Imagine your organization as a symphony orchestra. Each department, team, and individual plays a unique instrument, contributing to the harmony that drives your business forward.
But just like any orchestra, even a slight change in rhythm—by any one performer or section—can disrupt the entire performance. To keep the orchestra playing in perfect harmony, you need a conductor who understands each instrument’s intricacies and can guide each note, ensuring all performers work together seamlessly.
In your organization, this role is fulfilled by the Change Advisory Board (CAB). Much like the conductor, the CAB orchestrates changes within your organization, ensuring that every change management project aligns with your strategic goals and that the overall performance remains flawless. The CAB isn’t just about approving or rejecting changes; it is about carefully coordinating every move to maintain the balance and rhythm of your organizational symphony.
In this article, we’ll explore the role of a Change Advisory Board (CAB), examine its key roles, and discuss best practices for running effective CAB meetings. We’ll also examine how tools like Whatfix can enhance your board’s effectiveness, helping your organization achieve its goals without missing a beat.
What Is a Change Advisory Board (CAB)?
A Change Advisory Board (CAB) is a formal committee within an organization that oversees and guides the management of change initiatives, particularly those related to IT infrastructure, systems, and processes. Composed of members from various departments and levels of the business, including IT, business units, and other key stakeholders, the CAB operates under a well-defined set of procedures and guidelines.
Its primary responsibility is to evaluate proposed changes, carefully considering their potential impact on the organization. This includes assessing the risks associated with each change, ensuring alignment with the organization’s strategic goals, and minimizing disruptions to business operations. The CAB functions efficiently by establishing clear change management roles, responsibilities, and decision-making processes, systematically managing changes to maintain stability during organizational change, and supporting overall objectives.
Roles of a Change Advisory Board
A Change Advisory Board comprises diverse roles, each contributing a unique perspective to the change management process. These key roles include:
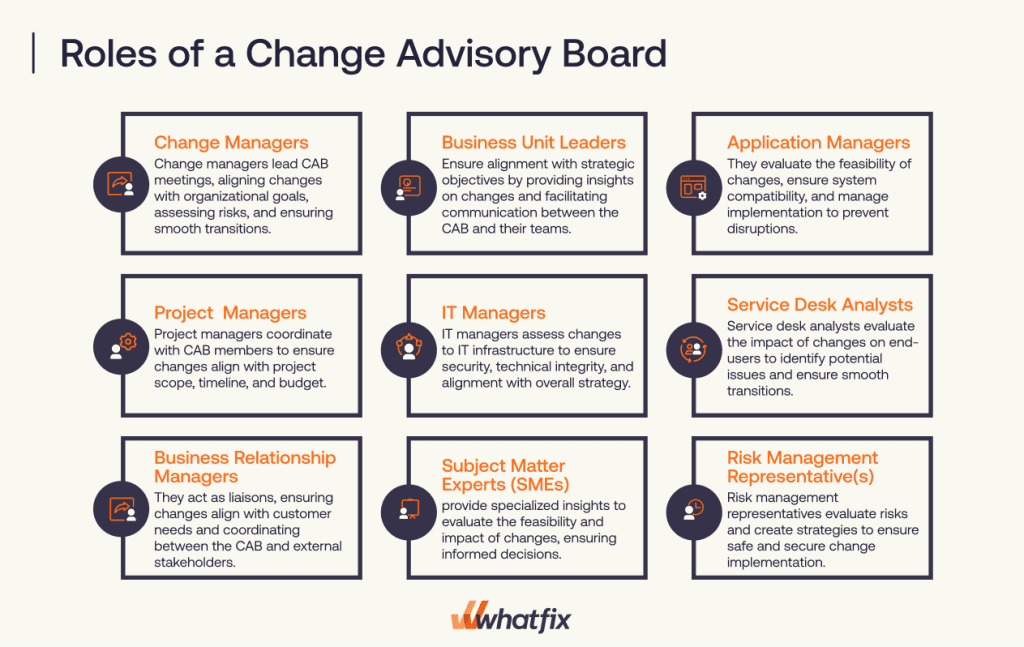
- Change Managers: Change managers lead CAB meetings, ensuring alignment with organizational goals and overseeing the evaluation, approval, and implementation of changes while conducting risk assessments to maintain stability during transitions.
- Business Unit Leaders: Business unit leaders provide insights into the impact of a change project in their areas, ensuring alignment with strategic objectives and facilitating communication between the CAB and their teams.
- Application Managers: Application managers assess the technical feasibility of changes, ensure compatibility with existing systems, and oversee the implementation to avoid disruptions.
- Project Managers: Project managers ensure changes fit within the project scope, timeline, and budget, coordinating with CAB members to align initiatives with project goals.
- IT Managers: IT managers evaluate the impact of changes on IT infrastructure, ensuring technical soundness, security, and alignment with the broader IT strategy.
- Service Desk Analysts: Service desk analysts assess how changes affect end-users, helping to identify potential issues and support smooth transitions.
- Business Relationship Managers: Business relationship managers ensure changes align with customer needs, acting as liaisons between the CAB and external stakeholders.
- Subject Matter Experts (SMEs): Subject matter experts provide specialized insights to evaluate the feasibility and impact of changes, ensuring informed decisions.
- Risk Management Representative(s): Risk management representatives assess potential risks and develop mitigation strategies to ensure safe and secure implementation of changes.
Each role within the CAB is vital in ensuring that organizational changes are evaluated, approved, and implemented with precision. Every member, from change managers to risk management representatives, contributes unique expertise to safeguard the organization’s stability and align changes with strategic goals.
By working collaboratively, these roles form a cohesive unit that drives the CAB’s success, ensuring that all changes are managed effectively and with minimal disruption to business operations.
Related Resources
Responsibilities of the Change Advisory Board
The Change Advisory Board (CAB) works as a cohesive unit to ensure that organizational changes are managed effectively and with minimal disruption. Each responsibility listed below represents the CAB’s collective effort to align changes with the organization’s strategic goals, mitigate risks, and ensure smooth transitions.
- Assessing and Prioritizing Change: The CAB collectively reviews and prioritizes change requests based on their alignment with strategic goals, urgency, and potential benefits. This collaborative approach ensures that the most impactful changes are addressed first, advancing the organization’s long-term objectives.
- Risk Analysis: Together, the CAB conducts thorough risk assessments for each proposed change, considering operational, security, financial, compliance, and reputational risks. The CAB helps safeguard the organization’s stability during transitions by identifying and mitigating these risks as a team.
- Change Communication: Effective change communication is a shared responsibility within the CAB. The board ensures that all stakeholders are informed about upcoming changes, impacts, and reasons. This collective effort minimizes resistance to change and prepares those most impacted.
- Documentation: The CAB maintains detailed documentation of all proposed changes, including the decision-making process, risk assessments, and implementation plans. This ensures transparency and accountability and provides a clear record for future reference.
- Decision-Making: The CAB is responsible for making informed decisions on approving, rejecting, or modifying proposed changes. This involves weighing the benefits and risks and considering the input from various stakeholders to align decisions with organizational goals.
- End-User Onboarding and Training: The CAB oversees end-user training development and delivery to ensure users are prepared for changes. This collective responsibility ensures that employees have the knowledge and skills to adapt successfully, reducing the risk of errors and increasing adoption rates.
In fulfilling these responsibilities, the Change Advisory Board plays a pivotal role in managing the complexities of organizational change. By carefully assessing, communicating, and managing changes, the CAB helps the organization navigate transitions smoothly, ensuring that each change contributes positively to the organization’s objectives.
CAB Meeting Structure and Processes
Effective Change Advisory Board meetings are critical to the success of change management initiatives. A well-structured CAB meeting ensures that changes are evaluated thoroughly, risks are assessed accurately, and decisions are made with the organization’s best interests in mind.
Below, we outline the key components of a CAB meeting structure, including the frequency of meetings, typical agenda items, and best practices for documentation and record-keeping.
Frequency of CAB Meetings
The frequency of CAB meetings can vary depending on the organization’s size, industry, and the volume of managed changes. However, most organizations hold CAB meetings regularly to maintain momentum and ensure timely decision-making. Common frequencies include:
- Weekly Meetings: CAB meetings are often held weekly in organizations with frequent changes, especially in dynamic industries such as technology or finance. This allows for a consistent review of change requests and ensures that urgent changes are addressed promptly.
- Bi-Weekly or Monthly Meetings: Organizations with fewer changes may opt for bi-weekly or monthly CAB meetings. This frequency is often sufficient to review and manage change requests without overwhelming the board or delaying decision-making.
- Ad-Hoc Meetings: In addition to regular meetings, ad-hoc CAB meetings may be convened to address emergency changes or critical issues that arise outside the regular meeting schedule. These meetings are typically called when urgent decisions are needed to mitigate risk or prevent disruptions.
Typical Agenda for CAB Meetings
A structured agenda is vital for running effective CAB meetings. The agenda ensures all relevant topics are covered, discussions remain focused, and decisions are made efficiently. A typical CAB meeting agenda may include the following items:
- Review of Previous Meeting Minutes: The meeting often begins with a review of the minutes from the previous CAB meeting. This helps ensure continuity and allows the board to follow up on any pending actions or unresolved issues.
- Change Requests Overview: The board reviews a list of all new change requests submitted since the last meeting. Each request is briefly introduced, and key details such as the type of change, affected systems, and the urgency of the change are highlighted.
- Risk Assessment: The board conducts a risk assessment for each change request. This involves evaluating the potential impact of the change on the organization’s operations, security, compliance, and overall business objectives.
- Discussion and Decision-Making: After the risk assessment, the board discusses each change request in detail. The CAB members may ask questions, seek clarifications, and debate the merits of the change before deciding to approve, reject, or request further information.
- Implementation Planning: For approved changes, the board may discuss the implementation plan, including timelines, resource allocation, and any additional steps needed to minimize disruption during the change.
- Review of Ongoing Changes: The board reviews the status of changes currently being implemented. This includes monitoring progress, addressing issues that have arisen, and ensuring that the changes remain aligned with the organization’s goals.
- Any other Business: The meeting concludes with a discussion of any additional topics not covered in the main agenda. This may include updates on change management processes, upcoming initiatives, or stakeholder feedback.
Documentation and Record-Keeping for CAB Meetings
Proper documentation and record-keeping are vital for maintaining accountability and ensuring that decisions made during CAB meetings are communicated and followed up on.
Best practices for documentation include:
- Meeting Minutes: Detailed minutes should be recorded for each CAB meeting, capturing key discussions, decisions, and action items. Minutes should be distributed to all CAB members and relevant stakeholders promptly after the meeting.
- Change Request Log: A centralized log of all change requests should be maintained, tracking the status of each request from submission through approval, implementation, and review. This log helps ensure that all changes are managed consistently and transparently.
- Risk Assessment Records: Documentation of risk assessments conducted during CAB meetings should be kept on file. These records provide a reference for future decisions and help demonstrate due diligence in managing organizational risks.
- Decision Records: The CAB’s decisions, including approvals, rejections, and deferrals, should be documented. This helps prevent misunderstandings and ensures all stakeholders know the board’s decisions.
By following a structured meeting process, maintaining clear documentation, and holding CAB meetings at appropriate intervals, organizations can effectively manage changes and minimize disruptions to their operations.
Best Practices of Effective CAB Meetings
Implementing best practices that optimize Change Advisory Board meetings’ structure, process, and outcomes is essential to ensuring they are productive and aligned with organizational goals.
Here is a detailed guide on the best practices for running effective CAB meetings.
1. Assess existing CAB structures and gaps
To ensure the effectiveness of CAB meetings, it is vital to assess the existing CAB structure and regularly identify gaps. This involves evaluating the board’s current roles, responsibilities, and processes to pinpoint areas that could be improved.
By identifying and addressing these gaps, organizations can enhance the efficiency of their CAB meetings, ensuring that discussions are focused, decisions are well-informed, and the board remains aligned with the organization’s evolving objectives.
2. Establish clear CAB agendas
A well-defined agenda is critical for keeping CAB meetings focused and effective. Before each meeting, outline the specific change requests to be discussed and the associated risks, benefits, and potential impacts. Distribute the agenda in advance so all members can prepare and contribute effectively. Clear agendas help prevent meetings from veering off track and ensure that all relevant topics are covered.
3. Identify your CAB’s owner
Every effective CAB needs a designated leader or owner responsible for overseeing the board’s operations. This person ensures that meetings are scheduled, agendas are prepared, and decisions are communicated and followed up on. The CAB owner is crucial in maintaining the board’s focus and ensuring it remains aligned with the organization’s strategic goals.
4. Document processes for choosing change projects
Establishing a formal process for selecting and prioritizing changes is critical for consistency and fairness. Documenting the change control processes ensures that all change requests are evaluated against the same criteria, including risk, cost, impact, and alignment with business objectives. Clear process documentation also helps maintain transparency and accountability within the board.
5. Foster open communication and collaboration
Encourage open communication among CAB members to facilitate collaborative decision-making. This includes creating an environment where all members feel comfortable sharing their insights, concerns, and suggestions. Effective collaboration within the board can lead to more informed decisions that better serve the organization’s needs.
6. Conduct thorough impact and risk assessments
One of the CAB’s primary responsibilities is to assess the potential impact and risks of proposed changes. Best practices involve conducting a detailed analysis of how each change might affect different areas of the organization, including IT systems, business processes, and stakeholder interests. Thorough impact and risk assessments help the CAB make informed decisions that minimize disruptions and align with the organization’s goals.
7. Determine cadence for meetings, follow-ups, and reviews
A consistent meeting schedule is essential for maintaining momentum and ensuring timely decision-making. Additionally, a cadence for follow-ups and reviews should be set to track the implementation and effectiveness of approved changes. Regular reviews allow the CAB to assess whether changes deliver the expected outcomes and make adjustments as needed.
When implemented, these practices can significantly enhance the effectiveness of CAB meetings, ensuring that changes are managed effectively (and efficiently) with minimal disruption to the organization.
How Whatfix Supports Change Advisory Boards
Just as a conductor relies on precise tools and techniques to lead an orchestra, your Change Advisory Board (CAB) needs the right instruments to guide your organization through complex changes.
Whatfix serves as the digital conductor’s baton, ensuring that every department and individual in your organization can work together seamlessly during periods of change. With its suite of in-app guidance and support tools, Whatfix empowers the CAB to orchestrate change effectively, keeping your organizational performance aligned and ensuring that every change initiative is executed precisely.
1. Increase user adoption with interactive flows
One of the most challenging aspects of change management is ensuring that employees adopt new tools and processes.
Whatfix addresses this challenge with interactive flows that guide users step-by-step through complex tasks within the application. By embedding these flows directly in the software, Whatfix enables employees to learn by doing, reducing the learning curve and ensuring the entire organization is aligned with the change.
This support is crucial for the CAB, as it allows them to ensure that changes are effectively implemented and that all team members can confidently navigate new systems.
2. Real-time feedback for immediate action
To effectively manage change, the CAB needs to have access to real-time insights into how employees are interacting with new systems. Whatfix provides real-time feedback by capturing immediate insights into user behavior, enabling the board and change agents to quickly identify where users are struggling or which features are underutilized. This information allows for rapid adjustments to the change management plan, ensuring the transition remains on track and employees feel supported.
3. Contextual support with smart tips
Immediate and contextual support is critical for employees to transition to new processes smoothly. Whatfix’s Smart Tips offer just-in-time assistance, delivering in-app guidance precisely when users need it without disrupting their workflow. These customizable tips allow the CAB and people managers to address specific challenges directly within the application, helping employees build confidence and capability as they adapt to new systems.
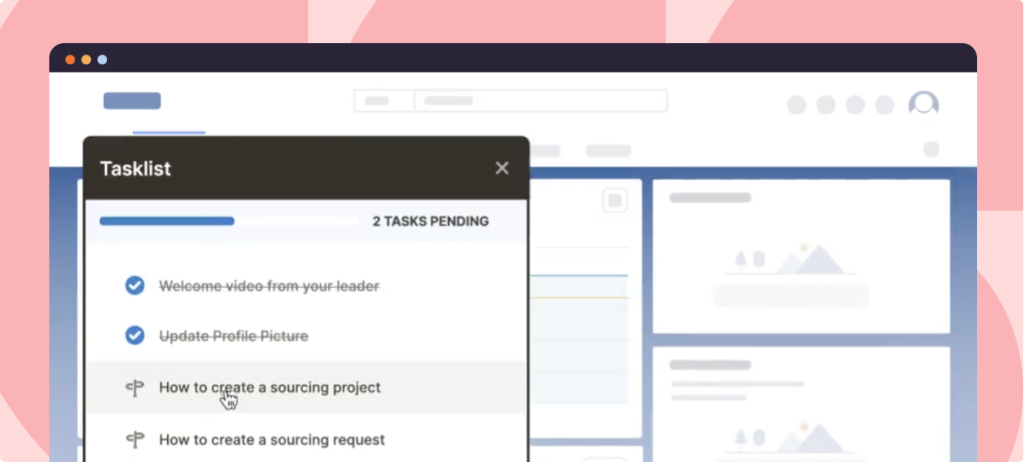
4. Streamline onboarding with task lists
Successful onboarding is critical to change management, specifically when introducing new systems or processes. Whatfix’s task lists enable project managers and end-user training professionals to break down complex onboarding workflows into manageable steps. This approach helps users track their progress and ensures no critical tasks are overlooked. By simplifying onboarding, Whatfix accelerates employees’ time-to-competency, reducing errors and supporting the CAB’s goal of a smooth and efficient change implementation.
5. Facilitate communication with beacons and surveys
Effective communication is essential for ensuring that everyone in the organization understands and supports the changes being implemented. Whatfix facilitates this communication with tools like Beacons and in-app surveys. Beacons draw attention to new features, updates, and important information within the application, ensuring that users are always informed. In-app surveys allow the CAB to gather feedback on how changes are being received, enabling proactive adjustments and enhancing overall engagement.
6. Increase user engagement with pop-ups and overlays
Keeping users engaged throughout the change process is vital for maintaining momentum and facilitating the adoption of new methods and workflows. Whatfix’s pop-ups and overlays deliver critical announcements and contextual information directly within the application, making sure users remain informed and engaged. These tools help the CAB and business stakeholders drive higher engagement and ensure the successful adoption of new practices.
Change Clicks Better With Whatfix
The Change Advisory Board (CAB) serves as the conductor, ensuring that each department, team, and individual works in harmony. The CAB maintains the rhythm, ensuring that every decision and action aligns with the organization’s strategic objectives.
However, even the most skilled conductor needs the right tools to bring out the best in each instrument. Tools like Whatfix provide the in-app guidance and support necessary to ensure that every part of the organization follows the conductor’s lead and performs at its best. By integrating Whatfix into your change management strategy, you can enhance the CAB’s ability to guide the organization through change with precision and confidence, ensuring that your business continues to thrive harmoniously with its strategic goals.
In the end, the success of your change management efforts depends not just on the structure of your CAB but also on your ability to provide the right support and guidance to your team. By combining the strategic oversight of the CAB with the real-time, practical support provided by Whatfix, your organization is not just prepared for change—it’s positioned to lead and thrive in a rapidly evolving global economic landscape.
To learn more about Whatfix, schedule a free demo with us today!