Over the past decade, organizations have adapted to an ever-changing corporate world by adopting new digital processes and technologies to become more successful, driving efficiency, productivity, and revenue through digital transformation.
To keep up with the “fourth industrial revolution” (or “Industry 4.0”), organizations must invest in a corporate learning and development (L&D) strategy to provide a framework for reskilling and upskilling their workforce to meet the demands of these new enterprise challenges.
The growing need for an established L&D function has captured the attention of the C-suite. LinkedIn’s Executive Confidence Report found that 90% of executives plan to increase their L&D budget over the next year to overcome growing skill gaps and enable employees.
In this article, we explore the world of learning and development, provide steps to create a corporate L&D strategy, showcase L&D’s impact, break down its essential elements, look at L&D examples of effective learning organizations, and the factors that influence the success of L&D strategies.
What Is a Learning and Development Strategy?
A learning and development (L&D) strategy is a systematic and comprehensive plan that outlines how an organization trains and develops its workforce, improves employee skill sets, and establishes companies as learning organizations. An L&D strategy is a strategic framework that aligns with an organization’s employee training objectives, identifies the learning-related needs of different employees, and outlines the actions and initiatives required to address those needs.
A well-crafted L&D strategy encompasses various learning methodologies, approaches, and resources to support employee growth and drive organizational success. It outlines the key L&D focus areas, learning objectives, training programs, and training evaluation methods to ensure the development of a skilled and engaged workforce capable of meeting current and future workplace challenges.
10 Steps For Building an Effective L&D Strategy
While every enterprise will have contextual needs that will shape their L&D strategy, there are core fundamentals all L&D teams must consider when building out their program.
Here are ten steps for organizations to craft an L&D strategy that is effective and engaging:
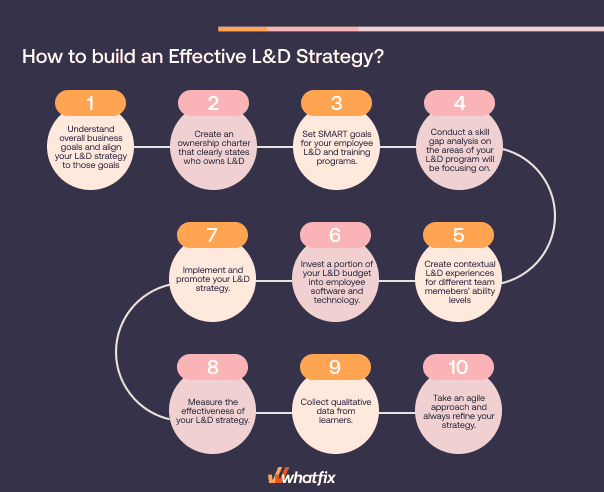
1. Align L&D goals to business needs
As with all corporate programs, you must first understand overall business goals and align your L&D strategy with organizational goals. This directs the L&D and HR teams tasked with creating your L&D strategy – and what types of upskilling and skill development they’ll need to accomplish to achieve training ROI.
Tying business objectives, goals, and strategies to your L&D framework provides a blueprint for securing leadership buy-in and getting them to invest proper resources into your learning strategy for developing talent.
Examples of tying business outcomes to L&D goals include:
2. Determine ownership of L&D between HR and individual department heads
Before developing your L&D strategy, you’ll need to define clear ownership of the project. This can be a major L&D challenge for enterprises, especially those with less common organizational structures.
Post-COVID, many larger organizations have created dedicated L&D teams and have invested a larger budget and more resources in that L&D strategy (LinkedIn Workplace Learning Report.)
For SMB organizations, learning and development typically falls under the HR umbrella.
You’ll need to create an ownership charter that clearly states who owns L&D – is it the HR department? Individual team leaders? A new, dedicated L&D department that reports directly to the C-suite?
No matter the ownership structure, be sure to create a cross-functional team incorporating individuals from various departments across your organization. This allows you to get input on upskilling and reskilling needs across different business functions – as well as secure buy-in from all leaders throughout your organization.
3. Set clear corporate L&D and training goals
After assigning ownership and understanding business goals, it’s time to set clear objectives for your employee L&D and training programs. These should be tied back to organizational development and be people-centric. Make these goals SMART (ie. specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound.)
Also, make your goals accessible and visible across the organization to improve transparency on the purpose of your L&D strategy.
4. Conduct a skills gap analysis
Once you understand the goals of your L&D strategy, conduct a skills gap analysis on the areas your L&D program will be focusing on. This will be different across business departments – and you may need to create a few different skill gap analyses (i.e., think of analysis for the accounting team, the marketing team, etc. – as well as an analysis for leadership, manager training, etc.)
Once completed, you’ll have a better understanding of the depth of reskill training needed for different departments and individual employees. This will allow you to be hyper-targeted in your approach, create personalized learning experiences, and focus more resources on the areas of greatest need.
5. Design contextual learning paths for different roles
With the skills analysis complete, use this information to create contextual L&D experiences for different team members’ ability levels. Try incorporating different employee training methods, as well as various multimodal learning formats such as video, audio, reading, and interactive training content to cater to different learning styles.
Repurposing L&D content into interactive, in-app experiences that provide employees answers to their problems in the flow of work is a major L&D trend – and should be incorporated into your employee learning journeys.
With a digital adoption platform (DAP) like Whatfix, L&D leaders are empowered with a no-code editor to create in-app content that overlays on their digital applications and processes. With a DAP, L&D teams can empower employees with a more engaging experience that walks them through contextual workflows and processes.
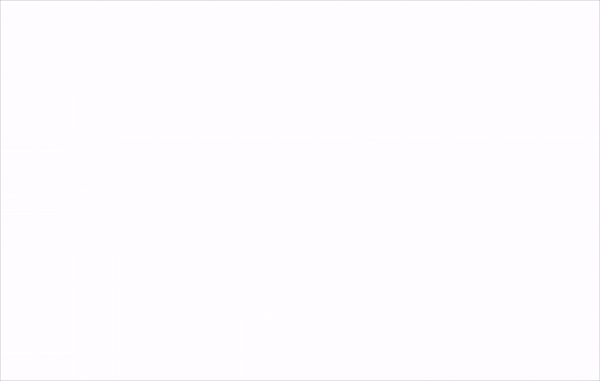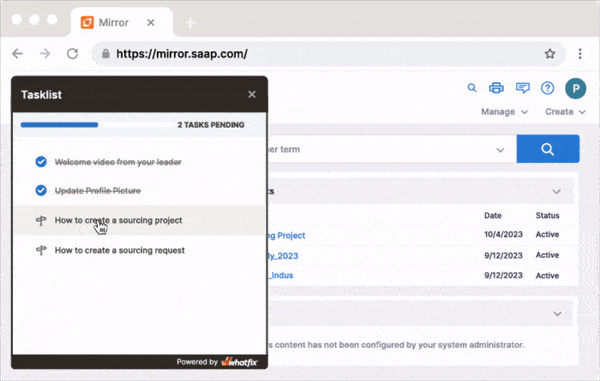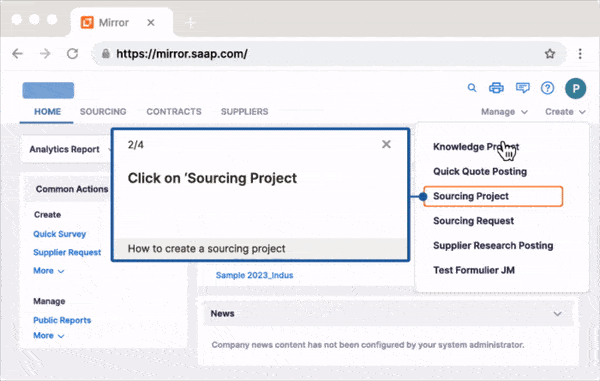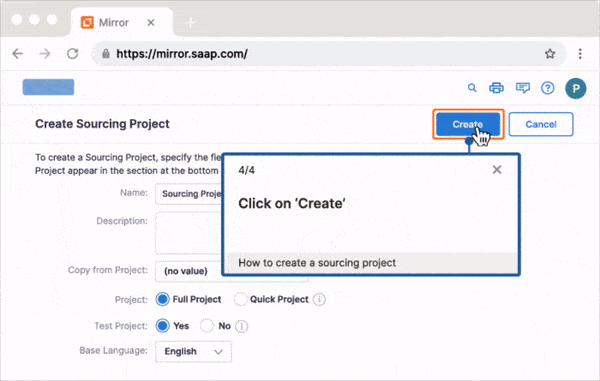
With a DAP like Whatfix, L&D teams can:
- Create contextual in-app guidance for different teams and roles, such as guided walkthroughs, step-by-step instructions, task lists, pop-up messages, field validations, and more.
- Provide self-help IT support for employees in an embedded self-help wiki that automatically crawls your knowledge repositories (ie. your company’s process docs, LMS, intranet, help desk, training materials, company handbook, etc.). This provides employees a searchable case management and knowledge support resource to find answers to their own questions.
- Analyze employee experiences, software adoption, and process engagement to identify dropoff areas, underadopted software features, areas of confusion in your tools or processes, measure license usage, and identify what employees or teams need a little more attention.
- Drive awareness and completion of L&D courses, initiatives, and programs with in-app pop-ups and messages that overlay on your team collaboration tools (like Slack, MS Teams, Zoom), company email, HCM (like Workday or SuccessFactors) or any other enteprrise software application.
- Collect employee feedback with in-app surveys that provide real-time feedback directly after your employees complete an L&D program or interact with an in-app element or widget.
6. Invest in your L&D software stack
To create engaging learning paths, and to properly measure the effectiveness of your training, you’ll need to invest a chunk of your L&D budget into various types of L&D tools.
Modern L&D tools empower L&D teams to author, design, and publish learning courses in different formats, track progress, host courses, assess knowledge retainment, collect feedback, create in-app experiences, and more.
A few of the most popular tools in an L&D tech stack include:
- Learning Management Systems (LMS): A foundational tool in most L&D tech stacks, an LMS is used to manage, deliver, and track training content and courses. It provides a centralized platform for organizing learning materials, creating courses, managing learner enrollments, and tracking learner progress and completion.
- Learning Experience Platforms (LXP): An LXP focuses on delivering a more personalized and learner-centric learning experience. It often uses AI-driven recommendations to suggest relevant content and facilitates informal learning through user-generated content and social learning features.
- eLearning Content Authoring Software: Authoring tools enable instructional designers and subject matter experts to create and develop eLearning content without requiring extensive programming knowledge. These tools allow the creation of interactive and engaging multimedia content, such as videos, quizzes, simulations, and more.
- Employee Training Software: Employee training software allows HR teams, training facilitators, and people managers to create and assign role-based training and development courses, as well as monitor progress and track completion rates.
- Digital Adoption Platforms: Digital adoption platforms deploy training via in-app guidance such as product tours, walkthroughs, task lists, smart tips, self-help menus, and more to guide the user through every aspect of an application. This empowers organizations to find true ROI of their internally-used software applications and digital transformation, onboard users and customers to their products and websites, understand how end-users are adopting and engaging with applications, and create a more intuitive training experience for their employees, customers, and all end-users.
- Online Course Providers: Online course providers, sometimes called MOOC (Massive Open Online Course) platforms, are websites that package learning content into self-paced online courses. They help professionals improve their current skillset and work on their professional growth by providing alternative paths for learning outside of traditional in-person classroom training sessions.
- Employee Performance Support Systems: With a performance support tool, leaders can create self-help interactive content such as in-app guidance, interactive walkthroughs, knowledge bases, smart popups, and more – all aimed at providing contextual resources to solve employee problems. Essentially, a performance support tool provides personalized, 24/7 support that provides answers within seconds within the context of work.
7. Implement your L&D strategy
Once you’ve crafted your L&D strategy, it’s time to implement it. Before scaling it to the entire organization, take time to present it to leadership and gather their feedback to help you identify areas to adjust and tweak.
You should also look to “soft-launch” your L&D program with certain, limited audiences – such as one or two pre-selected teams. A beta launch will allow you to work out the growing pains of an initial launch and make those changes before you have a full-scale L&D launch to the entire organization.
Once launched, be sure to actively promote and drive awareness of your L&D initiatives and programs. Explain to your workforce that you’re investing in their growth – and that you need their buy-in to succeed. Enlist the support of L&D advocates in key roles across your organization to help drive the adoption of your development programs.
8. Measure the effectiveness of your L&D strategy
A major employee training challenge facing enterprises is how to measure ROI.
Using L&D software equips you with the tools to measure the effectiveness of your corporate training programs. Set learning KPIs such as course completion rates, training progression rates, assessment scores, lowering skill gap analysis, improving proficiency or productivity for different teams, improving digital adoption rates, etc.
This will allow you to find trouble spots in your L&D program and correct them as soon as they’re made apparent. You’ll also be able to benchmark your learning and development progression, set future goals to target improvement and identify training gaps.
You should also overlay business performance with your L&D program to see if there have been any improvements in overall business KPIs that can be tied back to employee learning and development. It can be difficult to tie correlation to causation – but big data mined from your team’s L&D software stack can help pull out insights.
9. Gather employee feedback
Outside of gathering data on the effectiveness of your L&D strategy, also collect qualitative data from team members who are taking part in your L&D strategy. This highlights areas of need and helps reveal if your employees are finding value in your initiatives and programs.
If team members see your L&D strategy as an HR mandate, time-consuming, or not helpful, you’ll not be able to achieve the objectives you’ve set, as employee buy-in will drop.
Look to gather feedback from different stakeholders and team members at various times, including:
- In the moment of learning with in-app surveys.
- Post-training surveys after key courses have been completed.
- In 1-1s and performance review.
10. Take an agile approach and always refine your strategy
Be flexible in your L&D approach. You’ll need to take initial learnings, training progress, team member feedback, new business objectives, and more all into account – and use them to refine and improve your L&D strategy continuously.
Fostering an agile approach to employee learning and development will allow you to take new data and insights and pivot to new learning opportunities.
Benefits Of an Enterprise L&D Strategy
A well-crafted L&D strategy drives growth and positively impacts every area of an enterprise. Here are a few of the major benefits organizations experience with a strong L&D strategy in place:
1. More proficient and skilled employees
A well-designed L&D strategy equips employees with the knowledge, skills, and capabilities they need to perform their roles effectively. It addresses skill gaps, improves job proficiency, and boosts overall employee performance, leading to increased productivity and quality of work.
2. A culture of knowledge sharing
An effective L&D strategy promotes a culture of knowledge sharing and collaboration within the organization. It encourages employees to share insights, best practices, and lessons learned, fostering a continuous learning environment and creating opportunities for innovation and improvement.
3. Adaptability and agility
Continuous learning and development enable employees to stay up-to-date with industry trends, technologies, and best practices. This fosters organizational adaptability and agility, allowing employees to adapt to change, embrace new and emerging trends, innovate, and meet evolving business needs more effectively.
4. Employee engagement and retention
Investing in employee development with robust L&D fosters a sense of value and investment in employees. It demonstrates a commitment to their growth and career progression, leading to higher levels of engagement, job satisfaction, and increased retention rates.
5. Succession planning and leadership development
An effective L&D strategy includes succession planning and leadership development initiatives. It identifies high-potential employees, provides them with targeted development opportunities, and prepares them for future leadership roles. This ensures a strong talent pipeline and supports the organization’s long-term growth and stability.
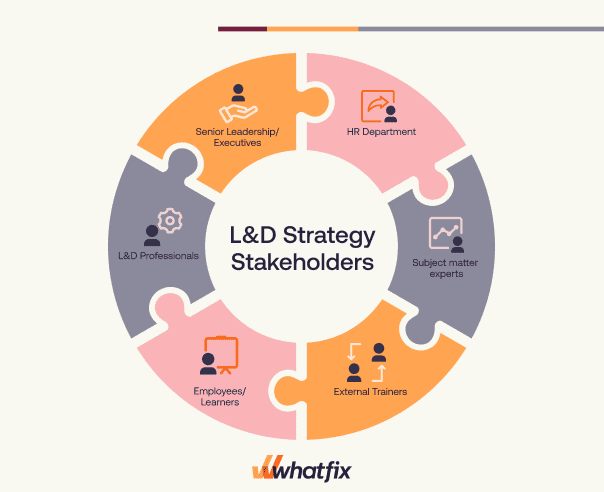
Key Stakeholders Involved In an L&D Strategy
A well-designed L&D strategy involves various stakeholders who play critical roles in its development, implementation, and success.
- Senior leadership and executives: Senior leaders provide strategic direction and support for the L&D strategy. They establish the vision, goals, and budget for employee development initiatives and ensure alignment with the organization’s overall strategic objectives.
- HR department: HR professionals are instrumental in the development and implementation of the L&D strategy. They assess training needs, design and deliver programs, manage learning platforms and resources, and monitor the effectiveness of the strategy. HR plays a key role in talent development, performance management, and succession planning.
- L&D professionals: L&D professionals, such as instructional designers, trainers, and facilitators, contribute their expertise in designing and delivering learning initiatives. They collaborate with subject matter experts to develop engaging and effective training programs aligned with organizational goals and employee development areas.
- Employees and learners: Employees are the primary beneficiaries of the L&D strategy. They actively participate in learning initiatives, apply newly acquired knowledge and skills to their work, and contribute to a culture of continuous learning. Employees provide feedback, insights, and suggestions for improving the L&D strategy based on their experiences.
- Subject matter experts: Subject matter experts (SMEs) possess specialized knowledge and expertise in specific areas. They collaborate with L&D professionals to ensure the accuracy and relevance of training materials. SMEs provide insights, contribute to curriculum design, and may even serve as trainers or facilitators in their respective domains.
- External trainers: Some organizations engage external training providers or vendors to deliver specialized training programs or access industry-specific expertise. These providers may offer off-the-shelf courses, customized training solutions, or access to subject matter experts not available internally.
12 Examples of Effective Corporate Learning and Development Strategies
Now that you understand the foundation of building a learning and development strategy, let’s explore twelve examples of effective corporate learning strategies and L&D programs to inspire your workforce training and development programs:
1. IBM
IBM is a pioneer in employee education. Its first executive training program started in 1916. Today, IBM spends over $574 million annually on employee training and development, making its program the most extensive L&D program in the world.
IBM employees spend over 28.6M hours annually in team member training and education initiatives. Employees can enroll in different training initiatives and have no chance of getting bored with what they do.
To provide growth opportunities to their staff, IBM has created a leadership management process for identifying, assessing, and developing high-potential leaders. One of the company’s most famous programs is Basic Blue, an in-house management training program for new managers. The program involves role-playing and focuses on developing the emotional intelligence and coaching skills that an IBM manager should have.
Hands-on training is also a part of IBM’s employee education plan. To enhance employees’ careers, IBM’s L&D practices job rotations. Participants spend some time working on projects that further their career goals. IBM’s employees call it “growth through rotation and transformation.”
2. Google
Learning is a foundational element of Google’s success. Its holistic, innovative L&D programs have long attracted and developed the best talent.
Google’s philosophy for learning is built around four pillars:
- Learning is a process
- Learning happens in real life
- Learning is personal
- Learning is social
These guiding L&D principles share the design and delivery of employee training and upskilling. It realizes that not every employee is the same and that training experiences must be experiential to make an impact. It has led Google to design and launch highly effective and innovative L&D initiatives over the years, including:
- G2G Program: Launched in 2007, the Googler-to-Googler program is a peer-to-peer learning initiative where employees self-nominate themselves to own different training topics—anything from personal development to leadership, presentation, or technical skills. Its L&D team provides instructional training to these volunteers to give them the skills to lead classes. Course owners use Google’s LMS to manage classes and assess performance. In 2020, 80% of all formal learning was a G2G course.
- 20% Time: Google cofounders Larry Page and Sergey Brin integrated learning into the fabric of Google by asking employees to spend 20% of their workweek (equal to one day per week) on a work-related passion project or skill development that didn’t have anything to do with their day-to-day role. This has empowered Google employees over the years, leading innovations like AdSense and Google News launched from 20% Time ideas.
- Whisper Courses: Google takes a microlearning approach to L&D through a weekly email series. These emails provide simple suggestions or tasks for a manager to experiment with in the next week. Employees build knowledge of more complex ideas or task mastery throughout the 10-week email campaign through bite-sized microlessons delivered to employees’ inboxes once a week.
3. McDonald’s Hamburger University
McDonalds built a state-of-the-art training facility at its Chicago HQ, which provides hands-on and simulated training experiences to high-potential restaurant managers, middle management, and franchise owners. Named Hamburger University, its mission is to become an “organizational culture hub that introduces a continuous approach to education to transform knowledge into business results.”
The program is attended by 5,000+ McDonald’s employees each year, with over 300,000 alumni. Its programs include restaurant operation basics, customer service scenario training, operational procedure training, and general leadership and career growth classes.
4. Goldman Sachs
Goldman Sachs is another corporate giant known for its investment in employee development. The company’s learning programs vary from skills-based training and high-performing leadership programs to roundtable discussions and workshops hosted by senior leaders.
One of the examples of learning and development initiatives by Godlen Sachs is “Talks at GS,” a series of conversations and interviews with experts in various niches, from the arts and entertainment to politics and business. The company invests in this initiative to support its employees in constant learning and help them pursue career growth opportunities.
5. Formlabs
Formlabs is a leading 3D printer developer and manufacturer. The company works with hundreds of resellers that represent Formlabs worldwide. To ensure its partners deliver the best customer service, the manufacturer has implemented a learning management system (LMS) to educate internal employees and external representatives.
To make the program more engaging, the company uses certificates and gamification. For instance, partners get points for performing specific actions, increasing training completion rates, and improving brand-partner relationships. It takes a few weeks to fully onboard new partners and introduce all their technicians to Formlabs’s machines.
6. REG
REG (Renewal Energy Group) has 1,200+ employees and relies on multiple enterprise software systems for its day-to-day operations and to achieve its business goals. It optimizes its business processes through a continuous improvement cycle where changes are often made in its enterprise application workflows, making updating application training difficult.
REG standardized its application user training for its mission-critical enterprise software applications with Whatfix DAP. With Whatfix, REG enables its employees with in-app guided experiences, hands-on training, and on-demand performance support to learn by doing.
Simple step-by-step instructions within the application (called ‘Flows’), for example, are used extensively to help users learn an objective or complete a task through a series of actions. REG can break down complex JD Edwards, Salesforce, and other application journeys into intuitive steps. On-demand performance support combined with in-application guidance and internal knowledge bases is also helping to create a self-learning culture, empowering REG to take charge of its application knowledge.
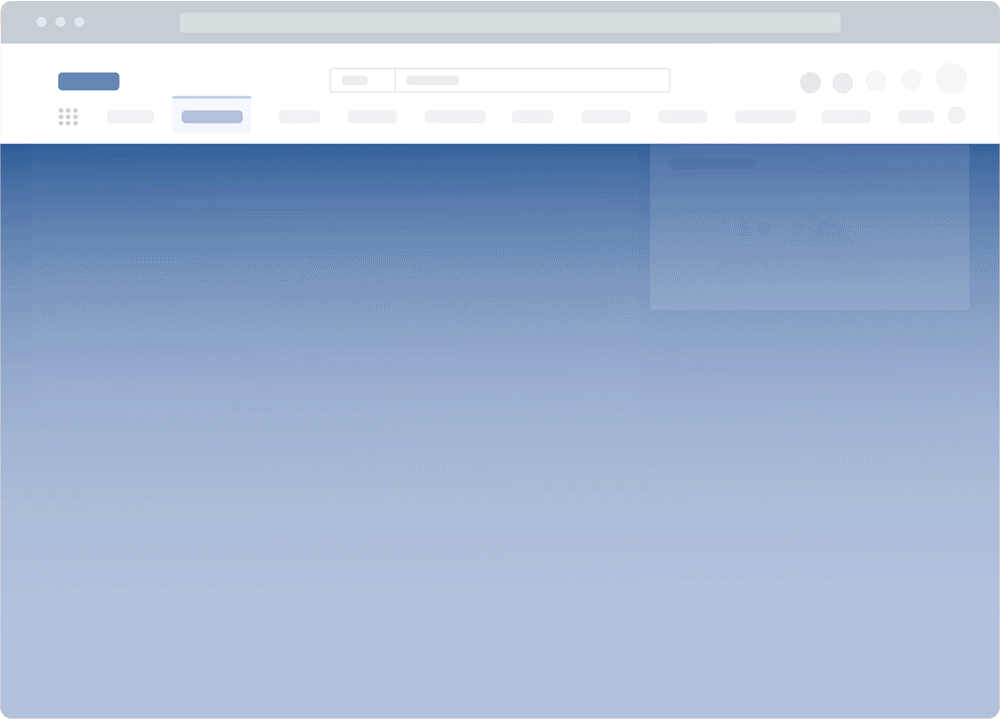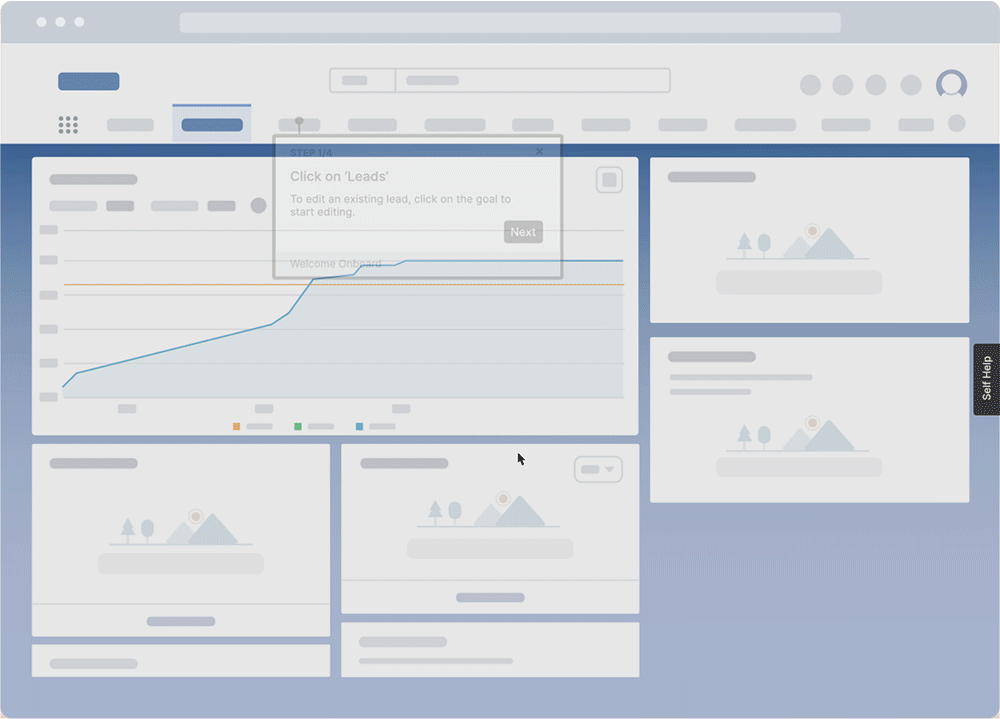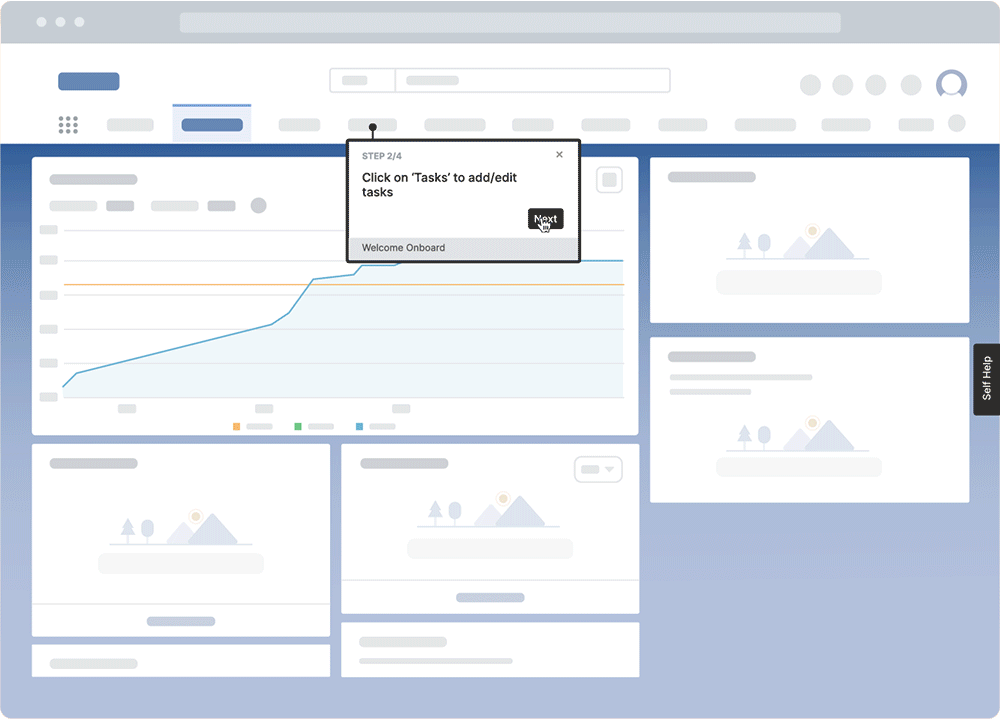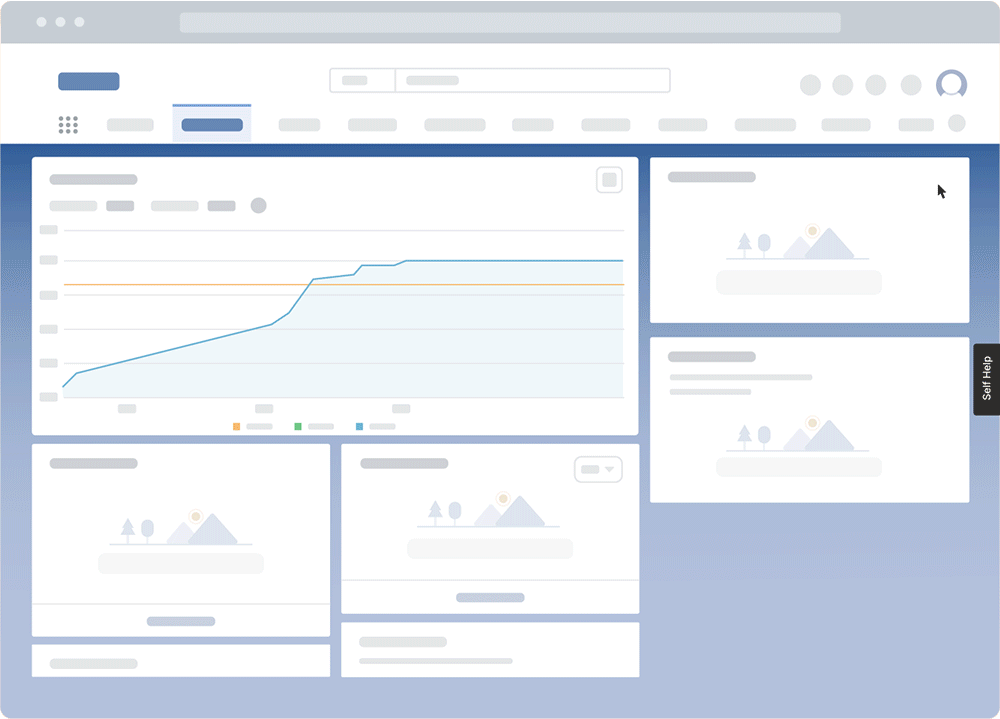
This accelerated the time-to-proficiency for new hires by 50%—the equivalent of a 3-month reduction in onboarding new employees. It also allows REG to push in-app training and live tutorials to employees when processes change, allowing for less confusion, more productive employees, and better task governance.
You can read the entire REG + Whatfix success story here.
7. Abstracta
Abstracta is a software testing company that was experiencing a lack of good software testers when they decided to create an internal training program (that later evolved into an external program).
To fill the significant skills gap in the market, the company has launched 34 online courses — most of which are accessible to both internal and external learners. They deliver training through an LMS so it’s easy to manage the courses and monitor the learners’ progress.
This is a great example of how your internal learning and development strategy can help build a foundation for an external training program and strengthen customer relationships.
8. Yelp
Yelp has created a strong learning culture with continuous, organization-wide training. Learning and development opportunities arise daily at Yelp, so improvement and growth become the core elements of the company culture.
To keep their training programs relevant, Yelp regularly surveys employees on how employees really feel in their positions and what skills they would like to gain. Also, new hires are given onboarding surveys after 30 days on the job to collect feedback on their onboarding process.
The data Yelp gets from regular employee surveys helps them fine-tune their training processes and build more personalized learning experiences.
Moreover, L&D isn’t mandatory at Yelp. The company uses a soft approach by making participation optional but makes it clear that active learners have higher chances for greater success.
9. RingCentral
RingCentral, a cloud-based communication and collaboration service provider, strives to create a strong team spirit among employees through continuous learning and development. The company supports its employees’ career development by offering all employees leadership training, education, workshops, and coaching. Collaborative training is one of the main methods that RingCentral uses in its learning and development strategy.
10. Adobe
Adobe’s learning and development strategy focuses on creating an employee community where everyone feels included and has equal opportunities.
The company has created unique training programs to help employees gain new skills and reach their full potential. Early-career employees and the most experienced professionals have access to educational resources, mentorship, and interest-based communities.
Adobe also runs the Leadership Circles program, which helps high-potential female employees achieve their career aspirations. Throughout the year, participants attend masterminds, meet with their executive coaches, and do exercises to implement their learnings. The program aims to diversify the leadership pipeline with talented female leaders.
11. Cisco
Cisco offers an entire library with learning and development resources for their staff. Employees can access certifications, instructor-led courses, cross-training, and other training formats.
The company heavily invests in management training. Cisco has a program where they rotate high-performance employees through a range of assignments to broaden their skill sets and career opportunities. The company offers participants to choose from a range of local positions and overseas opportunities based on their interests. Each assignment lasts about two years so that individuals participating in the rotation have time to fully prepare for eventual company progression.
Furthermore, the organization runs the Cisco Leadership Series and Cisco University, an online portal where employees can access career development activities and manage their individual careers.
12. Squarespace
Squarespace has a solid learning and development program to seamlessly onboard new hires and guide them throughout their entire journey with the company.
They offer a variety of training initiatives for employees to navigate their growth, from on-demand learning resources to professional development sessions to employee education reimbursement benefits.
To keep employees connected and empower them to do their jobs well, Squarespace hosts annual company kick-offs, quarterly all-hands meetings, year-end wrap-ups, regular workshops, and many other collaborative learning events.
What Factors Influence an L&D Strategy’s Success?
Here are some factors that influence the design and development of an L&D strategy within an organization.
1. Organizational goals
The L&D strategy must align with the overall goals and strategic direction of the organization. It should support key objectives such as improving performance, driving innovation, or enhancing customer experience. Understanding the organization’s priorities and long-term vision is crucial in shaping the L&D strategy.
2. Workforce needs and skill gaps
Assessing the current and future skill requirements of the workforce is essential. Identifying skill gaps and understanding the specific learning needs of employees help determine the focus areas and content of the L&D strategy. This analysis ensures that the strategy addresses critical development areas and supports the organization’s talent development objectives.
3. Industry trends
Keeping up with industry trends, emerging technologies, and market dynamics is vital in designing an effective L&D strategy. Understanding how the industry landscape is evolving helps identify relevant skills and competencies that employees need to remain competitive and adapt to changes in the market.
4. Budget and resources
The availability of financial resources and dedicated L&D personnel influence the scope and implementation of the L&D strategy. Budget constraints may require prioritization and careful allocation of resources to deliver impactful learning initiatives within the organization’s means.
Upskilling Clicks Better With Whatfix
A well-crafted L&D strategy is a powerful tool for organizations seeking to unlock the potential of their workforce and drive sustainable success. As businesses continue to adopt new technologies, invest in new digital transformation projects, and markets evolve, upskilling and training becomes a hyper-critical factor for the success of modern work.
With a Whatfix, enterprises can drive adoption of mission-critical software and maximize value realization.
- With Whatfix Mirror, L&D leaders can create replicate sandbox environments of their enterprise applications (like an ATS, CRM, ERP, or HCM) to provide interactive, hands-on user training in a risk-free environment.
- With Whatfix DAP, enables end-users with contextual in-app guidance that supports employees in the flow of work. Task Lists and Tours help guide employees through core features and how to complete their tasks. Flows and Smart Tips help end-users complete infrequently done tasks and follow the correct path in complex, multi-step workflows. Self Help integrates with your knowledge repositories and brings that institutional knowledge inside your digital applications for on-demand help.
By simplifying complex processes, reducing learning curves, and offering just-in-time assistance, Whatfix enhances user proficiency and engagement, thereby accelerating the learning process and driving the success of L&D initiatives.
Ready to learn more? Schedule a Whatfix demo today!