Your inbox is overflowing, Slack pings never stop, and your phone lights up with notifications around the clock—digital overload isn’t just common, it’s overwhelming.
Unsurprisingly, we often feel tethered to our devices—smartphones, laptops, collaboration platforms—when technology seems to keep us connected 24/7.
In theory, all this digital innovation should simplify our lives and free up our time. And it’s true that, in many ways, our daily lives have never been easier. But along with these conveniences comes an unexpected burden: technostress.
According to the American Psychological Association, over 70% of adults in the United States report experiencing significant stress tied to their technology use. For employees—particularly in fast-paced or rapidly growing companies—this doesn’t just mean a little extra frustration. It can erode productivity, dampen morale, and even impact overall mental well-being. In the very midst of the digital era, technostress emerges as a subtle but powerful force that demands our attention.
So, how do we strike a balance and prevent our devices from becoming a source of anxiety?
In this article, we’ll explore technostress, uncover the key factors that contribute to it, highlight its real-world impact on individuals and teams, and offer practical strategies for beating it—ensuring technology truly remains our ally, not our adversary.
What Is Technostress?
Technostress is the mental strain and discomfort people feel when they struggle to keep pace with evolving technology. It’s not just about frustration with complex systems or tools—it’s the anxiety, burnout, and overwhelm that arise when technology feels more like a burden than a benefit.
The term was first introduced by psychologist Craig Brod in his 1984 book “Technostress: The Human Cost of the Computer Revolution” when personal computers were just starting to infiltrate workplaces. Fast-forward to today, and technostress has grown into a much broader and more complex issue as digital transformation reshapes how we work, communicate, and interact with technology daily.
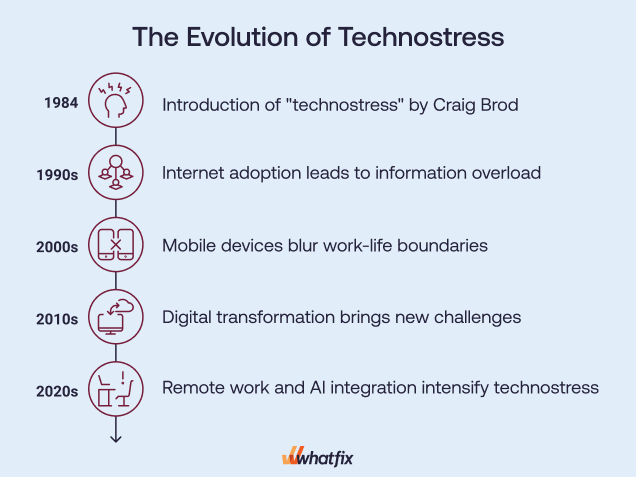
Technostress: Then vs. Now
- 1984 – The Beginning: Psychologist Craig Brod introduces “technostress” in his book Technostress: The Human Cost of the Computer Revolution. Heescribes anxiety from learning and adapting to computers entering workplaces.
- 1990s – Internet Adoption: The internet goes mainstream, leading to information overload and pressure to stay connected.
- 2000s – Mobile Devices & Connectivity: Smartphones and mobile devices blur work-life boundaries. There is pressure to be constantly available increases technostress.
- 2010s – Digital Transformation: Cloud computing, social media, and collaborative tools become essential to work. Technostress evolves to include data privacy concerns, cybersecurity, and the need to upskill continually.
- 2020s – Remote Work & AI Integration: The shift to remote and hybrid work models intensifies technostress.: New challenges include video call fatigue, information overload, and adapting to AI-driven tools.
What Causes Technostress In the Workplace?
Technostress doesn’t emerge from technology alone—it’s about how that technology is integrated, used, and experienced in the workplace. Understanding the core causes of technostress can help companies develop targeted strategies to minimize its negative impact.
Here are some of the reasons employees often feel overwhelmed by workplace technology:
1. Information overload, AKA “Techno-overload”
The relentless influx of digital communications—emails, instant messages, and notifications—can overwhelm employees, fragment their attention, and plummet productivity.
Deloitte reports that after an interruption, it takes an average of 23 minutes and 15 seconds to refocus on the original task. This constant bombardment leads to techno-overload, where the pressure to process excessive information within limited timeframes becomes a significant stressor.
2. Constant connectivity, AKA “Techno-invasion”
We live in an era of unlimited technology. The pressure to be available and accessible undeniably impacts our health.
The expectation for employees to remain perpetually connected blurs the lines between personal and professional life, fostering stress and burnout. In 2022, employees’ willingness to support enterprise changes dropped to 43%, down from 74% in 2016, suggesting growing fatigue and resistance to continuous connectivity demands.
This phenomenon, known as techno-invasion, compels employees to be available around the clock, undermining their ability to disconnect and recharge.
3. Rapidly change in technology, AKA “Techno-complexity”
Technological advancements create a scenario known as techno-complexity, where employees struggle to keep up with increasingly sophisticated systems.
Gartner found that 60% of employees experienced frustration with new software within the past 24 months, with 56% wishing management would revert to previous systems. This struggle to adapt often results in anxiety, reduced confidence, and lowered productivity.
4. Poor user experience (UX) and interface design, AKA “Techno-uncertainty”
When technology is unintuitive or cumbersome, even basic tasks can become sources of frustration and stress. Poor interface design increases cognitive load, leading to confusion and inefficiency.
Companies that prioritize strong user experience (UX) design can improve productivity; conversely, neglecting UX can create techno-uncertainty, leaving employees feeling overwhelmed, anxious, and unsure of how to effectively perform their tasks.
5. Fear of technology, AKA “Techno-insecurity”
Some employees experience techno-insecurity, a fear or anxiety surrounding technology usage, particularly when it’s perceived as complex or threatening to job security. This fear can amplify technostress, especially if the technology is perceived as unreliable or difficult to use.
Research from the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health indicates that techno-insecurity significantly contributes to workplace stress. Employees may feel pressured to continually upgrade their technological skills, heightening anxiety and potentially impacting their overall performance.

Related Resources
The Impact of Technostress On Businesses
Technostress in the digital age casts a long shadow over our collective well-being. The adverse effects of technostress range from biological to work-related effects like burnout and lost productivity. While responses vary among employees, several common, significant impacts of technostress consistently surface in modern workplaces:
1. Decreased job satisfaction
Constant frustration with workplace technology doesn’t just reduce productivity—it directly diminishes employee satisfaction.
Employees who frequently encounter issues like software glitches, information overload, or overly complex systems become increasingly irritable, anxious, and disengaged. A Gallup report emphasizes that engaged employees are 21% more productive, suggesting that unresolved technostress directly impacts organizational effectiveness.
2. Decreased productivity
Technostress significantly impacts productivity by increasing cognitive load and disrupting workflow. Employees who struggle with the technology tools they’re provided often experience task delays, inefficiency, and errors. According to a survey by Pegasystems, employees switch applications about 1,100 times daily, wasting significant time and causing mental fatigue.
3. Increased absenteeism and turnover rates
Technostress directly influences employees’ motivation and emotional investment in their work, leading to increased absenteeism and turnover. Employees facing continual stress due to technology are more likely to seek roles elsewhere, often citing the need for better work-life balance and more supportive technological environments.
A Work Institute study found that replacing an employee costs roughly 33% of their annual salary, highlighting the costly implications of high turnover rates driven by technostress.
4. Burnout
Chronic technostress is a major contributor to burnout, a condition characterized by emotional exhaustion and a diminished sense of personal accomplishment.
A Deloitte study found that burnout leads to a 33% decrease in employee performance and makes employees 54% less likely to stay with their employer. This “always-on” culture is particularly prevalent among remote and hybrid workers, who frequently report feeling compelled to respond immediately, further exacerbating their stress levels.
5. Behavioral impacts
Technostress often triggers negative behavioral changes, including reduced initiative, diminished energy, cognitive decline, and increased irritability. A two-year study published in the Journal of Occupational Health Psychology found significant cognitive impairment—including poor concentration, memory issues, and impaired decision-making—among employees experiencing high IT demands.
How To Deal With Technostress In Your Organization
The average person’s day is heavily tethered to screens, highlighting a paradox where digital engagement simultaneously connects and isolates, helps and hinders. Understanding and balancing digital habits is crucial for mitigating its impact.
Here are a few ways to deal with technostress in your organization.
1. Set boundaries for technological use
Many employees experience the pressure to remain “always on,” which can contribute to burnout and conflicts between work and family life. Establishing clear boundaries around technology use can help reduce this stress and promote a healthier work-life balance.
Organizations should establish policies that discourage after-hours communication, such as:
- No emails or messages after 7 PM unless in emergencies
- Do Not Disturb (DND) modes on work devices after hours
- Time-blocking strategies to set aside specific periods for deep work without digital interruptions
How to implement boundaries effectively:
- Define and communicate clear tech-free periods, like “no Slack messages after work hours.”
- Encourage employees to use DND settings on workplace apps
- Provide training on healthy digital habits and work-life balance
- Lead by example—ensure leadership respects these boundaries
2. Embrace technological change systematically
Sudden changes in technology can significantly impact employees, often resulting in increased stress and resistance to new systems. To alleviate these issues, it is beneficial to adopt a structured and gradual implementation process. This method helps employees adjust more smoothly, reducing anxiety and promoting a more positive transition to new technologies.
Step-by-step roadmap for smooth adoption:
- Assess needs: Identify which technologies employees struggle with the most
- Pilot test: Run a trial with a small group before organization-wide implementation
- Provide training: Offer hands-on workshops and real-time guidance using a digital adoption platform (DAP) like Whatfix
- Collect feedback: Regularly check in with employees to gauge their comfort levels
- Iterate and improve: Use feedback to refine processes and ensure smoother transitions
How Whatfix simplifies the transition:
- Provides in-app, step-by-step guidance to help employees learn at their own pace
- Offers analytics to track engagement and identify areas where employees struggle
- Reduces the learning curve with interactive walkthroughs, tooltips, and pop-ups
3. Work-life balance initiatives
Maintaining a balance between professional and personal life is essential for minimizing technostress among employees. Organizations should be aware of the importance of allowing employees to disconnect and create strategies that promote this balance effectively.
Work-life balance strategies:
- Flexible work hours to accommodate individual productivity rhythms
- Wellness programs offering mental health support, meditation, or exercise sessions
- Mandatory tech-free breaks during meetings and work hours to reduce screen fatigue
- Encouraging “focus time”—dedicated, uninterrupted work periods
4. Implement a digital adoption platform (DAP)
Techno-complexity and techno-uncertainty are major drivers of technostress, often stemming from employees struggling to navigate new digital tools. A digital adoption platform (DAP) like Whatfix helps reduce this stress by offering real-time, interactive guidance directly within applications.
With a DAP like Whatfix, employees don’t need to spend hours searching for help documentation or reaching out for IT support. Instead, they receive step-by-step walkthroughs, contextual tooltips, and on-demand self-help resources, all embedded within the software they’re using. This accelerates onboarding and training and ensures employees feel confident navigating digital tools without frustration.
How a DAP reduces technostress:
- Eliminates guesswork by providing real-time, contextual guidance
- Speeds up onboarding with interactive walkthroughs and self-help features
- Encourages continuous learning with microlearning resources embedded in the workflow
How Whatfix can help:
- Guided learning experiences: Interactive walkthroughs break down complex workflows into easy-to-follow steps, reducing cognitive overload
- Real-time assistance: Contextual tooltips and pop-ups provide immediate, in-app support, eliminating guesswork
- Self-help accessibility: A searchable knowledge base embedded within applications allows employees to find answers without disrupting their workflow
- Automation and task simplification: Whatfix enables organizations to automate repetitive processes, reducing manual effort and streamlining daily tasks
5. Improve user experience and interface design
A poorly designed digital interface increases cognitive load, making employees feel frustrated and overwhelmed. If employees constantly struggle to find what they need, remember complex workflows, or navigate cluttered dashboards, their technostress levels rise. Optimizing the UX of workplace technology can alleviate this burden.
Whatfix enhances the user experience by simplifying interactions with enterprise applications. Whatfix ensures employees can use software efficiently without feeling lost or frustrated through interactive onboarding, embedded tooltips, and contextual walkthroughs. By integrating intuitive UI/UX elements, organizations can minimize confusion, increase adoption, and improve overall productivity.
Practical ways to enhance UX/UI:
- Use clean, intuitive layouts to make navigation effortless
- Implement dark mode options to reduce eye strain
- Reduce unnecessary clicks by offering shortcut keys and automation
- Provide user-friendly error messages that offer solutions instead of vague warnings
How Whatfix improves UX and reduces technostress:
- Simplifies navigation: Step-by-step walkthroughs help employees seamlessly move through software workflows without trial and error
- Enhances discoverability: Contextual help widgets and pop-ups surface relevant information when and where needed
- Reduces errors: Interactive guides prevent mistakes by providing proactive guidance during critical tasks
- Customizes the user experience: Personalized learning paths ensure employees receive the right information based on their role and proficiency
6. Reduce digital noise and cognitive overload
Constant pings, alerts, and open browser tabs can create a work environment filled with distractions, making it difficult for employees to focus. Digital overload—caused by excessive notifications, frequent context-switching, and information fragmentation—contributes significantly to technostress.
Organizations should implement strategies to help employees regain control over their digital workspaces. These include reducing unnecessary notifications, streamlining digital communication, and using productivity tools that promote deep work.
How to minimize distractions:
- Use productivity tools to track and limit time spent on non-essential apps
- Enable focus modes on workplace apps to temporarily silence notifications
- Set designated times for checking emails and messages instead of reacting instantly
- Encourage batch processing tasks to improve efficiency
Software Adoption Clicks Better With Whatfix
Technostress isn’t just an inconvenience—it’s a productivity killer that leads to frustration, burnout, and disengagement. Organizations that proactively address it create a healthier, more efficient work environment where employees feel empowered rather than overwhelmed by technology.
A DAP like Whatfix plays a crucial role in reducing technostress by transforming how employees interact with enterprise software. Instead of struggling with confusing interfaces, endless training sessions, and overwhelming information, Whatfix empowers users with real-time, in-app support that simplifies technology adoption at every step.
Whatfix helps organizations combat technostress by providing:
- On-demand, in-app guidance: Interactive walkthroughs, tooltips, and pop-ups provide real-time, step-by-step instructions, so employees never feel lost or overwhelmed
- Self-help knowledge bases: Embedded self-service menus connect employees to FAQs, training materials, and company resources without breaking their workflow
- Automated onboarding and training: Personalized learning paths and contextual tutorials ensure employees learn software features progressively, reducing information overload.
- Smart notifications and task automation: Reduce cognitive load with proactive alerts and automation that simplify repetitive tasks and improve efficiency.
- Data-driven insights: Analytics track software usage, identify roadblocks, and help organizations continuously optimize employee training and support.
Organizations that invest in a digital adoption platform like Whatfix don’t just reduce technostress—they create an environment where employees feel confident, capable, and engaged with the technology they use daily.
Schedule a free demo today to see how Whatfix can transform your workplace and eliminate technostress.






