Corporate learning and development is undergoing a revolution. Changing workforce demographics and a dynamic market for digital products and services have changed organizational learning.
Effective long-term learning is no longer achieved with traditional, one-off classroom training sessions that overwhelm learners with too much information at once, making it difficult to retain key information.
Consider the last training program you completed. You may have found the program helpful post-training and could put that learning into action. However, as weeks pass, you realize that you no longer remember the nuances of that training program and need help to adopt it in your workflows. What happened? Why do we forget so quickly?
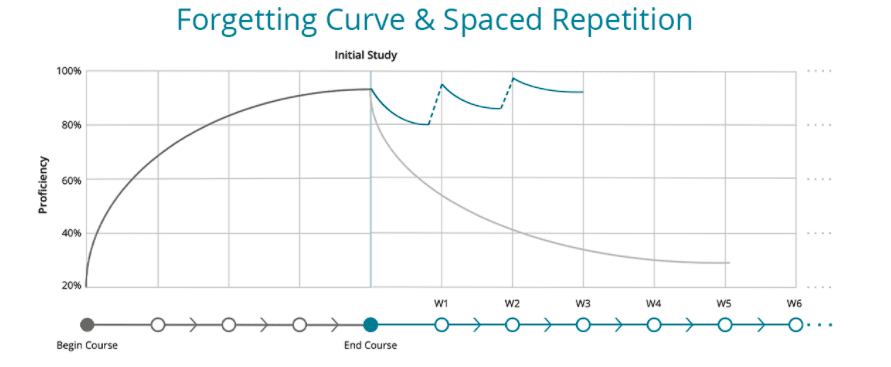
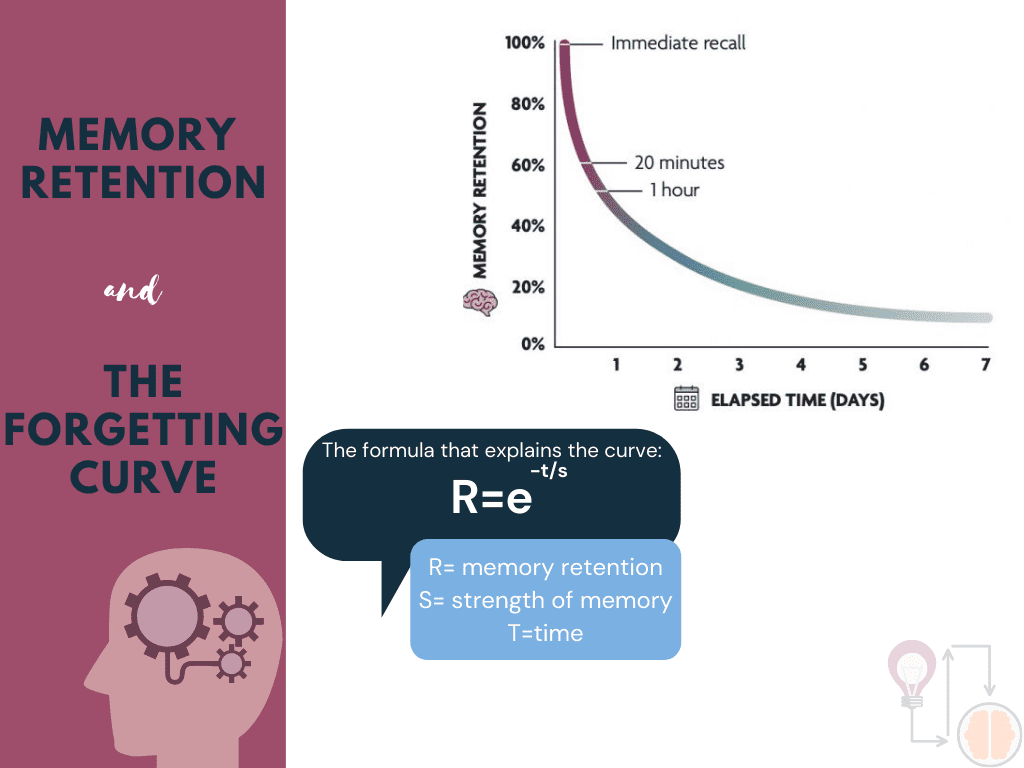
German psychologist Hermann Ebbinghaus asked similar questions. Through self-experiments, he discovered that 70% of what we learn can be forgotten within a day. This concept is called the Ebbinghaus Forgetting Curve and demonstrates the rate at which information is forgotten over time if no effort is made to retain it.
Fortunately, Ebbinghaus also identified a solution to his forgetting curve: spaced repetition. Spaced repetition, which involves spreading learning sessions over time, helps counteract the forgetting curve. By revisiting material periodically, more information is retained, and learners are better able to apply their knowledge in practical situations.
What is Spaced Learning?
Spaced learning is based on the concept that learning is enhanced when knowledge is repeated after certain intervals. Spaced learning breaks down extended employee training programs into several sessions or modules of shorter durations, with spaced intervals in between. Parts of these sessions are reintroduced multiple times over the next few days or weeks for learners to recall information, driving long-term knowledge retention.
This approach is based on the idea that repeated exposure to information, with intervals between each exposure, helps reinforce memory and enhances long-term learning retention. By revisiting the material periodically, learners can better retain and recall information, making spaced learning an effective method for deepening understanding and applying knowledge in practical situations.
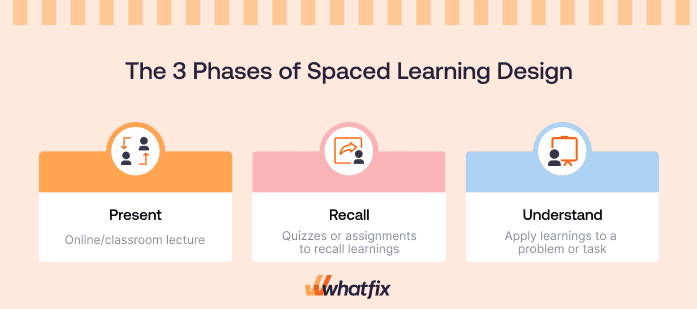
The 3 Phases of Spaced Learning Design
Spaced learning in conventional use consists of three intensive instructional periods, separated by 10-minute breaks or distracting material unrelated to the learning outcome.
These three instruction periods present the same information, each with a different emphasis. This sequence in a session is “present, recall, understand.”
1. Present
The present phase is the initial stage, where new information is introduced to learners. During this phase, the core material is delivered concisely and focused, often through lectures, reading materials, videos, or interactive activities.
The goal is to clearly understand the topic, ensuring learners grasp the essential concepts before moving on to the subsequent phases. This phase is typically short, followed by a break or an unrelated activity, allowing the brain time to process and begin encoding the information into memory.
2. Recall
The recall phase involves revisiting the information learned during the “Present” phase, encouraging learners to retrieve the knowledge from memory actively. This phase is crucial for reinforcing learning and strengthening neural connections associated with the new material. Recall activities might include quizzes, discussions, or self-reflection exercises.
The timing of this phase is strategically spaced after the initial presentation to optimize memory retention. Repeated retrieval helps move information from short-term to long-term memory, making it more resistant to forgetting.
3. Understand
The understand phase involves deeper cognitive processing, where learners synthesize and apply the recalled information. This phase might include activities that require critical thinking, problem-solving, or using concepts in new contexts.
By engaging in these higher-order thinking tasks, learners deepen their understanding and solidify their knowledge. This phase ensures that the information is remembered and meaningfully integrated into the learner’s broader knowledge base, making it more accessible for future use.
Benefits of the Spaced Learning Technique
Let’s discuss a few benefits of spaced learning.
1. Overcomes the forgetting curve
Spaced learning effectively combats the forgetting curve by reintroducing training material at strategically timed intervals, helping to reinforce memory retention. This means that employees are more likely to retain critical training information over time, reducing the need for repeated training sessions and improving long-term knowledge retention.
2. Connects to the real-world
Spaced learning allows employees to apply what they’ve learned in real-world situations between learning sessions, helping to bridge the gap between theory and practice. This ongoing application of knowledge reinforces learning and helps employees see the relevance of their training in their day-to-day work.
As they encounter real-world challenges, employees can recall and apply what they’ve learned, leading to better problem-solving and decision-making skills.
3. Reduced mental exhaustion
Another advantage of using spaced learning in employee training is that information is delivered in short bursts. Shorter learning modules prevent fatigue, reduce mental exhaustion, and keep learners engaged with the content.
4. Improved understanding of complex concepts
Spaced learning facilitates a deeper understanding of complex concepts by allowing time for reflection and repeated exposure. Each learning session builds on the last, gradually increasing complexity as the learner’s understanding deepens. This method is particularly effective for topics requiring a nuanced understanding or critical thinking, as it allows one to revisit and refine one’s knowledge over time.
How to Implement the Spaced Learning Method
Here’s how to implement the spaced learning method for your workforce.
1. Identify learning objectives
Start by identifying the specific skills, knowledge, or behaviors you want your employees to acquire after the training program. Clearly defined training objectives help design a structured, spaced learning program tailored to your organization’s needs.
Ensure that these learning objectives align with the organization’s broader goals, such as improving productivity, enhancing customer service, or driving innovation. Every training program’s success requires buy-in from stakeholders. Therefore, before designing the spaced learning program, speak with the business partners to determine whether it meets their needs.
2. Identify the learning timeframe
Identify the maximum number of hours each learner needs to participate in the training program to obtain a commitment to schedule that time for learning. Learning periods can last as little as 30 minutes each day to a few hours each week, depending on the complexity of the training course, the time between training and implementing the learning, and the learner’s experience.
3. Combine spaced learning with microlearning
Microlearning is another important principle of learning and is closely related to spaced learning. Microlearning refers to breaking the learning content into small, bite-sized information modules rather than overwhelming the learners with too much information at once.
Smaller learning sessions offer just the information necessary to achieve a specific objective. This concept fits perfectly with spaced learning as you can deliver shorter nuggets of information with intervals in between.
4. Schedule your spaced repetition intervals and sessions
Schedule the learning sessions at intervals that allow for initial learning, followed by periods of review spaced out over time. Depending on the complexity of the material and the retention needs, this could be days, weeks, or even months apart.
Here’s an example of what a typical spaced repetition schedule looks like:
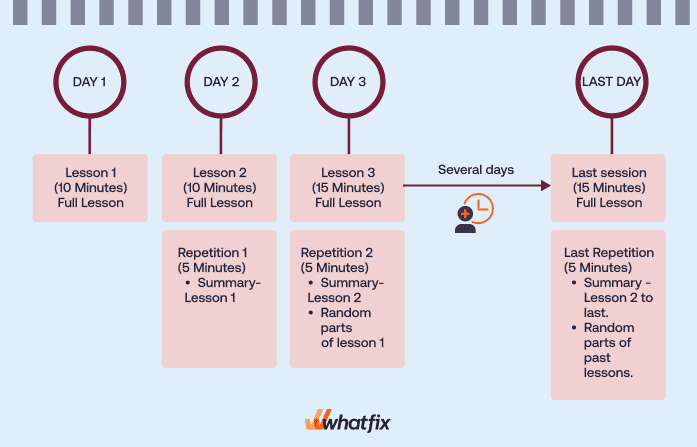
The research by Ebbinghaus highlighted that the first few repetitions must be made within a few days. As retention improves with time, repetition can be made within weeks or months, depending on how long the course lasts.
To simplify this process, keep in mind that there is no fixed optimal spaced period; it depends on the targeted retention interval. If you want to maximize performance on a test that is one week away, then a one-day spaced approach would be optimal. However, if the information needs to be retained for an entire year, a two-month spaced approach between learning sessions would be ideal.
5. Associate new knowledge with old knowledge
Learning content must be connected and grouped into related concepts to help learners create patterns between previously learned training material and the new learning content.
Designers must make associations and include examples and stories that integrate an underlying connection between two subjects or ideas. Stories are a great way to recall old topics and connect them to new ones while assuring maximum connection and understanding of how old and new topics fit together.
6. Repeat content in different formats
One key aspect of spaced learning is mixing up the learning approach. People engage better and absorb information thoroughly when received in different formats. Separate your learning material into bite-sized chunks of eLearning, making sure that each concept is repeated in various contexts, such as training videos, audio presentations, scenarios, case studies, gamification, or simulation training.
Implementing different training methods prevents boredom, caters to different employees’ different learning styles, keeps employees engaged in the program, and increases knowledge retention.
7. Incorporate active recall techniques
After each session, incorporate activities that require learners to recall the information, such as quizzes, flashcards, or practice exercises. Active recall reinforces memory and helps transfer knowledge from short-term to long-term memory.
Use different methods to keep the recall process engaging, such as peer learning, case studies, or problem-solving exercises related to the content.
8. Conduct a debriefing session
Include facilitator-led debriefing sessions where learners share the value of the information presented during the spaced learning program. These allow learners to review the training modules, self-correct, improve their future performance, and discuss any pitfalls and successes experienced during the course.
The facilitator guides these discussions, acknowledges the thoughts and feelings of the learners, addresses any doubts or misconceptions in the content, and highlights positive takeaways from the learning intervals.
9. Track results
Use data analytics to monitor the effectiveness of the spaced learning program. Track metrics such as engagement levels, quiz scores, and application success rates to determine if the learning objectives are being met.
Additionally, gather regular feedback from participants to understand their experiences and identify areas for improvement.
Challenges of the Spaced Learning Technique
Here are a few challenges you might encounter while implementing the spaced learning technique for your corporate programs.
1. Balancing spacing with curriculum timelines
One of the primary challenges of implementing spaced learning is finding the right balance between the spacing intervals and the constraints of the curriculum timeline. Organizations often have deadlines and schedules that must be adhered to, making it challenging to integrate spaced intervals effectively.
2. Overcoming resistance to new learning methods
Learners may be skeptical of the effectiveness of spaced learning, especially if they are used to cramming or intensive, short-term learning sessions. Instructors may also resist changing their teaching methods or might feel that spaced learning complicates the instructional process.
3. Monitoring and adjusting spaced learning intervals
One of the primary challenges of implementing spaced learning is finding the right balance between the spacing intervals and the constraints of the curriculum timeline. Organizations often have deadlines and schedules that must be adhered to, making it challenging to integrate spaced intervals effectively.
Spaced Learning FAQs
What is Ebbinghaus’ Forgetting Curve?
The Ebbinghaus forgetting curve demonstrates the rate at which information is forgotten over time when no effort is made to retain it.
What is the definition of spaced learning?
Spaced learning is based on the concept that learning is enhanced when knowledge is repeated after certain intervals.
How do I create a spaced learning corporate training program?
1. Meet with business leaders
2. Identify the learning timeframe
3. Combine spaced learning with microlearning
4. Repeat content in different formats
5. Conduct a debriefing session
6. Track results with quizzes
Training Clicks Better With Whatfix
To effectively overcome the challenges associated with the forgetting curve, consider implementing a digital adoption platform such as Whatfix.
Whatfix augments your training programs by enabling interactive, hands-on learning directly within a software application. This method eliminates the gap between theory and practice, which automatically engages employees’ memory and accelerates learning.
DAP helps overcome knowledge retention challenges and promotes effective employee learning via:
- Interactive walkthroughs: Guides users step-by-step through every task or process within an application. Interactive walkthroughs are used for onboarding and training programs to encourage a higher level of understanding and engagement.
- Learning in the flow of work – Contextual training content is embedded directly within the applications that employees use every day. This approach ensures that learning is continuous and seamlessly integrated into daily workflows, reducing disruption and improving retention.
- Continuous performance support: Whatfix offers continuous performance support through features such as step-by-step walkthroughs, tooltips, and FAQs, ensuring that employees have access to the right information at the right time.
- Learning analytics – By analyzing user behavior, engagement with training content, and performance data, organizations can gain insights into which areas need improvement and which training methods are most effective.
To learn more about Whatfix, schedule a free demo with us today!