
Disha Gupta

Employees are switching companies, roles, and industries at a higher frequency than ever before. This has highlighted the need for HR teams to build new strategies to retain their highest-performing employees.
One of the most important, impactful areas of employee retention is investing in its talent with a comprehensive employee development strategy.
Different employee have unique set of strengths, experiences, and skill gaps, just like every position requires a unique set of competencies. Because of this, it often makes the most sense to pinpoint specific areas of development in corporate L&D strategies to build contextual employee development plans that encourage growth and empower internal employees to fully realize their potential through upskilling, new skill development, and the refinement of these skills.
In this article, we’ll explore the key areas of employee development that organizations should focus on to build future leaders and high-performers from within your current workflow.

Employee development areas, also called competencies, are core skill and knowledge areas that employees need to do their jobs effectively. Organizations can provide employees with development opportunities to upskill and improve existing knowledge and experience in specific development areas.
Identifying and targeting these different areas is a fundamental part of developing an effective L&D strategy. Engaging in development activities helps employees understand which areas they excel in, and which ones have room for improvement.
Employee development areas may differ from employee to employee or from position to position. Here are some of the most consistently critical development areas employees need to excel in the workplace – with examples of types of development and training for each:
First things first, all employees need to be proficient in the skills required to carry out day-to-day job duties. After initial onboarding, employees should regularly engage in development activities that can help them improve and expand on those skills, especially as technology and methods evolve.
Some examples of professional skills include database management, data analysis, and industry-specific operational skills.
Examples of professional skills development training include:
Being able to effectively collaborate and communicate is absolutely essential for employees who operate as members of a team. Encouraging employees to develop these skills leads to more efficient and active dissemination of information and encourages dialogue that can lead to innovation.
Targeting written and verbal communication as well as active listening and interpersonal skills in L&D programming can help organizational leaders build a safe environment for productive dialogue and effective teamwork.
Examples of collaboration and communication development and training include:
Employees who can organize their workspaces and minds, and lay out strategic professional goals for themselves are instrumental in the achievement of larger organizational goals. By including goal setting and organizational skills in development efforts, L&D teams can help employees become more self-sufficient, ultimately reducing stress and increasing productivity.
Some examples of goal-setting and organizational skills include schedule and deadline management, multitasking, task prioritization, and productivity. Across all of these skills, time management plays a huge part.
Examples of goal setting and organization skills development and training include:
When working as part of a team, conflicts are bound to arise from time to time. At this point, employees need to tap not only into communication skills but empathy and professionalism as well. Building conflict resolution skills into employee development allows employees and managers to address and de-escalate conflicts, reducing tension, improving morale, and building stronger teams in the long run.
Common skills related to this employee development area include stress management, emotional awareness, active listening, and patience.
Examples of conflict-resolution development and training include:
Today’s workplaces are becoming increasingly dynamic, requiring employees to be flexible and agile to thrive. By including adaptability-related skills in employee development, team members become better equipped to handle complex situations, acclimatize quickly, and stay productive in the face of challenges.
Some skills that fall into this area are improvisation, direct action, and the ability to learn new skills.
Examples of adaptability development and training include:

Productivity is a critical employee development area because it is relevant to every aspect of work and ultimately determines the success of an organization. When employees can hone their productivity skills, they not only have a positive impact on business outcomes but also tend to become more engaged and satisfied at their work.
Key skill sets related to productivity include time management, planning, and self-awareness.
Examples of productivity and time management development and training include:
By training employees to understand and carry out tasks that lie outside their regular job responsibilities, L&D teams can help employees gain new perspectives on workplace challenges and be prepared to take on new responsibilities as needed. This employee development area is especially important in times when positions become vacant and remaining employees need to pitch in to keep things running smoothly.
Skills useful for the accumulation of cross-functional knowledge are agility, communication, and of course, the relevant core professional skills.
Examples of cross functional knowledge development and training include:
Employees at every level can benefit by developing their leadership skills. By giving employees opportunities to hone their management skills, they become better communicators, problem solvers, and team members.
Successful leaders tend to have strong strategic thinking skills, developmental planning, decision-making, and delegation.
Examples of leadership development and training include:
Creativity is a development area that impacts just about every aspect of work. Encouraging creative thinking among employees empowers them to address common issues in innovative ways and helps keep businesses competitive in evolving industries.
Skills that contribute to this employee development area are pattern identification, imagination, critical thinking, and confidence.
Examples of creativity development and training include:
Of course, the particular skill areas that will be most important to focus on may differ across organizations. Before charging ahead in any one direction, it is essential to perform thorough assessments to determine which employee development areas are the most relevant to the needs of individual team members and the goals of the larger organization. From there, L&D teams can build out the most effective employee development strategy for their organizations.
There are many different approaches to employee development, with different levels of formality and different objectives. Choosing the right method will depend on organizational needs, the values of employees, the employee development areas you need skill team members on, and organizational objectives and intended business outcomes.
Here are a few of the most commonly used training delivery methods and techniques for effectively developing employees:
Formal face-to-face learning and traditional training workshops are the most familiar and conventional methods of team member development. These activities vary significantly in format and modality but often include a traditional classroom setting with a blended learning approach that provides online learning, in-person lectures, videos, and practical exercises.
This type of learning generally works well for teaching employees both hard and soft skills. Still, in recent years, we have learned that many employees benefit from alternative methods, whether they supplement traditional training or replace it completely, often depending on the individual learning styles of different team members.
With mentorship or coaching, employees are paired with more senior colleagues or designated coaches to learn the skills they need to be successful in their roles. These relationships can be formal or casual, but in any situation, these relationships require commitment and energy from both parties.
This method serves not only as a tool for skill acquisition, but a leadership opportunity for employees doing the mentoring. Coaching relationships tend to be shorter-term and can involve hiring professional dedicated coaches to improve performance, while mentorships tend to last years and focus more on overall development rather than immediate performance.
On-the-job training is an employee development method that happens during regular work hours, within everyday workspaces. This approach often entails observational learning in combination with hands-on activities under supervision by an experienced team member.
This method is about learning by doing, speeding up the time to proficiency, and creating an environment where employees can ask questions and develop relationships with their supervisors using their real tasks and processes to learn in the flow of work.
With a digital adoption platform (DAP) like Whatfix, L&D teams can enable their employees with in-app experiences that guide them through complex processes contextual to their role with step-by-step instructions that overlay their applications. With Whatfix Self Help, employees can use a searchable self-help wiki to find all contextual documentation, company information, playbooks, training materials, tutorial videos, and more – related to the task they’re working on.
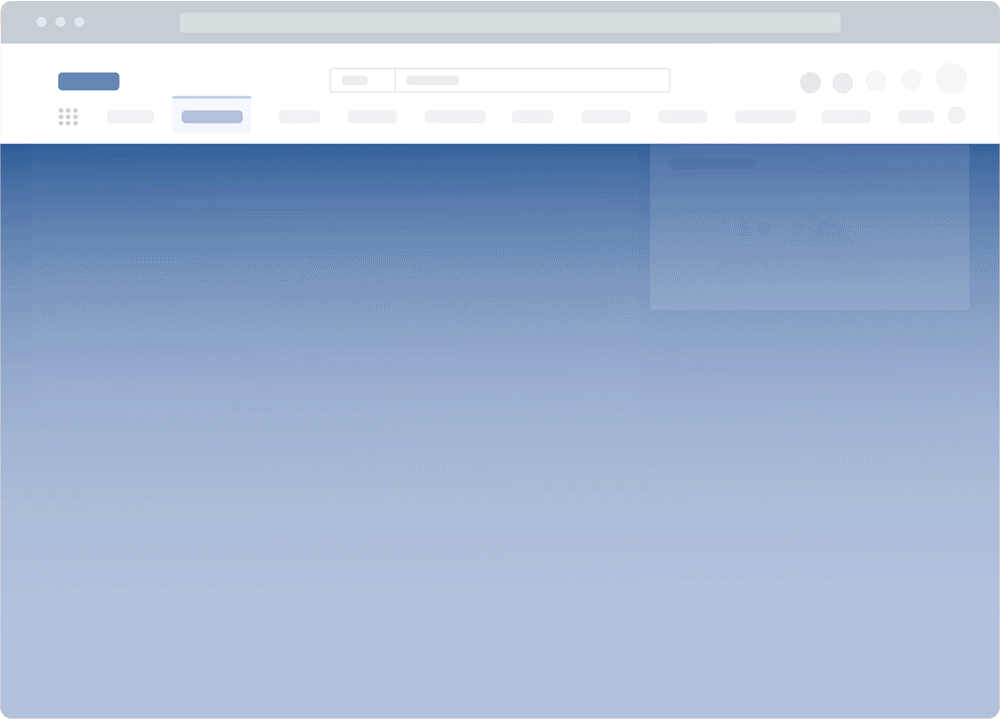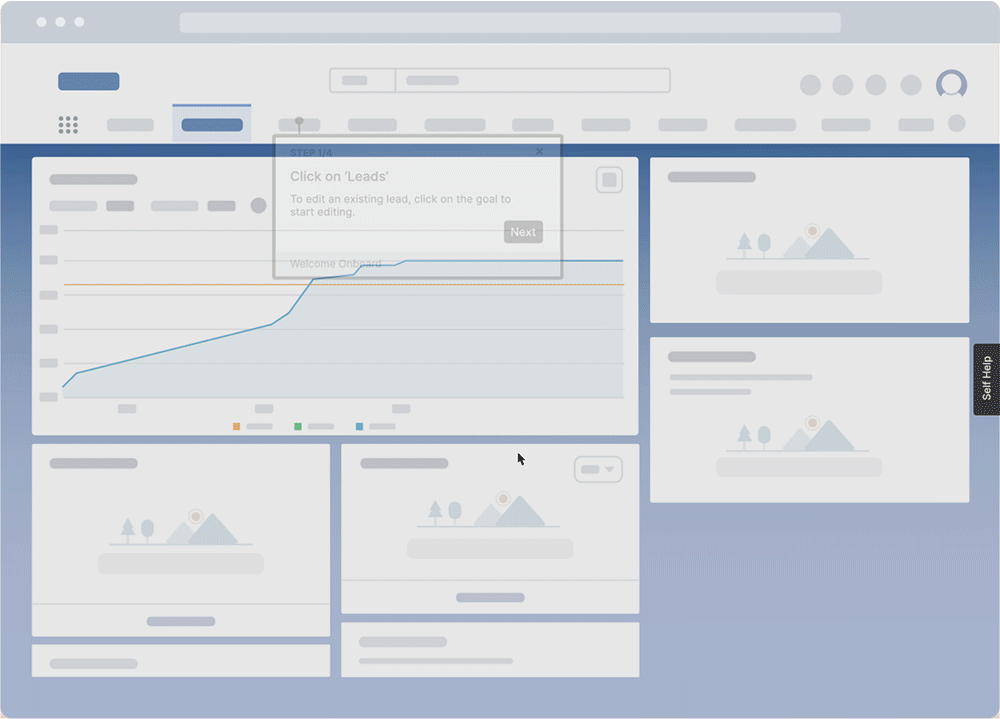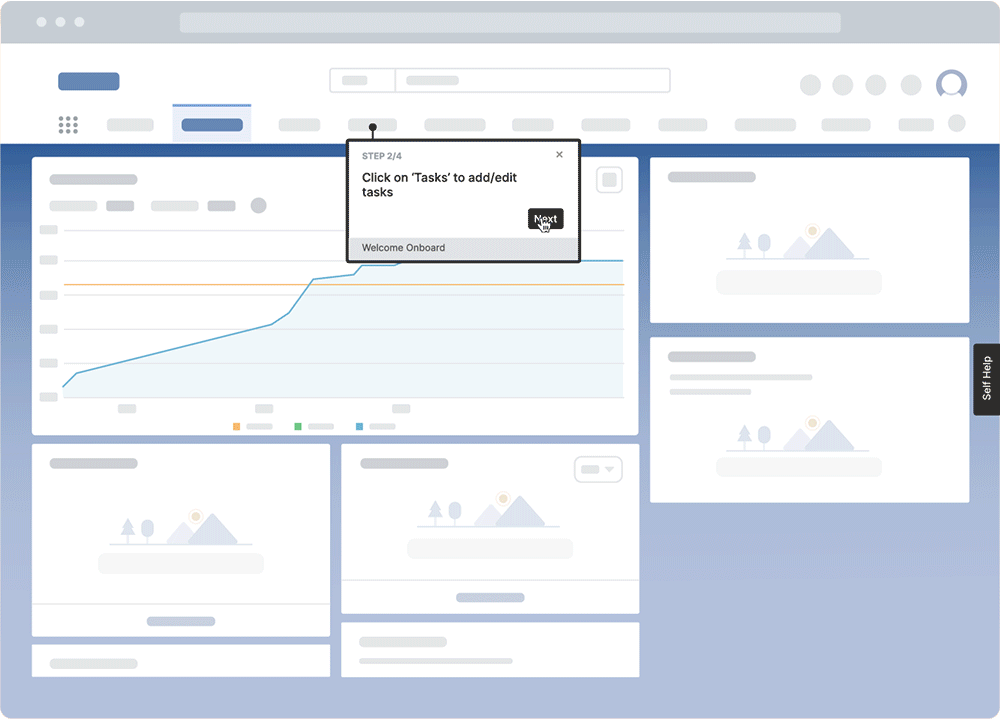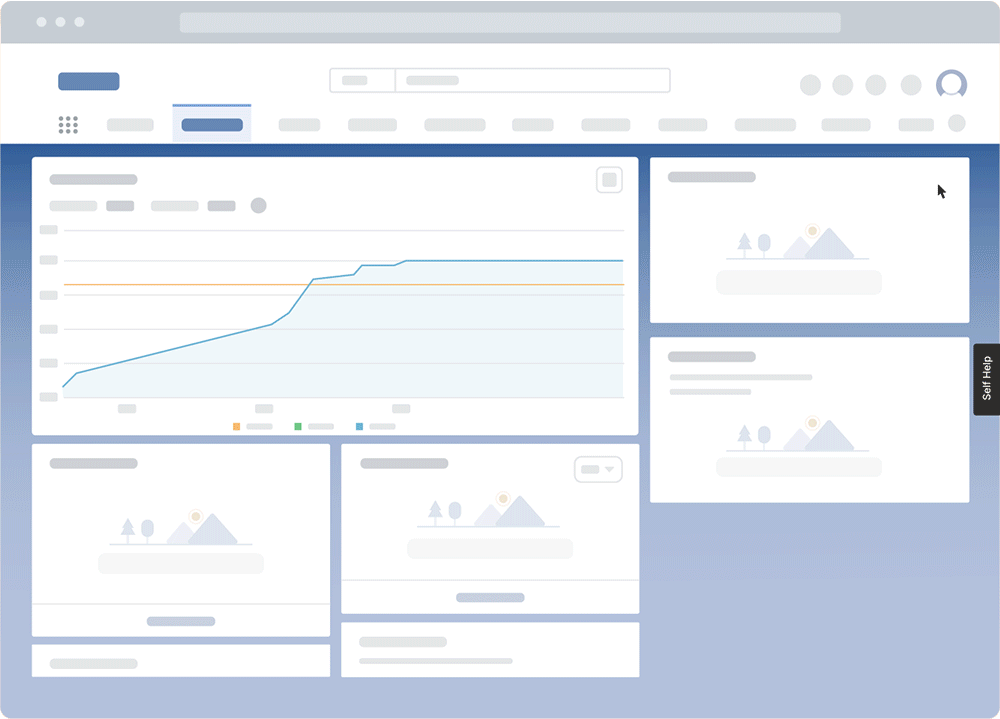
Whatfix is the ultimate learn-while-doing, augmented approach to employee development that blends real-time support with contextual experiences that enable employees to maximize their potential through better skill development and digital empowerment.
Cross-training is a professional development method where employees learn to perform tasks outside of their usual roles to help them become more well-rounded and versatile, as well as build company and product knowledge. This approach often involves pairing two employees from different areas for an exchange of information, similar to mentoring and job shadowing.
In cross-training activities, one employee typically visits another to learn about different job functions, sometimes shadowing them and even carrying out various tasks under supervision.
This method is relatively informal, and it benefits both parties by allowing the visiting team member to build on their communication and leadership skills. In contrast, the learning team member gains a more holistic understanding of different areas of business. This practice also prepares employees to be more versatile and move into new roles and responsibilities more efficiently.
Another more traditional professional development method is feedback and performance reviews. In this approach, managers meet with their employees at least once per year to discuss employee progress and performance and determine realistic goals for overcoming areas of need moving forward.
These reviews are opportunities for managers and their employees to align their understandings of employee responsibilities and performance. They also allow supervisors to identify ways to help employees grow professionally in the future. Use these opportunities to create personal development goals for employees that can be used to measure growth.
Another very effective method of professional development is peer-to-peer learning. In these activities, employees with different skills or areas of expertise gather to exchange knowledge. This can happen in one-on-one situations or by scheduling regular group meetings where a different employee leads the group each week, teaching the others what they know best.
With this method, teams can build an engaging and collaborative work environment, and give team members opportunities to boost their confidence and demonstrate their strengths, all while helping employees grow and learn.
eLearning is the obvious approach to developing employees, and it is at the core of all modern L&D strategies. With this approach to employee development, learners engage in learning activities delivered virtually via learning digital experiences, web apps, and software.
These applications are practical for employee development because many include adaptive learning features that curate lessons and longer learning journeys for employees based on their specific needs in real-time. They also provide learners with regular assessments that help managers keep track of progress.
L&D teams often utilize learning management systems (LMS) to create, distribute, host, manage, and track online learning development and progress. LMSs are the centerpiece of modern employee development strategies.
While not typically used as a stand-alone solution to employee development, mobile learning is an employee development method delivered via mobile devices that takes a microlearning approach. This approach gives employees the freedom of mobility as they learn and allows them to engage with learning content at a pace that works for them.
Mobile learning applications are sometimes included in more extensive eLearning software and learning management systems. This approach encourages a mindset of continuous learning, improving knowledge retention and keeping employees engaged.
The most structured and formalized version of traditional training and workshops is instructor-led training. With this method of employee development, a designated instructor delivers training to many employees at once.
This method works best when the training subject is particularly complex or new to the entire group. This can also make it beneficial for organizations to bring in professional trainers or outside subject matter experts to serve as instructors rather than selecting experienced employees from within the organization.
Leadership development programs are comprehensive initiatives to grow valuable employees into successful leaders. These initiatives are often long-term endeavors that provide employees with learning experiences, practical experience, and regular evaluation.
These programs generate future leaders for organizations while helping employees become more productive, self-sufficient, and capable of taking on more advanced opportunities in the workplace.
Organizations often partner with an online course provider like Udemy, Coursera, or LinkedIn Learning to provide employees with a variety of learning opportunities available anytime, at no cost to team members.
Businesses that utilize digital adoption platforms like Whatfix for employee development benefit from a streamlined learning process. Whatfix’s in-app guidance can provide employees with customized learning paths to meet their unique upskilling needs. This software delivers interactive, personalized learning experiences that make employee development intuitive and accessible.
With a digital adoption platform like Whatfix, enable your employees with in-app guidance and contextual self-help IT support to accelerate the adoption of new software implementations, employee onboarding, change initiates, and more. Whatfix’s no-code editor enables IT teams with a no-code editor to create product tours, interactive walkthroughs, task lists, smart tips, pop-ups, self-help wikis, and more. Analyze and measure user engagement and software usage to identify friction points, measure digital adoption, and improve employee digital experiences.
Thank you for subscribing!