
Today, companies in every industry face mounting cybersecurity risks. These risks are significantly compounded when employees don’t understand their role in guarding against attacks – human error almost always plays a role in security breaches. The key to strengthening your business’ organizational security is cybersecurity training for employees.
What is Cybersecurity Training for Employees?
Cybersecurity training also referred to as cybersecurity awareness training, is an approach to building organizational security and mitigating user risk of cyber attacks. These solutions educate employees on how they can individually prevent cybersecurity breaches and data hacks by implementing best practices while using email and other web services.
Why Is Cybersecurity Training in the Workplace Important?
Cybersecurity attacks have become both frequent and creative over the past two decades, and even more so since the start of COVID-19.
Cyber attackers most often target financial accounts and private information that, if allowed to fall into the wrong hands, can be detrimental to the success of a company and the interests of its employees. We know that employees tend to be a weakness in cybersecurity efforts.
Attackers try to get employees to click on a malware link (as seen in many Gmail phishing examples) or use fraudulent communications to obtain confidential information and steal passwords.
Implementing a robust cybersecurity training program in the workplace is crucial to prevent monetary loss, information breaches, noncompliance, damaged brand reputations, and even regulatory fines that can follow cyber attacks.
An understanding of cybersecurity is critical not only to IT employees but to team members throughout every organization. All employees need to embody the most current security best practices and be able to avoid falling into insidious traps.
Components of Cybersecurity Training
Comprehensive cybersecurity training must encompass all kinds of security threats:
1. Responsibility for company & customer data
First and foremost, employees need to be well trained to understand the ins and outs of their responsibilities related to protecting the company and customer data. Team members should receive in-depth training that underscores any legal regulations that affect how they handle information and company-established best practices.
2. Data incident reporting
Employees should be aware of how to detect and report suspicious activity and phishing attempts when they see them. Individual cases of cybersecurity breaches and even attempts should be communicated to the responsible parties along with sufficient background information so every effort to guard against future attacks can be made.
3. Passwords
Employees should understand the importance of using strong, unique passwords for company accounts. Businesses must enact policies to ensure employees are updating their passwords regularly and avoiding doubling up on personal passwords.
4. Unauthorized software installation
Employees should understand the intended use of their work devices and the rules about what can and cannot be installed on them. Team members should not be installing new applications from the internet unless deemed necessary for their role and signed off on by managers or IT team.
5. Fraud emails
Fraud emails are the primary vehicle for phishing attacks. In these emails, attackers pose as trusted persons or entities to gain some kind of access or information. Employees should be well-versed in scanning emails for signs of fraudulent activity.
6. Spot suspicious activity
Emails aren’t the only source of cybersecurity threats. Successful cybersecurity awareness training should enable employees to spot security threats across the web, in their messages, and from within the organization.
7. Reinforce confidentiality
Team members well-trained in cybersecurity measures must understand the importance of confidentiality and the measures necessary to protect it. They should receive detailed instructions on how to protect data and in turn, protect their customers, fellow employees, partners, and the company as a whole.
Challenges of Cybersecurity Training in the Workplace
There is no one-and-done solution to workplace cybersecurity training. Because cyber threats are complex and ever-changing, cybersecurity awareness training needs to be robust and adaptive. There are several challenges that security professionals face when designing and implementing training. Let’s discuss a few of them.
1. Training is an investment
Training requires investment – both in terms of time and monetary cost – to be effective. Conducting a training needs assessment before going all-in on cybersecurity training will help avoid waste, allowing you to identify which specific areas need more training. However, securing a budget for cybersecurity training can be challenging at large organizations.
2. Avoid the blame game
While it is true that employees can be a source of cybersecurity weakness, blaming individuals for their part in security breaches misses the point and causes more harm than good. It is the larger responsibility of an organization’s leaders and IT security teams to equip their team members with everything they need to keep the business and its data safe.
3. Getting leadership on board
Like with most organization-wide projects, it’s critical to get upper management on board. In order to keep leadership excited and involved, continue pointing them to the importance of cybersecurity training for employees. Be clear and transparent about how cybersecurity affects the overall success of the company, and highlight the harm security attacks could have. Use analytic and reporting tools to demonstrate the effectiveness of your training program once in place.
4. Cyber threats are always evolving
Cybersecurity threats evolve and adapt at a pace that is unnerving, to say the least. In order to ensure that employees are well-equipped to handle the newest threats, cybersecurity training needs to be updated along with them. Many cybersecurity awareness training programs are designed to be delivered in small doses over long periods of time. Taking advantage of one of these solutions will give IT the opportunity to deliver up-to-date information about evolving cybersecurity threats as they emerge.
10 Cybersecurity Training Tools for Employees
Here are the top 10 cybersecurity training tools for your employees.

1. KnowBe4
G2 rating: 4.7/5
Pricing: starts at $9 per user per year and differs by tier and number of users
KnowBe4 is a security awareness training platform used by more than 35,000 organizations around the world. Their enterprise awareness training program uses innovative, simulation-based assessments and web-based training to build cybersecurity awareness in an organization. KnowBe4’s approach to cybersecurity awareness training for employees involves tools like interactive video lessons, games, and newsletters, in addition to sending random simulated attacks to employees as they go about their day-to-day business.
KnowBe4 provides user-specific training analytics, enterprise reporting, and virtual risk scoring to empower security teams to provide more training where it’s needed. They also offer a sizeable library of security awareness training content


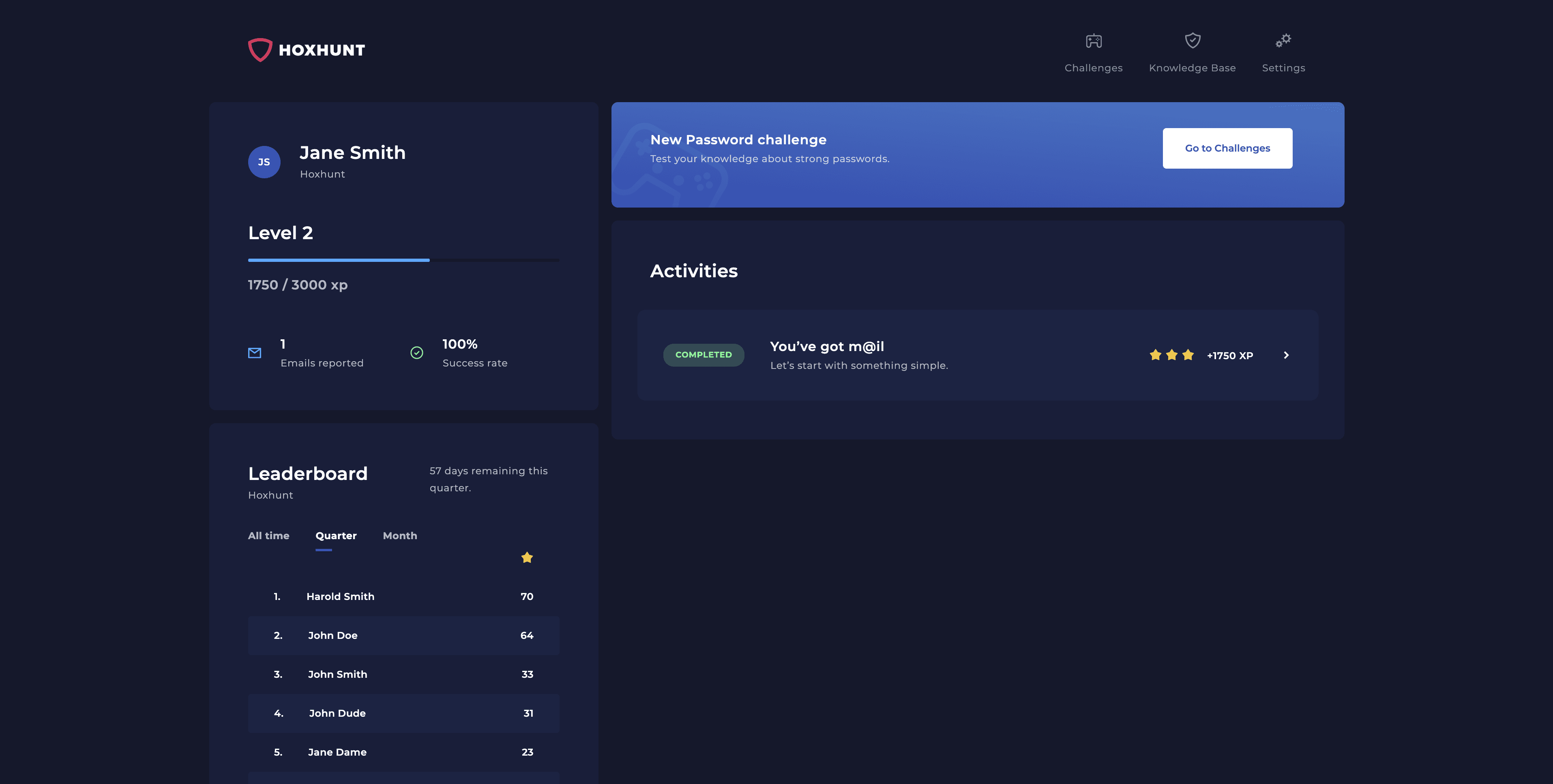
2. Hoxhunt
G2 rating: 4.7/5
Pricing: starts at $9 per user per year and differs by tier and number of users
KnowBe4 is a security awareness training platform used by more than 35,000 organizations around the world. Their enterprise awareness training program uses innovative, simulation-based assessments and web-based training to build cybersecurity awareness in an organization. KnowBe4’s approach to cybersecurity awareness training for employees involves tools like interactive video lessons, games, and newsletters, in addition to sending random simulated attacks to employees as they go about their day-to-day business.
KnowBe4 provides user-specific training analytics, enterprise reporting, and virtual risk scoring to empower security teams to provide more training where it’s needed. They also offer a sizeable library of security awareness training content

3. MetaCompliance Security Awareness Training
G2 score: 4.6/5
Pricing: Basic plan starts at $10/user/year
MetaCompliance offers a variety of security awareness training solutions for different sectors including financial services, governments, education, and healthcare. Metacompliance’s training features include phishing simulations and cybersecurity eLearning programming in addition to privacy management, policy management, and incident management.
This solution prioritizes providing industry-specific training for more employee engagement and better outcomes. Metacompliance offers automated security awareness training with a built-in security awareness campaign planner for pre-scheduled training programs. Additionally, this platform provides required regulatory reporting to show they’ve met compliance requirements

4. SoSafe
G2 score: 4.7/5
Pricing: Contact vendor for a quote
SoSafe delivers eLearning content designed to match the most current behavioral psychology insights. This cybersecurity awareness training software is comprised of microlearning lessons featuring engaging and interactive storylines to build strong habits.
Training content is delivered automatically to employees as story-driven learning experiences called ‘learning moments,’ fully equipped with reminder nudges and gamification. This solution can be customized with your company’s policies and e-learning content.

5. Infosec IQ
G2 score: 4.5/5
Pricing: Contact vendor for quote
Infosec IQ aims to help companies build cybersecurity awareness among their employees by transforming company culture. This cybersecurity training solution features customizable learning content and phishing simulations that utilize animation and gamification to keep employees engaged in learning.
Solutions are customizable to cater to industry-specific compliance standards and can be delivered as live boot camps featuring instructor-led training. Additionally, the Infosec IQ platform includes a training library with eLearning content such as assessments, infographics, and newsletter templates. Its analytics dashboard lets managers adapt training efforts to meet the needs of their highest-risk employees.

6. NINJIO Security Awareness
G2 score: 4.9/5
Pricing: Contact vendor for quote
NINJIO security awareness uses a microlearning and gamification approach to creating fun and engaging training content. The company’s NINJIO AWARE™ anime uses gamified, anime-style videos to educate employees about cybersecurity threats. These videos are housed in an extensive training library, updated every month with new content based on real-life examples of recent security breaches.
NINJIO offers a number of features to fit different business needs as well. Its ‘corporate’ solution uses more conservative anime styles, ‘nano’ offers super short episodes for busy team members, and ‘phish’ is specifically geared toward simulating phishing attacks to test and analyze employee vulnerability on a regular basis.

7. Proofpoint Security Awareness Training
G2 score: 4.5/5
Pricing: Contact vendor for a quote
Proofpoint aims to change how employees interact with cybersecurity threats and improve security outcomes for its customers. This cybersecurity awareness solution is targeted to the specific vulnerabilities, roles, and competencies of a company’s employees, providing microlearning content to build sustainable habits.
Proofpoint’s system utilizes baseline knowledge & culture assessments, adaptive learning, behavioral enforcement, and evaluation tools to deliver and adapt training as needed. Its phishing and USB simulations are based on real-life threats to identify your company’s most frequently attacked and most click-happy team members.

8. Usecure
G2 score: 4.7/5
Pricing: Contact vendor for a quote
Usecure’s cybersecurity awareness training platform uses tailored training programs and automated delivery of simulated phishing attacks to measure a company’s human risk and boost employee cybersecurity awareness. The platform’s features include policy management, dark web monitoring, and human risk reporting. Usecure’s compliance tracking tools include audit and progress reports as well as training adoption tracking to demonstrate efficacy.


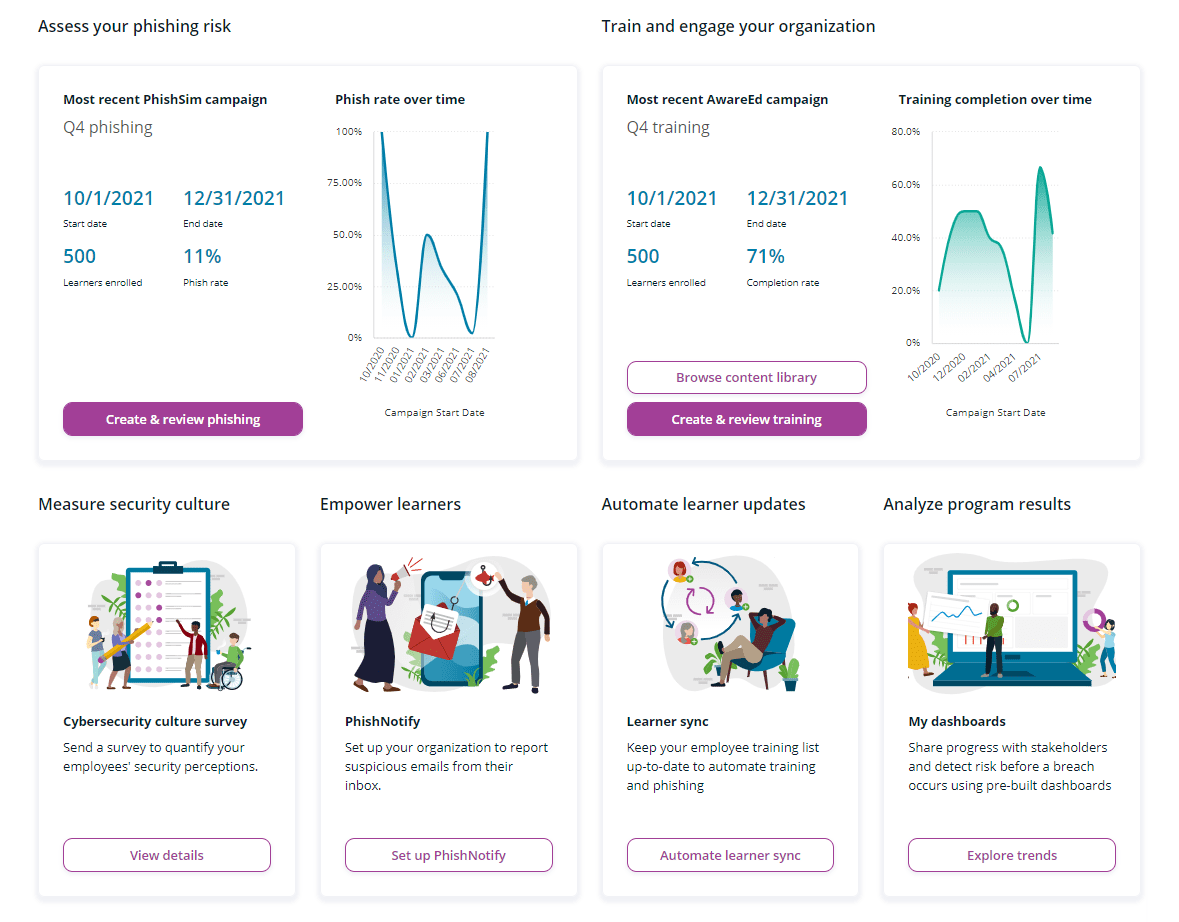
9. Immersive Labs
G2 score: 4.7/5
Pricing: Contact vendor for a quote
Immersive Labs provides cybersecurity training for security-oriented teams such as developers, cyber teams, business leaders, engineering teams, and security hiring teams. This solution focuses on building employee resilience by providing hands-on training and realistic simulations so security teams can measure cyber readiness in relation to industry benchmarks.
Immersive Labs’ features include a cyber crisis simulator, immersive training, candidate screening tools, and even emulated production environments for security testing.
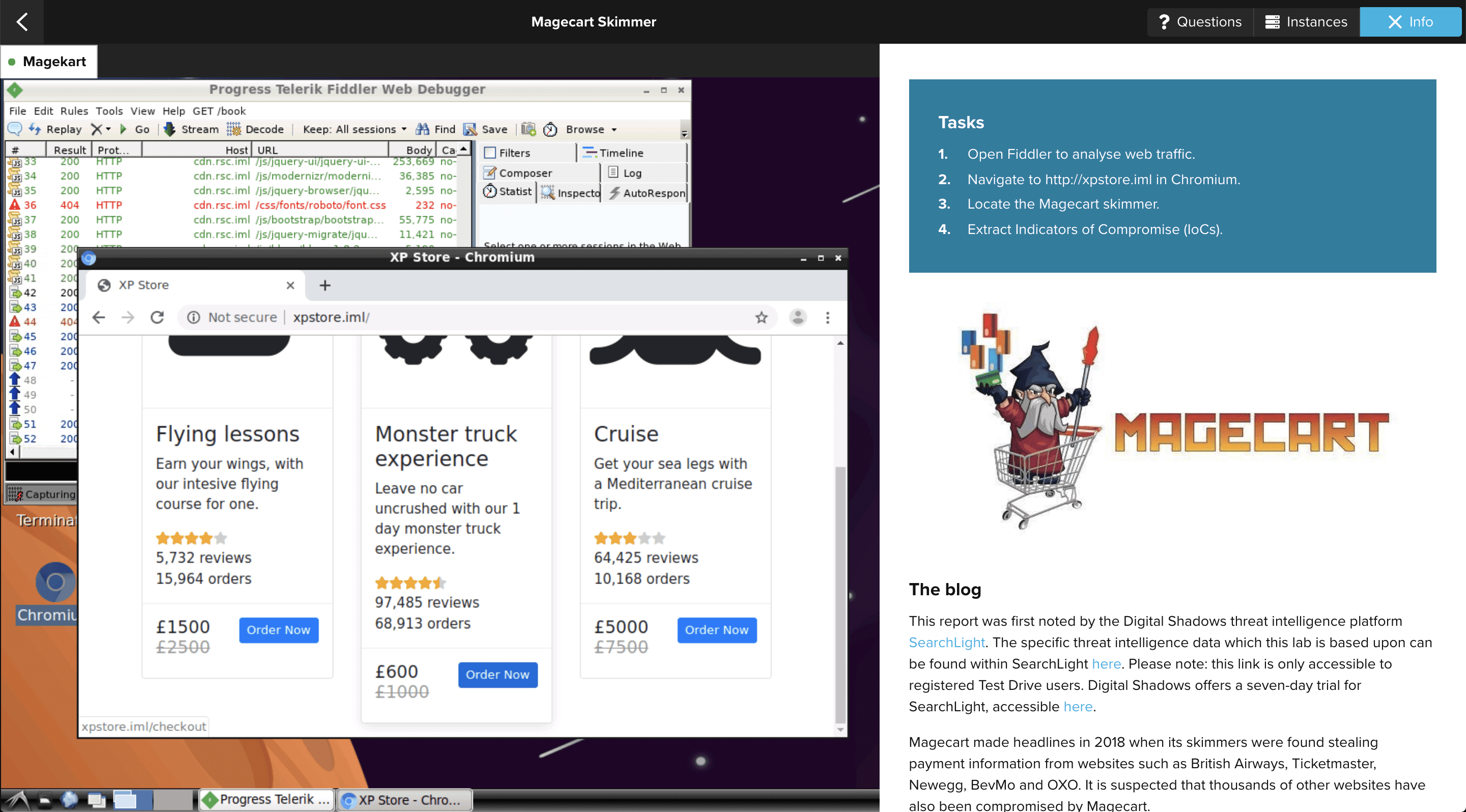

10. Cybeready Security Awareness Training Platform
G2 score: 4.7/5
Pricing: Contact vendor for a quote
Immersive Labs provides cybersecurity training for security-oriented teams such as developers, cyber teams, business leaders, engineering teams, and security hiring teams. This solution focuses on building employee resilience by providing hands-on training and realistic simulations so security teams can measure cyber readiness in relation to industry benchmarks.
Immersive Labs’ features include a cyber crisis simulator, immersive training, candidate screening tools, and even emulated production environments for security testing.
8 Best Cybersecurity Training Courses in 2024
For cybersecurity training on a more individual basis, managers and employees might elect to complete or assign an online cybersecurity training course rather than deploying a company-wide initiative. Here are the best cybersecurity courses in 2024.
1. Cybersecurity Specialization Certification by the University of Maryland
Available on Coursera, the University of Maryland has created a cybersecurity certification for employees seeking out an understanding of fundamental cybersecurity knowledge and technical skills. This five-part specialization is designed for employees with some existing knowledge of cybersecurity to be taken over the course of several months, with a suggested pace of about two hours per week. Learners earn a shareable certificate upon completion.
2. Udemy’s The Complete Cyber Security Course
Created by a cybersecurity expert with 25 years in the field, this course is aimed at teaching security-primed learners the ins and outs of maintaining security, privacy, and anonymity online and covers Windows, MacOX, and Linux. The Complete Cyber Security Course is comprised of four volumes and is available to Udemy users and for purchase by volume.
3. SANS Cyber Aces Free Cyber Security Training Course
Started by the SANS institute, this course teaches the core concepts needed by cybersecurity professionals. Cyber Aces course material comes in the form of videos and tutorials that are engaging and updated regularly.
4. TryHackMe
TryHackMe uses short, gamified, real-world labs to teach users about cybersecurity. This platform was created in an effort to make learning about cybersecurity more accessible and straightforward. TryHackMe has a variety of hands-on training content geared toward teaching learners whether they are seasoned professionals or just starting out.
5. Cybrary
Cybrary is an online cybersecurity learning platform with solutions for individuals and teams. This platform contains over two thousand cybersecurity training courses in addition to certification preparation tools and simulations. Cybrary starts out free and has a variety of helpful premium features like custom paths, skill proficiency reporting, and even a discord community.
6. StationX VIP Membership
StationX is a cybersecurity training and career development platform aimed at helping individuals pass top certification exams and excel as cybersecurity professionals. StationX offers courses on topics like IT essentials, ethical hacking and penetration testing, and even passing specific certifications. VIP Membership includes direct support from security experts and completion certificates for each course taken.
7. edX Essentials of Cybersecurity
The University of Washington offers this cybersecurity training certificate through edX as a set of four courses to be completed over the course of six months. Through this program, learners understand the inner workings of the cybersecurity industry, the types of security threats, and learn the information they need to pursue a career in cybersecurity.
8. The Absolute Beginners Guide to Cyber Security 2022
The Absolute Beginners Guide to Cyber Security 2022 is a multi-part course on Udemy that covers basic IT and cybersecurity concepts like malware hacking, and defenses. This is a great course for employees who want to lay the groundwork for a future career in IT or cybersecurity.
At the end of the day, promoting cybersecurity awareness is key to safeguarding an organization’s personal data and financial interests. Keeping employees abreast of the latest security threats and well-equipped to intercept them is critical to any business’ success.
You can leverage employee training software and corporate learning management systems to deliver online employee training experiences. They allow you to create training modules efficiently, make them engaging, securely deliver them to the employees, track employee engagement with the training material, analyze performance, and give feedback.
A digital adoption platform (DAP) is a training software that integrates with your enterprise applications in order to help the user learn while working on the application itself. DAP uses interactive walkthroughs, videos, and self-help menus to guide users through every aspect of the application.
Thank you for subscribing!



