As enterprises undergo digital transformation efforts, understanding the cornerstones that underpin successful change management has become a non-negotiable imperative for organizations worldwide.
These foundations, often encapsulated in the “People, Process, Technology” framework, form the bedrock of progressive enterprises seeking to harness the power of innovation in their journey of evolution for internal process improvements. But what exactly is the “People, Process, Technology” framework?
In this guide, we examine the roots of the People, Process, Technology (PPT) framework, its core components, and its real-world application within modern enterprises. You’ll learn about the three pillars – people, process, and technology – exploring how each contributes to the overall functioning of an organization.
We’ll then take you through practical, hands-on business use cases where the framework can transform organizations, empowering them to navigate digital transformation successfully. By understanding the interplay between people, processes, and technologies, you’ll gain the strategic insight to apply this framework effectively within your organization.
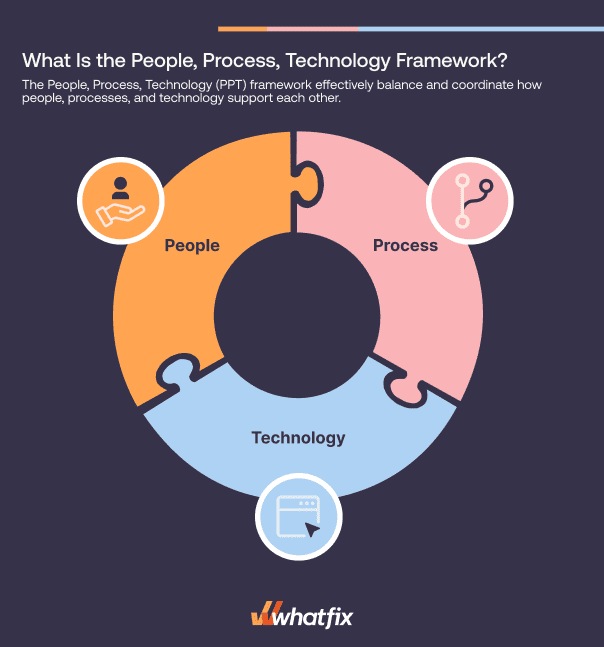
What Is the People, Process, Technology Framework?
The People, Process, Technology (PPT) framework was designed to help companies build systems that effectively balance and coordinate how people, processes, and technology support each other. The PPT framework is based on the idea that all three elements—people, process, and technology—need to work in harmony for successful business operations or change management. If one aspect is weak or not aligned with the others, it can impact the overall efficiency and effectiveness. The objective is to create synergy where each component enhances the other, improving business outcomes.
It is most commonly applied to project management and change management initiatives, but it’s a great starting point for companies to think holistically about all aspects of their business — like setting targets, managing risks, and pivoting strategies.
The History of the PPT Framework
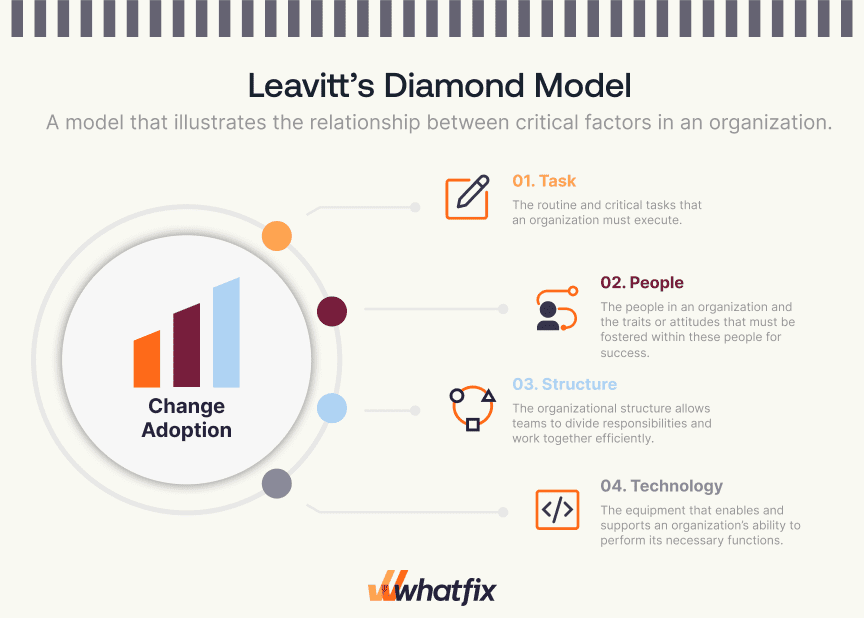
In the 1960s, Harold Leavitt designed Leavitt’s Diamond — a model that illustrates the relationship between critical factors in an organization. The model is based on four interdependent components:
- Tasks: The routine and critical tasks that an organization must execute.
- People: The people in an organization and the traits or attitudes that must be fostered within these people for success.
- Structure: The organizational structure allows teams to divide responsibilities and work together efficiently.
- Technology: The equipment that enables and supports an organization’s ability to perform its necessary functions.
This model began a systematic approach to change by assessing the relationship between different organizational factors.
The phrase “People, Process, Technology” rose to prominence in the 1990s when security technologist Bruce Schneier highlighted how these three organizational components did not evolve in isolation.
“It was an important notion; security back then was largely technology-only, and I was trying to push the idea that people and process needed to be incorporated into an overall security system,” Schneir wrote on his blog, explaining the need for the PPT framework in the context of a rapidly evolving IT security ecosystem.
Although the exact terminology and application of the framework have shifted over the decades, the primary goal of this approach is to teach organizations that change is never siloed. It will impact an organization’s multiple facets, whether we intend it to or not.
Related Resources:
Explaining the People, Process, and Technology Components of the PPT Framework
It doesn’t matter what type of business you’re in, the core principles of the People, Process, Technology framework can serve as a general template for you to map out challenges and draw operational solutions one step at a time.
Let’s explain what each element of the PPT framework represents, with examples of how you can set up each for success:
The People
People refers to the individuals in your organization responsible for putting in individual work or completing a project. This includes the employees that execute tasks, managers and leaders who set goals and make decisions, or stakeholders who bring companies toward their goals.
Your people are the fuel that brings your vision to life. Kicking off a change management project with leadership and key stakeholders is a great way to ensure you get the engagement and buy-in you need to get things done.
What can you do to set your projects up with the right people?
- Identify the skills, knowledge, experience, and capabilities you need: Build a team of people who contextually understand the goal that needs to be achieved and who are willing to learn to get there. This means a mix of leadership, key stakeholders that will be impacted the most by a project, project managers and technical coordinators who have the right skillsets, and individual contributors who will put in the needed efforts to be successful.
- Provide adequate training and support to navigate change: If introducing something new, find intuitive ways to educate your team and empower them with resources to support them on a new tool and accelerate change adoption.
- Build a culture that embraces change: Understand what motivates your team and what you can do to set realistic expectations for both employees and leaders when change occurs. This also includes identifying any reasons for internal resistance to change and working to overcome those challenges before they happen.
- Manage the time and energy of your people: Be meticulous in planning out your people resources so your project isn’t held up when certain individuals aren’t available or that a project doesn’t burn out your key people.
The Process
Authors Thomas H. Davenport and Thomas C. Redman wrote for the Harvard Business Review that changes within an organization “requires an end-to-end mindset, a rethinking of ways to meet customer needs, seamless connection of work activities, and the ability to manage across silos going forward.”
Process enables this by acting as the foundation that aligns people with the culture and quality of work a project or initiative needs. You need processes to guide teams through the proper steps and protocols when executing tasks. However, processes can still lead to a dead end if they aren’t communicated effectively to everyone involved.
As you define the processes your team needs, go back to the basics.
Be clear about your expectations and map feasible pathways for individuals to meet those criteria. You’ll also want to think about preventing avoidable bottlenecks like missed deadlines, unclear instructions, and having too many dependencies. Here are a few process-related questions to help get started:
- How quickly do you need each task executed?
- What are the minimum requirements your tasks need to be considered successful?
- How should your team communicate, does communication change across different hierarchies in your work unit, and what historically has been your change communication strategy?
- How should work be divided across your team to ensure project continuity?
- How will you document your processes, who will do it, what format will it be in, and where will you organize your process documentation?
- What process mapping tools will you use to visualize new processes?
- How will you onboard and train your team on these new processes?
- How will you collect feedback and iterate on processes to improve them?
- How will you provide continuous employee performance support related to these new processes?
The Technology
The technology component of the PPT framework refers to the tools and systems you use to support or enable your team to carry out processes more efficiently. Today, technology has become the focal point of organizational transformation across industries. In the past six months, 54% of organizations said that the type of change they experienced at work was technological.
New tools can be a big investment. IT spending worldwide is projected to reach $4.6 trillion in 2024. But even with the most advanced tool in the market, you can’t reach your unique business goals unless you’ve evaluated, implemented, and adopted the technology properly. With the PPT framework, organizations have a strategy for IT evaluation, governance, implementation, and technology enablement. At a high level, the People, Process, Technology framework would support projects through:
- Evaluation: Engage with stakeholders to decide on the business objectives that need to be met and conduct a needs analysis outlining the requirements of your technology solution. Evaluate vendors carefully based on these criteria to the solution can adapt to how your organization works and what it needs to achieve.
- Implementation: Build a software implementation plan that clearly defines timelines, goals, processes, and resources required to integrate new technology into existing work. Operationalize your workflow to streamline technology integration efforts and set a foundation for repeatable success. You can do this by setting up data capture processes, automating manual tasks, and streamlining feedback collection.
- Adoption: Invest in creating user experiences, in-app guidance, and self-help user support that shorten ramp-up times, reduce dependencies, and drive overall digital adoption of IT technology and software investments. In-app nudges, product tours, field validations, smart tips, and interactive flows are examples of content that help users build technology expertise through contextual learning that help drive adoption. For organizations like Sentry Insurance, technology proficiency is critical to reducing policy and claims processing errors and creating seamless workflows in internal and external communication. Sentry partnered with Whatfix to increase user adoption across eight internal applications, ranging from enterprise HCM and CRM applications to custom customer-facing applications.
What Are Business Use Cases of People, Process, Technology Framework?
The beauty of the PPT framework is its flexibility. Enterprises can easily modify it to meet business goals and overcome unique organizational challenges. Let’s explore a few scenarios where the PPT framework can be applied.
1. Your employees are taking too long to complete routine tasks
The People
Evaluate your team’s familiarity and proficiency with the systems involved in conducting these tasks. How much do they know about these tools and workflows? What are the biggest time-sinkers they experience? What are the key differences in completing these workflows for each contextual team member and business unit? Find out how to empower them with the right support so these tasks feel seamless and effortless, as well as contextual to their specific role.
The Process
Slow and outdated processes can hours of busy work to your plate. Identify areas where you can lean on automation and pre-built templates to move repetitive tasks along faster. You should also audit your end-to-end workflow to spot these manual tasks and shorten workflows where necessary.
The Technology
Be clear about benchmarks when assessing your tech stack. What defines success and efficiency if your goal is to streamline routine tasks? Do you have automated workflows, and if so, are these workflows saving you a sufficient amount of time? Are your tools helping you sort and map information for quicker decision-making? Did you provide contextual technology onboarding to your various business units and individual employees? Can those employees find task-related technology support when they need it?
2. Your employees are not adopting best practices for your digital applications and processes.
The People
Resistance toward best practices often stems from a lack of buy-in or poor end-user training. Start by understanding why your employees aren’t motivated to change their workflows. Do these best practices impose limitations on your employee productivity? Steep learning curves can demotivate individuals with little time to learn about new workflows from scratch.
The Process
Pinpoint key actions within your application that can benefit from additional guidance and training. From there, implement workflows that make it easy for employees to access training resources during onboarding and day-to-day interactions.
The Technology
Digital applications always evolve, so leverage tools to help you distribute and optimize training resources. Whatfix allows companies to measure employee engagement with in-app training content and guided product flows. You can use this data to analyze low engagement, identify employee friction points, and iterate on best practices to make them more impactful.
3. Your employees are not using the most efficient workflows in your applications and digital tasks
The People
Depending on your employees’ roles and responsibilities, their digital workflows will be based on different needs and priorities. What’s efficient for one function may not be efficient or relevant to another. Focus on personalization by assessing the goals of each team or department and understanding how digital tasks should be used to support them.
The Process
Assess the workflows your employees use across different tools in your tech stack. Are there parts of the workflows that can be condensed or removed? Are there opportunities for you to streamline workflows between disparate tools? Have you standardized and documented recommended workflows for employees to refer to on the job?
The Technology
Proactively nudge employees toward the most efficient workflows with in-app content like beacons, smart tips, and pop-ups. Ferring Pharmaceuticals uses Whatfix’s smart tips to help employees work faster and better by overcoming in-app friction immediately and independently. Over 4,000 smart tips are shown to their employees daily.
4. Implementing a new service request flow to improve your call center’s response times
The People
End-user training is critical for ensuring agents understand the new flow, as well as communicating why it’s happening (in this case, it may be to improve first-call resolution times.) This involves developing targeted training materials and providing hands-on training and practice sessions. Additionally, empowering agents with real-time, in-app guidance—such as contextual tips and automated workflows—will help them navigate the new system more confidently.
The Process
Updating the service request process requires examining the end-to-end workflow to remove task inefficiencies. This includes defining each step clearly, from call intake to resolution, and ensuring it aligns with customer expectations. Process mapping and ongoing feedback from agents help refine this flow over time.
The Technology
Your call center application must be configured to support your updated process flow, with features such as dynamic form fields, automated escalation triggers, and real-time customer information access. A digital adoption platform (DAP) like Whatfix enables agents with in-app support, task lists, and walkthroughs to reduce disruptions as they transition to the new service flow.
5. Implementing a new HCM system to streamline legacy HR processes
The People
End-user adoption will hinge on ensuring HR staff and end-users (both employees and managers) are well-trained on the new HCM system’s features. Change managers can facilitate initial end-user onboarding sessions, supplemented by ongoing, just-in-time guidance in the HCM system. DAPs like Whatfix can provide contextual support to reinforce workflows and help users independently resolve issues.
The Process
Clearly define and document your HCM workflows, such as hiring procedures, employee record management, and leave requests, to ensure compliance and consistency. Standardizing these HR workflows enables seamless task handoffs, reduces errors, and enables self-serviceability. Gathering feedback from early adopters helps refine the process before full deployment.
The Technology
The new HCM system is configured to reflect the organization’s policies, workflows, and compliance requirements. Integrating a DAP provides HR teams and employees with interactive, in-app guides for routine tasks, such as filling out timesheets or initiating leave requests, enhancing accuracy and efficiency.
Software Clicks Better With Whatfix
Technology connects people and processes so teams can do better work faster. However, this can only happen if employees are aligned on how to maximize their tools. Whatfix places powerful training and support at the pinnacle of every digital transformation initiative to motivate employee adoption.
Unlike training courses and static documentation, you can embed step-by-step guidance within the UI of your enterprise applications without using any code. Organizations use Whatfix to create and deploy in-app training content like interactive walkthroughs, tooltips, and self-help resource centers. All you need to do is choose a pre-built widget, customize it, and deploy it at high-friction points in your user journey across your CRM, ERP, HCM, CPQ, or any digital workflow.
With Whatfix DAP, it’s never been easier to enable employees in the flow of work, share recommended best practices, track employee engagement, and update content when processes change.
With Whatfix’, organizations can maximize software ROI and enable employees with:
Sandbox environments can be easily created, providing end-users with a replica application environment for interactive, hands-on user training in a risk free sandbox.
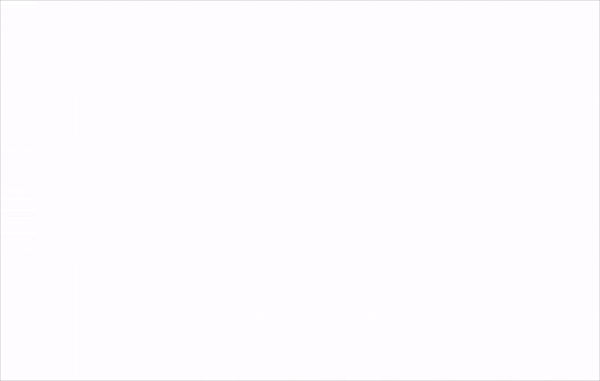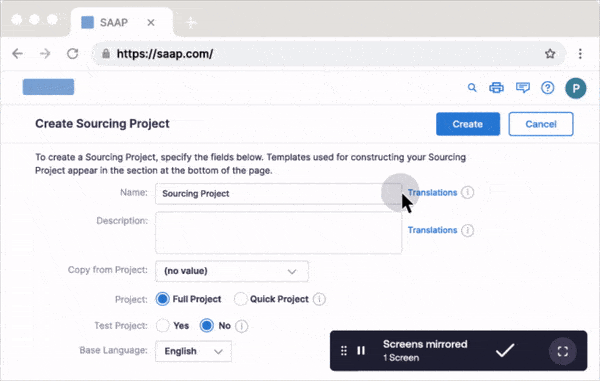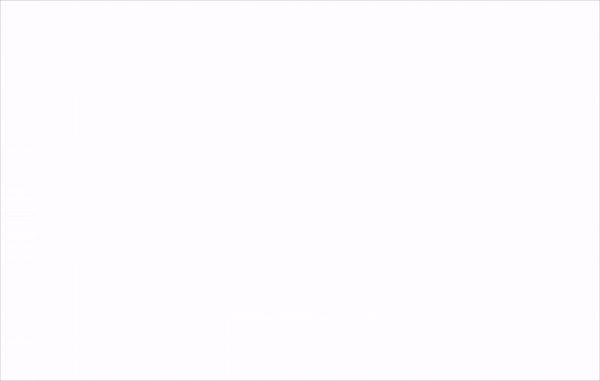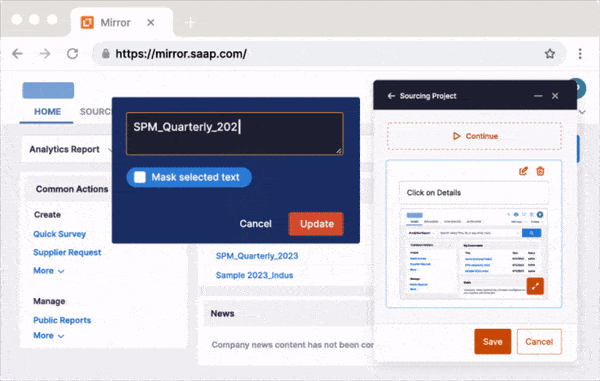
In-app guidance such as product tours, onboarding task lists, process flows, field validations, pop-ups, smart tips, and more – all providing contextual guidance for your employees at the moment of need, driving technology and business process adoption.
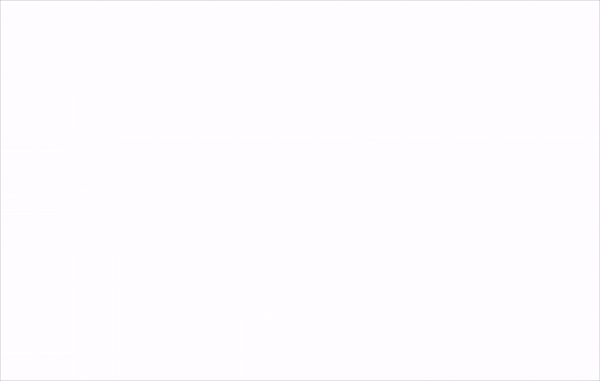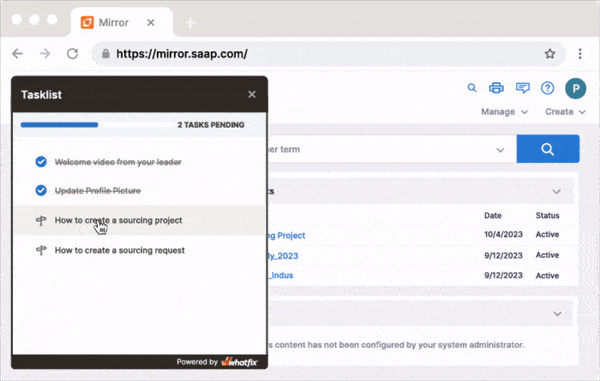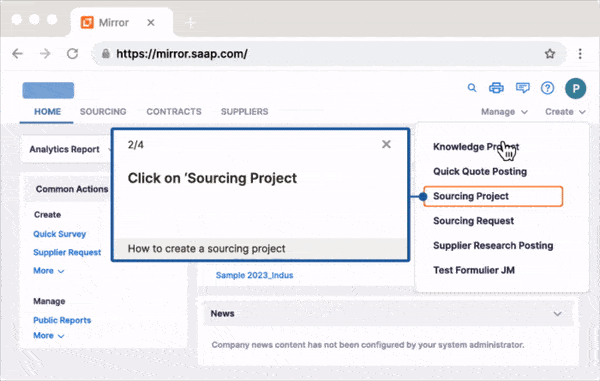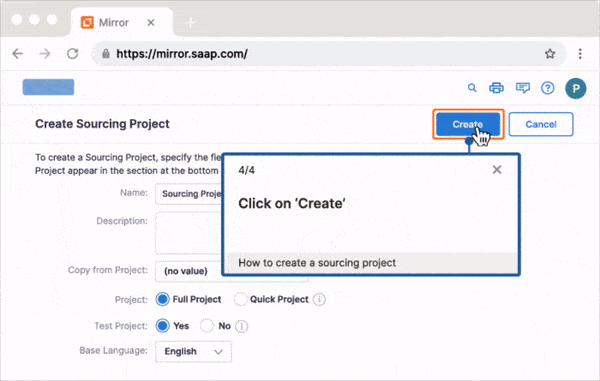
Self Help overlays on your digital workplace apps and integrates with your knowledge repositories such as your process documentation, intranet portal, internal wiki, Google Drive, LMS, and more. Users can search for any issue they’re facing, IT roadblock, or process-related question with its search functionality. Self Help can provide conversational genAI-powered answers that are trained by your internal knowledge and documentation. This enables end-users with support in the flow of work, without leaving the application.

Application analytics that enables continuous process improvement and a data-driven technology adoption strategy that captures insights into how your people are engaging and adopting your applications and digital workflows, helping you to uncover friction areas, under-adopted workflows or features, and tasks that are not being done correctly.
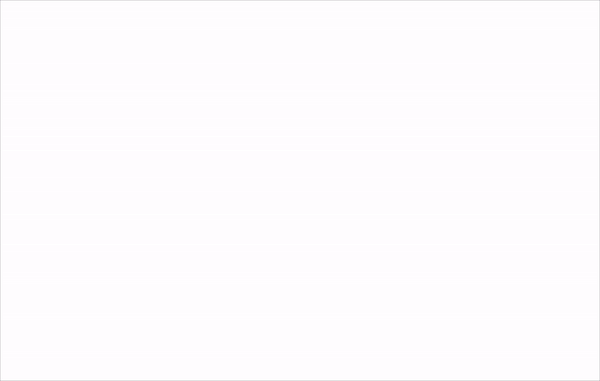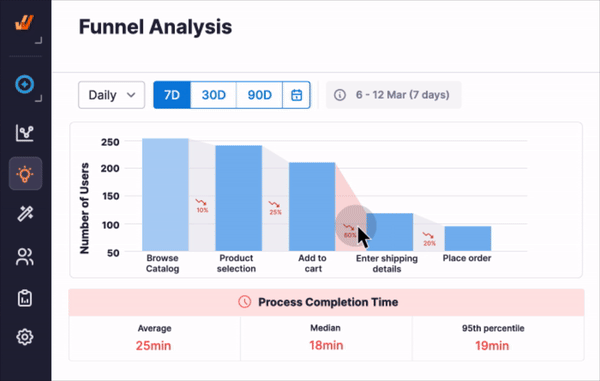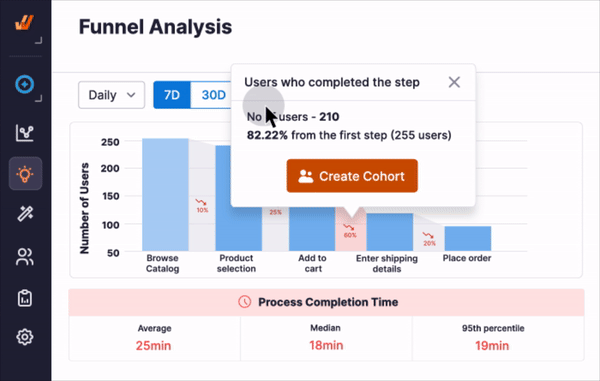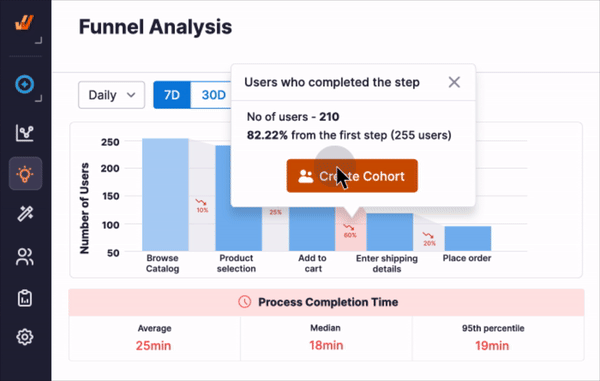
Whatfix supports organizations with the people, process, and technology-related support they need to reach their potential through people-centric IT and software enablement.
Ready to get started? Request a Whatfix demo now!






