As businesses grow and operational complexity increases, ensuring that complex tasks and larger projects are done efficiently and consistently becomes a challenge
To address process governance issues, organizations create method of procedure (MOP), a form of process documentation to manage business processes more efficiently, enhancing organizational performance. MOPs provide clarity and structure to employees responsible for complex tasks and workflows, empowering companies to successfully navigate the intricacies of project execution, task completion, regulatory compliance, process governance, and workforce coordination.
In this article, we will go through the MOPs in detail, including how to develop them and some of their most significant use cases for organizations.
What Is the Method of Procedure?
A Method of Procedure (MOP) is a formal, detailed document that outlines step-by-step instructions for executing specific tasks, processes, or projects within an organization. It serves as a standardized user guide to ensure consistency, accuracy, and safety when carrying out complex or critical operations. MOPs typically include descriptions of the task’s objectives, the roles and responsibilities involved, the tools and resources required, and any safety precautions that must be followed, helping to minimize risks and errors during execution.
Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) vs. Method of Procedure (MOP)
While Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs), Method of Procedures (MOPs), and Emergency Operating Procedures (EOPs) all provide structured guidelines for completing tasks, they serve distinct purposes and are used in different contexts. Here’s how they differ.
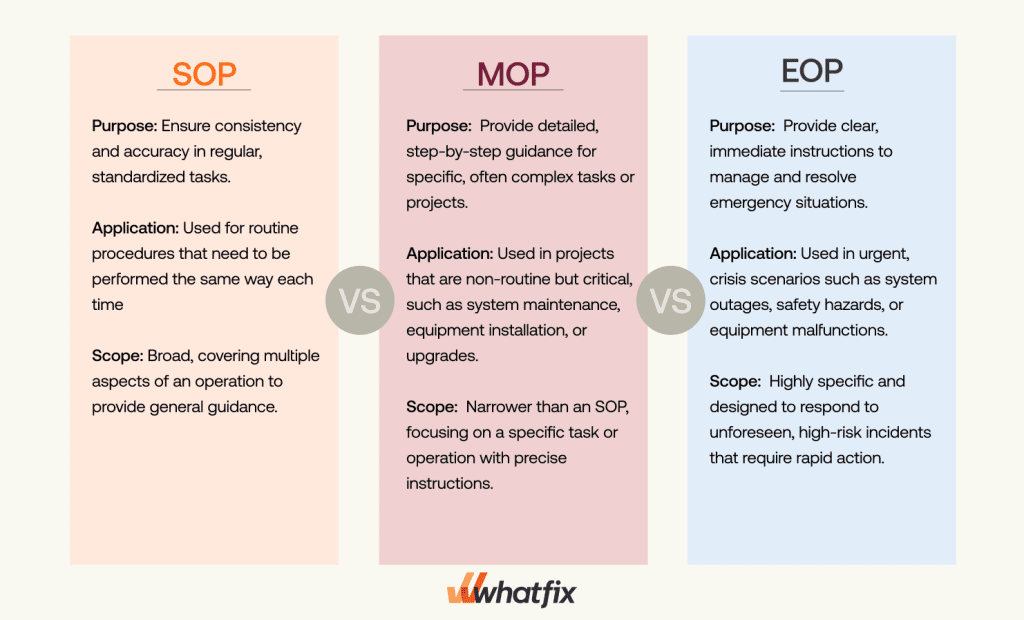
1. Standard operation procedure (SOP)
An SOP is a comprehensive document that provides detailed, step-by-step instructions for performing routine or standardized tasks in a consistent and repeatable manner. SOPs are used to ensure that operations are carried out correctly and efficiently across an organization. They often apply to everyday procedures and are designed to maintain quality, compliance, and safety in day-to-day activities.
- Purpose: Ensure consistency and accuracy in regular, standardized tasks.
- Application: Used for routine procedures that need to be performed the same way each time, such as data entry, equipment maintenance, or customer service protocols.
- Scope: Broad, covering multiple aspects of an operation to provide general guidance.
2. Method operation procedure (MOP)
A Method of Procedure (MOP) is more specific than an SOP and is used for complex tasks that require detailed, step-by-step instructions, often involving multiple people, teams, or systems. MOPs are typically used for tasks that require careful execution, such as system upgrades, installations, or integrations, where precision and attention to detail are critical.
- Purpose: Provide detailed, step-by-step guidance for specific, often complex tasks or projects.
- Application: Used in projects that are non-routine but critical, such as system maintenance, equipment installation, or upgrades.
- Scope: Narrower than an SOP, focusing on a specific task or operation with precise instructions.
3. Emergency operation procedure (MOP)
An Emergency Operating Procedure (EOP) is a specialized document that outlines the steps to take during an emergency situation to ensure safety and minimize damage. Unlike SOPs and MOPs, EOPs are focused on crisis management and are activated only when unexpected incidents, such as system failures, natural disasters, or other emergencies, occur. The goal is to provide immediate, clear actions to mitigate risk, restore normal operations, and protect people and assets.
- Purpose: Provide clear, immediate instructions to manage and resolve emergency situations.
- Application: Used in urgent, crisis scenarios such as system outages, safety hazards, or equipment malfunctions.
- Scope: Highly-specific and designed to respond to unforeseen, high-risk incidents that require rapid action.
Related Resources:
Components of Method of Procedure Documents
A Method of Procedure is a structured document that outlines the steps and resources needed to execute specific tasks or projects. It ensures clarity, consistency, and compliance in complex operations. Here are the essential components of an MOP:
- Objective: A clear statement of the purpose and goal of the procedure to explain what the task aims to accomplish and why it is being performed.
- Scope: Describes the boundaries of the procedure, including what is covered and what is excluded.
- Roles and Responsibilities: Identifies the individuals or teams responsible for each part of the procedure to assign accountability and ensure everyone understands their duties.
- Step-by-Step Instructions: To complete the task, detailed, sequential actions are needed. This provides clear and precise guidance for carrying out the procedure, minimizing confusion and errors.
- Tools and Materials: A list of equipment, software, and materials needed to execute the procedure.
- Safety Considerations: This section describes the safety precautions that must be taken during the procedure to ensure the safety of personnel and compliance with regulatory requirements, such as wearing protective gear or following specific protocols.
- Pre- and Post-Execution Checks: Actions to be performed before and after the procedure, such as inspections or validation steps.
- Testing and Verification: Instructions for verifying that the procedure has been successfully completed, including any tests to be run.
- Risk Assessment: Identify potential risks associated with the task and mitigation strategies.
- Approval Process: Details of who must approve the MOP before execution to ensure that the procedure is authorized by the relevant stakeholders, such as compliance or security teams, before being carried out.
- Sign-Off and Documentation: A section for signatures from responsible parties to confirm task completion.
How Product Teams Use a Method of Procedure
Here is how method of procedure documents enables product operations:
1. Product development
In the product development phase, MOPs help standardize complex processes, ensuring that all team members follow the same methodology. Product development often involves multiple teams, and a well-defined MOP ensures consistency in tasks such as designing prototypes, writing code, or setting up infrastructure.
MOPs provide step-by-step instructions for key tasks such as setting up development environments, defining coding standards, and creating design mockups. They ensure that all developers and designers are aligned and working towards the same goal with clear instructions.
This ensures uniformity in development processes, improves efficiency, and reduces errors during product creation.
2. Testing and QA
Testing and QA require precise procedures to ensure that the product functions as expected. MOPs guide the team through testing protocols, detailing the steps for performing unit, integration, system, and user acceptance testing.
An MOP for QA might include detailed steps for setting up test environments, running automated tests, documenting bugs, and verifying fixes. It ensures consistency in test execution and minimizes the chances of missing critical tests.
This guarantees that the testing process is thorough, repeatable, and free of inconsistencies, resulting in high product quality.
3. Product launch and release
During the launch and release phase, an MOP is essential to ensure a smooth rollout. Product teams often face strict deadlines, and any misstep can cause delays or introduce bugs. MOPs help guide the release process by providing clear steps for deployment, version control, and post-launch monitoring.
MOPs define specific steps for deploying software into production, managing version control, communicating with stakeholders, and handling potential issues. For example, an MOP may include instructions for staging deployment, backup procedures, and rollback steps in case of failure.
This helps avoid release-day mishaps and ensures that the launch process is carried out smoothly and efficiently.
4. Maintainance and updates
Once the product is live, ongoing maintenance and updates are necessary to fix bugs, enhance features, or improve performance. MOPs ensure that these tasks are carried out in a controlled and predictable manner, reducing downtime and avoiding disruptions.
MOPs in this phase detail the procedures for deploying updates, running patch management, and monitoring system performance. They may also outline the steps for notifying customers of planned maintenance and managing incidents.
This ensures updates are delivered with minimal disruptions and reduces the risk of errors during maintenance activities.
5. Collaboration
MOPs also serve as a valuable tool for fostering collaboration across different teams, such as developers, testers, and project managers. They provide a shared reference point, ensuring that all team members are aligned in their roles and responsibilities.
MOPs clearly define the responsibilities of each team member, ensuring that everyone knows their role in the product lifecycle. They act as a common document that facilitates smooth handoffs between teams, such as between development and testing or between product management and customer support.
This improves coordination across teams, prevents communication breakdowns, and ensures that tasks are handed off efficiently.
Why Use a Method of Procedure?
Here are the most significant benefits of implementing the method of procedure.
1. Eliminates guesswork
When employees aren’t supported with proper MOP documentation, outcomes are often not as expected and are low in quality. Having a method of procedure acts as a job aid to employees, increasing efficiency by eliminating all guesswork, as they have step-by-step guides to help them work through and complete processes, projects, and tasks.
2. Improves efficiency
With specific instructions for executing tasks, organizations spend more time experimenting with new workflows each time they complete a process. MOPs provide rules and guidelines to streamline processes and ensure employees complete a workflow as per a set standard. This saves time, improves employee productivity, drives team efficiency, and allows organizations to become process-orientated.
3. Provides clarity
MOP explains every step in detail. When created correctly, the language used is simple, crisp, and concise. Many MOPs also include images and screenshots to help provide additional attention to detail. This, in turn, offers clarity to employees.
4. Improves accountability
Having MOPs in place empowers managers to measure employee performance based upon a predetermined set of guidelines provided by them, giving transparency on who is responsible if (or when) things go wrong. Without proper work standards, understanding and improving employee performance becomes much more difficult for leaders and people managers.
How to Develop an Effective MOP
Here are the steps to follow to create an effective MOP for optimizing business processes.
1. Identify the task
The first step in developing an effective MOP is clearly identifying the task or process that needs to be documented. This task could be routine, complex, or a one-time operation that requires precise execution.
Define the specific operation that requires an MOP. Whether it’s a system upgrade, software deployment, or maintenance task, understanding the task’s purpose will provide the foundation for the procedure.
2. Consult the experts
Consult subject matter experts (SMEs) or team members who are deeply familiar with the task. Their input will help you capture all necessary steps and details, including nuances that could be missed by someone less experienced.
Gather information from SMEs, such as engineers, developers, or technicians who regularly perform the task. Ask them to walk you through the entire process, noting critical points.
3. Break down into smaller steps
Divide the task into clear, manageable steps. Each step must be simple enough to be followed without ambiguity but detailed enough to ensure nothing important is overlooked.
Break down the task into individual, sequential steps, ensuring each action is distinct and described in logical order. Include steps for preparation, execution, and post-task wrap-up.
4. Focus on clarity
Ensure that the language used is clear, concise, and easily understandable by anyone following the MOP, regardless of their expertise level. Avoid jargon unless it’s necessary and well-understood by the intended audience.
Use simple, direct language and clear instructions. Define any technical terms that might be unfamiliar to users. Write in the active voice to make the steps actionable.
5. Include diagrams, annotations, and visuals
Incorporate visual aids such as diagrams, screenshots, flowcharts, or annotations wherever required. Visuals can greatly enhance understanding, particularly for complex procedures or technical setups.
6. Beta test the procedure
Before finalizing the MOP, conduct a beta test by having someone unfamiliar with the task follow the procedure. This will help identify any gaps, unclear steps, or potential issues.
Select a team member or an independent tester to go through the MOP and execute the task as outlined. Monitor the process and gather feedback on whether the instructions are clear and accurate.
7. Review, analyze effectiveness, and revise
Review the results from the beta test, adjust the MOP for any errors or unclear instructions, and ensure it meets organizational and regulatory standards. Continuously update the MOP to reflect any process changes over time.
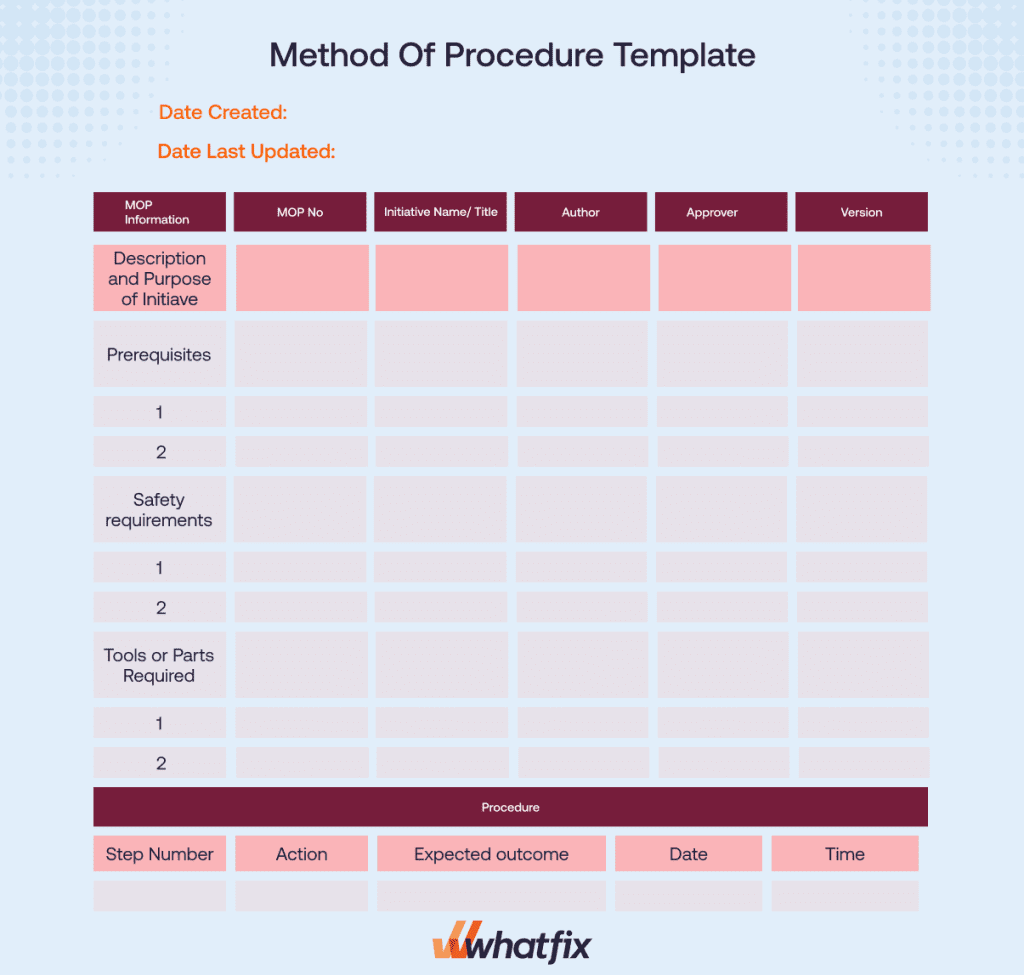
Free Method of Procedure Template
Download a customizable copy of our method procedure template to create your own MOPs quickly:
✓ Thank you, the checklist will be sent to your email
MOP Use Cases in Different Industries
Here are some of the most significant use cases of MOPs across different industries.
1. Telecommunications
In the telecommunications industry, MOPs are critical for maintaining and upgrading complex network infrastructures. They guide engineers through tasks such as installing new hardware, configuring software, upgrading systems, or troubleshooting network issues. Given the high stakes of network downtime, MOPs ensure precision and minimize disruption.
Use Case: When upgrading a telecom network tower, an MOP outlines every step, including equipment setup, safety protocols, software configuration, and testing. This reduces the risk of outages and ensures that systems are installed or maintained correctly.
2. IT and data centers
In IT and data centers, MOPs are used for tasks such as system upgrades, server migrations, backups, disaster recovery, and routine maintenance. With the complexity of managing vast amounts of data and mission-critical infrastructure, MOPs help standardize processes, reduce human error, and ensure compliance with security protocols.
Use Case: During a data center server migration, an MOP details the steps for safely shutting down servers, migrating data, verifying integrity, and bringing the system back online, all while minimizing downtime and data loss.
3. Construction
In construction, MOPs are used to guide the execution of construction projects, equipment installations, safety inspections, and other on-site tasks. They ensure that every part of a construction project is carried out in accordance with design specifications, safety regulations, and industry standards.
Use Case: For the installation of structural steel on a building, an MOP would outline the exact procedures, safety measures, equipment needed, and the sequence of installation steps, ensuring everything is done safely and accurately.
4. Manufacturing
In manufacturing, MOPs guide the operation, maintenance, and troubleshooting of machinery, as well as quality control processes on the production floor. They ensure that production lines operate efficiently, reduce waste, and meet safety standards, particularly in industries such as automotive or electronics manufacturing where precision is crucial.
Use Case: For a production line reconfiguration, a MOP provides detailed instructions on how to adjust machinery settings, replace parts, and perform safety checks, ensuring minimal disruption to manufacturing and high-quality outputs.
5. Healthcare
In healthcare, MOPs are used to standardize procedures for medical equipment maintenance, software systems (like EHRs), and even clinical workflows. They ensure that complex medical processes are carried out accurately, minimizing the risk of human error and ensuring compliance with healthcare regulations (such as HIPAA in the U.S.).
Use Case: When upgrading a hospital’s Electronic Health Record (EHR) system, a MOP provides a step-by-step guide for safely migrating patient data, ensuring the integrity of records, and testing the system post-migration.
Leveraging Whatfix for Superior MOP Management
While Method of Procedures (MOPs) provide the foundation for consistency, accuracy, and efficiency in complex operations, managing and updating them effectively is essential for long-term success. This is where Whatfix can play a pivotal role.
By leveraging Whatfix’s digital adoption platform, organizations can create interactive, real-time guidance for MOPs, ensuring that teams follow procedures accurately and seamlessly. With in-app walkthroughs, task automation, and performance tracking, Whatfix helps businesses reduce human errors, improve compliance, and streamline operational tasks. Adopting Whatfix for MOP management not only enhances productivity but also empowers teams with the tools they need to execute procedures confidently and efficiently in today’s fast-paced environments.
To learn more about Whatfix, schedule a free demo with us today!