Human resources is a people-oriented function. But its contribution isn’t limited to extending offer letters and onboarding new hires. HR professionals are responsible for developing and sustaining a comprehensive workforce management strategy.
In today’s data-driven world, HR leaders increasingly use analytics to make informed decisions and drive strategic initiatives. The importance of HR analytics lies in its ability to provide deep insights into workforce dynamics, helping HR leaders predict potential issues, identify areas for development, and implement strategies that drive better performance and employee engagement.
This article explores the significance of HR analytics, its key applications, and how organizations can leverage it to unlock the potential of their workforce.
What Is HR Analytics?
HR analytics uses data, statistical analysis, and data-driven insights to inform and optimize HR strategies, policies, and decision-making. It involves collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data related to various HR functions, including recruitment, talent management, employee engagement, performance management, learning and development, onboarding, training, and workforce planning.
Organizations leverage HR analytics to gain deeper insights into their workforce, identify people-related trends, make data-driven decisions to improve employee productivity, and align HR initiatives with organizational goals.
Workforce Analytics vs. People Analytics vs. HR Analytics
The terms HR analytics, people analytics, and workforce analytics are often used interchangeably.
However, each type of HR-related analytics serves a different purpose. HR analytics, people analytics, and workforce analytics collectively empower organizations to make data-driven decisions to improve workforce performance, employee engagement, and other people-related initiatives.
Let’s break down the key differences between HR analytics, people analytics, and workforce analytics below:
| Aspect | HR Analytics | People Analytics | Workforce Analytics |
| Definition | Focuses on collecting and analyzing HR-related data to optimize HR processes such as recruitment, performance, retention, and compensation. | Focuses on analyzing individual-level data to understand employee behavior, motivation, and engagement. | Focuses on analyzing data related to the entire workforce, including headcount, productivity, and demographics to improve overall operational efficiency. |
| Scope | Specific to HR functions and processes, such as recruitment, turnover, and training effectiveness. | Narrower focuses on employee experiences, behavior, and interpersonal factors. | Broader, looking at workforce trends and operational metrics across the organization. |
| Data sources | HR systems, employee performance metrics, compensation, and benefits data. | Employee surveys, feedback, performance reviews, behavioral data. | Workforce data (headcount, demographics, productivity, attendance). |
| Goal | To enhance HR processes and make data-driven hiring, development, and retention decisions. | To improve employee satisfaction, engagement, and retention by understanding behavior. | To optimize workforce planning, productivity, and resource allocation. |
| Use case | Recruitment efficiency, employee turnover, training ROI, compensation analysis. | Employee engagement, performance management, team dynamics. | Headcount planning, workforce utilization, diversity analytics. |
Types of HR Analytics
There are four main types of HR analytics: descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive. Let’s examine how each works.
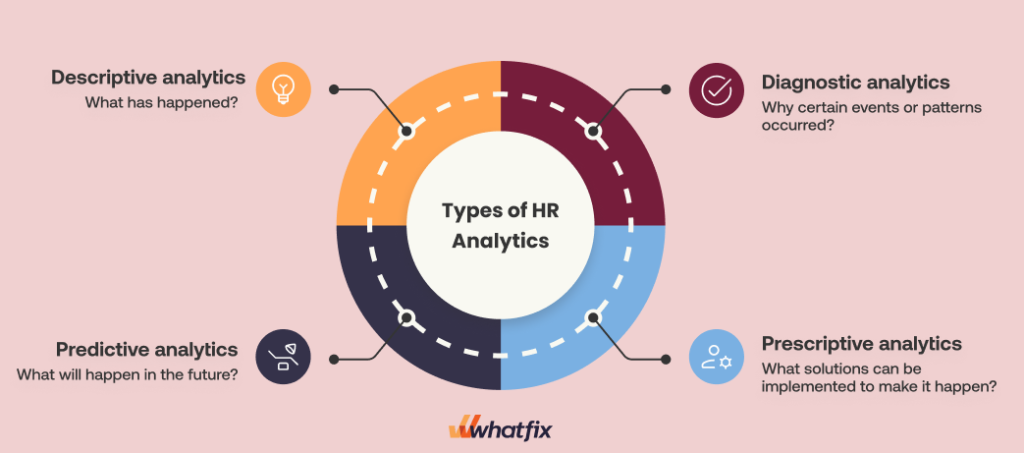
1. Descriptive analytics
Descriptive analytics focuses on understanding and summarizing past data to provide insights into historical trends. This type of analytics helps organizations understand what has happened in the workforce, such as employee turnover rates, absenteeism, performance levels, or recruitment metrics.
Descriptive analytics takes raw HR data (from sources such as HRIS systems, surveys, or performance reviews) and organizes it into easily interpretable formats such as reports, dashboards, or charts.
Example of descriptive analytics: An HR team can use descriptive analytics to analyze the company’s annual turnover rate by creating a report that shows how many employees left the organization in the past year.
Benefits of descriptive analytics: Provides a foundational understanding of workforce trends, enabling HR teams to pinpoint specific areas that need improvement or investigation.
Limitations of descriptive analytics: It only looks at past data and does not explain why things happened or predict future outcomes.
2. Diagnostic analytics
Diagnostic analytics goes further by analyzing why certain events or patterns occurred. It focuses on discovering the root causes of trends seen in descriptive data, helping HR teams understand underlying issues in their workforce.
Diagnostic analytics uses statistical analysis, correlation analysis, and data mining techniques to explore HR data more deeply and find relationships between variables.
Example of diagnostic analytics: If an organization experiences high turnover in a specific department, diagnostic analytics might reveal that the primary causes are poor leadership or a lack of growth opportunities.
Benefits of diagnostic analytics: It provides actionable insights into the causes of HR problems, allowing HR leaders to make informed decisions about addressing them.
Limitations of diagnostic analytics: It explains why something happened but does not predict what will happen next.
3. Predictive analytics
Predictive analytics uses historical data to forecast future workforce trends and outcomes. Identifying patterns and correlations in past data predicts the likelihood of future events, such as employee turnover, hiring success, or performance improvement.
Predictive analytics uses advanced techniques, such as machine learning, regression analysis, and statistical modeling, to forecast future trends based on historical HR data.
Example of predictive analytics: HR departments can use predictive analytics to identify employees at risk of leaving the company within the next six months based on factors such as job satisfaction scores, length of tenure, or engagement levels.
Benefits of predictive analytics: Allows HR teams to proactively address potential issues (e.g., high turnover or poor performance) before they occur.
Limitations of predictive analytics: Predictive analytics is based on historical data and probabilities, so it cannot guarantee future outcomes with absolute certainty.
4. Prescriptive analytics
Prescriptive analytics goes beyond predicting future outcomes by recommending the best action. It uses optimization algorithms, machine learning, and simulation techniques to suggest potential solutions to HR challenges.
It uses data from predictive models and decision-making frameworks to identify the best actions to improve future outcomes. Prescriptive analytics evaluates different scenarios and provides suggestions on what steps must be taken to achieve the most favorable result.
Example of prescriptive analytics: If predictive analytics identifies employees at risk of leaving, prescriptive analytics might recommend offering promotions, pay raises, or additional training programs to retain those employees.
Benefits of prescriptive analytics: It forecasts future trends and suggests practical, data-driven solutions to address potential issues, enabling HR leaders to make strategic decisions.
Limitations of prescriptive analytics: Implementation can be complex, requiring sophisticated algorithms and significant amounts of data to generate accurate recommendations.
HR Areas to Improve with HR Analytics
Here are some examples of how to incorporate HR analytics in your organization.
1. Employee turnover
HR analytics helps identify patterns and reasons for high turnover by analyzing factors such as job satisfaction, engagement levels, performance reviews, and exit interviews. By pinpointing the root causes, such as poor management, lack of career growth, or compensation issues, organizations can take corrective actions to reduce turnover.
Example: Predictive analytics can help HR teams forecast which employees are most likely to leave, enabling proactive interventions such as offering promotions or improving working conditions.
2. Employee recruitment
HR analytics can streamline recruitment by evaluating the effectiveness of different hiring channels, reducing hiring time, and improving candidate quality. Analytics can also identify which recruitment sources produce the best long-term employees, improving the hiring process.
Example: Analyzing data on past hires can reveal that candidates from certain platforms or with specific qualifications are more likely to succeed and stay long-term, helping HR refine its recruitment strategies.
3. Workforce planning
HR analytics enables data-driven workforce planning by forecasting future labor needs based on business growth, employee attrition, and market trends. Analytics can help HR teams predict staffing needs, identify skill gaps, and plan for future recruitment or training initiatives.
Example: Using historical data, HR analytics can predict seasonal spikes in staff demand, allowing companies to hire temporary workers in advance or provide additional training for existing employees.
4. Employee performance
Performance analytics can provide insights into individual and team productivity, helping managers identify high performers and those needing improvement. HR analytics can track performance trends and identify factors contributing to high or low performance.
Example: Analyzing performance data alongside engagement or training completion rates can show which employees benefit from development programs and which areas need improvement.
5. Employee engagement
Analytics can track engagement levels through surveys, feedback, and absenteeism rates, helping HR teams understand what drives or hinders employee engagement. By analyzing this data, organizations can implement strategies to improve employee satisfaction and retention.
Example: HR can track engagement data over time to determine the impact of initiatives such as flexible working policies or wellness programs, adjusting strategies based on the results.
6. Learning & development
HR analytics can help measure training effectiveness by evaluating course completion rates, post-training performance improvements, and training initiatives’ return on investment (ROI).
Example: By analyzing post-training performance metrics, HR can determine which learning and development programs drive the most improvement and adjust the content or delivery of future programs.
Related Resources
Key HR Metrics and KPIs
To better understand what type of data and insights your team can extract from an HR analytics strategy, let’s explore different types of data points and survey analysis that can be done with HR analytics software or an HR analytics framework:
HR Analytics Examples for Employee Engagement
- Engagement Surveys: These are one of the most common ways to measure employee engagement. HR analytics can help gather and interpret this data, identifying patterns, trends, and areas for improvement.
- Pulse Surveys: Unlike engagement surveys, pulse surveys are brief and conducted more frequently to gauge employee feelings and engagement levels in real-time. The data generated can give quick insights into the impact of recent changes or initiatives.
- Productivity Metrics: HR analytics can track metrics like output per hour or quality of work to assess engagement. Highly engaged employees are often more productive.
- Employee Net Promoter Score (eNPS): This is a measure of how likely employees are to recommend their workplace to others. This can be a valuable measure of overall engagement.
- Social Network Analysis: This involves analyzing the communication and collaboration networks within an organization. Strong networks can indicate high engagement.
- Exit Interviews: Analyzing data from exit interviews can provide insights into reasons for employee disengagement and areas for improvement.
- Performance Metrics Analysis: Comparing engagement survey results with performance metrics can give a deeper understanding of the relationship between engagement and performance.
HR Analytics Examples for Hiring & Recruiting
- Time to Hire: This metric measures how long it takes to fill a vacancy from the moment the job is posted to when an offer is accepted. Analyzing this can help identify bottlenecks in the hiring process and improve efficiency.
- Quality of Hire: This involves evaluating the performance of new hires after a certain period. It can be determined through factors like job performance ratings, turnover rates, and feedback from managers and peers.
- Source of Hire: Tracking where successful candidates are coming from (e.g., job boards, social media, employee referrals) can help refine recruitment marketing strategies.
- Applicant Drop-off Rate: By analyzing at which stage applicants drop out of the process, HR can identify and fix issues in the recruitment process.
- Candidate Experience: Surveys can be used to collect data on candidates’ experiences during the recruitment process. This can provide insights to improve the overall experience, enhancing the employer’s brand.
- Cost per Hire: This metric measures the total cost associated with hiring a new employee. By reducing this cost, companies can achieve significant savings.
- Offer Acceptance Rate: This measures how often job offers are accepted. A low rate may indicate issues with salary, benefits, company culture, or the way offers are presented.
- Diversity Metrics: Analytics can be used to evaluate diversity in hiring practices. This can be crucial for companies committed to diversity and inclusion.
- Skill Gap Analysis: By comparing the skills of successful employees with those of applicants, HR can identify any gaps and adjust their hiring criteria accordingly.
- Employee Referral Rate: Analytics can help determine how many candidates are coming from employee referrals, which can be a valuable source of qualified candidates.
HR Analytics Examples for Employee Retention & Turnover
- Turnover Rate: This is the percentage of employees who leave the company during a certain time period. It can be calculated overall or broken down by department, role, tenure, etc.
- Voluntary vs. Involuntary Turnover: Analyzing the reasons behind employee departures (voluntary or involuntary) can help identify potential issues within the organization.
- Turnover Cost: This metric includes costs associated with recruiting, onboarding, training, learning and development, and lost productivity. Understanding these costs can motivate strategies to increase retention.
- Exit Interview Data Analysis: Through analysis of exit interview responses, HR teams can gain insights into the reasons employees are leaving, which can inform strategies to improve retention.
- Retention Rate by Manager: If a particular manager has a high turnover rate in their team, it could indicate issues with management style or team dynamics.
- Absenteeism Rate: High absenteeism can be a predictor of turnover, as it may indicate employee disengagement or dissatisfaction.
- Promotion Rate: Understanding the rate of promotions within the organization can also be useful. A low promotion rate might indicate a lack of career development opportunities, which could lead to increased turnover.
HR Analytics on Learning & Development
- Training Completion Rate: This measures how many employees complete their training programs within a specified time period. A low rate might indicate that the training content or format is not engaging or accessible.
- Pre- and Post-Training Assessments: These post-training assessments measure the knowledge and skills of employees before and after training. Comparing these results can demonstrate the impact of training on employee knowledge and skill levels.
- Learning Application: Surveys or interviews can be used to determine how much of the training content employees apply in their work. This can provide valuable information on the practical relevance of the training programs.
- Training Cost per Employee: This measures the total cost of training divided by the number of employees trained. It can be helpful for budgeting and deciding whether to develop in-house training or hire external vendors.
- Training ROI: By comparing the cost of training programs with the benefits they deliver (increased productivity, reduced errors, etc.), companies can calculate the ROI of their training initiatives.
- Time-to-Proficiency: This metric tracks how long it takes for an employee to reach a defined level of competence after starting a training program.
- Employee Satisfaction with Training: Employee feedback can provide insights into how training programs are received and what improvements might be needed.
- Career Progression Post-Training: Tracking promotions or increased responsibilities post-training can provide insight into the effectiveness of training in terms of career development.
- Attrition Rate Post-Training: If attrition rates are high following specific training programs, this could indicate a problem with the training content, delivery, or relevancy.
- Performance Metrics Post-Training: Tracking changes in performance metrics after training can provide insights into the effectiveness of the training programs.
How to Get Started With HR Analytics
Here are the steps to help you get started with HR analytics in your organization.
- Define your objectives – Clarify the specific HR challenges or areas of focus where analytics can provide insights and solutions. Determine the goals you want to achieve through HR analytics, such as improving recruitment, optimizing workforce planning, or enhancing employee engagement.
- Identify relevant HR metrics – Determine the KPIs and metrics that align with your HR objectives. These could include metrics related to employee turnover, time-to-fill vacancies, training effectiveness, or diversity and inclusion.
- Assess data availability and quality – Evaluate your current data and its quality. Ensure that the data from sources like HRIS systems, surveys, and performance reviews is accurate, complete, and consistent. This step is crucial because poor-quality data can lead to inaccurate conclusions.
- Build analytical capabilities – Develop the necessary skills and expertise within your HR team to conduct HR analytics. This involves upskilling team members in data analysis, statistical techniques, and visualization tools. Alternatively, consider partnering with experts or leveraging external resources for support.
- Select appropriate analytics tools – Identify and implement suitable HR analytics tools and technologies, such as data visualization software, statistical analysis tools, or specialized HR analytics platforms.
- Analyze and interpret data – Use the selected tools to analyze the HR data and look for trends, correlations, or patterns aligning with your objectives. This step helps identify critical insights that can inform decision-making.
- Application – Use the insights gained from your analysis to improve HR practices. This involves making strategic decisions related to recruitment, retention, or employee development based on the findings.
- Communicate findings – Present the insights and recommendations from the HR analytics to relevant stakeholders, such as HR leadership, managers, or executives. Communicate the implications and potential benefits of the analytics findings and collaborate on implementing actionable strategies.
- Monitor and refine – Continuously monitor and assess the impact of your HR analytics initiatives. Collect feedback, evaluate the outcomes, and refine your analytics approach. This iterative process helps improve the effectiveness and value of HR analytics within your organization.
6 HR Analytics Software
HR analytics software tools are designed to collect, analyze, and interpret human resources and workforce management data.
HR analytics are often a specialized capability within a broader HCM system like Workday, ADP Now, or SAP SuccessFactors that analyzes your HR and people data to identify areas of employee friction, improve decision-making, and provide better HR services.
Let’s explore both stand-alone HR analytics software and broader HCM suites with HR analytics capabilities that can power your HR transformation:
Best stand-alone HR analytics software
These HR analytics are stand-alone products that add value to your HCM by collecting, analyzing, and forecasting based on your HR-related workforce data
1. intelliHR
intelliHR is a cloud-based HR analytics software designed to help organizations manage employee performance, engagement, and development. It provides real-time insights into workforce trends, enabling HR teams to make data-driven decisions that improve employee well-being and performance. Its user-friendly interface and customizable reports make it easy to track and measure key HR metrics.
Key features include:
- Real-time performance and engagement tracking.
- Advanced reporting and data visualization.
- Continuous employee feedback and sentiment analysis.
- Integration with other HR systems and payroll software.
- Customizable analytics dashboards for various HR metrics.
2. Crunchr
Crunchr is a specialized HR analytics tool focused on people analytics, workforce planning, and talent management. It offers a user-friendly interface that allows HR professionals to visualize, analyze, and report on workforce data, helping organizations understand workforce trends and optimize decision-making.
Key features include:
- Predictive analytics for workforce planning.
- Real-time insights into employee lifecycle data.
- Scenario planning and headcount forecasting.
- Customizable dashboards and reports.
- Integration with various HR systems for seamless data analysis.
3. Visier
Visier is a powerful HR analytics platform that provides comprehensive workforce insights. It is widely used by large enterprises to analyze employee turnover, engagement, and performance, as well as to plan for future workforce needs through predictive analytics.
Key features include:
- Predictive analytics for retention and turnover forecasting.
- Workforce planning and talent management insights.
- Data visualization with customizable reports and dashboards.
- Integration with existing HR systems for real-time data analysis.
- In-depth analysis of diversity, equity, and inclusion metrics.
4. Lattice
Lattice is a human resource management solution that enables HR teams to save time by automating review cycles for regular performance tracking. HR specialists can create custom templates for weekly, monthly, or quarterly reviews, and schedule their distribution ahead of time. The software has an accessible layout and offers a smooth navigating experience.
The employee review analytics feature makes it easy to complete and keep track of self, peer, and manager reviews and present team-oriented action plans, research-backed actionable insights, and real-time results analysis.
5. IBM Workforce Planning
IBM Workforce Planning software helps HR managers with workforce planning and forecasting. It enables teams to collect HR data sets from different sources and provides easy-to-interpret insights. The reports can be customized to generate the data and easily create predictive insights.
The software is powered by machine learning workforce forecasting, which makes it an ideal HR tool for planning and forecasting labor requirements.
6. Sisense
Sisense is a business intelligence and analytics platform that offers specialized solutions for HR analytics. It enables HR teams to create custom dashboards and reports to analyze employee performance, engagement, recruitment, and more, providing deep insights into workforce data.
Key features include:
- Customizable dashboards for employee performance tracking.
- Predictive analytics for recruitment and retention.
- Seamless integration with HR systems and data sources.
- Advanced data visualization and reporting tools.
- Real-time insights into workforce trends and employee engagement.
Best HCM systems with HR analytics capabilities
Modern HCM software comes with workforce analytics capabilities to analyze people’s data, automate reporting, and make data-driven HR decisions. Here are the best HCM software to power your HR analytics strategy:
1. Workday
Workday is a leading provider of enterprise cloud applications for HR, finance, and planning. It offers financial management, human capital management, and analytics applications.
Core HR reporting and analysis in Workday delivers secure, self-service access to a powerful analytics and reporting toolkit. You can track predefined metrics with configurable dashboards, detailed reports, responsive drag-and-drop custom and delivered discovery boards.
2. ADP Workforce Now
ADP Workforce Now is a comprehensive HCM solution that includes robust HR analytics capabilities. It helps HR teams analyze employee data related to payroll, benefits, and performance to make data-driven decisions that improve operational efficiency and workforce management.
Key features include:
- Customizable dashboards and real-time reporting.
- Analytics for payroll, benefits, and workforce trends.
- Employee performance and engagement tracking.
- Integration with payroll, compliance, and HR systems.
- Automated alerts and notifications for key HR metrics.
3. Leapsome
Leapsome is a customizable HR analytics software that offers a variety of features for HR teams to track employee performance, growth, and engagement. The software can also integrate easily with your existing tools — including HRIS, Slack, Teams, Calendar, or Jira.
One of the best features of Leapsome is its engagement analysis capabilities. This feature helps you set up employee engagement surveys using in-built templates. The tool then crunches the survey answers to identify engagement drivers and levels and interpret the sentiment of responses.
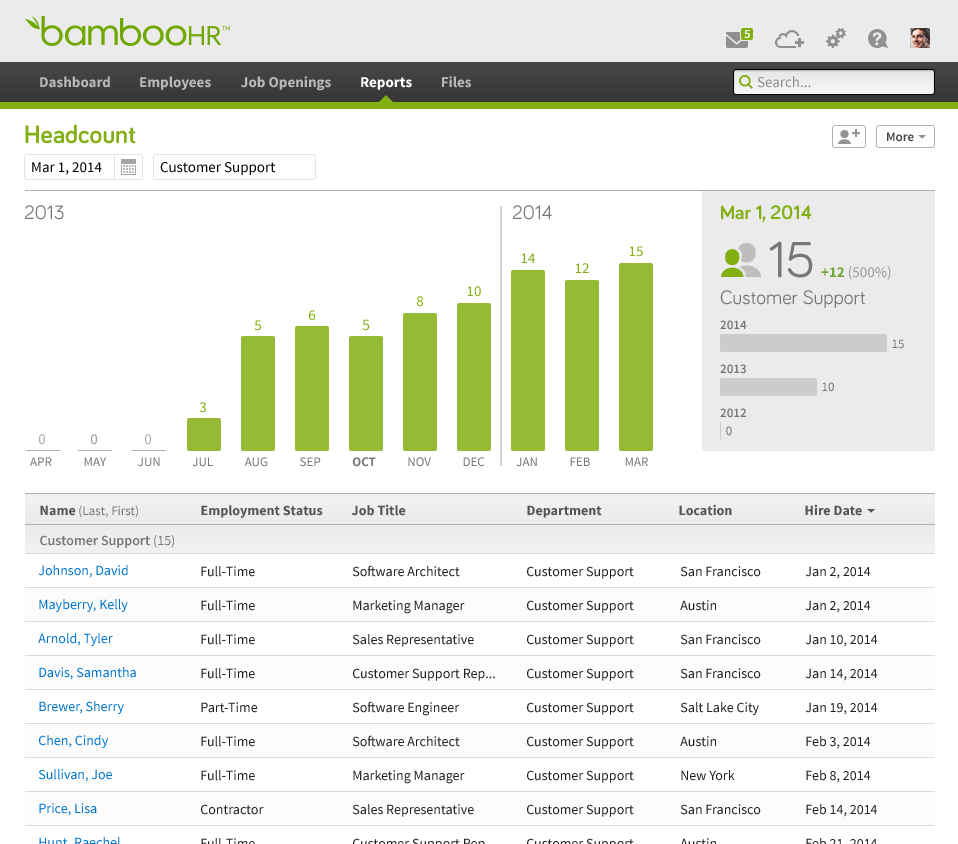
4. BambooHR
BambooHR is an all-in-one HR platform that facilitates gathering, storing, and analyzing employee data. The platform allows HR teams to create secure employee databases by using templated workflows or custom fields. You’ll also find detailed HR reports, charts, records on individual employees, and other critical data for making people-prelated decisions.
Besides providing people data and analytics features, BambooHR also offers helpful tools for hiring, onboarding, workforce management, and offboarding.
5. Hibob HR
Hibob is an HR platform that provides analytics for people management, employee engagement, and performance. It is ideal for small to medium-sized businesses, offering intuitive tools for tracking HR metrics, managing workflows, and analyzing workforce trends.
Key features include:
- Performance tracking and engagement analytics.
- Employee self-service tools and customizable workflows.
- Real-time reporting on employee satisfaction and retention.
- Integration with payroll and other HR systems.
- User-friendly interface designed for SMBs.
Trends in HR Analytics
Here are HR trends that can enable your HR team to prepare for the future and capitalize on emerging HR technology:
- AI and machine learning – AI and machine learning are revolutionizing HR analytics by enabling faster, more accurate processing of large data sets and uncovering hidden patterns in workforce data. These technologies allow for the automation of repetitive HR tasks, freeing HR teams for more strategic work. In the future, AI-driven HR analytics will become more sophisticated, capable of autonomously analyzing employee behaviors, identifying skill gaps, and predicting outcomes such as turnover, performance, and employee engagement with even greater accuracy.
- Sentiment analysis and employee experience – By analyzing employee sentiment, HR teams can better understand employee satisfaction, morale, and overall workplace experience in real time. The focus on employee experience will continue to grow, with organizations leveraging sentiment analysis to personalize employee development programs and improve overall well-being. AI-driven sentiment analysis will make processing large amounts of unstructured data easier, giving organizations timely insights into their workforce’s emotional and engagement levels.
- Predictive analytics – Predictive analytics allows organizations to anticipate future HR trends by using historical data to forecast outcomes like employee turnover and make proactive decisions. As predictive analytics becomes more advanced, HR teams increasingly rely on it to guide talent acquisition, workforce planning, and employee development strategies. Integrating AI and machine learning will enable even more accurate predictions, providing insights that allow companies to take proactive actions in a fast-evolving business environment.
Analytics Software Clicks Better With Whatfix
HR analytics can transform workforce management, driving data-driven decisions that enhance recruitment, retention, performance, and employee satisfaction. However, to truly maximize the potential of your HR analytics software’s potential, employees must efficiently navigate and use the available tools.
Whatfix’s in-app guidance offers real-time, interactive support to help HR teams master their analytics platforms, minimizing the learning curve and boosting productivity. Coupled with Whatfix’s advanced analytics, organizations gain deeper insights into how their HR tech is being used, ensuring optimized workflows and more informed decision-making. By integrating Whatfix into your HR analytics processes, your organization can unlock the full potential of its HR technology, leading to better outcomes and a more data-driven HR strategy.
To learn more about Whatfix, schedule a free demo with us today!






