In recent years, the healthcare industry has undergone a profound transformation driven by digital technologies. Research shows that 85% of CEOs and 79% of health system leaders still see substantial or transformative change ahead.
From electronic health records to telemedicine and artificial intelligence, digital transformation revolutionizes how healthcare is delivered, experienced, and managed. Hospitals can save lives with improved compliance guidelines.
This article explores the key aspects of digital transformation in healthcare, highlighting its impact on patient outcomes and the future of healthcare.
What Is Digital Transformation In Healthcare?
Digital transformation in healthcare means using digital technologies, tools, and platforms to improve the quality of healthcare delivery, enhance patient experience, and enable better healthcare outcomes. AI, IoT devices, and cloud computing create a connected healthcare ecosystem that enables real-time patient monitoring, data-driven decision-making, and predictive care models. These are all part of the digital transformation revolution in healthcare.
Use Cases Of Digital Transformation In Healthcare
Here are a few most significant use cases of digital transformation in healthcare.
1. Improved patient care
Digital transformation enables hospitals and service providers to collect and analyze patient data to provide a personalized healthcare experience. Digital solutions like Electronic Health Records (EHRs), telemedicine, and Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) help improve patient participation, increase provider collaboration, and lower the risk of errors in healthcare.
For example, Epic is a full-stack electronic medical records platform that does it all. Whether you’re a one-person practice or a medical director at a university hospital, Epic makes it easy to manage your entire medical workflow inside one source of truth.
2. Increased operational efficiency and resource allocation
Digital transformation helps streamline hospital operations by eliminating mundane tasks while reducing administrative effort. Reducing manual tasks helps healthcare staff focus more on patient care. Digital tools such as patient scheduling systems, inventory management systems, and electronic billing systems allow the most optimized utilization of human resources.
Predictive analysis based on past data helps predict demand and enables hospitals to allocate resources beforehand. This also allows the medical service provider to handle medical inventory optimally, which can be crucial in a crisis.
Many healthcare organizations use technology to support care coordination. This way, patients get the right treatment in a timely manner and have a seamless journey from one step of the process to the next.
3. Patient disease history analysis
Digital transformation has made analyzing a patient’s disease history easier and efficient. Disease history analysis tools provide doctors with recommendations about treatment outcomes.
Boston Gene can serve as a good example here. The company provides a unique solution that performs sophisticated analytics to aid clinicians in evaluating viable treatment options for each patient’s genetics, clinical characteristics, and disease profile.
4. Efficient supply chain management
Digitally transforming the supply chain can reduce process costs by 50 percent and increase revenue by 20 percent. Technology can automate the process of ordering, reconciling, and paying for medical, surgical, and pharmaceutical supplies.
This decreases the cost burden on inventory management and supply chain management. A robust supply chain management system helps hospitals cope with supply-side shocks in emergencies like the COVID-19 pandemic.
5. Use of patient portals for convenience
Another leading technology in healthcare trends is patient portals. These are platforms where patients can access their health records, schedule appointments, message their doctors, and more.
For example, WebPT empowers rehab therapists with digital patient intake forms that streamline the patient registration process. Once new patients arrive, they’ll spend less time in the waiting room.
This trend promotes convenience and transparency. People can easily see their test results, care histories, and doctor visit notes—all online. They can easily share this data with multiple providers, eliminating the need to call and manually transfer records. This is more convenient for the patient and reduces the burden on office staff.
One example is FollowMyHealth, a platform that multiple healthcare systems use.
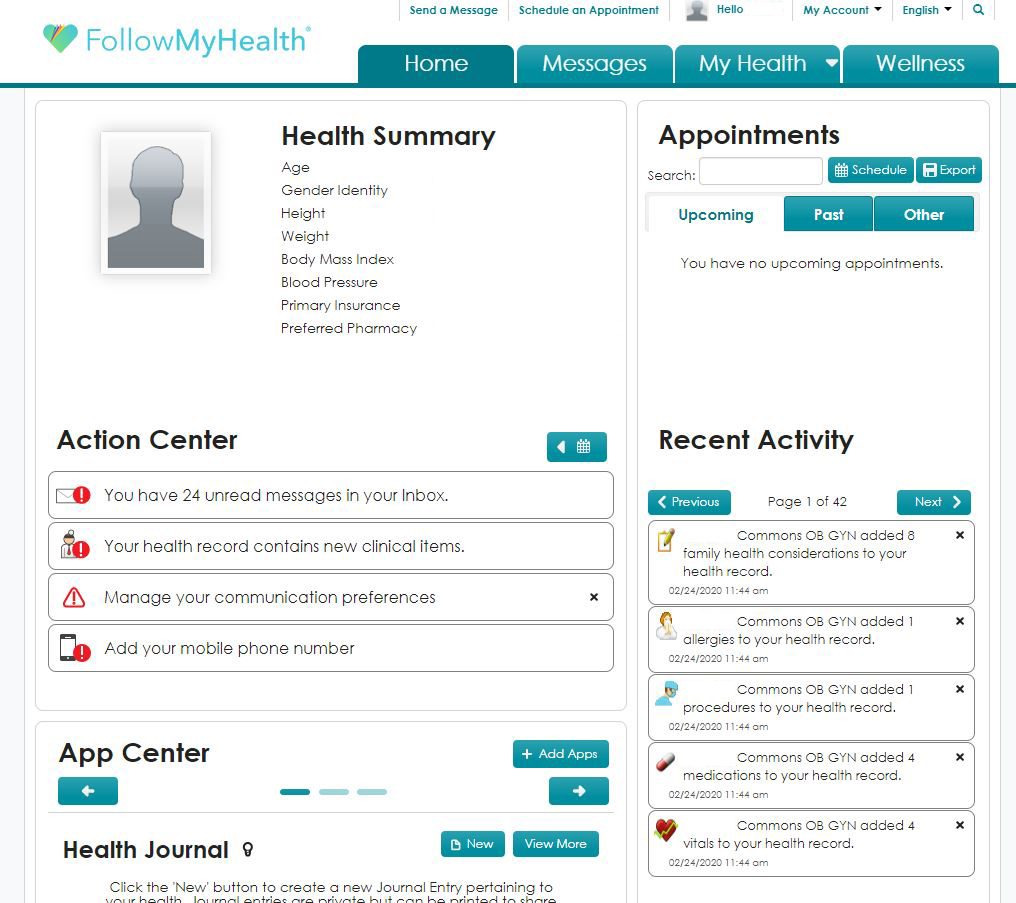
With FollowMyHealth, patients can use the same platform for general medicine and specialist visits. They can message doctors and access their complete medical histories from one central location.
Implementing a digital adoption platform for onboarding can accelerate patient portal adoption significantly via interactive walkthroughs, in-app guidance, and 34*7 self-help support. This enables users to take full advantage of everything the online portal has to offer.
6. Data aggregation
While patient portals help pull data on the patient end, many hospitals also work on aggregating back-end data. Currently, doctors’ offices have data coming in from a wide variety of sources, including:
- Patient-provided data
- Internal electronic health records
- External electronic health records (such as from outside specialists or urgent-care centers)
- Lab results
- Imaging
- Insurance claims
- Data from medical devices
- Pharmacy data
With all of these sources, it’s easy to overlook important patient medical history data. Data aggregation enables fast, informed patient-care decisions, and doctors don’t have to worry about missing key information.
The top goals driving data aggregation are improved patient care and lower costs. All of the data for a patient is brought together to create a comprehensive profile. Having a single source of truth reduces the time staff spends sorting through patient data and paperwork, resulting in fewer patient wait times and administrative hours.
Mayo Clinic is pursuing data aggregation by partnering with Google to implement cloud solutions. They use the cloud to host data storage and analytics all in one place. Google’s cloud offers a single, secure location for storing, organizing, and accessing patient data, allowing for more comprehensive diagnostics. At the same time, Google’s cloud computing and artificial intelligence (AI) capabilities will aid in the Mayo Clinic’s research efforts.
Benefits of Digital Transformation in Healthcare
Hospitals can leverage digital transformation to improve their overall operational efficiency, enhance patient care, improve a hospital’s financial performance, and enhance security and compliance. Here are some of the most significant benefits of digital transformation in healthcare and pharma digital transformation.
1. Improved patient care, outcomes, and engagement
Predictive analytics uncover health issues before they become severe, giving care teams a crucial head start. Remote monitoring keeps doctors informed with real-time patient data. Patients actively participate in their healthcare journey through mobile apps, tracking medications and vital signs from home.
2. Increased operational efficiency and streamlined workflows
Digital tools transform administrative tasks into streamlined processes. Teams access patient information instantly, eliminating the endless hunt for paper records. By automating routine tasks, healthcare staff can dedicate more time to what matters most—patient care.
3. Cost reduction and better resource management
Smart inventory systems prevent costly supply shortages and equipment downtime. Digital billing speeds up reimbursement by catching claim errors early. Improvements like these free up resources for essential medical equipment and facility upgrades.
4. Enhanced data security and improved regulatory compliance
How do healthcare organizations keep up with all the data they need to manage? Advanced encryption and blockchain technology work together to protect patient privacy. Digital systems maintain detailed audit trails of data access. Automated compliance tools remove the guesswork from HIPAA requirements, so patient information stays secure.
5. Greater accessibility to healthcare services and telemedicine capabilities
Healthcare now reaches patients wherever they are through virtual visits and digital consultations. Quick messaging systems let patients get answers without scheduling appointments. Remote care options make specialist expertise available to underserved communities, too.
7. Enhanced collaboration among healthcare providers
Digital platforms connect entire care teams instantly, including primary doctors and specialists. Shared health records eliminate communication gaps between departments. Treatment plans are updated in real-time, keeping everyone aligned on patient care decisions.
8. Real-time data and insights for informed decision-making
Clinical support systems put information at providers’ fingertips when needed. This means population health trends can show up through digital dashboards. Smart monitoring alerts doctors to changes in patient conditions before complications develop.
9. Better management of chronic diseases and accelerated innovation
Digital therapeutics create personalized treatment plans based on individual patient data. Remote monitoring helps patients manage long-term conditions effectively at home. That can help prevent complications, leading to better outcomes for chronic conditions.
5 Examples of Technology Driving Healthcare Transformation
Here are five examples of emerging healthcare technologies transforming the industry:
1. Enterprise Health Record
Electronic Health Records (EHR) are digital versions of patients’ medical records and health information. They contain comprehensive and up-to-date information about a patient’s medical history, diagnoses, medications, allergies, immunizations, laboratory results, and other relevant health data. Electronic Health Records replace the traditional pen-and-paper method of storing patient data.
To implement effective in-app EHR training and boost EHR adoption, consider implementing a digital adoption platform such as Whatfix. Whatfix’s in-app guidance allows you to generate custom onboarding flows that overlay on top of your software. Furthermore, customized tooltips, popup recommendations, and a self-help widget pull data from your knowledge base to support employees throughout the software adoption process.
2. Hospital Management System
A Hospital Management System (HMS) is software designed to automate and streamline various administrative, operational, and clinical processes within a hospital or healthcare organization. It is implemented to streamline operations, improve efficiency, enhance patient care, and optimize resource utilization.
A few features of the hospital management system include:
- Patient Management
- Appointment Scheduling
- Laboratory Information System (LIS)
- Inventory Management
- Electronic Prescribing
3. Patient Portals
Healthcare organizations must provide exceptional levels of service to modern patients. That means quickly responding to patient queries and providing self-service resources for patients to find health records and test results, ask the doctor a question, refill a prescription, book an appointment, and more.
Patient portals are online healthcare platforms that allow patients to access their medical records, lab results, prescription details, and appointment histories directly. By providing patients with easy access to their health information, patient portals empower patients to manage their own care proactively.
Patients can book or modify appointments, request medication refills, and communicate with healthcare providers, reducing the need for phone calls or in-person visits. This streamlined experience enhances patient satisfaction, as individuals can manage their healthcare on their terms and reduce the likelihood of miscommunication.
4. AI agents diagnosing and screening
AI screening tools analyze medical imaging with high accuracy. Radiologists use these systems to detect subtle abnormalities in X-rays and MRIs. The technology works well at routine screenings, flagging potential issues for specialist review. This speeds up diagnosis and catches problems earlier.
5. Predictive healthcare
Machine learning models spot disease patterns before traditional symptoms appear. These systems flag early warning signs of complications. Hospitals use predictive tools to reduce readmissions by identifying high-risk patients. Care teams receive alerts when patient data suggests declining health, which supports early intervention.
6. Process mining and optimization
Process mining tools uncover bottlenecks in clinical workflows. These systems analyze electronic health records to map actual care patterns. The technology reveals unexpected delays and resource constraints. Teams can use these insights to streamline patient flow and reduce wait times.
Effect of COVID-19 on the Healthcare Industry
The COVID-19 pandemic Created a situation where all healthcare systems had to innovate. This came with its own challenges and opportunities. The global health emergency overwhelmed the healthcare infrastructure of even the most advanced nations. Since then, people have experienced a shortage of beds, healthcare workers, and other medical aids. To address this, a major chunk of patients have adopted home health care.
1. Overwhelmed healthcare infrastructure
The global health emergency overwhelmed the healthcare infrastructure of even the most advanced nations. People have experienced a shortage of beds, healthcare workers, and other medical aids since. To address this, a major chunk of patients have adopted home-health care.
2. Accelerator for digital transformation in healthcare
COVID-19 has played a major role in accelerating digital transformation in healthcare. High optimism and positive sentiments related to digital healthcare have resulted in significant growth – as has the rise of virtual hospitals.
Worldwide corporate funding for digital health companies has doubled to $21.6 billion. Investment in telemedicine alone has reported an impressive figure of $4.3 billion. Additionally, the US witnessed the largest deal in the sector when telemedicine provider Teladoc acquired digital disease management company Livongo Health for $18.5bn in October 2020.
3. Digital supply chain
The pandemic has disrupted supply chains for all businesses. According to Capgemini, 60% of organizations are looking at increasing their investment in the digital supply chain with an increased focus on automation, AI/ML, and robotics.
For instance, Melbourne Health Logistics has undertaken a Supplier Improvement Pilot Project, which involves 10 Australia-based SMEs and aims to address the challenges in supply chain and inventory management through digitization.
Three key focus areas of the project are implementing data-capturing technologies, improving data quality, and introducing suppliers to Electronic Data Interchange (EDI). It further partnered with the federally funded AusIndustry Entrepreneurs program to empower suppliers to develop digital capability.
Roadblocks In Digital Transformation In Healthcare
Here are some of the challenges faced by digital transformation in healthcare.
1. Interoperability and data integration
Healthcare organizations struggle with fragmented systems that don’t connect. This makes information sharing between departments and facilities difficult. Critical patient data gets isolated, leading to incomplete medical histories and delayed care decisions.
Healthcare providers overcome these barriers through standardized data protocols and integration platforms. Modern APIs connect disparate systems, and data transformation tools support a consistent information flow across healthcare systems.
2. Resource constraints
Digital transformation requires investment in infrastructure, software licenses, and staff training. Many healthcare organizations, especially smaller clinics and rural hospitals, lack the capital. Limited budgets force difficult choices between maintaining existing systems and investing in new capabilities.
Strategic planning and phased implementations help organizations manage costs. Cloud-based solutions reduce initial infrastructure expenses, and modular approaches let healthcare providers prioritize critical improvements first
3. Resistance to change
Medical staff may hesitate to adopt new technologies that disrupt established workflows. Years of experience with familiar systems create resistance, and concerns about patient safety and care quality during transitions add to this resistance.
Successful organizations address these concerns with early stakeholder involvement and clear demonstrations of technology benefits. Hands-on training and peer champions help staff embrace new tools that streamline their daily work.
4. Healthcare professional skill gaps
Many healthcare workers lack experience with digital tools, creating anxiety about technology adoption. The pace of innovation makes it challenging to keep skills current. Training requirements may compete with patient care responsibilities for limited staff time.
Training programs with flexible learning options help bridge these gaps. Just-in-time learning resources and peer support networks give staff confidence in new technologies, and regular skill assessments keep everyone sharp.
5. Regulatory and compliance challenges
Healthcare regulations create uncertainty around digital innovation. HIPAA requirements and patient privacy laws affect technology choices and implementation approaches. These compliance obligations add extra verification steps to digital transformation projects.
Healthcare organizations navigate these challenges with careful vendor selection and compliance frameworks. Regular audits make sure new technologies meet regulatory requirements.
6. User experience and usability
User experience and usability pose significant roadblocks to digital transformation in healthcare. The complexity and fragmented nature of healthcare systems often result in unintuitive digital interfaces, leading to poor user experiences. Healthcare professionals, already burdened with demanding workloads, may struggle to navigate through intricate software and utilize it to its full potential. Inadequate training and support further exacerbate the usability challenges.
To overcome this barrier, a Digital Adoption Platform like Whatfix can enable user adoption via personalized in-app guidance, interactive walkthroughs, and 24*7 self-help support. Maxwell Health uses Whatfix to reduce its support requests with self-service interactive guides. Whatfix has helped them reduce more than 25,000+ support queries, enabling them to serve multiple clients while providing proactive support in real-time.
15 Digital Transformation Trends In Healthcare
Here are some of the biggest digitalization trends impacting healthcare in 2025.
1. Cloud migration
Cloud migration became part of the healthcare industry in 2016. Since then, it has significantly reduced data management costs. The technology helps streamline and share electronic medical records and prevent data losses.
Furthermore, cloud migration provides access to siloed data which can be used for decision making, resource allocation, and predictive analytics.
2. Smart hospitals
The global smart hospital market was valued at $29 billion in 2021 and is expected to jump to $59 billion by 2026.
A smart hospital uses artificial intelligence, big data, the Internet of Things, cloud platforms, and augmented reality to provide best-in-class facilities to patients. Data and technology are also used to reduce emergency waiting room time and track healthcare facility availability and accessibility.
3. Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT is a rising trend in the healthcare industry. The technology efficiently collects data from multiple sources, which can be further utilized in multiple ways, such as resource allocation, monitoring patients, and managing supply-side shocks.
An Internet of Things-based healthcare architecture consists of a perception, network, and application layer. The perception layer consists of sensors that collect vital information using GPS, medical sensors, smart devices, and RFIDs.
This layer helps acquire a multitude of physiological parameters about the patient. The network layer includes wired and wireless networks that communicate and store information collected in the perception layer. This information is shared either locally or at a centralized location. Finally, the application layer processes this data and delivers application-specific services to the user.
IoT makes access to accurate healthcare information convenient and affordable. One example of such technology is smart insulin pens. Smart insulin pens track the patient’s insulin dose and provide reminders to take their medication. Connected inhalers can monitor usage and provide feedback on proper inhalation techniques.
4. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning
AI in healthcare is used in various diagnostic, predictive, rehabilitative, drug discovery, surgical practices, general administration, and operational excellence use cases. AI analyzes large sets of data and makes intelligent, patient-centered decisions. AI can unlock clinically relevant information hidden in a massive database.
One example of an artificial intelligence (AI) device in healthcare is the AliveCor KardiaMobile EKG Monitor. This device uses AI algorithms to analyze heart rhythms and detect abnormal patterns that could indicate a heart condition. The AI algorithms can also detect atrial fibrillation (AFib), which is a common heart condition that can lead to stroke if left untreated.
Artificial Intelligence has the ability to provide essential data points to healthcare providers. This data has the ability to diagnose and treat complex health issues.
5. Telehealth
Telehealth, or telemedicine, refers to providing healthcare services remotely through digital communication technologies. According to a survey by doctor.com, 83% of the surveyed patients are ready to use telemedicine. The pandemic played a major role in positively impacting these numbers.
Telehealth allows healthcare professionals to monitor patients’ progress remotely, provide guidance on post-treatment care, and address any concerns or questions. Telehealth platforms can also deliver educational resources, such as videos, articles, or interactive tools, to empower patients with knowledge about their health conditions and self-care practices.
Brigham Health Hospital Network in Massachusetts regularly uses virtual visits. Patients schedule appointments online and can chat with their providers via video on their phones or desktops.
6. Blockchain
Blockchain can potentially revolutionize the healthcare industry by enhancing data security, interoperability, and patient privacy. Some of the multiple use cases of blockchain in healthcare include:
- Medical record management
- Clinical trials and research
- Healthcare data exchange and interoperability
- Drug traceability and supply chain management
One example of blockchain technology being used in healthcare is Blockpharma. Blockpharma is a blockchain platform that focuses on drug traceability and anti-counterfeiting efforts. It enables consumers to verify the authenticity of medications using a smartphone app and provides real-time data on drug provenance, expiration dates, and supply chain transactions.
SAP Pharma Blockchain is a similar example. A software company SAP has developed a blockchain solution specifically for the pharmaceutical industry. SAP Pharma Blockchain enables end-to-end traceability, serialization, and authentication of pharmaceutical products, helping combat counterfeiting and ensure the safety and quality of drugs.
7. Healthcare chatbots
Healthcare chatbots are software applications that use artificial intelligence (AI) and natural language processing (NLP) to interact with users conversationally, simulating human-like conversations. They are designed to provide healthcare information, answer questions, assist in symptom assessment, offer basic diagnosis, provide medication reminders, and offer general support and guidance to users.
Partners HealthCare created a chatbot to screen potential patients. The bot asks a series of questions and then recommends that a patient be tested for COVID-19 or suggests their next steps. The bot reduces the number of people waiting for COVID-19 screening and lowers the workload for hospital staff.
8. Smart wearables
Smart wearables are significantly contributing to digitally transforming healthcare by providing individuals with real-time health monitoring, improving patient care, and enabling remote healthcare services.
Smart wearables with sensors can monitor vital signs like heart rate, blood pressure, and blood glucose levels. This allows healthcare providers to remotely monitor patients’ health conditions and provide timely interventions, reducing the need for frequent hospital visits.
9. Virtual reality for patient treatment
Research suggests that the global market for virtual and augmented reality in healthcare will reach $5.1 billion by 2025. VR is profoundly changing the way patients are treated. It’s a safer and more efficient alternative to drugs. It is used to treat chronic pain, post-traumatic stress, anxiety, and stroke.
10. Big data
Hospitals can collect data from various sources to provide data-driven, actionable insights. Big data can be used to predict the number of patients expected in a hospital to improve staffing.
Resource management is crucial considering how overwhelmed healthcare staff has been.. Big data analytics can further be used for real-time alerts and informed strategic planning.
11. Augmented reality (AR) for surgery and diagnostics
Surgeons navigate procedures with precision using AR anatomical overlays. Training programs have transformed surgical education with risk-free AR simulations. During consultations, doctors use AR visualizations to explain procedures and diagnoses to patients.
12. Robotic process automation (RPA) in administrative tasks
Healthcare administration has shifted from paper to automated workflows. RPA handles tasks like insurance verification and appointment scheduling without human intervention. Front desk staff spend their time helping patients instead of wrestling with paperwork.
13. Generative AI
Patient conversations transform into clinical documentation. For example, medical teams get instant summaries of lengthy patient histories and research papers. The technology catches details humans might miss in lab reports and clinical notes.
14. Self-service patient experiences
Healthcare now fits into patients’ daily lives through digital tools and mobile apps. Quick remote check-ins replace long waiting room delays. Care teams stay connected with patients between visits through secure messaging and monitoring.
15. In-app guided healthcare worker experiences
New team members adapt quickly to healthcare transformation with contextual help at their fingertips. Training time drops significantly as staff learn through hands-on practice. Support resources integrate into daily workflows.
Whatfix‘s interactive guidance tools provide step-by-step assistance to healthcare professionals navigating new systems. Whatfix DAP allows you to build tailored, interactive training courses via in-app guidance.
Digital Transformation Clicks Better With Whatfix
Healthcare organizations face increasing pressure to adopt technology like AI diagnostics, IoT patient monitoring, and telehealth platforms while maintaining HIPAA compliance. Whatfix adds contextual guidance and automated workflows to your clinical systems to make adoption smoother.
Your healthcare teams gain:
- Real-time support inside EHR systems, telehealth platforms, and patient portals
- Interactive workflows that guide staff through complex processes like insurance verification, telehealth setup, and remote patient monitoring
- Analytics that identify where clinical staff struggle with new technologies so that you can make targeted training improvements
- In-app surveys that capture feedback from physicians and nurses about system usability
Whatfix integrates with major healthcare platforms to provide support at the point of care. By reducing the cognitive load on clinical staff, you decrease charting time, prevent documentation errors, and increase face-to-face patient interaction.
To learn more about how Whatfix drives digital transformation, click here to schedule a free demo with us today!