Joe Connolly, founder of Visana Health, describes the rise of digital health as a battle for the consumer. “The consumer will ultimately decide the next set of digital health winners,” he writes in his newsletter.
Investment in digital health saw a record-breaking spike in 2021, with US-based startups in the healthcare technology space raising $29.1 billion in funding. The technologies emerging into the market — greatly influenced by the pandemic — ranged from digital therapeutics to healthcare marketplaces and virtual care platforms.
Digital transformation in healthcare and healthcare change management is ever-changing. The challenge lies in each organization’s ability to integrate these changes into everyday processes and employee experiences. Without a clear digital adoption strategy in healthcare, technology will fail to deliver its intended ROI and, instead, hold both employees and patients back.
What Is Digital Adoption in Healthcare?
Digital adoption in healthcare refers to the process of improving and redefining traditional healthcare processes by integrating new technologies. These new tools and platforms empower healthcare organizations with the resources to do more transactional administrative activities faster — such as scheduling more appointments virtually, managing staff availability, addressing patient questions quicker, and diversifying pathways for treatments and payments.
The boom in new healthcare applications and services allows healthcare organizations to forge new partnerships, take preventative action, and rethink patient care and communication. A digital adoption strategy ensures that healthcare workers and patients are up to speed with these new technology developments and are prepared to navigate changes without disruptions.
Benefits of Digital Adoption in Healthcare
Healthcare digitization has lagged behind other industries due to its heavily regulated nature, fragmented legacy systems, and lack of data interoperability.
However, the pandemic gave these organizations no choice but to adopt a convenient and consumer-driven approach to service and care, prioritizing more transparency, availability, and accessibility. On top of that, an uptick in burnout among healthcare staff called for better resources and tools to prevent staff shortages, upgrade processes, and lessen the impact of financial constraints on the industry.
Digital adoption allows the healthcare industry to be agile and forward-thinking, giving organizations the following benefits:
1. Enhanced patient care and outcomes
Patient care is quickly moving toward digital channels to simplify activities such as health monitoring, scheduling appointments, and getting treatments. Patients are monitored remotely with wearable healthcare devices like smartwatches and biosensors to capture data on a patient’s mobility patterns, heart rate, and temperature rate.
Healthcare staff can use this innovation to get accurate data with fewer manual administrative tasks while giving patients more options to receive timely treatment or virtual consultations even if they cannot make an in-person appointment.
2. Improved access to healthcare
The convenience of digitized healthcare processes helps reduce the likelihood of patients deferring treatment due to barriers like location, scheduling conflicts, or having limited options for treatment costs and healthcare staff.
The rise of digital interoperability in the healthcare space has made it easier for emerging healthcare startups to introduce new solutions that improve access to healthcare. Chris Hogg, CEO at Marley Medical, describes an ecosystem of digital solutions that help patients access treatment plans and get matched to specialists all from the comfort of their homes.
“Today, I can acquire a user on Facebook, give them access to physicians via a partnership with Wheel, have medicines seamlessly shipped to their homes via Truepill, deliver a home-lab experience via EverlyWell, integrate a wireless blood pressure cuff from Omron, create a seamless referral flow with data from Ribbon, and even get paid for much of this via traditional fee-for-service reimbursement, processed via Eligible,” he writes.
3. Real-time data
Digital adoption helps healthcare providers create more value from patient data. Manual data management and paper-based processes have a long history of weighing down hospital staff and overall efficiency.
Legacy healthcare software—such as early software for hospital information systems, electronic health record systems, revenue cycle management, and more—is often disjointed. The lack of integration between different software makes it impossible for healthcare organizations to analyze data from various sources at scale.
On the other hand, today’s ecosystem of healthcare technologies enables seamless communication. When employees and patients are trained to utilize these technologies effectively, hospitals can automate data collection, make faster decisions, and deliver information instantly.
4. Personalized and precision medicine
Healthcare providers now have access to an abundance of molecular-genetic data that help them tailor treatment plans according to a biological distinction a patient might have.
James Tabery, professor of philosophy at the University of Utah, writes that precision medicine aims to help “healthcare organizations deliver the right treatment, to the right patient, at the right time.”
The accessibility of this medicine has a long way to go. Implementing more robust digital management processes and regulatory frameworks is crucial for streamlining healthcare data across different systems and devices. Adopting digital tools to safely collect, store, and interpret unstandardized data creates more opportunities for patients to take ownership of their data and work better with their healthcare providers.
5. Enhanced efficiency and productivity
Healthcare organizations use technology to streamline operational processes, eliminate manual administrative tasks, and fill digital literacy gaps.
Shield Healthcare used Whatfix’s digital adoption platform to boost the efficiency of insurance billing and medical supply sales processes. Shield Healthcare built an in-house tool, Core2, to replace its legacy software, which was prone to overcomplicating processes and taking too much time.
To ensure the proper integration of Core2 into employees’ existing workflows, Shield Healthcare used Whatfix to automate creating and distributing training material for their new platform in the form of contextual in-app guidance.
6. Patient engagement and empowerment
The emphasis on consumer-centric healthcare products gives patients more access to data and services wherever they are, driving consumer-centric healthcare. Companies like hims & hers were established to make consumers more engaged in their healthcare decisions through telemedicine.
By removing barriers introduced by scheduling conflicts, location, and limited transportation, patients are motivated to be proactive and curious about their health. Beyond conducting consultations online, patients can use the platform to get personalized treatment plans, fill out patient surveys, and order prescription medicine shipped directly to their door.
Related Resources
Technology Adoption Challenges Unique to Healthcare
The healthcare industry isn’t like most sectors out there. With government protocols and budgets setting the stage for most initiatives, there are distinctive bottlenecks in enabling digitization and process changes.
The industry has to balance innovation with a human-first approach that respects the sensitivity of patient care and its impacts on society. Let’s explore how digital adoption can be appropriately delivered to overcome these challenges without compromising the quality of services:
1. Addressing data security, privacy concerns, and compliance issues
As healthcare organizations turn to digital solutions for real-time information sharing and virtual communication, more patient data is uploaded to cloud-based servers.
Cybersecurity threats are rampant across all industries, and the sensitivity of patient information has pushed the industry to impose strict regulations that protect how healthcare organizations collect and manage data. Data breaches happen frequently in the healthcare space.
For example, hackers attacked the Oregon Health Plan vendor software in early August to get access to sensitive patient data like Social Security Numbers, addresses, and claim information.
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is an industry-grade standard for patient data protection in which companies must follow the following patient privacy rules:
- Privacy rule: Gives patients the right to dictate how their protected health information (PHI) is used and disclosed.
- Security rule: Oversees the specific technical and administrative safeguards to keep electronic PHI safe.
- Breach notification rule: Ensures that all healthcare organizations follow the proper steps when a data breach occurs.
2. Training and upskilling healthcare professionals for digital integration
The digitization of healthcare tools and services is still relatively new. It is seen as a distinct set of skills because it isn’t taught in traditional healthcare education and employee training programs. Digital adoption calls for organizations to address skill gaps preventing employees from using new technologies effectively.
Research published in 2021 discovered that healthcare employees in the UK typically fall behind in using data analytics and familiarizing themselves with emerging technologies. Suppose doctors, nurses, and administrative staff lack adequate EHR training and education to use electronic health records or telehealth platforms.
In that case, they are more at risk of compromising patient service and data integrity without them even knowing. The research recommended five action items for the UK National Health Service that the healthcare sectors across the globe can also draw motivation from:
- Focus on training senior managers to create a culture of urgency surrounding digital adoption.
- Invest in digital upskill training for front-line health practitioners to become more familiar with the tools at their disposal and work faster — an initiative that digital adoption platforms can support.
- Deliver employee training programs centered around data security.
- Implement communication protocols that help front-line and back-line staff use tools more efficiently for real-time collaboration.
- Teach healthcare staff how to analyze and act on data coming in from different digital sources.
3. Integrating digital solutions into existing healthcare workflows
The number of employees, volume of patient requests, cost of upgrades, and time taken to approve changes are some obstacles that discourage the healthcare industry from trying out new solutions and refining outdated workflows. Digital adoption is most successful when organizations prioritize system interoperability and self-serve training so employees don’t spend more time trying to make new processes work.
For example, some companies build in-house custom technology infrastructures to support new digital solutions while having enough flexibility to maintain or transform existing workflows.
Shield HealthCare developed its digital tool to streamline fragmented processes into a unified dashboard instead of patching together different systems that may not work as intended. The team then used Whatfix’s digital adoption platform to integrate employee training directly into the platform so employees can learn as they go instead of having to sit through long, static training courses.

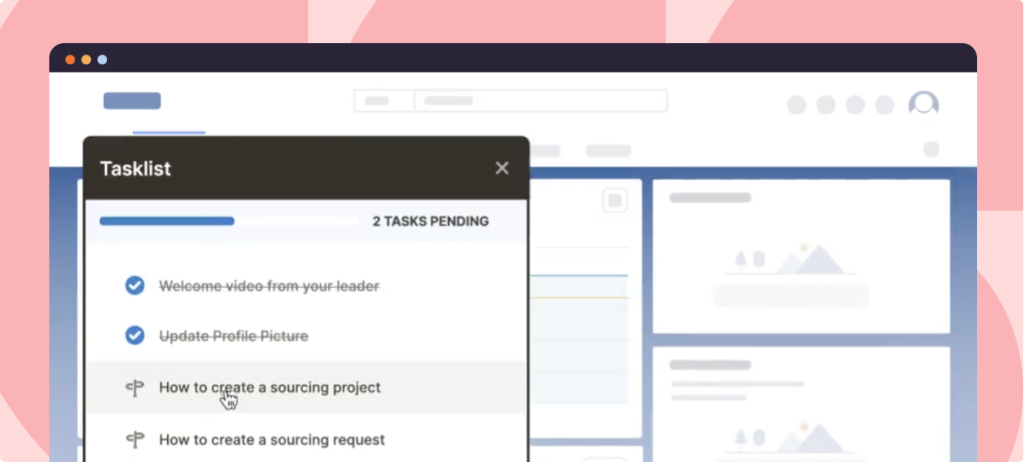
→ Guide users through complex apps with contextual, role-based in-app guidance.
→ Support users at the moment of need with AI-powered Self Help and embedded workflow assistance.
→ Analyze user engagement to identify friction points and optimize business processes.
Trends Driving Digital Adoption in Healthcare
In the realm of healthcare digitization, the shift toward simple digital processes opened up the doors to more mature and data-driven technologies.
As the industry saw an uptick in consumer interest in digital solutions, simple shifts — like mobile applications and online portals — grew into more interconnected healthcare experiences.
Here are a few examples of the digital trends and technologies driving the need for digital adoption today:
1. Telehealth and virtual care
Although many patients did have the option to use telehealth years before the pandemic, it was a technology that was underused and underfunded — hence giving patients and healthcare staff an inconvenient user experience that they would rather not use.
But in 2020, $250 billion of US healthcare spending was funneled toward virtual or virtually-enabled care as it was the most feasible way for patients to access healthcare services. Today, telehealth and virtual care have evolved beyond just being a backup solution during COVID-19.
Patients and healthcare organizations want to leverage this technology to:
- Improve access to frequent consultations for patients with chronic disease.
- Reduce the number of costly trips to the ER.
- Provide healthcare services to rural areas that are too far away from hospitals and clinics.
- Reduce wait times for meetings with specialists and experienced doctors.
2. Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
IoMT refers to medical devices with built-in internet connectivity that allows real-time data transfer to different healthcare apps and systems. These devices include wearables like fitness trackers, blood pressure monitors, biometric patches, and medical alert watches. Like telehealth platforms, IoMT devices help healthcare staff and caregivers make healthcare consultations and diagnoses possible even if patients aren’t at a physical appointment.
Accurate and instantaneous data sharing also allows healthcare providers to deliver more comprehensive care for at-risk patients with remote patient monitoring, proactive alerts, and preventative care.
3. Artificial intelligence (AI)
From business operations to manufacturing, banking, and hospitality, AI in healthcare is shifting how we communicate, execute tasks, and make decisions.
With its legacy systems and strict regulations, the healthcare industry is undoubtedly a major opportunity for AI to improve processes. AI is being used in healthcare today to transform patient engagement and services, improve the accuracy of treatments and diagnosis, and accelerate administrative activities.
Research published by the National Library of Medicine highlights a few specific categories of AI currently in use:
- Machine learning: To power precision medicine by analyzing patterns in patient data and predicting treatments that are most likely to succeed based on a patient’s specific attributes.
- Natural language processing: To analyze clinical notes, create and interpret medical documentation, and transcribe patient interactions.
- Robot process automation: To perform administrative workflows using a combination of rules involving digital systems, such as patient billing and updating medical records
4. Electronic health records (EHRs)
EHR software is the foundation of healthcare digitization. Without these electronic records, all your essential and historical healthcare information would be stored as physical copies that are easy to lose and destroy.
EHRs include all your medical conditions and treatments, test results, and even doctor notes. Healthcare organizations need to structure their software systems and processes around the ability to manage and share EHRs seamlessly.
Healthcare data is typically dispersed across disparate tools that facilitate a unique process – clinical solutions, patient scheduling, billing, etc. Software that manages EHRs must be equipped to handle data per the organization’s size, its volume of patients, and the system interoperability needed to bridge fragmented data sets together.
5. Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR)
VR and AR technologies are newer healthcare trends. Still, investment is climbing steadily, with researchers predicting a market worth close to $10 billion in the next four years.
VR and AR help healthcare organizations enhance their digital channels with an added layer of real-world context. For example, remote consultations and procedures can be conducted using simulations that help healthcare practitioners gather more information and improve precision. One use case of Microsoft’s Holo Lens 2 — a mixed reality device — is helping healthcare professionals receive holographic on-the-job guidance, allowing complex surgeries to take place even if subject matter experts aren’t around.
This level of precision simply cannot occur via telehealth platforms, especially for complex and high-risk procedures.
6. Cybersecurity and data privacy
The proliferation of data calls for the healthcare industry to be constantly on high alert. But thankfully, as our digital channels have matured, so have our privacy and security tools and strategies.
Hospitals and healthcare organizations can use technology to implement robust safeguards for patient data, including:
- Using firewalls and intrusion detector systems to monitor networks and alert personnel in the case of a breach.
- Enabling data encryption to ensure data is only readable to authorized parties.
- Implementing Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems that log incident data across systems so organizations can respond to risks in real-time.
- Utilizing protected email gateways that allow organizations to filter or flag emails that put employees at risk of phishing, spam, and social engineering attacks.
- Adopting security training platforms that provide all healthcare employees with comprehensive education and real-world simulations on how to respond to security threats.
7. Digital adoption platforms (DAPs)
With healthcare organizations introducing new software tools and workflows across their patient-facing and back-end operations, having the right technology training is essential to success.
A 2021 survey discovered that 37% of healthcare workers felt frustrated with new technologies. One in five survey respondents even went as far as saying that technology was making them unproductive. The dissatisfaction with new technologies stems from a need for familiarity in leveraging software correctly to streamline different processes.
When software users have to spend extra time figuring out what to do and fixing errors that come from doing the wrong things all the time, they end up getting less important work done.
Healthcare organizations use Whatfix’s DAP to embed clear, concise, and interactive training content directly into a software application. Not only does this help users learn by doing, but it also provides them with 24/7 self-help content that is accessible without any dependencies.
Success Stories in Healthcare Technology Adoption
What is the impact of successful technology integration in healthcare organizations? Here are two real-world examples of digital adoption at work:
1. Ouva transformed patient observation
Kaiser Permanente Roseville Medical Center uses the AI-powered patient observation system, Ouva, to engage patients, deliver educational content in a non-intrusive way, and measure patient engagement. T
The Ouva Sensory Experience is an LED screen that provides patients with a relaxing environment while feeding healthcare organizations real-time metrics that the platform can use to improve its actions and increase patient satisfaction.
2. AbleTo scaled and accelerated patient and provider onboarding
AbleTo is a virtual mental healthcare provider that rapidly grew during COVID-19. To meet the challenge of rapid growth, it needed a new way to onboard and support its 2,500+ providers to its patient portal and app.
With Whatfix, AbleTo met this demand by creating in-app guided onboarding and self-help contextual support for its doctors, therapists, and patients that guided them through onboarding and various app processes.
Before Whatfix, if a provider needed support with a particular AbleTo feature, they would pause their live training and consulting sessions, log into a different system, and send over a training aid. Although these training meetings were supposed to be dedicated to discussing care quality, up to 80% of these calls were focused on AbleTo system training and support.
AbleTo supported its patients and providers with more contextual onboarding and support, helping to:
- Increased patient compliance by increasing follow-up message delivery to patients by 50% with in-app smart tips.
- Reduced clinical provider churn with better, more contextual provider onboarding with in-app product tours and checklists.
- Scaled provider onboarding from 200 to 2,000.
- Increased productivity with 100% of clinical team calls now focused on enhancing quality of care, which previously were almost exclusively devoted to AbleTo system training and issues.
- Reduced support ticket volume from providers through the use of in-app smart tips, which were engaged with over 500,000 times.
3. Grifols boosted staff productivity
Grifols is a pharmaceutical company that develops plasma-derived medicines for hospitals and pharmacies. With more than 24,000 employees globally, their team needed a more efficient CRM for their sales and marketing team to better engage with customers.
Grifols opted to implement Salesforce but found it challenging to maximize the platform’s adoption, manage a high volume of support tickets, and deal with long training times.
With Whatfix’s digital adoption platform, Grifols delivered interactive in-app software onboarding and adoption tutorials that helped them save over 400 hours spent on training and support ticket resolution.
Digital Adoption Clicks Better With Whatfix
Hospitals, clinics, and pharmaceutical companies implement Whatfix’s digital adoption platforms to enable end-users (both internal doctors, nurses, and administration – as well as patients) to better use new technology and software. With Whatfix, enable patients with more user-friendly technology experiences, provide contextual in-app support and training to your healthcare workers, and continuously improve your tech experiences with user behavior analytics.
DAPs enable healthcare organizations to deliver interactive in-app Tours, Task Lists, Flows, Smart Tips, Field Validation, and more to enable and guide end-users through complex technology and enterprise software, like EHR systems, care management systems, or patient portals.
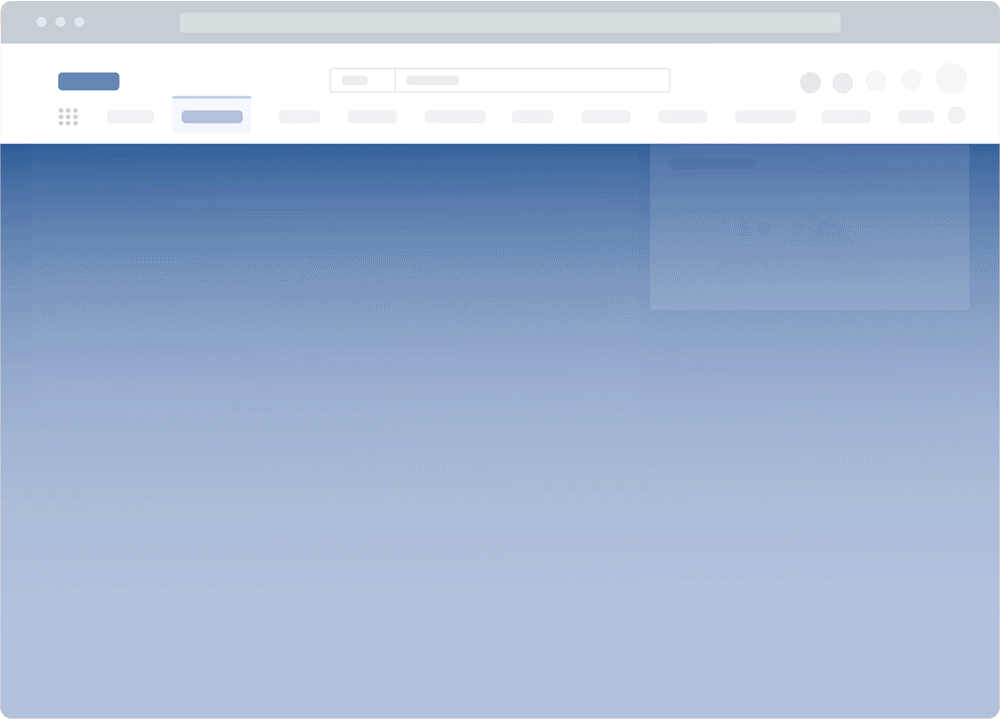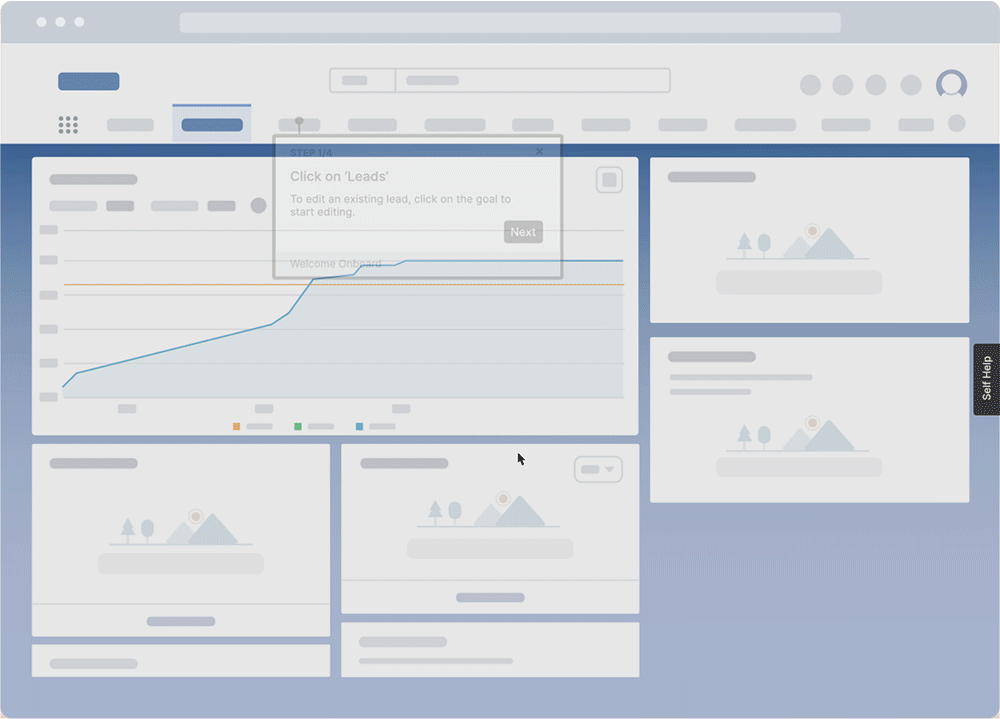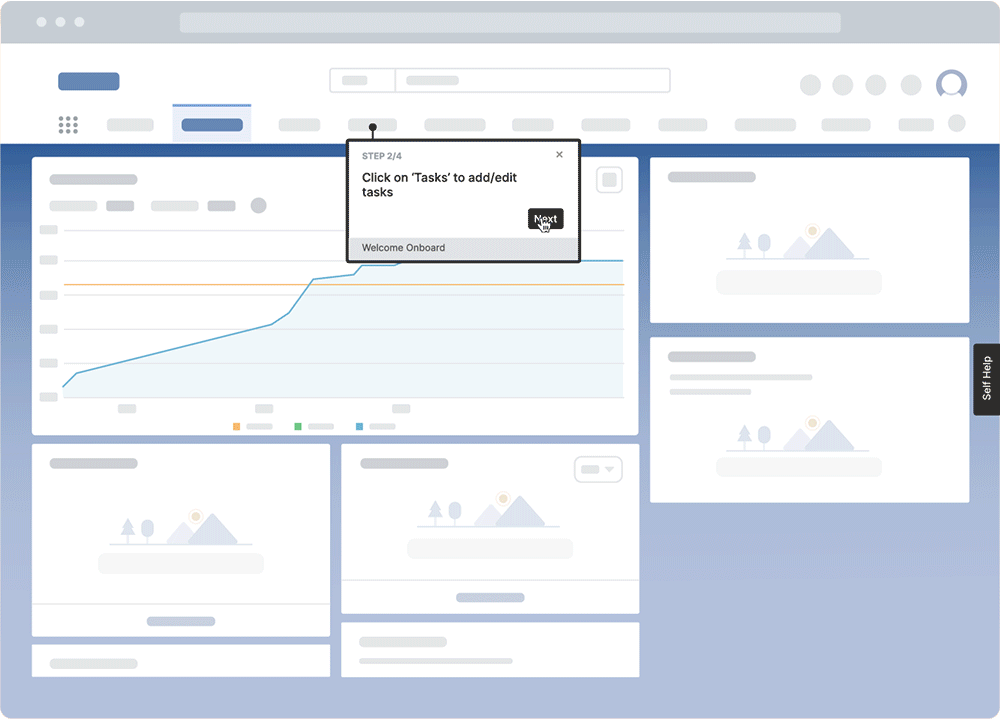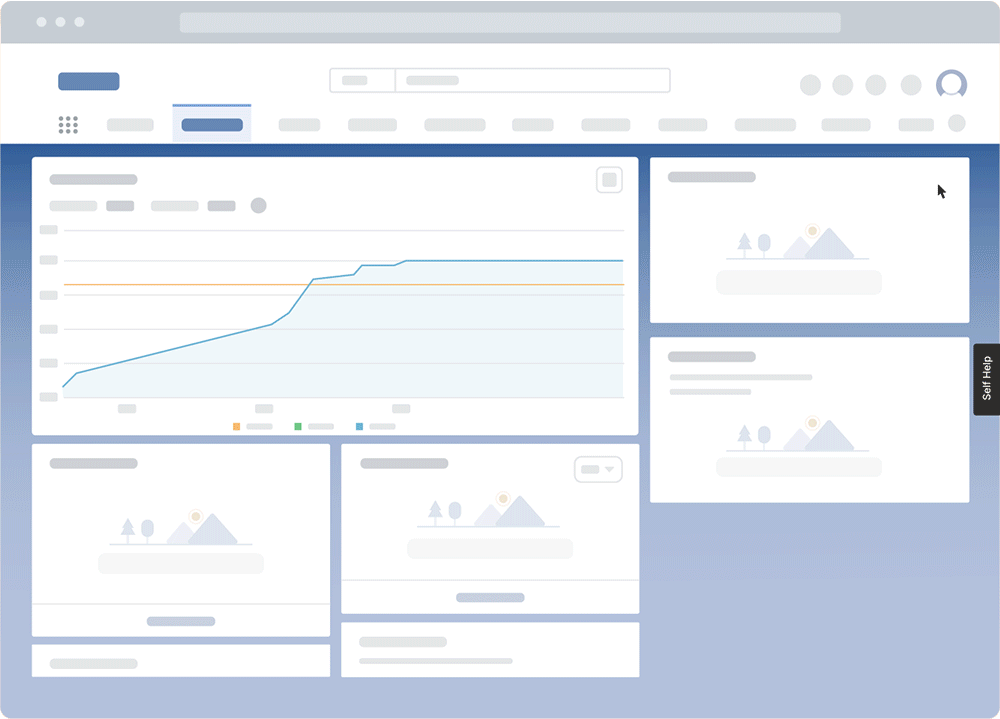
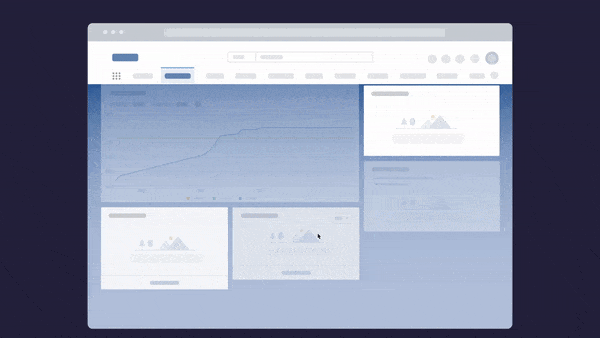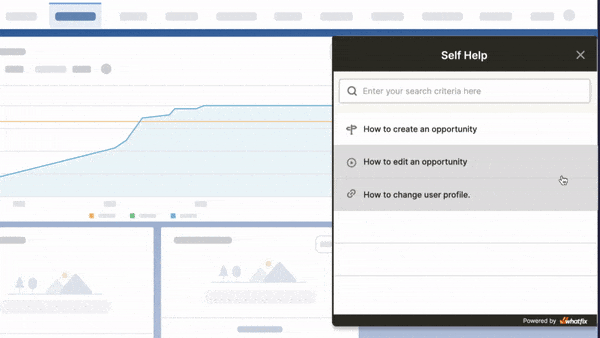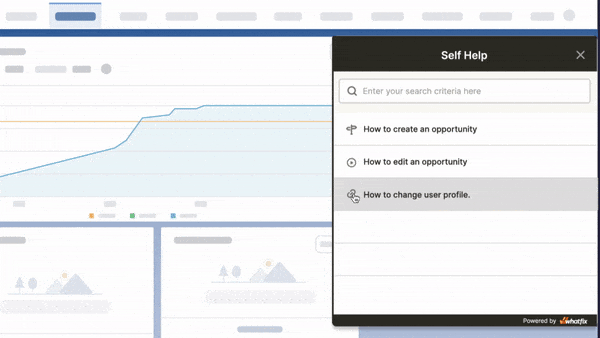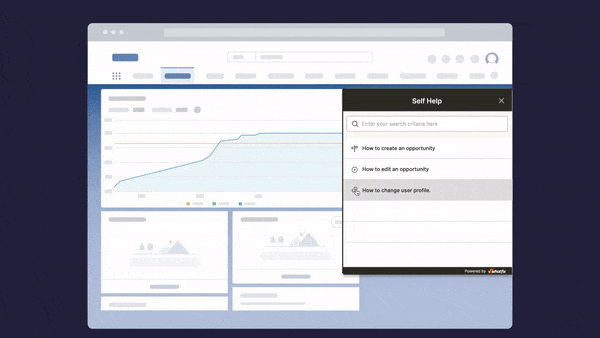
With Whatfix Self Help, provide moment-of-need support to your end-users with a resource center that overlays your technology UI. Self Help automatically crawls your entire end-user support resources, from SOPs, software tutorials, and training docs for internal applications, to FAQs, help guides, and knowledge bases for patients, providing a searchable wiki for end-users to find answers to any IT or software support-related question they encounter.
Its user behavior analytics empowers healthcare enterprises to track, monitor, and analyze end-user actions to:
- Build role-based user segments that enable you to create more contextual experiences.
- Optimize your user journeys and flows to drive efficiency and adoption.
- Identify areas of end-user friction and eliminate dropoff areas.
- Understand software license usage and overall end-user adoption rates.
- Track any end-user action with custom event tracking.
To learn more about Whatfix, schedule a free demo with us today!







