital adoption platform (DAP) like Whatfix, you’re not just introducing change; you’re handholding your employees through it. Whatfix ensures a seamless transition by providing in-app guidance and interactive walkthroughs that enable employees to learn and adapt within the context of their actual work environment. Employees are actively engaged instead of passively receiving training, reducing the learning curve and accelerating productivity.
What makes Whatfix stand out among other tools is its commitment to real-time, personalized training experiences. With 24/7 end-user support available in multiple formats and embedded directly within your applications, it eradicates the conventional barriers to learning. Through intuitive task lists, customized pop-ups, and self-help modules, Whatfix supports users, especially during those crucial initial stages of change.
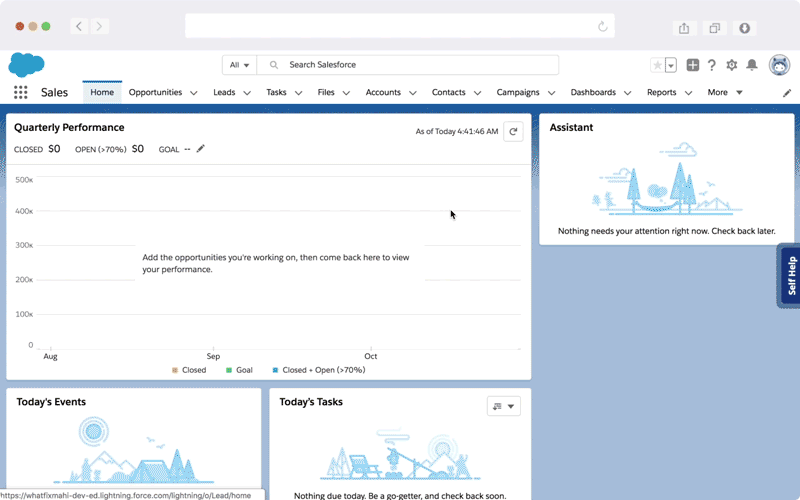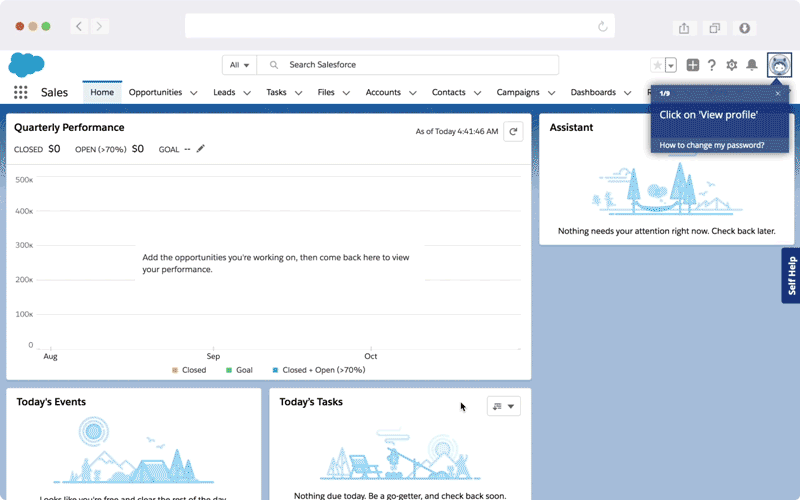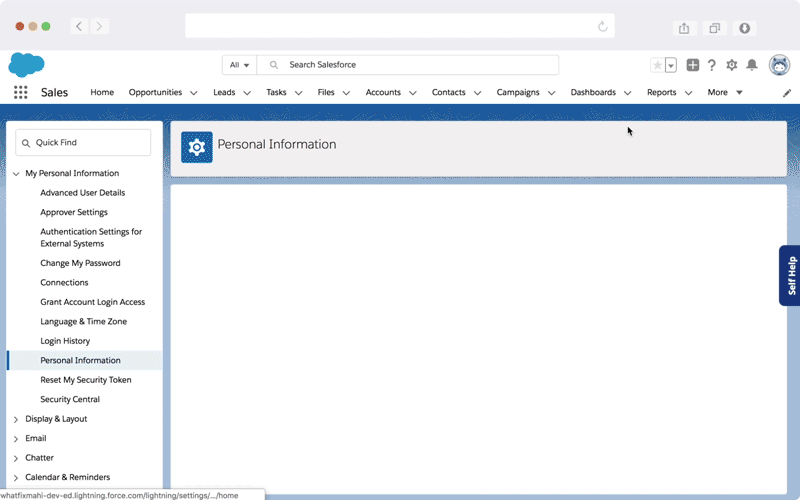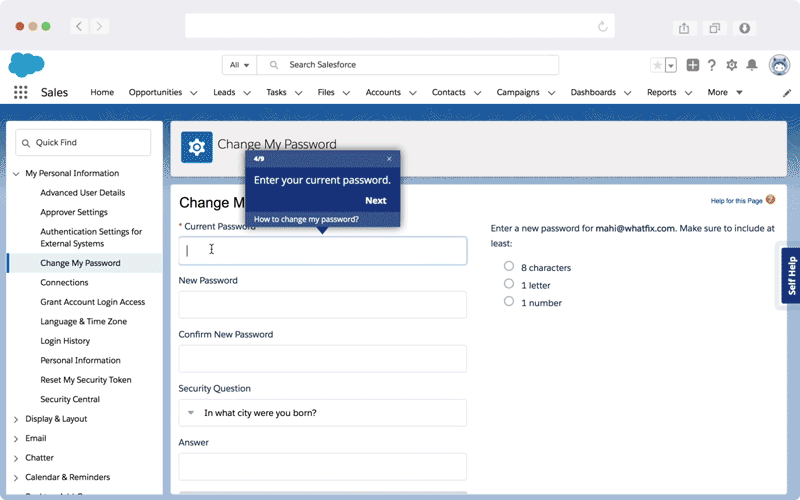
While understanding the mechanics of the change control process is vital, ensuring its successful adoption is where true success lies. With Whatfix, you’re not just managing change; you’re championing it. Whether you’re undertaking significant system modifications, software implementations, or any other change process, consider Whatfix as your ally in ensuring change is implemented and embraced.
Explore Whatfix today and transform your change control process into an empowering and seamless experience for your entire organization.
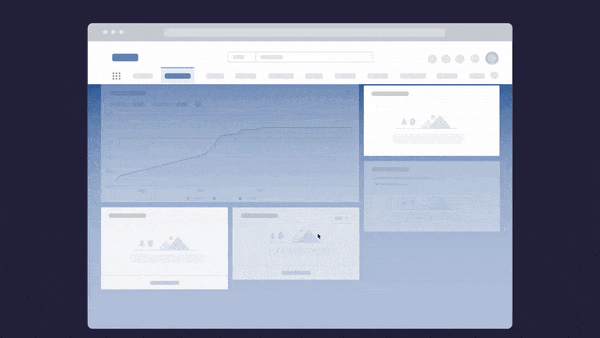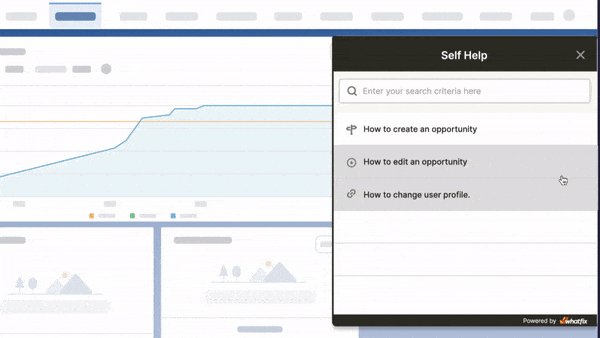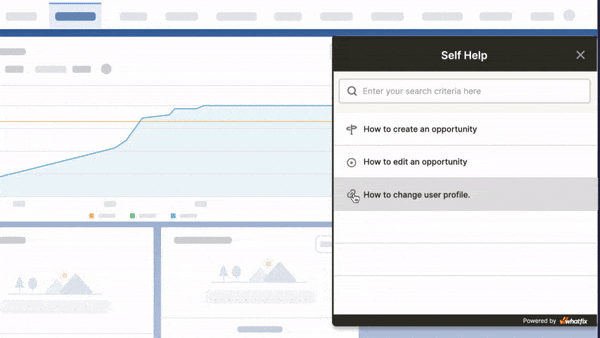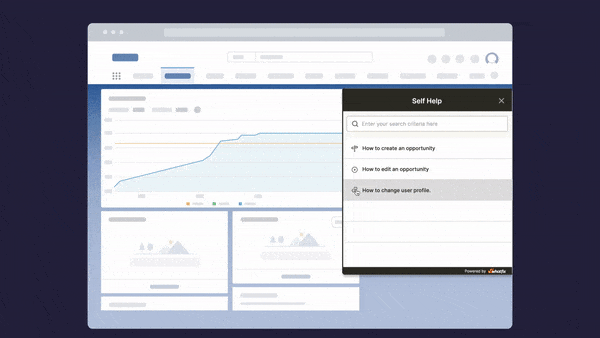
Above: Enable your employees with contextual user support and accelerate IT adoption with Whatfix's digital adoption platform.
The Whatfix Digital Adoption Platform empowers IT teams to create in-app guidance and self-service user support on all internal desktop, web, and mobile applications. Enable employees with Self Help, which overlays onto your CRM, HCM, ERP, CPQ, and other digital workplace applications. Self Help connects to your process and IT documentation, LMS, video tutorials, onboarding documents, and other IT support-related content to provide employees self-help, at the moment of need. Create additional in-app guidance and pop-ups to contextually guide users through applications and alert them to process changes.

Thank you for subscribing!
Thank you for subscribing!