No name is more famously associated with lean manufacturing than that of Henry Ford, founder of the first assembly line who succeeded in reducing the amount of time it took to assemble vehicles by more than 75%.
Forty-two years later, Ray Kroc applied similar principles of process efficiency to perfect the meal assembly design of a new restaurant called Mcdonald’s. Its “Made for You” production system clocks 90 seconds from order to delivery, cutting out waste and inefficiencies along the way.
These two examples show the value of increasing process efficiency for companies. While organizations constantly look for new ways to drive growth, from new tools, new accounts, new channels – sometimes the most impactful way to grow is to simply create more efficient processes.
In this guide, we’ll define the benefits of process efficiency, challenges that come with improving processes, and how to refine your business with process improvement methodologies.
What Is Process Efficiency?
Process efficiency is making your business or system processes more efficient. This measurement factors in both time and resources spent on a process and either directly or indirectly affects a company’s revenue.
The efficiency of your business mostly reduces to the following four items:
- The overall efficiency of the process. Do you usually earn more than the value of the labor, time and cost that you invest?
- Throughput. What’s your average production during any specified period of time?
- Labor productivity, namely how much work do you generally produce within that unit of time?
- Resource efficiency. Do you minimize your waste and maximize your assets (e.g., money, materials, and staff)?
4 Benefits of Creating Efficient Processes
While it’s obvious that efficient processes are inherently better, but here are four direct results of having highly-efficient business processes:
1. Improved productivity & performance
Harvard Business Review reports that in its experience, companies lose more than 20% of their productive capacity, or the equivalent of more than one day a week, to unproductive processes. A productivity mindset leads to better-informed decisions.
Result? Happier customers and more effective, more motivated employees. There’s also less turnover.
2. More agile workforce
More efficient processes make for a more agile workforce since the workforce communicates in sync across divisions, deadlines are kept and projects are automated. Work expectations are well-defined, employees stimulated and there’s a collaborative environment that spurs innovation.
3. Fewer errors
Better processes mean fewer errors. That’s because tasks are monitored and adjusted in real-time for improvement, waste is reduced, operations are simplified, workers are invested and the process is automated. According to Frevvo, a US-based provider of cloud-based electronic forms and workflow applications, tools for improving business efficacy can eliminate a considerable portion of human errors.
4. Reduced operational expenses
Efficient operations mean cost-savings in rectifying errors, smaller teams, and reduced work hours. It also means you know whom to hire for which jobs and which material to buy. Your budget is streamlined, and so are your costs. Frevvo relates that 31% of business leaders agreed that process automation lowers labor costs.
Indirect pay-offs include increased customer satisfaction, more time for marketing, innovation, staff training, and a vibrant and sustainable workplace.
Related Resources
Key Reasons For Inefficient Processes
Want to improve your processes but don’t know how? Most inefficiencies track to the following deficits:
1. Lack of necessary skills
You or your employees may simply lack the vocational, academic, or know-how skills to complete the job. A Gartner 2018 study found that most companies have only 20% of employees qualified for their roles.
2. Poor process documentation
Your paperwork is all over the place. Your IT system, if you have one, is mismanaged and needs to be updated, there are lost or changed clauses and brand inconsistency. Compliance and security risks, including audit failure, ransomware, and data theft, abound.
3. Shadow processes
Businesses should have their well-laid out processes. In areas with gaps or dated bureaucracy, employees tend to muster their own solutions. For example, if you have no process in place for customer calls, employees may set aside their work to answer random calls, costing you interrupted labor and missed work opportunities, among other issues. In accumulation, these shadow processes can cost companies millions of dollars in time and resources, impact customer and employee experiences and could cause your business havoc if ignored.
4. Lack of common terminology
Employees don’t know their duties, there’s miscommunication, maybe cultural misunderstanding with brand inconsistency and contradictory messages between individuals, departments, and the entire company. Sometimes, different teams have their own perspectives and goals. According to David Riess, CEO of Equinox IT, it’s often the case that the IT department experiences a disjunct from the rest of the company, to the detriment of the business as a whole.
KPIs & Metrics to Measure Your Process Efficiency
- Overall efficiency
- Productivity level
- Throughput
- Cycle time
- Turnaround time
- Takt time
- Error rate
- Effectiveness
- Cost-effectiveness
- Capacity indicators
- Quality rate
- Profitability
- Competitiveness indicators
- Value
- Return on investment
- Timeliness
Measuring your processes’ efficiency levels is a complex challenge and will be unique to each contextual process. Let’s break down four of the most common metrics to calculate, benchmark, and improve your process efficiency:
- The overall efficiency of the process = production time / total process time. For example, let’s say you’re trying to gauge the efficiency of your pizza-making process. You should measure the time it takes to make the pizzas, in relation to the entire process from buying the ingredients to delivery.
- Throughput = number of units produced / production time per unit. This efficiency metric is useful for gauging your production level. For example, if a cookie company baked 30,000 cookies in 12 hours, it produced 2,500 cookies per hour.
- Productivity = outputs produced by a company/ inputs used in its production. Use this calculation to gauge overall employee productivity. For example, let’s say your new field donations agent earned $1.2 million after spending 12 hours door-to-door canvassing for your charity. At $100,000 per working hour, you’ll want to do everything you can to keep that new employee.
- Resource efficiency = value of final product/ value of consumed resources. Do you maximize your resources? Is your final product worth the value of the resources it took to create it? Take into consideration the environmental impact of consuming resources (but in production, and when in use) when measuring a product’s final value.
8 Steps to Improve Your Process Efficiency in 2024
Research indicates that few businesses are aware of business process improvement methodologies such as business process management (BPM), business process improvement (BPI), and business process re-engineering (BPR).
Once business leaders use these and other models described below, they’re more likely to not only experience cost reduction and profit increase but also witness improvement in all areas of their business.
Make your business process more efficient by incorporating these models:
1. Understand and map out the current process
Use models like a Business Process Modeling Notation (BPMN) diagram, flowchart, swimlane diagram, value stream map (VSM), or process mapping to examine your processes. Supplement with Root Cause Analysis, Cause and Effect Analysis, business process analysis, or the 5 Whys to track the problem to its origins.
At the same time, figure out what’s working well with your systems and optimize those strengths.
Total quality management (TQM) can also help you figure out bottlenecks and loopholes in your enterprise as it focuses on providing unremitting quality customer services in all areas of your operations.
2. Gather feedback from various employees involved in the process
The Kaizen methodology, made up of the words Kai (change) and Zen (good), is an incremental system of change for fostering ongoing improvement. The reputed program starts and ends with involving employees in your plan. Speak to those who are affected by the system and solicit their opinions and ideas for change.
Strategies for making focus groups or group sessions work include:
- Brainstorming where you mine for a group’s ideas then narrow your list to possible solutions.
- An Impact Analysis to analyze the likely results of suggested ideas.
- A Risk Analysis to understand potential risks of those suggested ideas.
- A Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) to identify possible risks and points of failure within your team’s ideas.
3. Identify improvement opportunity areas in your current process
The best model for this step is the Kaizen framework with its five Ws and 2 H.
Five Ws.
- What: Describe the actions, steps, project, process. What is it? What has to be done?
- Why? Does this project or process add value to your service or customers? If not eliminate it.
- Where will it be done? In the best location? If not, adjust
- When will it be done? Is that the best time/ date/ deadline? Or should it be rescheduled for better results?
- Who, or which staff workers are responsible for those operations? Are they the best for the job?
Two Hs:
- How will it be done? Could you simplify it? Make it more efficient?
- How much will it cost to make? What’s involved? Can you scale back?
4. Set business goals to measure the success of your process improvement project(s)
Here’s where you use A/B testing or baseline testing to improve your operations. A/B testing compares two side-by-side versions of a particular situation or project (for example) and measures the difference in efficacy. Baseline testing benchmarks the performance of an application or event at its initial stage to evaluate the overall effectiveness of subsequent procedures.
Business leaders also set key performance indicators (KPIs), or quantifiable metrics, to measure the success of their initiatives.
How do you know whether you’re successful?
The journal Life Cycle Engineering suggests you can find that out by:
- Evaluating your financial results. Are you earning more than in the past?
- Using an assessment tool that contrasts your results against best-in-class comparisons. These tools help you analyze your business data, target processes that need change, and identify areas where you spend too much time and expense. They also help you compare your business to competitors and track your historical performance, among other items.
- Gather feedback from all stakeholders, either directly or indirectly, involved with your business.
5. Redesign your process to the ideal state
Improvements in business efficiency could include implementing new software, improving communication, and even hiring project managers.
Use a quality management system (QMS) and QMS implementation to foster a collaborative culture where employees aren’t afraid to make mistakes and where they become highly committed to your organization’s success.
6. Communicate the change to all stakeholders
Sit down with your team, share your findings, solicit their feedback, discuss the issues and collaboratively create a detailed action plan. The Kanban framework with its kanban board helps team members visualize projects and focus on their workflow. You can use tools such as Kotter’s 8-Step Change Model and the Change Curve to help employees handle change.
7. Implement the process change
The Lean Six Sigma model could help you here. “Lean” refers to eliminating any task or step that doesn’t provide value to your clients. (Think of McDonald’s “Made for You” production system targeted for 90 seconds).
Other models include the PDCA of the Kaizen methodology. Identify the issue (plan), adopt a solution (do), review the data for effectiveness (check) implement the plan if it’s successful (act).
8. Monitor the impact and use data to optimize
Business management software like Odoo or Apptivo are best for this stage. These tools use systems like data analytics to help you measure all aspects of your business, set key metrics and monitor whether and how change is achieved. They also help you reverse and redirect your plans if needed, optimize your resources and successfully implement continuous-improvement strategies such as Kaizen to continue your forward progress.
4 Tools to Improve Your Process Efficiency
Here are top four tools to improve your process efficiency:
1. Workflow Software
These work management tools streamline your business processes by rooting out redundant tasks, automating steps that work and providing your team with a collaborative cross-functional platform.
Leading work management products include:
- nTask, is a user-friendly and affordable solution with its single pane of glass and third-party integration tools.
- Automate.io stands out from competitors by helping you create one-to-one integrations and sync data between apps.
- Gravity Flow is an attractive option for web-based businesses with its plugin to automate and customize your business workflows
- Nifty brings your team and clients together in one collaborative single pane of glass for meetings, tasks and events.
- Trello delights with its Kanban board, lists, and cards for launching meetings and events, managing projects, organizing tasks, and customizing workflows.
2. Diagramming Tools
Images are more evocative than words. Diagramming tools help you draw the dots from where you are to where you want to be. Their visuals also fuel your decision-making process. When it comes to process efficiency, such tools are ideal in that they help you reach your goals by designing, measuring and monitoring how your operations function.
Useful diagramming tools include:
- Flowcharts that use shapes and arrows to track process-flow. Along with showing how your operations work, they can also highlight shadow tasks and other areas of distraction. Best diagram tools for flowcharts are Microsoft Office, Google and MindManager.
- Mind maps is a brainstorming technique. You spear your central topic with lines or arrows that devolve into streams of associated ideas or thoughts. Best diagram tools for mind maps are: Google (Docs, Slides, and Sheets) and Microsoft Office (Word, Excel, and PowerPoint); Note-taking tools, e.g. Microsoft’s OneNote; and MindManager.
- Organization charts help you cut out organizational drag by showing who reports to whom and who is responsible for each task. Best diagram tools for organization charts are: Microsoft Office (SmartArt in Office and PowerPoint. Visio for charts that you can add to Excel); MindManager.
- Process infographics. Similar to flowcharts, these visualizations mix text with graphics to represent your operations. Best diagram tools for process infographics are Canva, Hubspot and MindManager.
- Swimlane diagrams show which individuals are responsible for which tasks. Best diagram tools for swimlane diagrams are: Google with Docs, Sheets, and Slides – or Google Drawings for more complex diagrams; Microsoft Office (Word, PowerPoint and Excel); MindManager.
3. Digital Adoption Platforms
Digital adoption platforms (DAPs) are software tools that guide users through key tasks and help them navigate your business applications or programs. They provide visual tours, interactive guides, tutorials customized for all levels, and ongoing instruction on functionalities, among other features.
Often used for deployment and onboarding, these DAPs are perfect for making your processes leaner, in that they help you reduce the time, labor, and cost it would otherwise take you to train your new employees.
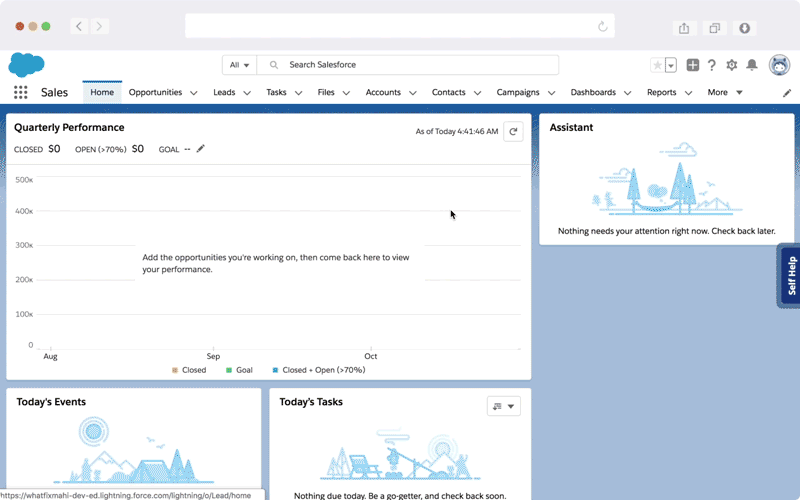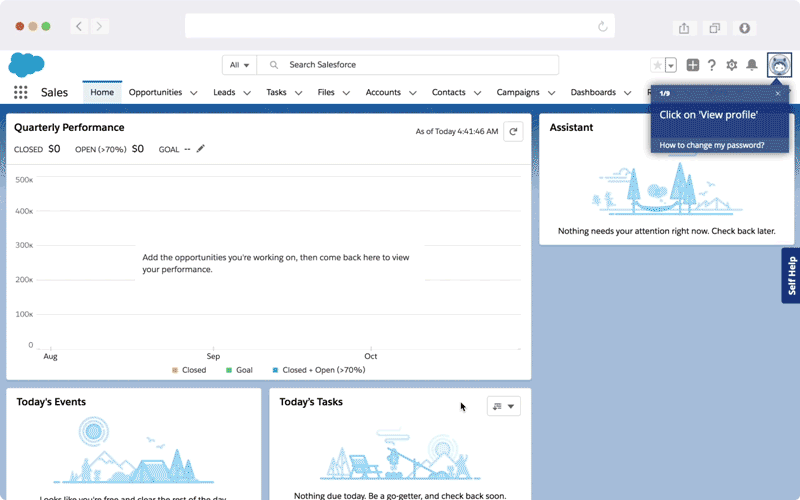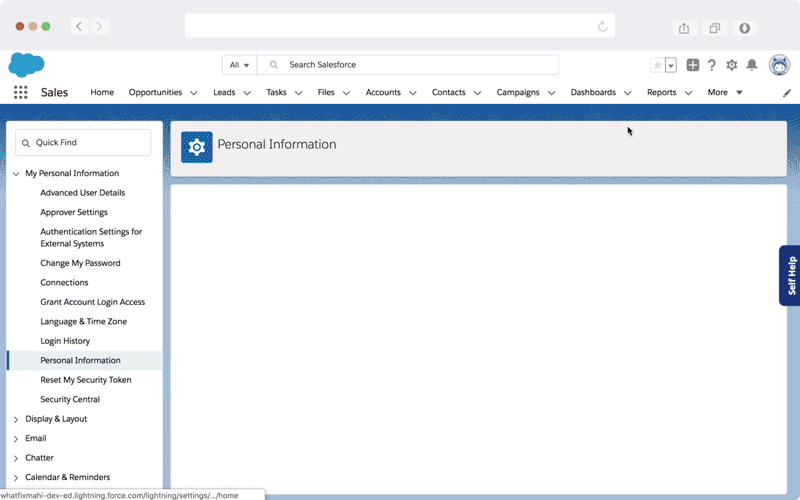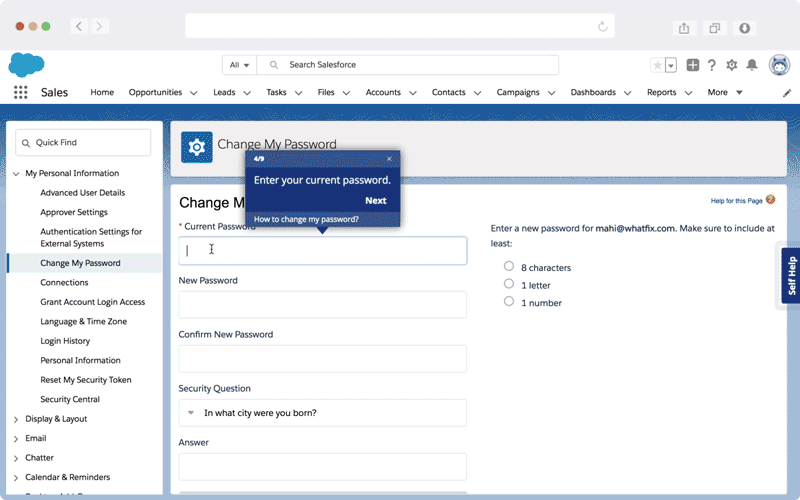
Whatfix DAP ensures effortless change rollouts for a smoother transition and experience by empowering your employees to learn in the flow of work through interactive walkthroughs and real-time in-app guidance.
Whatfix quickly brings your employees up to speed with its on-demand, personalized training experience and 24*7 availability of multi-format self-help support – all embedded directly within your applications and digital processes. Whatfix also provides its end-users with intuitive task lists and customized pop-ups to offer support in the initial stages.
4. Feedback & Survey Tools
For businesses to succeed you’ll want to know how your stakeholders evaluate your changes. Stakeholders include your shareholders, owners, customers, employees, partners and suppliers, and your community all of whom have a stake in your business. To better understand these stakeholders, you can rely on customer feedback tools.
Best customer feedback tools include:
- Clarabridge. A Customer Experience Management (CEM) platform that collects data across customer touchpoints. Clarabridge uses features like sentiment analysis, text analytics, linguistic categorization and intent detection for results
- HubSpot Customer Feedback is an online survey tool that helps you survey customers from a single dashboard that’s accessible to your team.
- SurveyMonkey is one of the best-known survey tools with its 15 types of surveys (such as multiple-choice, Likert scales, and open comments).
- CrazyEgg uses heatmaps to analyze visitor behavior for website optimization purposes. It tracks webpage items to help you improve what’s working on your website, fix what isn’t, and test new ideas.
- UserReport is a visitor opinion platform that helps you create online surveys as well as collect feedback to build a better brand or product.





