
6 Challenges for Enterprise Application Owners
- Published:
- Updated: November 1, 2024

Enterprise applications are mission-critical enterprise software that enables core business operations. Every large organization relies on software to operate, with examples ranging from software that spans verticals, like CRM and ERP systems, to vertical software like claims management software for insurance providers and EHR systems for healthcare providers.
While these applications are mission critical to daily operations, the success of these powerful platforms depends on employees correctly using them—from core features and daily tasks to advanced features and infrequently done workflows.
Application owners are responsible for ensuring employees are enabled with the well-designed workflows, end-user training, and IT user support that drive adoption and allow employees to use enterprise software to maximize their efficiency and productivity properly – ultimately driving business outcomes.
In this article, we’ll cover the role of application owners. You’ll learn about the challenges faced by enterprise applications owners, and how they can overcome them.
What Is an Application Owner?
An application owner is a stakeholder responsible for the management and success of a specific enterprise application, like an HCM, CRM, or ERP. They often serve as the point of contact and subject matter experts on that application.
They ensure proper digital adoption and monitor software usage to identify friction points. This way, users can maximize the value of the application. Business application owners may also help with integrating new features and updates.
Mission-critical enterprise software requires application owners who can manage the investment and technology infrastructure from choosing the right solution for their company’s needs, onboarding new users, enabling employees with support in the flow of work, providing IT end-user training, managing software license usage, and continuously improving end-user experiences.
Application owners enable organizations to drive business outcomes from technology investments by supporting enterprise software and employees across an application’s lifecycle.
Types of Application Owners
There are four types of application owner roles often found in large organizations, including:
- Application Monitor: This owner focuses primarily on tracking application performance and usage patterns. They use analytics to identify areas for improvement and ensure the application meets performance benchmarks. This includes end-user monitoring for performance-related application issues, identify areas of user friction in workflows, and overall end-user adoption
- Application Coordinator: Coordinators connect end-users and IT teams to provide provide support and communication. This can include managing change requests, providing IT help desk support, and keeping application workflows aligned with stakeholder needs.
- Application Administrator: Administrators handle the application’s technical aspects. They manage user access and configure settings. They often work closely with IT to resolve technical issues and implement updates.
- Application Subject Matter Expert: These owners are knowledgeable of the application’s capabilities and the business processes it supports. They often lead IT training initiatives and provide guidance on application use best practices.
Responsibilities of Application Owners
Application owners are responsible for the success of one or more enterprise software. Here are the key areas of ownership that application owners are responsible for:
- Lifecycle Management: Managing the entire application lifecycle, ensuring it evolves from planning and deployment to implementation, to maintenance, and eventually decommissioning it. Also includes aligning applications with business needs and technological advancements.
- Performance Monitoring: Monitoring application performance through key metrics, addressing issues proactively to maintain optimal functionality and user satisfaction.
- Security and Compliance: Application owners ensure that software and apps comply with security standards and regulatory requirements, implementing measures to protect data and conducting regular audits.
- Change Management: Application owners coordinate and manage application change projects, such as product updates, new feature integration, and process improvements, while ensuring minimal disruption to business operations.
- Business Process Optimization: Application owners continuously analyze and improve business processes by identifying areas of user friction, process inefficiencies, and implementing improvements.
- Driving End-User Adoption: They are responsible for promoting end-user adoption through contextual user onboarding, training, support, and resources. They ensure users understand and effectively utilize the application’s features, ultimately driving technology ROI.
- Stakeholder Communication: Application owners maintain regular communication with stakeholders, providing updates on performance, changes, and issues to ensure transparency and alignment with business objectives.
- Budget and Resource Allocation: They manage the application budget and IT resources for the application.
- SaaS Vendor Management: Application owners manage relationships with external software vendors, manage contracts and renewals, meet regularly with CSMs, and collaborate with the vendor to ensure their applications meets their business needs.
6 Challenges Facing Enterprise Application Owners
Here are six challenges enterprise application owners challenges will face in their role, with strategies to overcome them:
1. Providing adequate IT onboarding and training to end-users
A major challenge for application owners is enabling all end-users with IT onboarding and training for new applications. This involves creating comprehensive IT training materials and providing on-demand user support. The application owner must know how to cater to different learning styles and adjust to new features.
Whatfix Mirror provides organizations with a no-code tool to create replicant IT sandbox environments of your new system. This provides end-users with a hands-on interactive training experience where they can engage with your application and its workflows without impacting your real-life application and its data.
With Whatfix DAP, organizations can create in-app training experiences that guide users through their tasks and workflows. This provides a way for employees to learn in the flow of work, with on-demand support that enables them within the application itself.
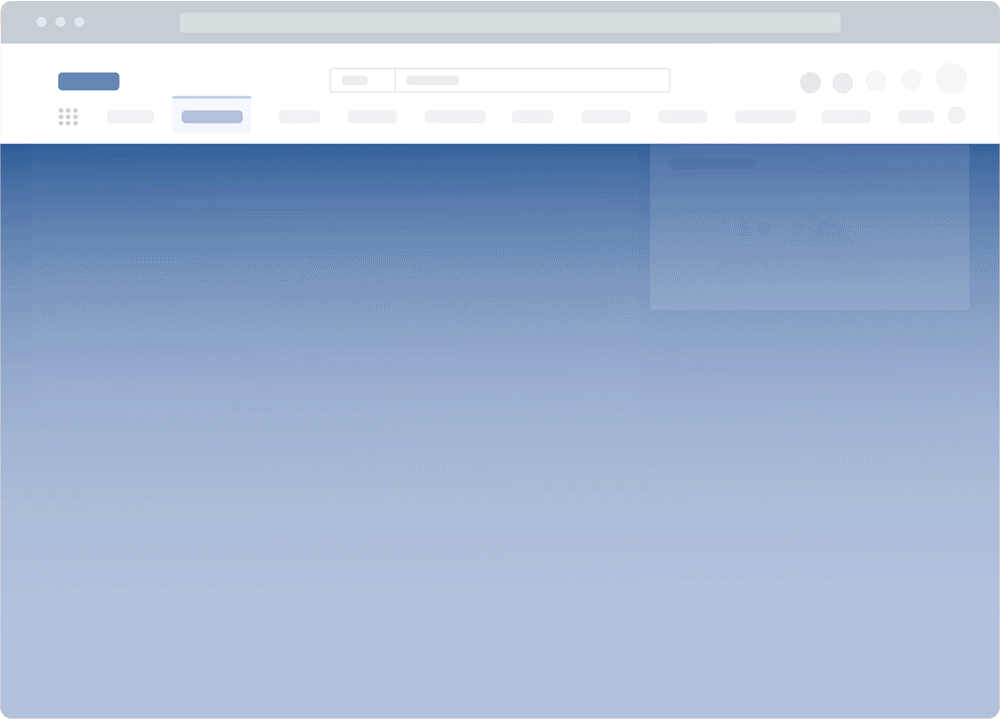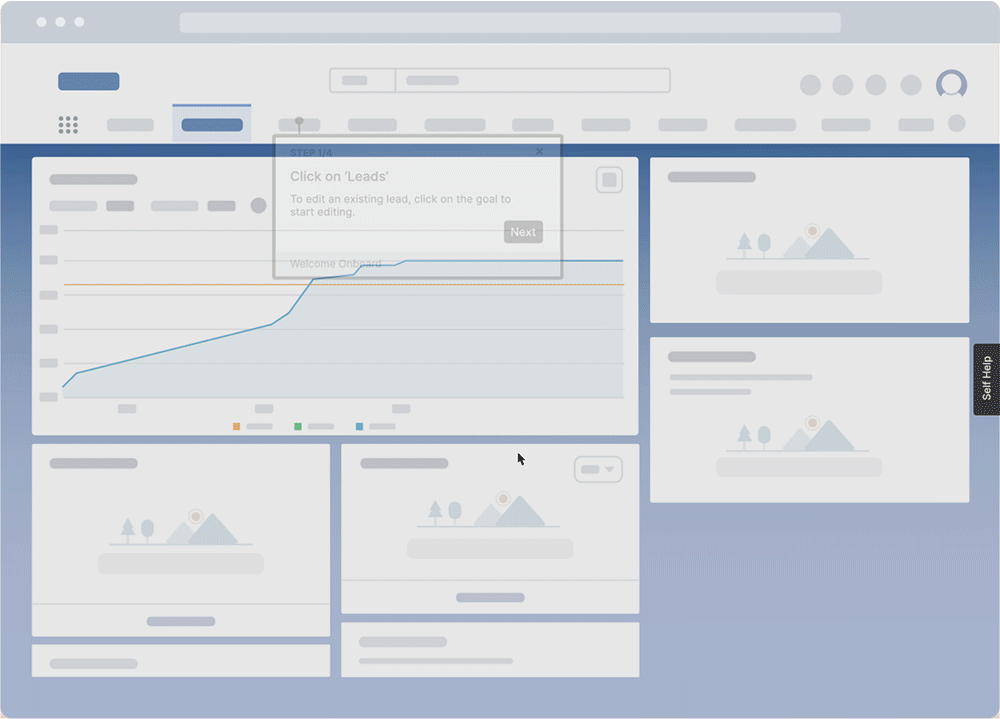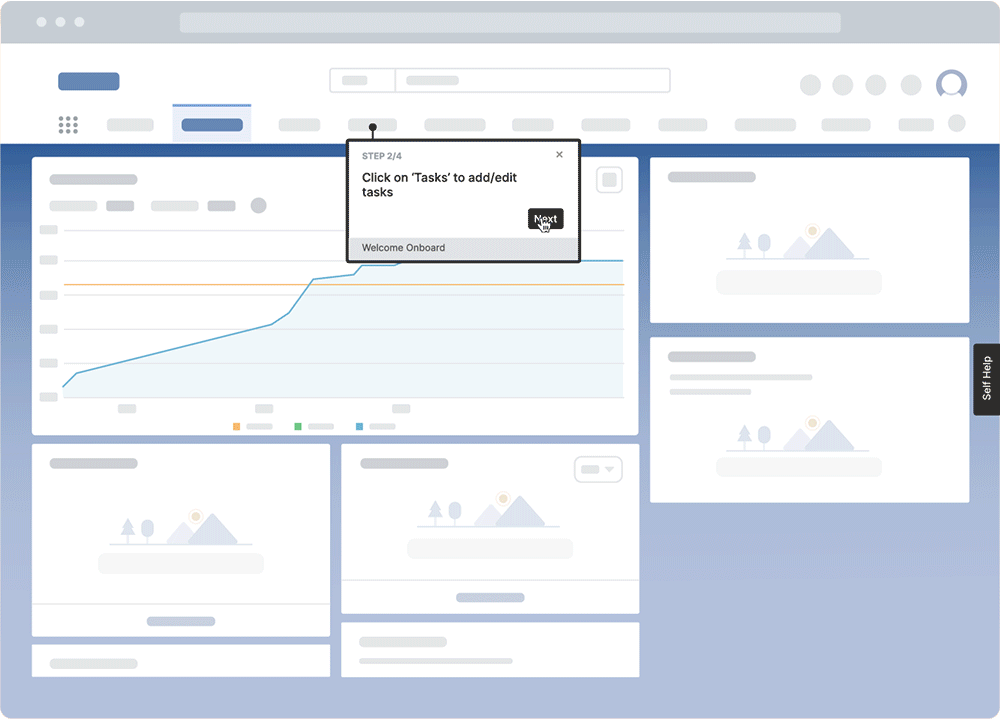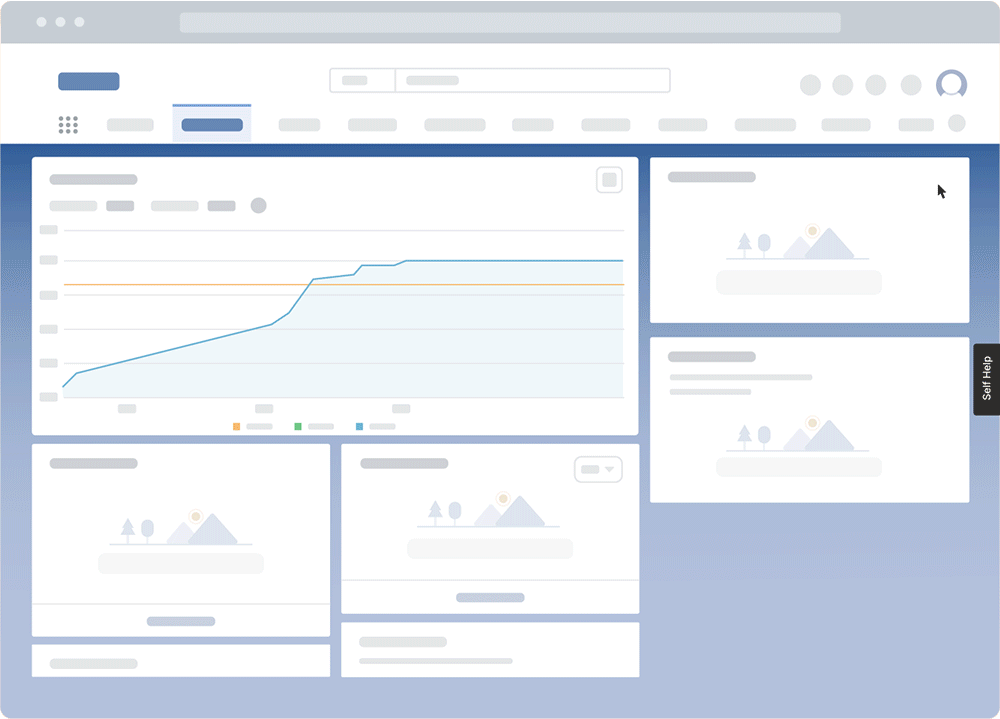
2. Managing constant change
Technology and software move fast. Business application owners need to be able to plan for and adjust to elements of that. They accomplish this by doing things like:
- Keeping applications updated
- Revising training materials and documentation when processes change
- Communicating changes effectively to end-users
- Overcoming resistance to change.
- Overcoming change fatigue with users.
Regarding this level of change, it’s all about knowing what to prioritize. For example, it’s important to inform users about an update to the UI. They need to know where to find the features they regularly use. Process changes may happen more slowly as you find new opportunities for improvement.
3. Designing optimized and efficient workflows
Creating streamlined processes within the application is important. This is what will help the organization maximize the value of the investment.
Before implementation, application owners design business processes that meet an organization’s contextual needs and drive critical business outcomes. They should also use analytics to understand application usage patterns and identify friction points post-launch to improve user experiences continuously.
The challenge is understanding users’ needs and how to create processes that fit any unique requirements the business may have. When considering both factors, application owners can use that information to hone in on solutions that work for everyone.
4. Monitoring and improving user adoption
High user adoption is necessary to unlock the full potential of enterprise applications. Application owners must track usage metrics and identify barriers to user adoption.
This way, they can implement strategies to encourage consistent use of the software. This often involves a mix of technical solutions. It requires user education and change management techniques that get employees behind the “why.” When they understand the goal of the change, they may be more likely to support it.
With Whatfix, track and analyze end-user behavior with User Actions. This empowers IT teams to identify areas of end-user friction, map optimal user flows, build flows for different user cohorts, and more. Use this data to create new in-app guidance and end-user support content and continuously optimize and test new workflows and features to create more efficient, user-friendly technology experiences that drive value.
5. Security and compliance concerns
Data protection and regulatory compliance are non-negotiable. Especially when shadow IT makes up 35% of the typical business software portfolio. That creates a lot of risk for organizations. It’s one reason why 82% of IT and SAM professionals say reducing security risks is a top business priority for 2024.
To be aligned on this priority, application owners must understand security. This includes managing user access rights and keeping the application compliant with relevant industry standards.
6. Keeping data clean
The total amount of data created, captured, copied, and consumed globally was forecast to reach 64.2 zettabytes in 2020. Over the five years that follow, up to 2025, global data creation is projected to grow to more than 180 zettabytes.
More data creates more room for error. But the value of any enterprise application is only as good as its data. Application owners need to maintain the quality of the data to make all processes effective.
This often means:
- Implementing data validation rules to ensure information is entered correctly
- Regularly auditing and cleaning existing data
- Training users on data accuracy and standardization best practices
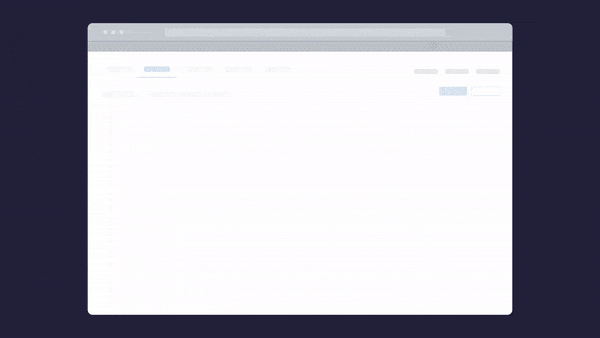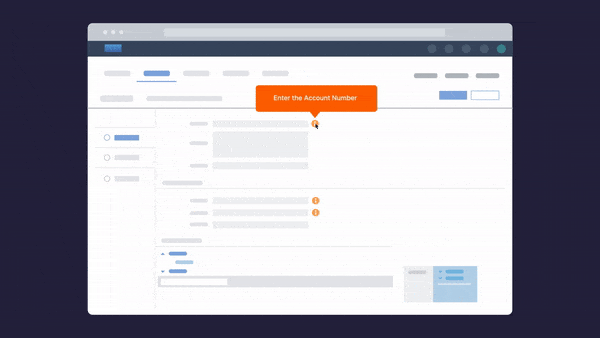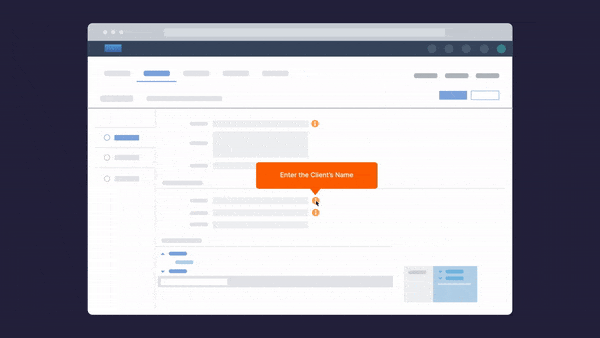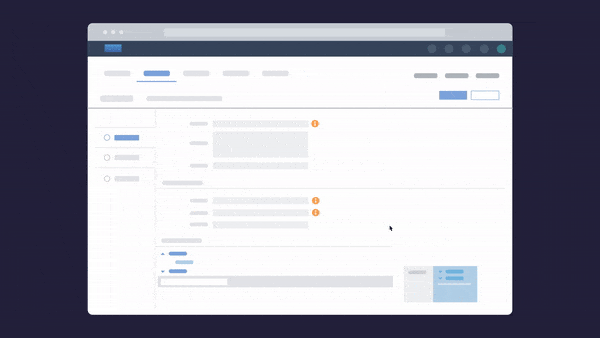
There are also solutions you can put in place to support clean data. For example, you can use Whatfix DAP’s Validation and Smart Tips widgets to verify the end user’s inputs on your application. Whatfix enables you to set a valid input and evaluate your end user’s response in a particular field of your application.
If your end-user input does not match the set data, Whatfix displays an error message. Validation and Smart Tips ensure that the end user input on forms can be validated. This helps users avoid errors before form submission.
By understanding and addressing these challenges, application owners can enhance the value and effectiveness of enterprise applications. They help bridge the gap between software capabilities and real-world business impact, helping organizations get more value from their digital transformation investments.
Implementing a new technology is costly, resource-intensive, and has lengthy implementation and migration cycles. To complicate matters, all digitalization projects are different and come with risks of losing data, hurting productivity, and impacting business outcomes.
Accelerate your software implementation by enabling your technology end-users (internal employees, customers, partners, suppliers, etc.) with contextual in-app guidance and real-time support with a digital adoption platform (DAP) like Whatfix.
Whatfix DAP provides IT teams and application owners with a no-code editor to create in-app assistance that provides contextual guidance for end-users on complex processes and digital experiences, enabling them to utilize digital platforms correctly and drive business outcomes – all while learning in the flow of work that doesn’t sacrifice output for training.
This reduces time-to-proficiency for new end-users and achieves new levels of productivity and proficiency through better software adoption post-implementation. It also provides customers with self-service, personalized, and guided user experiences.
Whatfix empowers organizations to drive technology adoption and achieve application-powered business outcomes. With Whatfix, application owners and ITSM teams can
- Create in-app Tours, Flows, and Task Lists that guide employees and customers step-by-step through digital processes and applications, from end-user onboarding to reinforcement training on complex, multi-step digital processes.
- Enable end-users with Self Help, providing a searchable help wiki that connects to all your process documentation, requirements, FAQs, help articles, and more – that overlays on your digital UI.
- Notify end-users of application process updates, compliance changes, company announcements, and more with Pop-Ups and Beacons.
- Provide contextual Smart Tips that enable end-users with timely information that nudges users to take the correct in-app action.
- Use Field Validation to ensure data is entered in full, in the correct format.
- Collect end-user feedback such as client NPS, staff training and onboarding feedback, and bug identification with In-App Surveys.
- Analyze end-user behavior with User Actions and Enterprise Insights by tracking custom in-app events to optimize user journeys, segment users into cohorts, identify areas of friction, track software license usage, and more.
With Whatfix, you can enable your end-users with contextual, guided, and self-service experiences to help them drive value from digital investments and maximize their productivity. It also actively works to identify areas of end-user friction to continuously optimize user experiences and build user-friendly digital solutions.
Ready to learn more? Request a demo to see how software clicks better with Whatfix now!

Thank you for subscribing!


