Processes are the foundation of consistency, quality, and operational efficiency. They help eliminate errors, ensure tasks are completed correctly, and drive better team outcomes. However, creating workflows and documenting procedures is only part of the solution. Ensuring those business processes are consistently followed, optimized, and aligned with business goals requires something more, like a defined, well-mapped approach to process governance.
A robust process governance strategy enables organizations to manage, monitor, and continuously improve their processes at scale.
In this article, we will explore process governance, why it is critical for enterprises, and how to build a governance model that drives sustainable success.
What Is Process Governance?
Process governance is the framework that oversees the creation, implementation, and management of business processes. It ensures that processes are carried out efficiently, consistently, and in alignment with organizational goals and regulatory requirements. A strong process governance model defines the rules, standards, roles, and strategies needed to implement new processes, monitor their performance, and drive continuous improvement.
For example, let’s say you have a new process to introduce to your organization. You document the steps your team should follow and the process according to your company guidelines. But the tricky part is: how do you introduce this new process to your team and ensure they follow it?
Process governance would tell you the rules, standards, and strategies for implementing a new process initiative. It also ensures compliance, assigns roles and responsibilities to team members, and helps overall process performance monitoring and reporting.
Process Governance vs. Process Management
Process governance and business process management are closely related but serve different organizational purposes. Both ensure that the right processes are created, implemented, and followed. However, their scope and focus are distinct.
- Process management is typically a subdivision of process governance. It ensures that teams consistently follow established processes, usually managed by supervisors or team leads.
- Process governance, however, takes a broader view, ensuring that processes align with overall business goals, are implemented correctly across teams, and meet regulatory and operational standards.
Both process governance and process management are essential components of a successful process strategy. Together, they foster a structured environment where processes drive consistency, efficiency, and business growth.
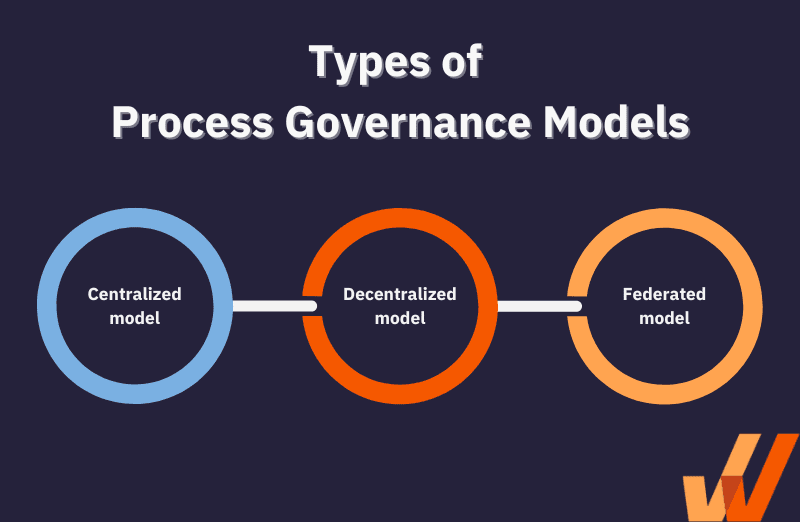
Process Governance Models
There is no one-size-fits-all approach to process governance. Here are three standard models organizations can adopt to provide process guardrails that ensure consistency and attention to procedural detail:
- Centralized Model: A single leader or team controls process planning, implementation, and oversight. This top-down approach ensures consistency and transparent decision-making but may limit input from frontline teams.
- Decentralized Model: Decision-making is distributed across teams, encouraging collaboration and ownership. While this model fosters engagement, it can lead to confusion without clear structures and accountability.
- Federated Model: This model combines centralized oversight with decentralized decision-making. Teams have autonomy within defined boundaries, while leadership maintains overall governance standards. This model balances flexibility with consistency.
Why Process Governance Is Critical for Enterprises
Here’s why a strong process governance framework is essential for organizations.
- Aligning process strategy with business objectives: Ensures that every process directly supports the organization’s strategic goals and priorities.
- Enabling compliance and risk mitigation: Maintains adherence to regulatory requirements and minimizes operational risks across departments.
- Reducing time-to-completion: Streamlines workflows and eliminates bottlenecks, enabling teams to work more efficiently.
- Supporting digital transformation and automation: Provides the structure needed to implement new technologies and automated systems successfully.
- Enhancing accountability and transparency: Clarifies ownership, improves process visibility, and fosters a culture of responsibility.
Related Resources
Key Components of a Process Governance Strategy
A successful process governance strategy relies on a few critical components that help ensure consistency, accountability, and continuous improvement across the organization:
- Roles and responsibilities: Clearly define the roles of every team member involved in process governance. Individuals must understand their responsibilities, promoting ownership, smoother collaboration, and collective success.
- Policies and procedures: Establish detailed standard operating procedures (SOPs) and process governance policies. These guidelines serve as a roadmap to maintain consistency, streamline workflows, and address challenges proactively. Regular reviews ensure they stay aligned with business needs.
- Key performance indicators and metrics: Set measurable KPIs and metrics to track the success of your processes. Benchmarking and continuous analysis allow you to optimize adoption, team effectiveness, and process efficiency using data-driven insights.
- Process control and validation mechanisms: Implement systems to regularly monitor, evaluate, and validate processes. Early detection of deviations or inefficiencies ensures high standards, fosters a culture of accountability, and promotes ongoing improvement.
- Stakeholder involvement: Actively engage key stakeholders in the governance process. Their involvement ensures better goal alignment, fosters ownership, and enhances communication between teams, leading to stronger governance outcomes.
- Communication strategy: Develop a clear plan for sharing updates, changes, and future goals. Transparent change communication promotes engagement, reduces misunderstandings, and strengthens collaboration across all teams and stakeholders involved in process governance.
Real-World Use Cases for Process Governance
Here are a few key real-world examples where strong governance frameworks make a measurable impact.
Regulatory compliance in highly regulated industries
Compliance with strict regulatory requirements is non-negotiable in industries such as healthcare, finance, pharmaceuticals, and energy. Process governance ensures that every workflow follows standardized procedures aligned with legal mandates, from process documentation to approvals. It creates clear audit trails, defines ownership for compliance activities, and enables organizations to adapt to new regulations without operational disruption quickly. Strong governance minimizes the risk of penalties, reputational damage, and costly remediation efforts.
Mergers, acquisitions, and organizational change
Mergers, acquisitions, and large-scale restructuring initiatives introduce significant complexity. Different systems, processes, and cultures must be integrated seamlessly. Process governance plays a critical role by establishing a unified framework for evaluating and standardizing processes across newly combined entities. It defines decision rights, transition plans, and change management strategies, ensuring that integration efforts are efficient, transparent, and aligned with overarching business objectives.
Digital transformation initiatives
Successful digital transformation requires more than simply adopting new technologies. Without strong process governance, digital initiatives often suffer from misalignment, slow adoption, and fragmented execution.
Governance frameworks ensure that technology implementations are strategically prioritized, that processes are adapted effectively to digital platforms, and that transformation projects deliver measurable outcomes. They also help manage cybersecurity, data management, and operational continuity risks.
Customer-facing process improvements
Customers expect consistent, seamless experiences across every touchpoint. Process governance enables organizations to design, implement, and continuously improve customer-facing processes such as onboarding, support, billing, and feedback collection.
It ensures that every team understands their role in delivering excellent service, enforces standardized workflows to reduce errors, and captures data that drives further enhancements. Strong governance translates directly into higher customer satisfaction, loyalty, and retention, ultimately acting as a foundation for modern, frictionless CX strategies.
Remote and hybrid work environments
As remote and hybrid work models become the norm, maintaining consistent and efficient operations across dispersed teams has become a significant challenge. Process governance provides the structure needed to ensure clarity, accountability, and performance regardless of location. It standardizes workflows, facilitates clear communication, and embeds flexibility into operational models, helping distributed teams stay aligned with organizational priorities while maintaining high productivity and engagement levels.
How to Design and Implement a Process Governance Strategy
Ready to implement your process governance? Here are a few common steps to help you on the path to designing process guardrails and rules that support your governance initiatives.
Step 1: Assess your current state
Before making any changes or decisions, conduct a gap analysis between your current and desired state. If you already have process governance or process management rules, this likely means determining what is and isn’t working for you. What areas can be kept the same? What areas need to improve?
If you’re starting from scratch, identify your long-term goals and the stepping-stone goals you can achieve to achieve them.
Step 2: Define your objectives and success metrics
Identify what you want to achieve with your process governance initiatives. What do those short-term and long-term goals look like?
As you break down your process governance objectives, consider the KPIs or metrics you might use to measure your success. How will you know if you’re on your way to reaching your goals? How will you know if or when you’ve achieved it?
Step 3: Establish a governance board or steering committee
When you assemble your process governance team, clearly defining each member’s roles and responsibilities is essential. This includes designating positions such as process owners, subject matter experts, compliance officers, and representatives from different departments.
Effective process governance relies on collaboration and communication among team members. Establishing regular meetings, outlining reporting lines, and promoting a culture of shared responsibility will help ensure smooth coordination and decision-making as a team.
Step 4: Build the governance structure
At this phase, choose the governance structure that best aligns with your team and long-term goals. Think back to the governance structure types we mentioned earlier.
Consider things like: How will your new process governance team work together? How will they interact with the rest of your team?
Step 5: Develop process governance documentation
Time to document your processes and systems. In the same way you’d create documentation for your other organizational processes, you’ll want to outline the steps, responsibilities, and activities your process governance team will follow.
In addition to creating documentation, you’ll want to ensure those documents are stored in an easily accessible place. Consider leveraging one of the many available process documentation tools to aid in documentation.
Step 6: Define controls, KPIs, and reporting loops
Implement process controls and establish mechanisms for continuous monitoring and reporting. Set clear performance indicators and feedback loops to track compliance, detect issues early, and drive ongoing improvements.
Step 7: Develop a training and communication plan
A successful governance framework relies on how well it is communicated and adopted across the organization. Build a structured and effective training program to educate teams about governance protocols, roles, and new processes. Pair this with a clear communication strategy to reinforce expectations and celebrate milestones.
| Example: Governing purchasing and supplier selecting processes in S4/HANA with Whatfix A manufacturing company faced challenges with decentralized purchasing processes across geographies, leading to missed opportunities for bulk discounts and increased procurement costs. The company streamlined purchasing, improved cost efficiency, and enhanced supplier relationships by leveraging Whatfix’s in-app guidance to enforce procurement governance practices in SAP S/4HANA. See the full use case here. |
Step 8: Execute phased rollout and validation
When introducing new processes, it’s best to implement them gradually to avoid overwhelming your team. This can be achieved through a phased implementation plan, which allows for a step-by-step integration of changes.
By breaking down the implementation into manageable stages, your team can adapt and become comfortable with each phase before moving on to the next. This approach minimizes resistance, optimizes learning, and ensures a smoother transition overall. An incremental approach also promotes continuity and helps maintain productivity while fostering a positive reception to process changes.
Challenges of Process Governance
Being aware of the challenges associated with process governance can help you prepare for upcoming hurdles and tackle problems more effectively. Here are the six biggest challenges of process governance.
- Organizational resistance: When implementing changes, it’s common for teams to exhibit resistance to change. To reduce internal resistance, it’s crucial to have a well-crafted plan that effectively communicates the importance and benefits of these changes. Providing clear explanations about the rationale behind the changes and how they align with broader organizational goals can help alleviate concerns and encourage buy-in from team members.
- Process adoption: By prioritizing proper training and support, you can equip employees with the knowledge and skills needed to understand the value of following processes consistently. Clear communication about the benefits and repercussions of adhering to processes, along with ongoing support and reinforcement, can help foster a culture of process adoption and ensure long-term success.
- Inadequate skills and resources: The right skills, resources, and training are essential to successful process governance. Make sure your leadership and team members have access to the tools and materials they need to make process governance as strong as possible. You will also need to assess your current team member’s skillsets and provide them with digital upskilling to prepare them for new digital processes.
- Lack of clear governance structure: Structure helps keep your team, processes, and projects organized. Without an established system in place, things start to slip through the cracks, or team members start to butt heads for the last day. Establishing a clear governance structure can help things move along smoothly.
- Process inconsistencies: Improving consistency is a key benefit of implementing processes — but what about when there are inconsistencies within the processes themselves? If your processes aren’t updated or accurate, it will be difficult for your process governance to succeed.
- Scalability: As you scale, your process governance should scale with you. But this is usually easier said than done. It can be difficult for your process governance team to keep up as your company grows, but building in scalability measures early on can make it easier to tackle those challenges when they arise.
Emerging Process Governance Trends
Changes in technology and the way we work are also impacting process governance. Here are some of the biggest trends to be aware of.
- Integration of AI and machine learning: AI and machine learning are making process governance more intelligent and predictive. AI-driven insights help detect inefficiencies, recommend optimizations, and automate compliance monitoring. Machine learning models continuously refine governance practices based on real-time data, enabling faster, smarter decision-making.
- Digital twin and process mining integrations: Digital twins create real-time virtual models of business processes, allowing teams to simulate changes and optimize operations without disrupting live workflows. Combined with process mining, organizations gain deeper visibility into how processes actually perform, enabling better governance, faster improvements, and reduced risks.
- Emphasis on data analytics: Data analytics is becoming central to effective process governance. Advanced tools track KPIs, highlight compliance gaps, and uncover process inefficiencies. With real-time insights, organizations can drive continuous improvement, increase accountability, and align governance efforts with strategic business goals.
FAQs
What are some best practices to strengthen process governance?
Best practices include regularly auditing processes, gathering stakeholder feedback, maintaining clear documentation, investing in employee training, leveraging automation tools, and staying compliant with evolving industry regulations. A continuous improvement mindset is key to effective governance.
Who is responsible for process governance in an organization?
Process governance typically involves a combination of leadership and operational teams. A governance board or steering committee often oversees the strategy, while process owners, team leads, and compliance officers handle day-to-day management and reporting.
What tools can help implement process governance?
pManagement (BPM) software, Digital Adoption Platforms (DAPs), workflow automation tools, process mining solutions, and compliance management systems can all support the implementation, monitoring, and optimization of process governance frameworks.
How do I measure the success of a process governance strategy?
Success can be measured by tracking KPIs such as process compliance rates, efficiency improvements, error reductions, employee adoption rates, and audit outcomes. Regular reporting and analysis help identify areas for further optimization.
How often should process governance policies be updated?
Process governance policies should be reviewed and updated at least annually or whenever there are significant organizational changes, new regulatory requirements, or major shifts in operational priorities. Regular reviews ensure continued relevance and effectiveness.
Processes Click Better With Whatfix
Strong process governance is essential for building efficient, scalable, and compliant operations. But effective governance is not just about creating rules — it is about ensuring processes are adopted, followed, and continuously improved across the organization.
Whatfix empowers organizations to operationalize their process governance strategies by providing in-app guidance, on-demand training, process compliance tracking, and contextual assistance directly within the flow of work. With WhatfixDAP, you can embed governance standards into everyday workflows, making it easier for employees to follow the right steps, adhere to compliance requirements, and quickly adapt to process changes without disruption.
Whether you are rolling out a new digital platform, standardizing global workflows, or improving operational compliance, Whatfix provides the tools you need to ensure your processes are not just documented but are truly adopted, optimized, and continuously improved.
To unlock the full potential of your process governance initiatives with Whatfix, schedule a free demo with us today!





