

Disha Gupta


Human resources is a people-oriented function. But the HR contribution isn’t just limited to extending offer letters and onboarding new hires. HR professionals are responsible for developing and sustaining a people and workforce management strategy.
In today’s data-driven world, HR leaders are increasingly turning to HR analytics to make informed decisions and drive strategic initiatives. When used strategically, workforce analytics transforms the way HR operates, providing them insights and allowing them to contribute to the organization’s bottom line in an active and meaningful way.
This article explores the significance of HR analytics, its key benefits, and how organizations can leverage it to unlock the potential of their workforce.
HR analytics, also known as people analytics, refers to the practice of using data, statistical analysis, and data-driven insights to inform and optimize HR strategies, policies, and decision-making.
HR analytics involves collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data related to various HR functions, including recruitment, talent management, employee engagement, performance management, learning and development, onboardinging, training, and workforce planning. Organizations leverage HR analytics to gain deeper insights into their workforce, identify people-related trends, make data-driven decisions to improve employee productivity, and align HR initiatives with organizational goals.
There are four main types of HR analytics; descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive. Let’s explain each category of HR analytics further
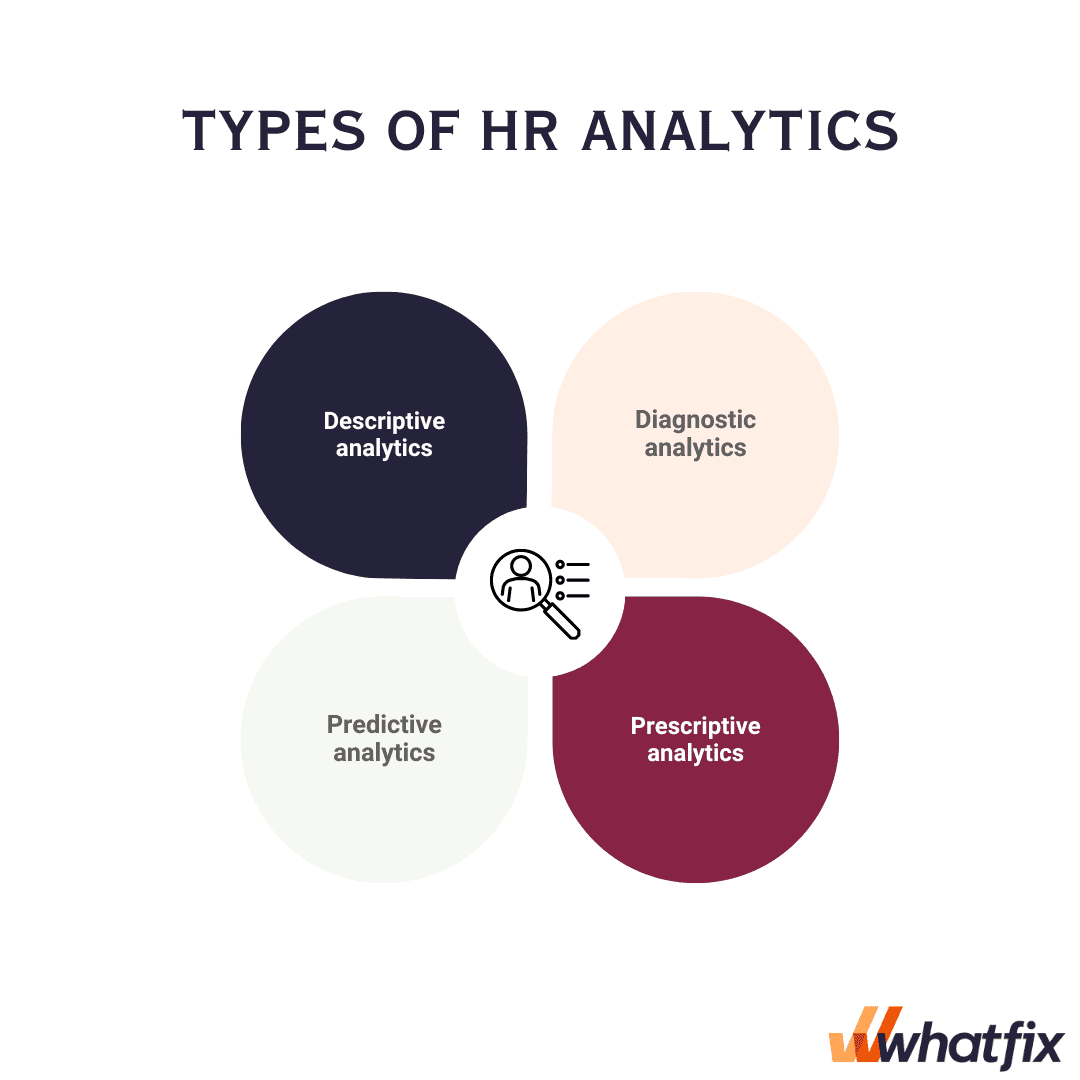
Descriptive analytics involves analyzing historical HR data to understand past trends and patterns. It provides a retrospective view of workforce metrics, such as headcount, turnover rates, diversity ratios, and employee demographics. Descriptive analytics helps organizations identify areas of improvement and establish benchmarks for future analysis.
Diagnostic analytics goes beyond descriptive analytics to uncover the reasons behind trends or issues within the workforce. Diagnostic analytics aims to answer “why” questions by exploring relationships between different HR metrics and identifying the drivers or predictors of specific outcomes. By conducting diagnostic analytics, HR professionals can gain deeper insights into the factors influencing employee engagement, turnover, performance, or other HR-related phenomena. This understanding allows organizations to address root causes, develop targeted interventions, and make informed decisions to improve HR practices and outcomes.
Predictive analytics uses statistical models and algorithms to forecast future outcomes and trends based on historical data. It involves analyzing factors that impact workforce behavior and performance to predict attrition risks, identify high-potential employees, and anticipate talent needs. Predictive analytics helps organizations proactively address challenges and make informed decisions.
Prescriptive analytics takes predictive analytics a step further by recommending specific actions or interventions to optimize outcomes. It uses advanced algorithms and modeling techniques to simulate different scenarios and predict the impact of different HR strategies. Prescriptive analytics assists in making evidence-based decisions by providing insights into the most effective courses of action.
Here are some examples of how to incorporate HR analytics in your organization.
An employee leaving to join another organization they feel is a better fit for them is not an ideal scenario for an employer – and turns out to be costly in terms of lost time and profit too. To prevent turnover from becoming an ongoing problem, organizations need to understand the overarching reason or trends for the turnover.
HR analytics provides relevant data and information collected from employee engagement levels, employee satisfaction index, exit interviews, etc., for HR leaders to study turnover rates and make better decisions to improve employee retention in the future.
HR analytics help prevent employee turnover by:
HR teams are constantly looking for candidates with the right skills and attributes that match the organization’s performance requirements and latest industry trends. However, sifting through stacks of resumes daily, shortlisting, and making recruitment decisions on fundamental information is an overwhelming job that might result in overlooking potential candidates.
Talent acquisition is a key area in which HR analytics can provide valuable insights, helping to streamline the recruitment process, improve the quality of hires, and reduce hiring costs.
HR analytics helps optimize the recruitment and selection process by analyzing data related to sourcing channels, candidate profiles, and hiring outcomes. It identifies the most effective recruitment strategies, improves candidate screening, and enhances the quality of hires, resulting in better talent acquisition outcomes.
HR analytics help streamline the employee recruitment process by:
As HR professionals confront new challenges in finding and retaining the right employees, workforce planning has become a key focus point. Strategic workforce planning starts with gaining insights on organization imperatives and talent implications for the company, followed by a measurement of talent gap risks, talent demand, and talent supply.
HR analytics helps with workforce planning by:
To stay on top of growth, companies need to improve employee performance and turn their workforce into valuable assets and high-performing team members. HR analytics provides HR teams with insights into employee engagement and overall performance to discover ways to improve their impact.
HR analytics help boost employee performance by:
For the area of employee engagement, HR analytics enables human resources professionals with the data to understand what motivates employees, how engaged they are, and can provide data that can help to increase satisfaction and productivity.
By analyzing employee feedback, sentiment analysis, and other factors influencing engagement, HR analytics identifies key employee engagement drivers and helps develop strategies to improve it.
HR analytics enable organizations to implement effective training programs by collecting big data and learning from historical patterns.
Training analytics determine which employees need the most help by looking at turnover rates for each role, exit interviews that consistently mention a lack of training, and key performance indicators (KPIs) that aren’t being met in a particular employee group. These insights highlight a significant skill gap and enable HR teams to create a training plan accordingly.
HR analytics also helps identify if employees are making full use of the knowledge provided during training programs by measuring training effectiveness. Training effectiveness can be measured via post-training evaluations or implementing digital adoption platforms that collect real-time data on how employees are engaging with the learning flows.
All these insights into learning and training programs empower HR teams to understand the training results better, readjust plans, and correct courses throughout the learning process.
To better understand what type of data and insights your team can extract from an HR analytics strategy, let’s explore different types of data points and survey analysis that can be done with HR analytics software or an HR analytics framework:
Here are the steps to help you get started with HR analytics in your organization.
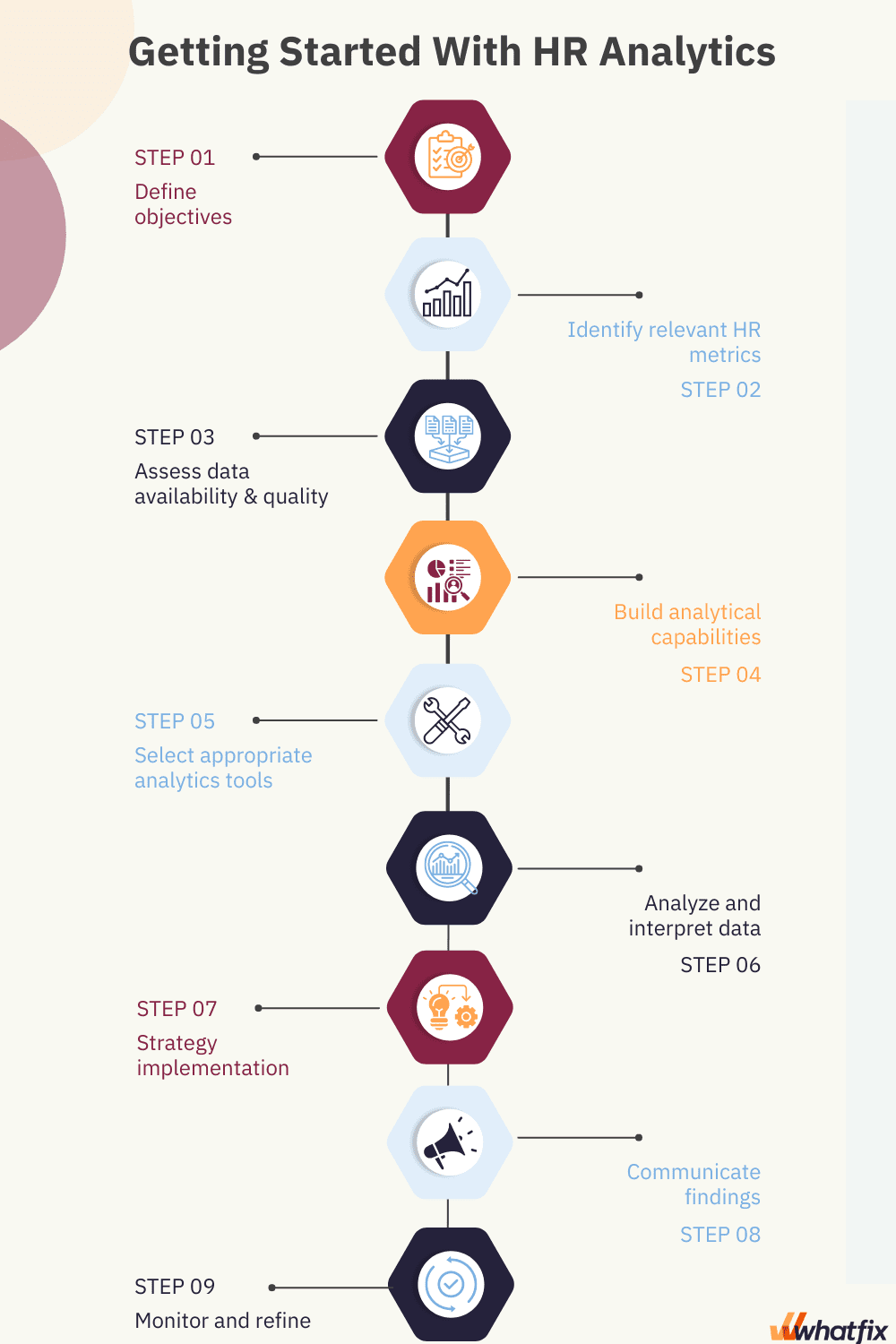
Clarify the specific HR challenges or areas of focus where analytics can provide insights and solutions. Determine the goals you want to achieve through HR analytics, such as improving recruitment, optimizing workforce planning, or enhancing employee engagement. This way, you’ll be able to gain actionable takeaways and measure the effectiveness of your actions.
Determine the KPIs and metrics that align with your HR objectives. This could include metrics related to employee turnover, time-to-fill vacancies, training effectiveness, or diversity and inclusion.
Collecting and tracking high-quality data is a crucial component of HR analytics as it provides insights into a lot of information and knowledge for the HR teams.
The kind of data collected for HR analytics includes:
The data can be gathered from HR systems, learning & development systems, cloud-based systems, or data scientists can be hired to sort and organize the data. A data scientist is best suited to assess the viability of an analytics solution, ensure the robustness of the statistical modeling and predictions, monitor the quality and accuracy of the data, and help HR professionals implement the data to their benefit.
Develop the necessary skills and expertise within your HR team to conduct HR analytics. This may involve upskilling team members in data analysis, statistical techniques, and data visualization tools. Alternatively, consider partnering with experts or leveraging external resources for support.
Identify and implement suitable HR analytics tools and technologies. This could include data visualization software, statistical analysis tools, or specialized HR analytics platforms.
Here are some key features to look for in your HR analytics solution:
With HR analytics, informed decisions are made based on data rather than assumptions, which is why it’s important to understand the significance of these insights and take action accordingly.
The collected data could be used to build various forms of reports, graphs, and charts. Here are a few formats that can be used:
With the data at hand, start developing and implementing a strategy for addressing the outlined problem. The HR department must work with the management team to discuss the findings and devise a solution.
For example, if a lack of employee training and development opportunities is identified as contributing to employee turnover, then the HR department needs to take immediate action to invest in development and upskilling training programs for the workforce.
Present the insights and recommendations derived from the HR analytics to relevant stakeholders, such as HR leadership, managers, or executives. Clearly communicate the implications and potential benefits of the analytics findings and collaborate on implementing actionable strategies.
Continuously monitor and assess the impact of your HR analytics initiatives. Collect feedback, evaluate the outcomes, and refine your analytics approach as needed. This iterative process helps improve the effectiveness and value of HR analytics within your organization.
While there are many HR analytics solutions on the market, here are five we recommend exploring:

Whatfix is a digital adoption platform and user behavior analytics tool that enables organizations to drive software adoption with in-app guidance, self-help support, and adoption analytics.
Whatfix enables HR, L&D, and IT teams to understand how employees are engaging and adopting digital processes and software with capabilities such as custom event tracking, user journey flows, employee cohorts, and more.
Whatfix also collects data on how employees are engaging with your in-app guidance and employee help content, allowing you to understand gaps in your training content and friction points in your digital employee experience.


intelliHR is a performance analysis human capital management (HCM) tool that helps organizations create useful reports on employee performance and satisfaction metrics. The software offers analytics features for HR teams to align their efforts with the organization’s strategic business objectives.
The software offers a variety of data collection solutions such as employee satisfaction surveys, employee net promoter score, performance and productivity data through self-review, peer review, and task completion statistics.

Qualtrics HR analytics software is a user-friendly simple-to-use tool suited for medium and large enterprises. It sorts the collected HR metrics in graphs and reports that are easy to digest. The tool provides a survey feature for collecting self-reported workforce data around culture and performance.
Qualtrics leverages machine learning and native language processing to interpret data from open text responses, which are much more flexible and informative than numerical ratings or multiple-choice questions.

ADP Workforce Now is an all-in-one cloud-based HR suite. The software features HR management, payroll, benefits, talent management, labor management, and learning and analytics capabilities.
ADP Workforce Now helps manage the workforce and make data-driven decisions informed by insights from the richest and most robust workforce database in the business. The software also seamlessly integrates with leading third-party solutions.

Hibob HR platform simplifies people management and helps drive engagement, culture, and productivity. It is configurable for the way you operate – onsite, remote, or hybrid.
The tool empowers HR managers to increase performance and retention, and streamline core HR processes such as onboarding, performance management, and compensation management using automated workflows to increase efficiency.
Here are some HR trends that your team can focus on moving forward.
Organizations used an average of 3.8 AI capabilities in 2022, that is double the 1.9 used in 2018.
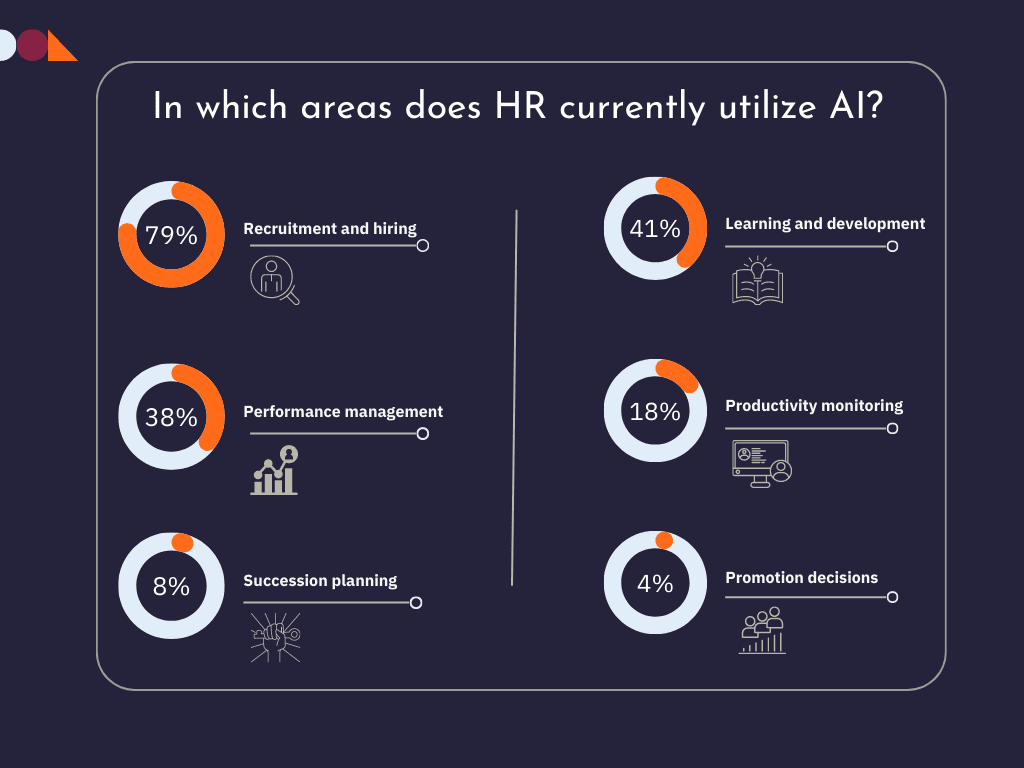
AI and machine learning technologies are poised to play a significant role in HR analytics. These technologies can automate data analysis, identify patterns, and make predictive recommendations, enabling more accurate and proactive decision-making.
For example, AI and ML can be used to predict employee turnover, identify high-potential candidates, and forecast future workforce needs.
HR analytics will increasingly focus on analyzing employee sentiment and feedback to understand the employee experience. This includes leveraging natural language processing (NLP) that enables machines to understand, interpret and generate human language. NLP can be used to analyze employee feedback from various sources, such as surveys, performance reviews, and social media, to identify insights and trends that can help organizations improve their HR practices.
The focus will shift from reactive to predictive analytics, where organizations can anticipate future workforce needs, identify high-potential employees, and forecast talent gaps. Predictive analytics will enable HR professionals to take proactive measures to address talent requirements and optimize workforce planning.
For example, predictive analytics can be used to identify which employees are at risk of leaving the company, or to identify which job candidates are most likely to succeed in a given role.
Unlock the full potential of your workforce with better support training and support content, embedded directly in your enterprise applications with Whatfix digital adoption platform.
Witness a 1.25x increase in employee productivity, as Whatfix enables you to:
Schedule a free demo with us to learn more about how Whatfix DAP supports HR teams!
Thank you for subscribing!