Every business process generates a trail of data—a digital footprint that tells the story of how work gets done. However, most organizations struggle to transform this data into actionable insights, relying instead on outdated assumptions that obscure inefficiencies. The cost? Lost opportunities for efficiency, innovation, and growth.
Enter process mining: a transformative business process management technology that bridges the gap between raw data, strategic decision-making, and process optimization. By analyzing the digital traces left by enterprise workflows, process mining uncovers hidden workflow bottlenecks, highlights process automation opportunities, and drives measurable improvements. Companies that adopt process mining are not just solving operational challenges but rethinking how work gets done.
In this article, we’ll explore the fundamentals of process mining, its benefits, how it works, and its diverse use cases across industries. We’ll also discuss common challenges and explain how integrating processing mining can empower organizations to turn insights into action, achieving sustained business outcomes.
What Is Process Mining?
Process mining turns the digital trail of your business processes into actionable insights. By analyzing data from enterprise systems and business processes, it maps, evaluates, and optimizes workflows, clarifying inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and areas for improvement. Unlike traditional process mapping methods, which rely on assumptions and subjective input, process mining leverages actual data, providing a precise and objective view of operations.
78% of organizations that automate business processes state process mining is critical to their robotic process automation (RPA) efforts. It ensures that automation targets the right tasks, improving efficiency and ROI.
By bridging the gap between how processes should work and how they function, process mining empowers organizations to drive meaningful change. It transforms operational data into a competitive advantage, helping businesses achieve efficiency, compliance, and strategic alignment.
Types of Process Mining
There are three main types of process mining, including process discovery, conformance checking, and process enhancement:
- Process discovery automatically designs a process model based on event data. This is the most common form of process mining.
- Conformance checking compares the actual process event data against the pre-designed process workflow to pinpoint where deviations are occurring and areas of user friction in the process.
- Process enhancement optimizes business processes once a process model is implemented, allowing for continuous improvement in the workflow.
Benefits of Process Mining
Process mining provides unparalleled insights into how business processes function, enabling organizations to identify inefficiencies, optimize workflows, and achieve measurable outcomes. By analyzing real-time operational data, this technology provides a foundation for informed decision-making and transformative improvements across various domains.
Here are the key benefits of process mining:
- Analyzes and Optimizes Business Processes: Process mining provides a comprehensive, data-driven view of workflows, uncovering inefficiencies and deviations in areas such as finance, procurement, HR, and supply chain operations.
- Accelerates Process Completion Through Automation: Process mining identifies workflow automation opportunities by pinpointing repetitive, low-value tasks. This reduces manual intervention, accelerates workflows, and improves overall productivity.
- Identifies Bottlenecks and Friction Points before Automating: Automation without insight can amplify inefficiencies. Process mining ensures automation efforts target the right tasks, addressing bottlenecks and friction points to maximize ROI and avoid unintended consequences.
- Drives Continuous Process Improvement: Process mining isn’t a one-time solution. It continuously monitors workflows, identifying areas for refinement to help businesses adapt to changing demands while maintaining operational excellence.
- Drives Business Outcomes Through ROI-Based Automation: Process mining prioritizes automation efforts based on potential impact and ROI, ensuring resources are directed toward initiatives that deliver the most significant value.
- Provides Objective Data and Insights into Process Health: Process mining offers unbiased, data-driven insights unlike subjective workshops or manual process mapping. Analyzing real-time data from enterprise systems provides an impartial view of process performance and enables evidence-based decision-making.
Process mining is a cornerstone of modern business digital transformation. Its ability to uncover efficiencies, accelerate automation, and provide actionable insights gives organizations leveraging this technology a significant edge in efficiency, agility, and strategic execution.
How Does Process Mining Work?
Process mining transforms raw event data into actionable insights through a systematic approach. By capturing, visualizing, and analyzing workflows, it reveals inefficiencies and drives continuous process improvement, as described in the following diagrams (and information):
1. Captures application event data on your processes
Process mining begins by extracting event data from enterprise software like SAP, Salesforce, Oracle, IBM, or any enterprise technology partner. Each event log contains three key attributes:
- Timestamp: Marks the exact time of the event.
- Case ID: Uniquely identifies a specific process instance (such as a single invoice or ticket).
- Activity: Defines the action performed (e.g., “Process Invoice”)
This event data forms the foundation of process mining, ensuring an accurate and detailed view of how business processes unfold in real-world operations.
2. Create a process model based on your event data
Process mining tools use the captured event logs to generate a process model or graph—a visual representation of workflows. This graph model highlights discrepancies between the ideal process and how it operates in practice:
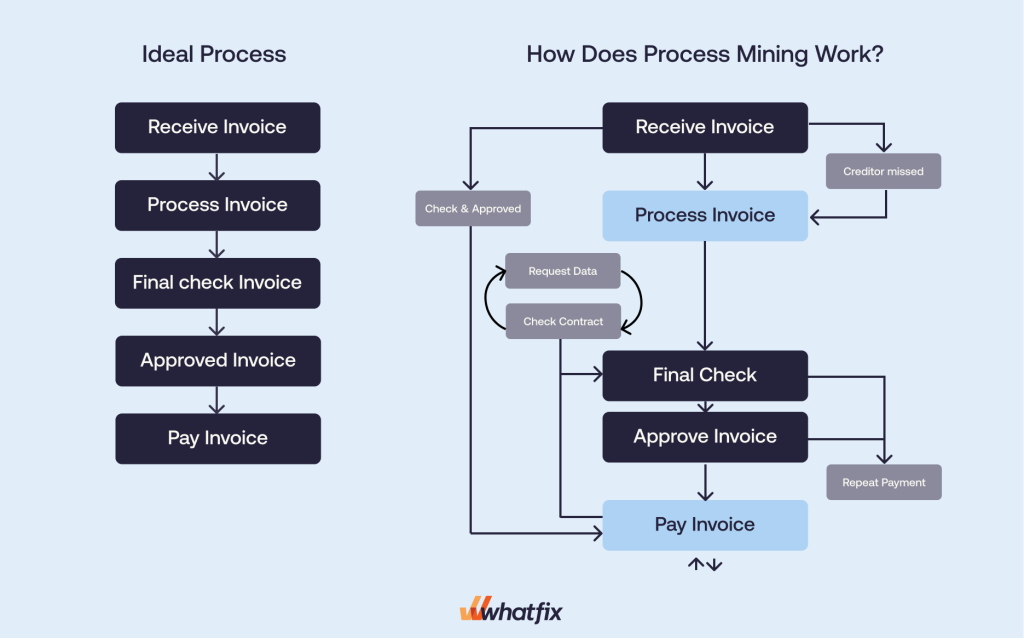
- Ideal Process: As illustrated in the left-hand graph (in the first and second images), an “ideal” invoice processing workflow flows sequentially from receiving the invoice to approving and paying it without interruptions or redundancies.
- What Process Mining Reveals: The right-hand graph (in the first and second images) describes real-world inefficiencies, such as duplicate steps, repeated approvals, and unnecessary clarifications. These deviations emphasize areas requiring attention and optimization.
For instance, consider a recruitment workflow in an applicant tracking system (ATS). It maps the flow from job postings to hiring, helping to identify inefficiencies like keyword mismatches or prolonged candidate evaluation phases. Process mining can be implemented for any enterprise software, with common use cases including ERPs, procurement systems, supply chain management software, HCM systems, and accounting software.
3. Analyzes areas of friction and highlights optimization opportunities
With the process graph in place, process mining software identifies inefficiencies such as:
- Bottlenecks: Points in the workflow where tasks are delayed (e.g., awaiting approval).
- Deviations: Steps that deviate from the intended process (e.g., skipping critical compliance checks).
- Rework Loops: Repeated actions that waste time and resources (e.g., processing the same invoice twice).
These insights clarify where automation or other process enhancements could deliver the greatest impact.
4. Monitoring performance for continuous process optimization
The final step is ongoing performance monitoring. By tracking workflows in near-real time, organizations can:
- Measure the impact of implemented changes.
- Detect emerging inefficiencies before they escalate.
- Continuously refine processes to maintain optimal performance.
This feedback look ensures businesses can adapt to technological changes, regulations, and customer expectations while maximizing operational efficiency.
Process mining is not just about identifying problems; it lays the groundwork for solutions. By turning data into actionable insights, organizations can streamline workflows, improve accuracy, and achieve measurable outcomes—all while ensuring scalability and long-term success.
Examples & Use Cases for Process Mining
Innovative tools like process mining are helping organizations across industries uncover inefficiencies, optimize workflows, and drive measurable outcomes. By providing clarity into how processes truly operate, process mining enables teams to identify areas for improvement and achieve strategic goals.
Below are examples of how organizations leverage this technology to enhance performance and deliver impactful results.
Finance Teams: Accounts Payable Optimization
Finance teams use process mining to streamline accounts payable processes by identifying bottlenecks, such as late invoice payments, duplicate payments, or vendor disputes. Process mining analyzes invoices’ lifecycles—from receipt to payment—and highlights inefficiencies, like approval delays or deviations from standard payment terms.
Outcomes:
- Reduced late payment penalties.
- Improved vendor relationships through timely payments.
- Lowered operational costs by eliminating duplicate payments or unnecessary steps.
Procurement Teams: Purchase-to-Pay Cycle Improvement
Procurement teams apply process mining to enhance the purchase-to-pay (P2P) cycle by uncovering inefficiencies in purchase order creation, supplier negotiations, and invoice processing. It identifies mismatches in 3-way matching (purchase orders, goods receipts, and invoices) and flags non-compliant purchases.
Outcomes:
- Improved compliance with procurement policies.
- Shorter cycle times from purchase order to payment.
- Increased cost savings through better supplier management and contract utilization.
Healthcare Industry: Patient Journey Optimization
Hospitals and healthcare providers leverage process mining to analyze patient journeys from admission to discharge. It identifies inefficiencies in clinical workflows, such as delays in diagnostic testing, redundant procedures, or long wait times for treatment.
Outcomes:
- Enhanced patient experience through faster service delivery.
- Reduced operational costs by streamlining workflows.
- Better resource allocation, ensuring staff and equipment are utilized efficiently.
Manufacturing: Production Line Performance Monitoring
Manufacturers use process mining to monitor production line processes and detect inefficiencies like machine downtime, assembly-line bottlenecks, or deviations from production schedules. It also identifies the root causes of quality issues or delays.
Outcomes:
- Increased production efficiency and throughput.
- Reduced downtime and maintenance costs.
- Improved product quality through consistent adherence to processes.
HR Services: Employee Onboarding Process Optimization
HR teams analyze the employee onboarding process, from job offer acceptance to onboarding completion, using process mining to identify delays in IT setup, training assignments, or document collection. This ensures employees are productive from day one.
Outcomes:
- Faster onboarding process for new hires.
- Improved employee satisfaction with a seamless onboarding experience.
- Reduced administrative workload through automation and process streamlining.
IT Service Management: Incident Management Process Optimization
ITSM teams leverage process mining to analyze and improve their incident management workflows by mapping the lifecycle of IT tickets from creation to closure. It identifies bottlenecks, such as delays in ticket resolution, escalations, or routing inefficiencies, and helps pinpoint common issues like the lack of ownership or incomplete ticket information.
Outcomes:
- Faster ticket resolution and reduced mean time to resolution (MTTR).
- Improved SLA (Service Level Agreement) compliance.
- Enhanced end-user satisfaction with IT support services.
- Reduced backlog by streamlining ticket prioritization and routing.
Higher Education: Enrollment and Admissions Process Improvement
Higher education institutions use process mining to analyze their enrollment and admissions processes, from application submission to student registration. It identifies pain points like delays in application reviews, missing documents, or bottlenecks in communication with applicants.
Outcomes:
- Reduced time-to-decision for student applications.
- Increased enrollment rates due to improved applicant experience.
- Better allocation of staff resources during peak admission periods.
- Enhanced compliance with institutional and regulatory deadlines.
When to Use Process Mining
Process mining is a powerful tool that gives clarity and actionable insights across various business scenarios. Whether undergoing a major transformation or seeking incremental improvements, organizations can leverage process mining to identify inefficiencies, optimize workflows, and enable data-driven decision-making.
Below are key scenarios where process mining delivers significant value:
- Merges and Acquisitions: Merging or acquiring businesses often involves aligning disparate processes and systems. Process mining provides a clear view of workflows across entities, identifying redundancies, standardizing operations, and realizing post-merger synergies faster.
- Legacy Application Modernization or System Migration: Transitioning from outdated systems to modern enterprise applications can be complex. Process mining ensures seamless migration by mapping existing workflows, identifying areas of improvement, and ensuring optimized processes are implemented in the new system.
- Searching for New Revenue or Value Streams: Organizations looking to uncover hidden revenue opportunities can leverage process mining to identify inefficiencies that may be hindering profitability. By analyzing workflows, businesses can discover new ways to streamline operations, reduce costs, and drive new revenue growth.
- Improving Compliance and Governance Programs: Maintaining regulatory compliance requires a transparent and auditable process environment. Process mining enables organizations to monitor processes in real-time, detect deviations from compliance standards, and ensure adherence to governance policies consistently across workflows.
- Transforming Finance or Operations Processes: Process mining can be applied to optimize key finance and operations workflows, such as accounts payable, order-to-cash, or purchase-to-pay cycles. It reduces bottlenecks, speeds up cycle times, and drives operational efficiency, aligning these processes with business objectives.
- Improving Supply Chain Resilience: Supply chains are complex and prone to disruptions. Process mining allows organizations to analyze supply chain workflows, identify bottlenecks, and uncover opportunities to increase resiliency. Optimized processes enable businesses to respond to challenges more quickly, maintaining smooth operations.
- Harnessing New Technologies like AI and Big Data: As organizations adopt and implement new technologies, such as AI (artificial intelligence) and big data analytics, process mining is a critical foundation for success. It clarifies current workflows, enabling businesses to integrate new technologies seamlessly and maximize their impact.
- Enabling the Workforce to Achieve New Levels of Efficiency: By identifying repetitive tasks and streamlining workflows, process mining empowers employees to focus on higher-value activities. It enhances productivity, reduces frustration, and drives satisfaction by allowing teams to operate more efficiently and effectively.
Limitations of Process Mining
While process mining is a powerful tool for uncovering inefficiencies and optimizing workflows, it has its challenges.
While these limitations may present challenges, they can often be mitigated through proper planning, robust data governance, and ongoing support. Organizations that proactively address these obstacles are better positioned to unlock the full potential of process mining. By ensuring data quality, integrating complementary tools like task mining, and fostering a culture of change, businesses can transform process mining from a diagnostic tool into a driver of operational excellence and innovation.
Understanding its key limitations (as described below) can help organizations address potential obstacles and maximize the value of its technology.
1. Data Quality and Availability
Process mining generates insights only as good as the data it analyzes. Poor-quality, incomplete, or inconsistent data can result in flawed analyses and misinterpreted insights. Additionally, event data is often scattered across multiple systems, requiring significant effort to merge, clean, and prepare it before it can be analyzed effectively.
Solution: Establish robust data governance practices and engage data analysts early to ensure data accuracy and integrity.
2. Inability to Track Events and Tasks Outside of Applications
Process mining relies on event logs from software systems. Manual tasks, offline processes, or non-digital workflows are often excluded, creating blind spots in the process analysis. For instance, verbal approvals or paper-based workflows are not captured, limiting visibility into these critical steps.
Solution: Integrate task mining alongside process mining to capture insights into manual tasks and bridge the gaps in analysis. Application analytics tracking tools like Whatfix Product Analytics enable application owners, CIOs, and digital transformation leaders the capabilities to set up and track any custom user event in their enterprise software to analyze and benchmark current-state KPIs and metrics (like time-to-completion and dropoffs), identify where issues are taking place with Funnels and Journeys, and more.
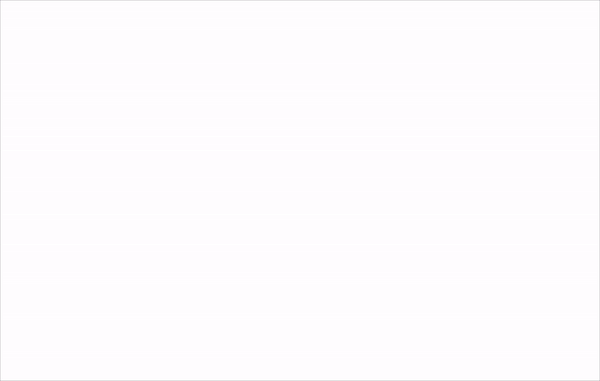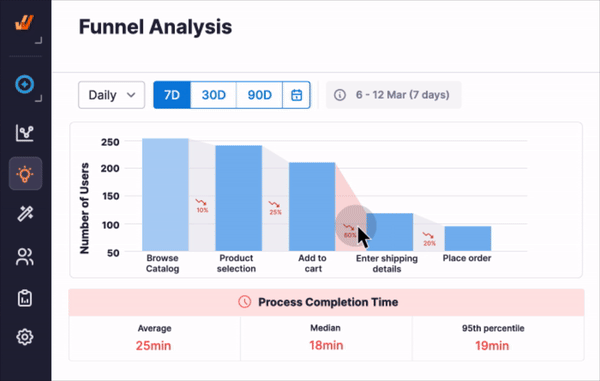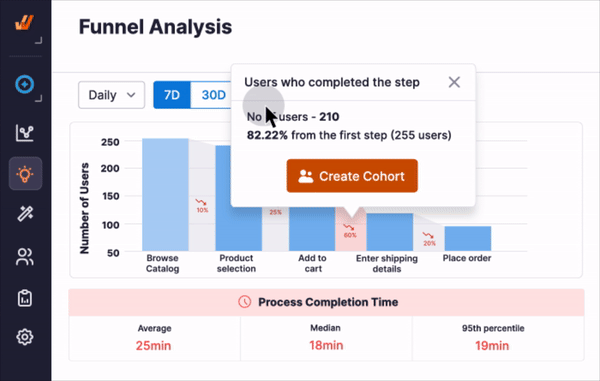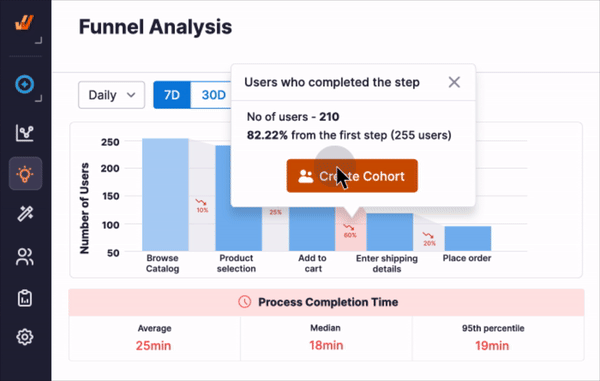
3. Integration Challenges
Integrating process mining tools with enterprise systems can be complex, especially in organizations with legacy software or custom-built applications. These systems may lack connectors, use incompatible data formats, or restrict data sharing due to security or privacy concerns. These integration challenges can delay implementation and reduce the overall effectiveness of process mining.
Solution: Choose process mining tools with robust integration capabilities and pre-built connectors for commonly used systems—like SAP, Oracle, and Salesforce. Tools like IBM have native-integrates with the IBM software ecosystem and is an obvious choice for IBM customers.
4. Complexities and Always-Changing Processes
In large organizations, processes are often complex and dynamic, frequently evolving to meet new demands. Process mining models can quickly become outdated as workflows are updated or adjusted to meet new demands.
Solution: Implement continuous process monitoring and updates to ensure process mining models remain current and relevant, reflecting real-time operations.
5. Resistance to Change
Introducing process mining often requires a cultural shift within an organization. Employees and teams may resist the adoption of process mining due to concerns over transparency, fear of being monitored, or reluctance to alter established workflows.
Solution: Implement effective change management strategies, such as clear communication, training, and stakeholder involvement, to overcome internal resistance to change and ensure end-user adoption.
Best Process Mining Software to Consider
Many technology vendors have recently emerged that offer process mining solutions, each with minor differences in its core capabilities, offerings, and solutions. The top business process mining software includes:
- Celonis
- IBM Process Mining
- UiPath Process Mining
- Appian
- Software AG ARIS
- ABBYY Timeline
- QPR ProcessAnalyzer
Software Clicks Better With Whatfix
Process mining uncovers inefficiencies and provides actionable insights to optimize workflows across industries and functions. However, identifying process gaps is only the first step—what truly drives transformation is enabling teams to act on these insights effectively. That’s where Whatfix comes in.
By layering Whatfix DAP on top of your enterprise applications, you can bridge the gap between process mining insights and action. Whether it’s guiding employees through new workflows with in-app Flows, reducing user friction with Smart Tips, or delivering real-time task support, Whatfix ensures your teams can execute optimized processes easily and consistently.
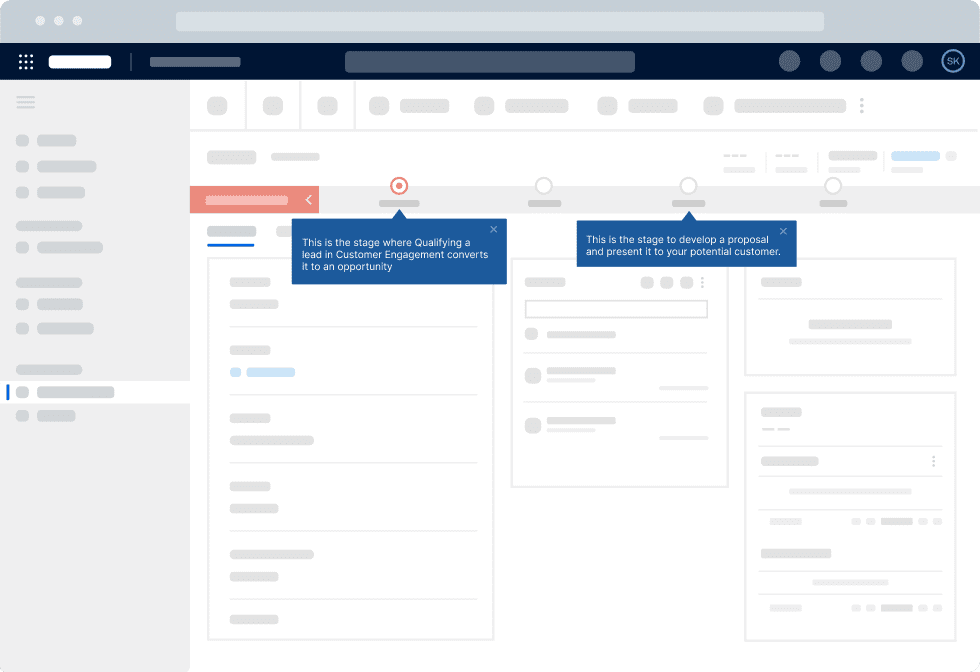
Use Whatfix Mirror to create sandbox application environments of your enterprise software and their processes and tasks to provide hands-on user training in a risk-free sandbox environment. Employees can practice workflows, refine their skills, and build confidence—all without impacting live operations.
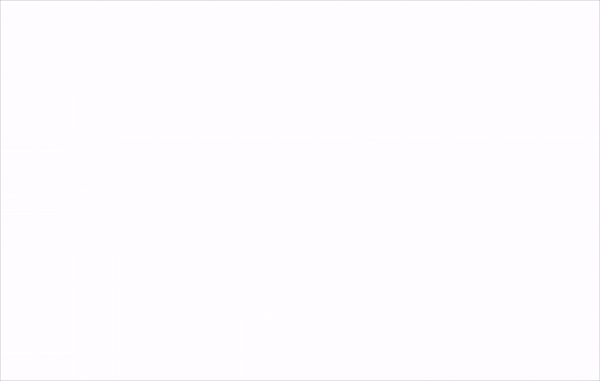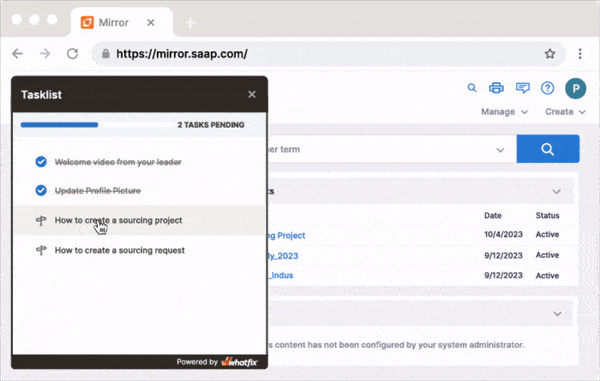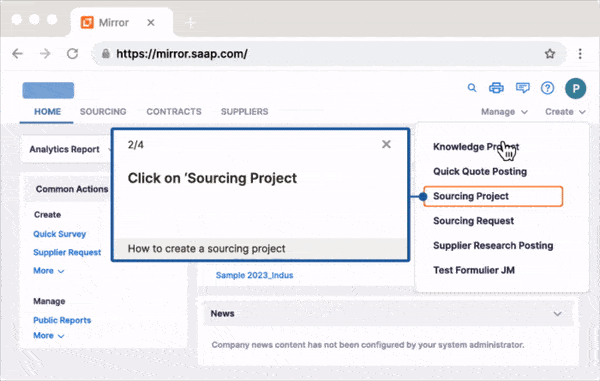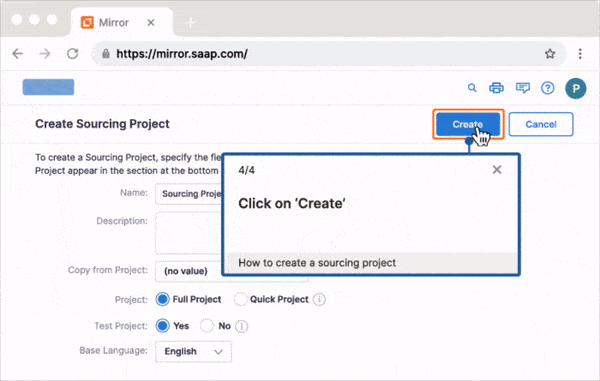
With Whatfix Product Analytics, custom event tracking can be set up to identify areas of friction. Configure Funnels and Journeys to track how end-users complete processes and use Cohorts to see which teams and users fail to follow the correct steps. These insights empower organizations to refine workflows, improve user experience, and achieve strategic goals.
Process mining uncovers the “what” and the “why” of inefficiencies, and Whatfix delivers the “how” by empowering employees with the right tools and guidance to drive sustained change. Together, they form a powerful combination for driving operational excellence and achieving measurable business outcomes.
Ready to turn process insights into action? Explore how Whatfix can accelerate your transformation journey or request a demo today!