Ebbinghaus’s Forgetting Curve: How to Overcome It
- Published:
- Updated: July 22, 2024


Modern L&D teams and instructional designers are tasked with creating effective employee training programs that drive knowledge retention.
However, how can organizations ensure that the knowledge and skills acquired are retained?
An answer may lie in understanding a 19th-century psychological theory, Ebbinghaus’s Forgetting Curve.
In our pursuit of creating a competent, skilled, and adaptable workforce, we frequently confront an invisible adversary – our brain’s tendency to forget. This natural but formidable phenomenon has far-reaching implications for learning and development in the workplace.
This article explores the forgetting curve theory, first introduced by German psychologist Hermann Ebbinghaus.
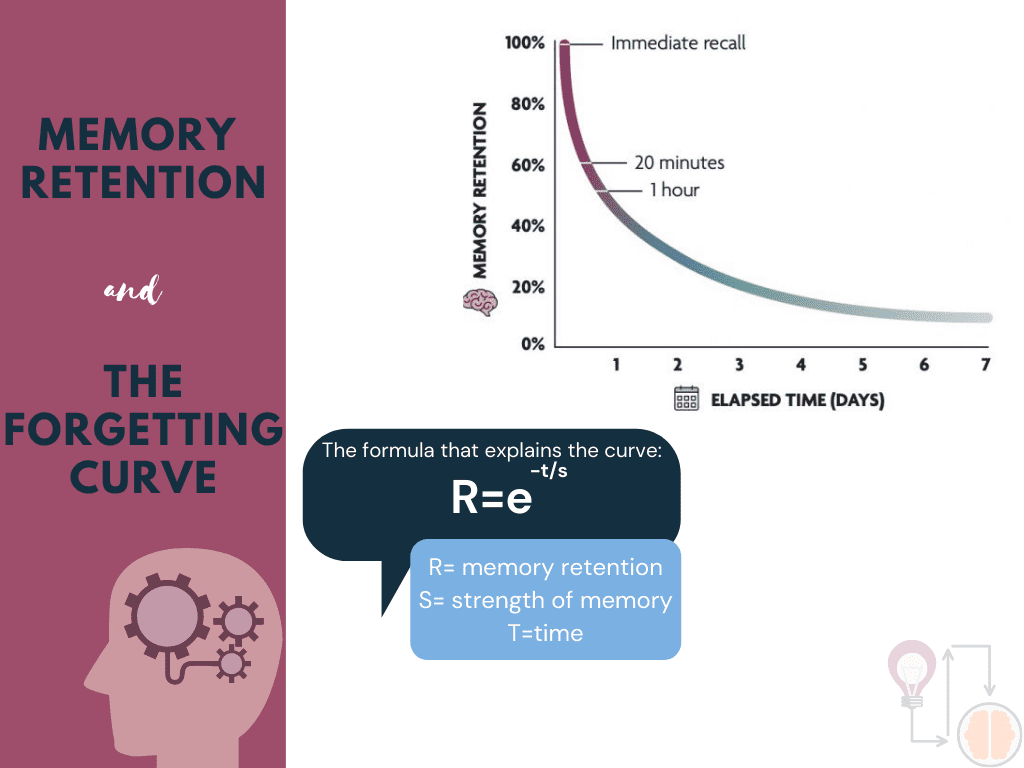
We’ll define the Forgetting Curve, which charts the decline of memory retention over time, as well as the ‘half-life’ of the curve, a crucial concept that quantifies the rate at which information is forgotten.
What Is the Forgetting Curve Theory?
The forgetting curve demonstrates the exponential rate at which information is forgotten over time when no effort is made to retain it. It is based on a psychological theory (and later mathematical formula) originated in 1885 by German psychologist Hermann Ebbinghaus. It showed learners forget information almost immediately and can overcome knowledge loss by practicing spaced learning and knowledge recall exercises. Ebbinghaus tested his memory over various periods and came up with a visual representation of how the learned information fades over time.
What Is the Forgetting Curve Formula?
The formula to calculate the forgetting curve is: R = exp(=t/S)
- R = retrievability (or memory retention)
- t = time
- S = relative strength of memory
The History of Ebbinghaus's Forgetting Curve
Herman Ebbinghaus, a German psychologist regarded as an early pioneer in studying human memory, first defined the forgetting curve. From 1880 to 1885, he conducted the study that led to his hypothesis of the forgetting curve in 1885.
He studied how he could memorize made-up syllables made up of a “consonant”-“vowel”-“consonant” (like “WID” and “ZOF”) and tested his knowledge retention over various periods of time.
Ebbinghaus’s original hypothesis was that the speed of knowledge loss was dependent on various factors, including:
- The importance of the learning material.
- The representation of the learning material.
- Physiological factors like sleep and stress.
However, his study concluded with the key finding that mnemonic skills and repetition can explain the difference in learning retention. Basic training in mnemonic techniques can enable learners to overcome differences in learning and forgetting.
His final assertion was that learning retention can increase through:
- Better memory representation through mnemonic techniques.
- Repetition based on active recall and spaced learning exercise repetition.
Spaced repetition's impact on learning
The foundation of Ebbinghaus’s theory was that each repetition in learning increases the time interval before the next repetition is needed (ie. every time you repeat a learning exercise, you slow down the exponential knowledge loss slope.)
He found that knowledge is more accessible to remember when it’s built on previous knowledge and that the forgetting curve is flattened each time an additional learning exercise is conducted. By taking a spaced learning approach, information can be solidified and the forgetting curve can be overcome.
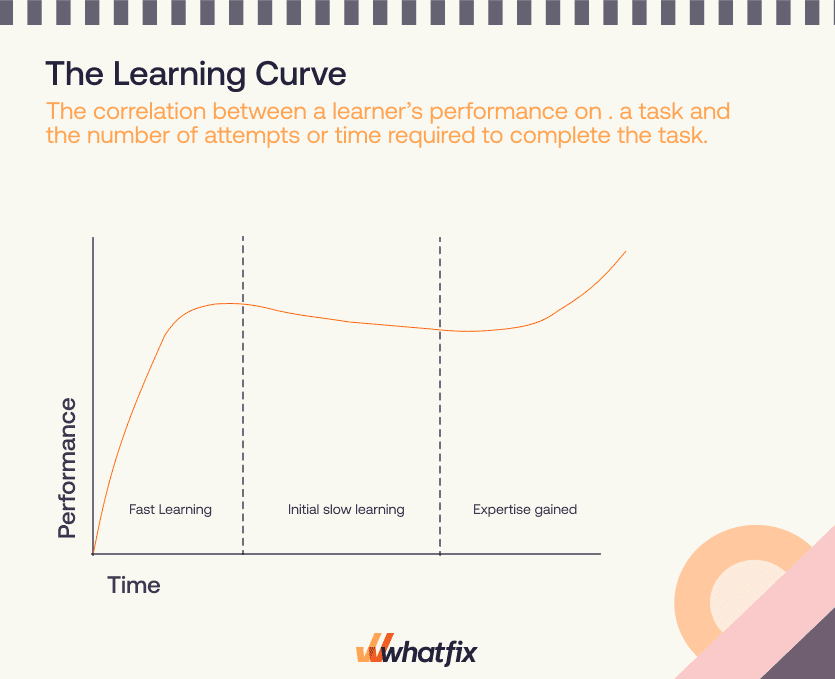
Learning curve theory
Ebbinghaus is also credited as the first person to describe the learning curve, which describes the rate a person can learn information. The basis of the learning curve theory states that the biggest increase in knowledge acquisition or task mastery happens after the first attempt and then gradually flattens for each additional exercise, meaning that less new knowledge is retained after each repetition.
What's the half-life of newly acquired knowledge?
With newly acquired information or knowledge, the forgetting curve shows that humans tend to halve their memory in days or weeks unless that information is consciously re-reviewed.
Unlearning speed depends on several factors, such as the difficulty of information, how meaningful it is to the person, how it is represented, and physiological factors such as stress and sleep.
Studies suggest that humans forget 50% of new information within an hour of learning it. That increases to an average of 70% within 24 hours.
Key Factors of the Forgetting Curve
While Ebbinghaus originally presented factors that influenced knowledge retention and loss, he (along with other psychologists) continued to refine and evolve their work on memory over time. This highlighted key factors that determine a person’s ability to retain knowledge and influences how fast a learner forgets information.
Here are the key factors that lead to the decline of knowledge retention.
- Information relevance: When our minds believe something is essential, we are more likely to remember it. This is why the significance of the information impacts how strong the memory is. The learning curve also shows us that knowledge is retained better when built on previously learned knowledge.
- Time: Humans forget 50% of new information within an hour of learning it and an average of 90% of new information is forgotten within the first seven days. This clearly states that the brain remembers less and less information as the hours and days go by.
- Complexity of learning material: Complex material may be hard to remember. The memory can only focus on so much before it starts forgetting the information. If you have nothing to connect complex material to or cannot focus on it for an extended period, it will get lost. This doesn’t mean you can’t learn complex material, you have to find ways to break down the material into pieces of information that are easier to remember.
- Presentation of material: How information is presented affects learning and how well the data is stored. You can make the same knowledge more or less memorable by changing how you communicate it. Typically, learners find it easier to absorb information 7% faster when provided visually
- Physiological factors: Physiological factors such as lack of sleep, stress, and anxiety are crucial for memory storage and brain health. Getting eight hours of sleep a night can improve your ability to restore memories from the day before. Similarly, keeping your stress and anxiety levels in check help store memories better.
How to Overcome the Forgetting Curve
Instructors, educational leaders, and L&D professionals constantly seek solutions to combat the forgetting curve and help learners retain knowledge better.
Here are eight strategies that will help you improve knowledge retention from your training.
1. Reinforce training regularly
If your organization carries out mandatory ad-hoc training events, the forgetting curve will be a constant challenge that overwhelms your employees.
As a solution, you need to create an open learning environment for employees to prioritize training and retention of relevant knowledge. Creating an open learning environment doesn’t need to be difficult. All you need to do is run frequent training events to reinforce learning and actively support knowledge sharing within your organization by conducting training days, workshops, and a thorough employee onboarding process.
Once your employees recognize that frequent learning and reiteration is part of your organization’s routine, they’re more likely to engage in training and retain critical knowledge.
2. Using different formats to deliver learning
The one-for-all approach of traditional training is no longer efficient in the digital age. They are not interactive, non-engaging, and require a large time investment from employees.
Different employees prefer different styles of learning – some are visual learners, some need hands-on experience, others require an instructor to guide them, and so on.
L&D teams must understand their employees’ learning requirements and build personalized training flows for various learning types to overcome the Ebbinghaus forgetting curve. When learning is delivered in their preferred way, employees understand the content better, which remains in their memory longer.
Some of the most common employee training methods that help boost engagement and knowledge retention are:
- eLearning: Also known as online learning, it enables employees to learn anywhere, from their desks or in the comfort of their homes, according to their individual learning styles and needs.
- On-the-Job Training: This approach involves hands-on experience within the typical working environment rather than in a classroom or online. With OJT, employees learn by observing, often working under a mentor or manager, and then putting what they’ve learned into practice.
- Instructor-Led Training: This face-to-face learning style mimics physical classroom spaces with an instructor present to lead the training session.
- Collaborative Training: A methodology where employees share their knowledge and expertise, teaching and learning from one another. This technique helps enhance the overall training experience for employees by capitalizing on their skills, ideas, and knowledge.
- Video Training: Creating training videos is one of the most effective employee training methods to engage employees and deliver sophisticated learning experiences at lower costs. Videos offer better engagement for your employees, resulting in a higher likelihood of information retention.
- Gamification Training: This type of training method incorporates gaming elements such as points and badges into your training courses. By leveraging psychology, gamified training engages learners, improves retention, and makes them more willing to take on repetitive tasks despite the risk of failure.
PRO TIP
With a digital adoption platform (DAP) like Whatfix, organizations can enable employees to learn in the of work with in-app guided experiences and on-demand performance support. With Whatfix, guide employees through contextual tasks with interactive Flows, Task Lists, and Smart Tips. With Self Help, employees can search an in-app help center to find answers to process-related questions or technical queries right inside the digital workplace.
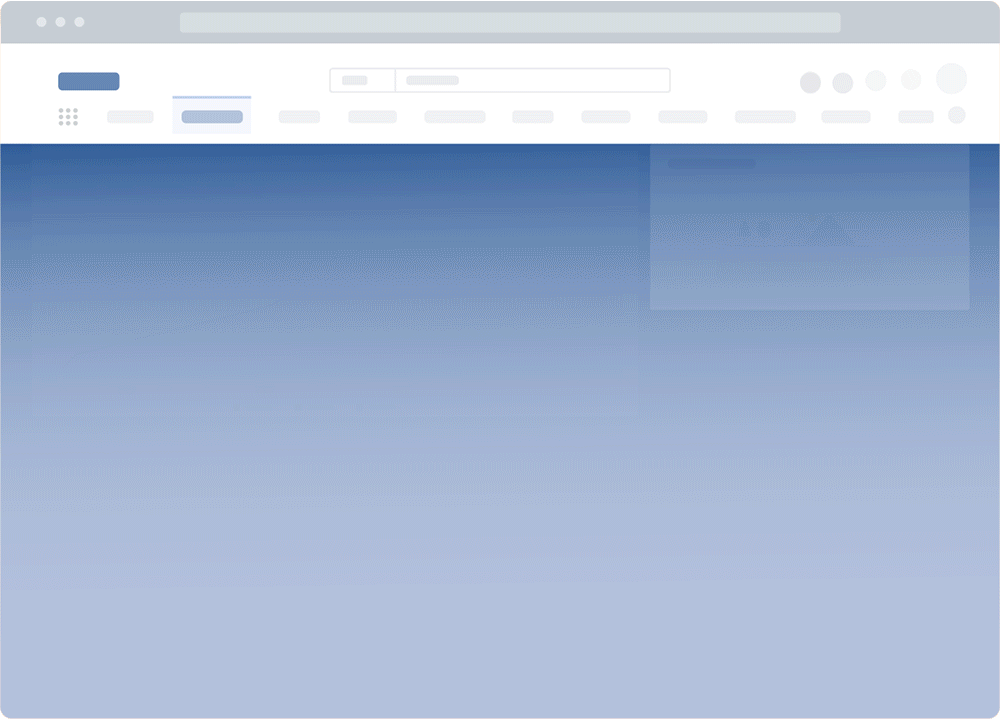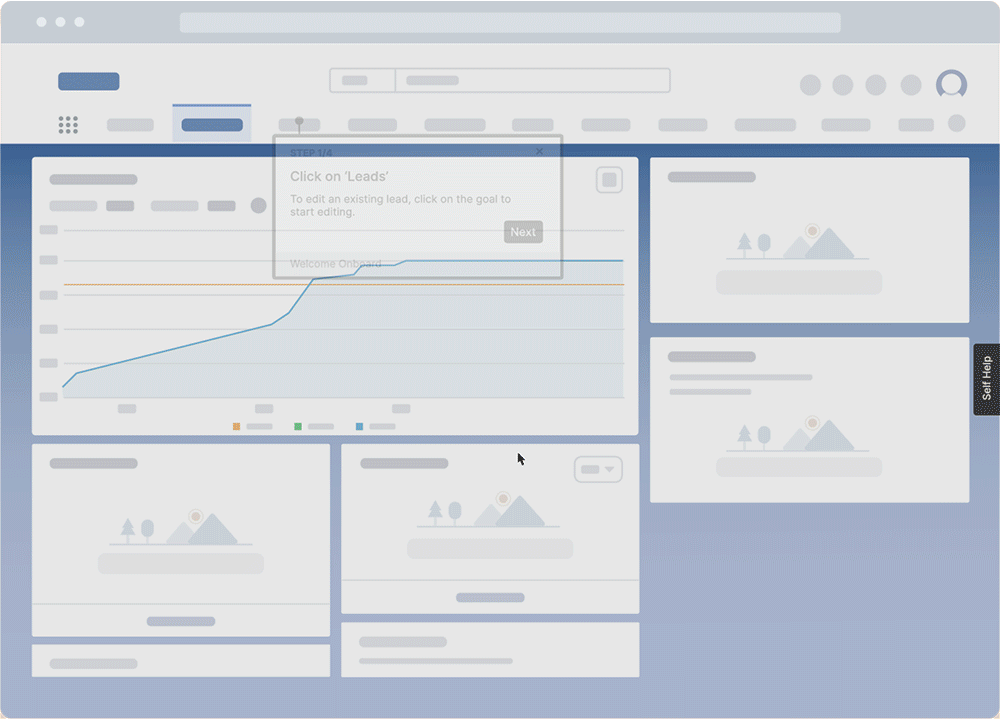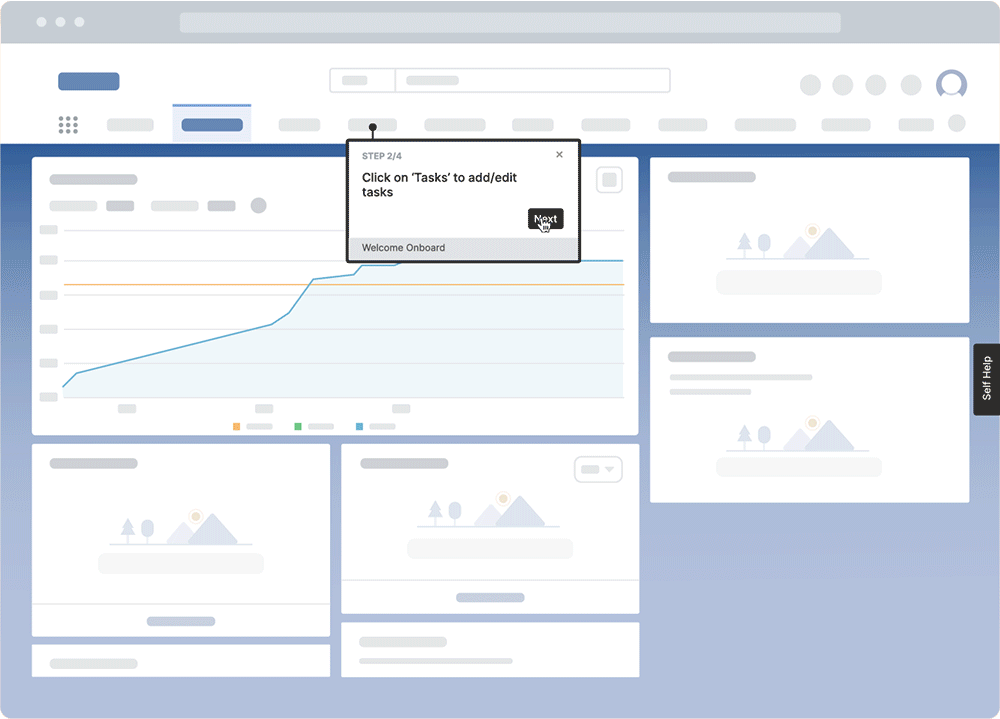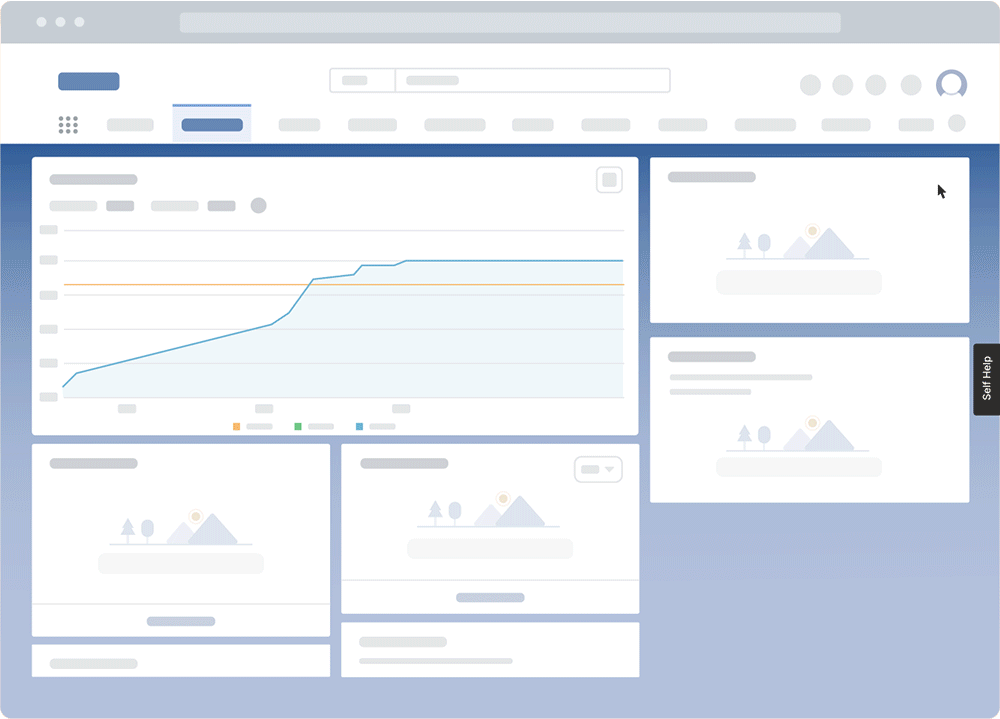
3. Keep it engaging
Learner concentration naturally wanes when asked to read large amounts of text or watch hours of presentations, which in turn reduces knowledge retention. On the other hand, when training content is engaging, it improves course completion rates and helps employees retain information for a longer time.
To overcome the Ebbinghaus forgetting curve, it is important to make your training content engaging, interactive, and easy to digest. People learn and retain better when they are being involved actively rather than observing passively.
Instead of conducting classroom training sessions or providing long training manuals for employees to read, mix things up. Keep your learner’s interest by providing varying content such as videos, images, and webinars and adding elements of gamification to the training material.
4. Learning in the flow of work
When employees have to wait for the opportunity to implement new skills or knowledge they learned in a training session, the information becomes stale and is difficult to recollect. To avoid such situations, employees need to learn within the context of their jobs and immediately apply the knowledge gained.
This is what Josh Bersin trademarked as learning in the flow of work.
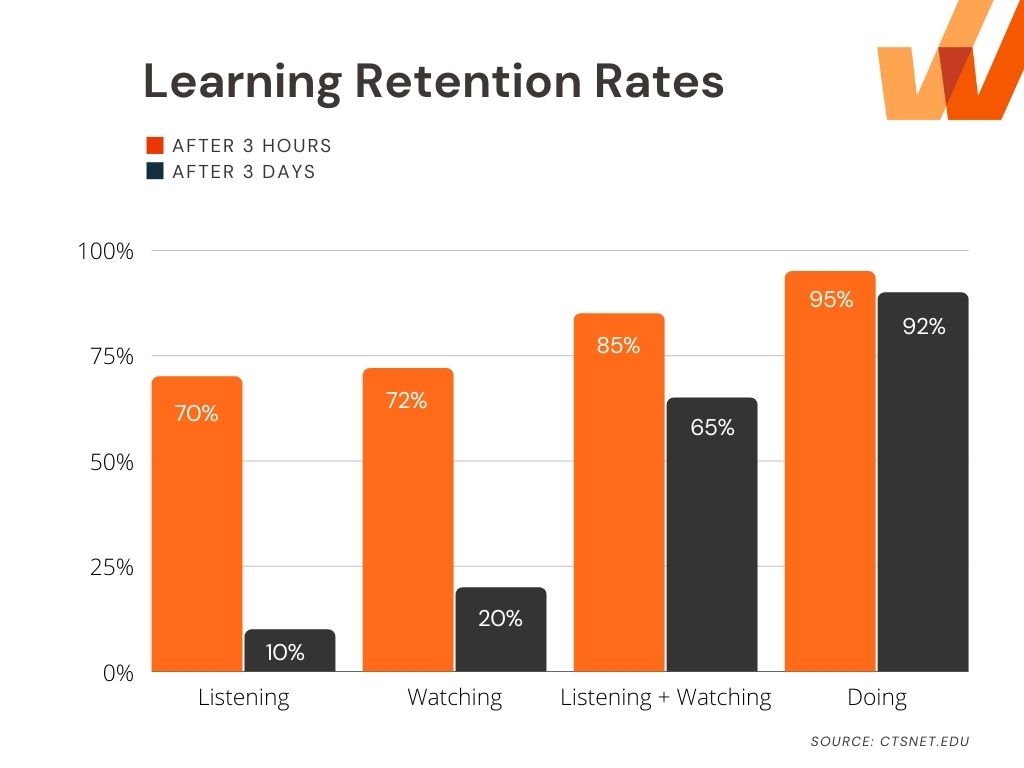
According to the learning pyramid, learners retain 75% of knowledge when they practice doing a task, compared with only 10% when reading instructions.
Learning in the flow of work is an active learning approach that allows people to absorb more information and learn while working on a software application or digital process. Applying this strategy to employee training leads to a better comprehension of technology, efficient learning, and better retention of training content.
Learning in the flow of work is much more effective than traditional training as it makes the material more meaningful and leads to in-depth understanding, greater retention, and better recall. Additionally, learning by doing is one of the simplest ways for employees to get the most out of downtime between tasks and pick up new skills without disrupting their daily routine.
5. Microlearning
Considering the fast-paced professional world and the reduced attention spans of the digital workforce, traditional long-form training programs that occur annually or semi-annually are not enough for employees to keep up with industry standards.
To ensure that employees are not distracted, properly engaged, and focused in the training programs, organizations need to introduce new learning methods in the workplace, such as microlearning.
The whole concept of microlearning is built around an employee’s actual learning cycle. In contrast to traditional classroom settings and long lectures, microlearning takes employees’ short attention spans into account and delivers information in smaller, manageable micro-packages that typically last less than 5 minutes. Microlearning is effective because learners apply the skills they’ve acquired before they lose attention, thus improving knowledge retention.
Research has shown that microlearning can improve knowledge retention by as much as 80% while improving learner engagement by 50%.
6. Spaced learning
Spaced learning is an effective learning strategy that meets the new-age corporate training needs by helping people learn as quickly and efficiently as possible while providing the added benefit of minimizing the loss of knowledge that occurs with one-time learning.
Spaced learning breaks down long employee training programs into several modules of shorter durations, with spaced intervals in between. Parts of these sessions are reintroduced multiple times over the course of the next few days or weeks for learners to recall information, driving long-term knowledge retention.
Additionally, learners practice retrieving the learned information using different formats, such as solving problems or completing assignments to recall and strengthen their learning and discover any gaps they need to focus on and relearn.
7. Relevant content
The human brain is selective and has a limited capacity. It tends to remember information with a personal meaning, whereas it loses weak and non-relevant memories in just a few hours.
Therefore, when planning your training material, it is crucial to make it as relevant to the learner as possible. The more relevant the training, the easier it is for employees to absorb and remember the information.
Now what does “relevant” mean for training materials? It means training must be relevant to the learner’s job. If they know that learning something will make their job easier or save them time, they’re more likely to accept and remember the training. The course content can be made relevant to the learners’ job function by including examples or scenarios that they experience every day.
8. Accessibility
If you want your training content to stick, it is important to make it accessible and convenient for your learners. Learners must have the ability to complete training whenever they want. This is possible with mobile learning. Mobile learning (or mLearning) is online learning via personal mobile devices. This training method empowers learning on the go, enabling users to access content whenever and wherever they want. Mobile learning content comes in various forms, such as podcasts, videos, quizzes, or eLearning courses that help increase engagement and boost learning retention.
Now that you have read tips to combat the challenge presented by the forgetting curve, learn how a Digital Adoption Platform can help apply these learnings to your L&D strategy.
DAPs augment your training programs by enabling interactive, hands-on learning directly within a software application or digital process. This method eliminates the gap between theory and practice, which automatically engages employees’ memory and accelerates learning.
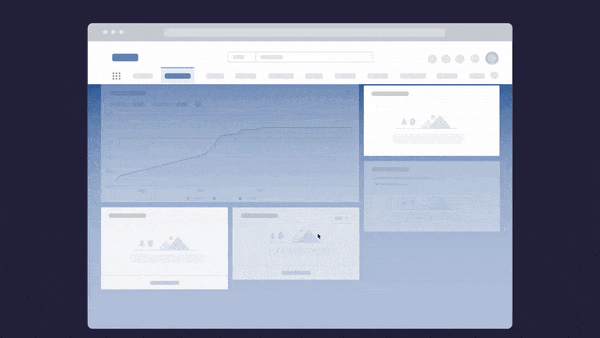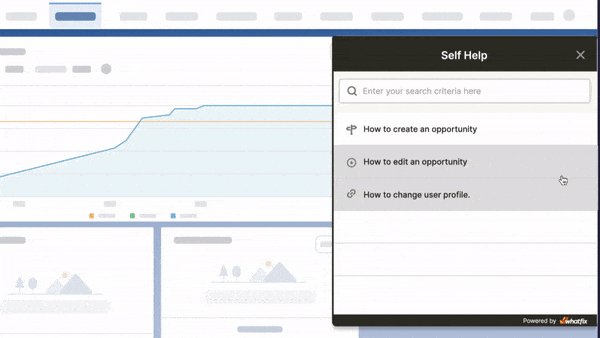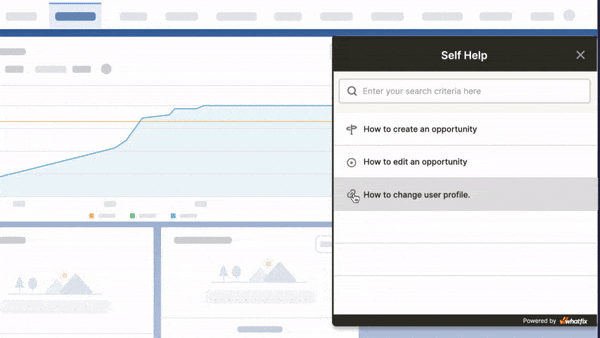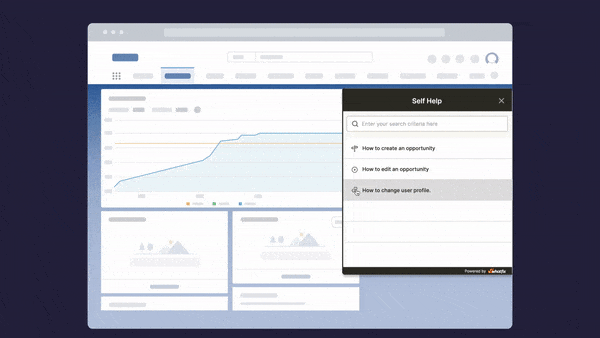
DAP helps overcome knowledge retention challenges and promotes effective employee learning:
- In-app guidance: DAP gives employees access to all relevant information, resources, documentation, and workflows they need to learn a new process or application.
- Interactive walkthroughs: Guides users step-by-step through every task or process within an application. Interactive walkthroughs are used for customer and employee onboarding and training programs to encourage a higher level of employee understanding and engagement.
- Contextual self-help: DAP provides contextual support in real-time without employees having to raise support tickets and wait for a resolution for their queries. Contextual help is provided directly inside the software and the guided steps can be immediately applied without having to break from the current task or search for answers online.
- Microlearning: DAP enables microlearning by bringing in short and concise snippets of training which are conducive to how the human brain remembers information.
- Learning analytics – DAP helps companies identify trouble spots or blind spots in employee learning. The powerful analytics tool monitors user analytics to see whether employees are getting stuck and creates additional walkthroughs or self-help articles if needed.
Schedule a free demo with our experts today to learn more about Whatfix!
Learn how to leverage Whatfix DAP to combat the Ebbinghaus forgetting curve and implement learning in the flow of work for effective, continuous employee learning.


