On-the-job training (OJT) is a hands-on learning method where employees acquire skills directly while performing their job duties, often under the guidance of experienced mentors. Unlike classroom or eLearning formats, OJT embeds learning into daily workflows, making it practical, contextual, and immediate.
This method matters more than ever. According to a 2025 industry report, 68% of employees say on-the-job training is the most beneficial learning method, reflecting a strong preference for learning that is directly tied to real work tasks rather than abstract or detached training formats.
For L&D leaders, that preference presents both an opportunity and a challenge. While OJT promises faster competency development and higher retention, it can go off-track without structure, measurement, and alignment to business goals.
In this article, we learn about on-the-job training in detail, including its benefits, examples, and implementation strategies and also see how Whatfix can power OJT across workflows with guided, measurable, and in-context support.
What Is On-the-Job Training?
On-the-job training (OJT) is a hands-on training approach where employees acquire job-specific skills and knowledge by performing tasks in their actual work environment. Guided by mentors or supervisors, employees learn through real-world applications, observations, and practice. This method combines practical experience with immediate feedback, making it an effective way to develop competencies, improve productivity, and ensure seamless integration of training into daily workflows. OJT is often tailored to the specific requirements of a role or organization, making it a dynamic and relevant training solution.
On-the-Job Training vs. Off-the-Job Training
Here are some of the most significant differences between on-the-job training and off the job training approaches.
| Aspect | On-the-Job Training (OJT) | Off-the-Job Training |
| Location | Conducted at the actual workplace | Conducted away from the workplace (e.g., in a classroom or training facility) |
| Learning Method | Learning by doing; hands-on experience with real tasks | Theoretical learning; simulations, lectures, or role-playing exercises |
| Trainer | Typically supervised by experienced colleagues or supervisors | Often conducted by professional trainers or external instructors |
| Cost | Generally low cost, as it uses existing resources and facilities | Can be higher due to the costs of training materials, venues, and trainers |
| Time Flexibility | Integrated into regular working hours | Requires dedicated time away from work duties |
| Focus | Specific, task-oriented learning relevant to the job | Broad, covering multiple areas, including soft skills and theoretical knowledge |
| Examples | Mentorship, job shadowing, apprenticeships, hands-on tasks | Workshops, seminars, conferences, classroom training |
The Business Benefits of On-the-Job Training For Enterprises
On-the-job training (OJT) delivers measurable value because it builds skills directly in the flow of work. For enterprises, this translates into faster productivity, stronger retention, and higher ROI on training investments.
- Faster onboarding and productivity: OJT enables new hires to adapt quickly by learning tasks in the real work environment. This shortens ramp-up time, reduces errors, and accelerates time-to-proficiency. All of these are critical metrics for L&D and business leaders.
- Cost-effective training at scale: By leveraging internal resources, mentors, and real systems, enterprises reduce dependency on external trainers and costly facilities. Training happens where work happens, making it more efficient and budget-friendly.
- Training that aligns with business objectives: Because OJT is tied to actual processes and tools, employees learn skills directly relevant to organizational goals. This ensures training is not just theoretical but designed to improve day-to-day performance and compliance.
- Higher retention and employee engagement: When employees receive practical, hands-on training, they feel supported in their roles and more confident in their abilities. This improves job satisfaction, reduces turnover, and lowers rehiring costs. All of these are direct wins for the businesses.
- Workforce growth and adaptability: OJT helps employees refine both job-specific and transferable skills, preparing them for evolving responsibilities. Enterprises benefit from a workforce that can adapt faster to new technologies, workflows, and business requirements.
Core methods of on-the-job training with examples
On-the-job training can take many forms depending on the skills being taught, the complexity of the role, and the business objectives. Below are the most common methods enterprises use, along with examples of how they work in practice.
Job shadowing
Employees observe experienced colleagues to understand workflows, tools, and best practices. This is particularly effective for onboarding and role transitions.
Example: A new nurse shadows a senior nurse during patient intake to learn documentation and EHR workflows in real time.
Mentoring and coaching
One-on-one guidance from managers or senior colleagues helps employees refine skills and build confidence. Mentoring often focuses on career development, while coaching is more performance-specific.
Example: A sales manager coaches a rep on handling objections during live calls while tracking progress against sales KPIs.
Job rotation and cross-training
Employees rotate across different roles or functions to build broader skill sets and increase flexibility within the workforce.
Example: A finance analyst spends three months working with the procurement team to understand vendor contract processes.
Stretch assignments and project-based learning
Employees take on new responsibilities slightly beyond their current skill level, encouraging growth through challenge.
Example: A software engineer is asked to lead a small sprint team, gaining experience in leadership and project management.
Apprenticeships and internships
Structured programs that combine paid work with training, often used for technical or trade roles.
Example: An IT apprentice supports network maintenance while completing guided coursework to become a certified technician.
Simulation training
Employees practice in safe, controlled environments that mimic real systems or processes. This reduces risk while allowing hands-on learning.
Example: Customer service agents use a sandbox CRM environment to practice handling tickets before moving into the live system.
How to Create an On-the-Job Training Program
Here’s how to create an effective on-the-job training program for your organization.
1. Identify training needs
The first step in creating an on-the-job training program is assessing the specific skills, knowledge gaps, and competencies required for employees to perform effectively. This involves analyzing job descriptions, conducting performance reviews, and gathering feedback from managers and employees. Conducting a training needs assessment ensures that the program is targeted and relevant, addressing critical areas for individual and organizational growth.
2. Set clear objectives
Defining clear and measurable training objectives provides a roadmap for the training program. Objectives must align with organizational goals and specify the skills or knowledge employees are expected to acquire. Clear objectives ensure all stakeholders understand the purpose of the training and provide a basis for evaluating its success.
3. Design a structured plan
A structured training plan outlines the content, methods, schedule, and duration of the program. It includes step-by-step instructions, resources, and tools necessary for effective learning. A well-designed plan ensures consistency, minimizes disruption to daily operations, and provides a clear framework for both trainers and trainees.
4. Select trainers and mentors
Choosing experienced and skilled trainers or mentors is crucial for the success of the program. Trainers must possess both technical expertise and strong interpersonal skills to guide and motivate employees effectively. Matching trainees with mentors who understand their roles and challenges enhances the learning experience through personalized support and insights.
5. Leverage technology
Technology plays a central role in scaling on-the-job training and making it more effective. A variety of platforms can support OJT depending on your organization’s needs:
- Learning management systems (LMS): Centralize formal training, organize content, assign modules, and track employee progress. LMS platforms are especially valuable for compliance training and structured learning paths.
- Knowledge management systems (KMS): Provide employees with searchable access to SOPs, process documents, and best practices. Having information readily available helps employees resolve questions in the moment.
- Microlearning platforms: Deliver short, focused lessons that employees can complete during their workday without major disruption. This format is especially effective for reinforcing knowledge and reducing forgetting.
- Collaboration and communication tools: Platforms like Microsoft Teams or Slack can be integrated with training resources to provide reminders, peer-to-peer learning, and easy access to materials.
- Digital adoption platforms (DAPs): Embed in-app learning directly into enterprise software, offering step-by-step guidance, interactive walkthroughs, and self-help content in the flow of work. DAPs bridge the gap between training and real-world application by turning daily tasks into learning opportunities.
By combining these technologies, enterprises can deliver OJT that is structured, accessible, and aligned with how employees actually work.
6. Define evaluation metrics
Setting evaluation metrics helps measure training effectiveness. Metrics may include improvements in employee performance, retention rates, productivity, or participant feedback. Defining these metrics ensures the program’s impact is quantifiable and provides data to identify areas of improvement.
7. Create a feedback mechanism
Establishing a feedback loop allows employees to share their experiences and trainers to assess the effectiveness of their methods. Regular feedback sessions help address challenges, clarify doubts, and refine training processes. A robust feedback mechanism ensures the program remains dynamic and responsive to participant needs.
8. Review and improve
Continuous review and improvement of the training program ensure its relevance and effectiveness over time. This involves analyzing feedback, updating content, and incorporating new tools or techniques. Regular assessments help align the program with changing organizational goals, technological advancements, and industry standards.
On-the-Job Training Challenges
Here are some of the most common challenges you might encounter while implementing on-the-job training for your organization.
- Balancing training while also accelerating productivity – On-the-job training can disrupt daily operations as employees must balance learning new skills with meeting performance expectations. The challenge lies in designing training schedules that minimize workplace disruptions while enabling employees to quickly apply their new knowledge to boost productivity.
- Ensuring consistency in training – Inconsistent training methods or varying trainer expertise can lead to discrepancies in the knowledge and skills employees acquire.
- Addressing skill gaps – Employees may start training with diverse backgrounds and varying levels of expertise, making it challenging to address specific skill gaps effectively. Tailoring the training program to individual needs while maintaining overall program objectives is key to bridging these gaps.
- Managing the learning curve – Employees often face a steep learning curve when adapting to new skills or technologies, which can impact morale and productivity. Providing adequate support, such as mentoring or access to resources, helps employees overcome initial challenges and gain confidence in their roles.
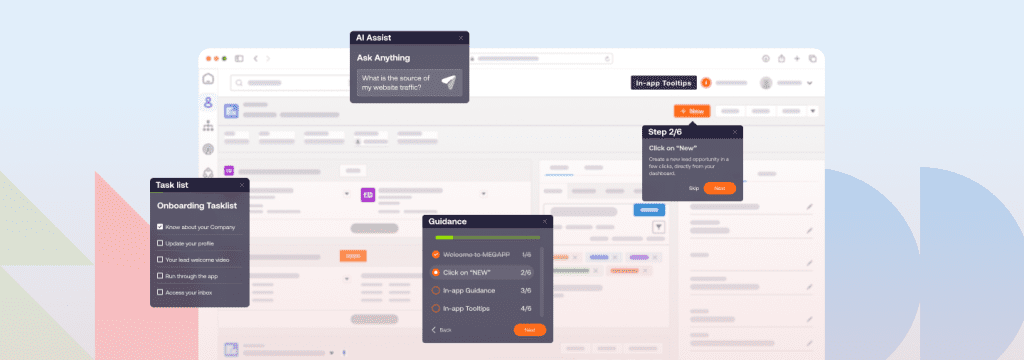
How Whatfix Enables On-the-Job Training In the Flow Of Work
On-the-job training delivers the most value when employees can learn while working, not by leaving their tools to search for answers. Whatfix embeds learning directly into enterprise applications, enabling employees to build skills, reduce errors, and apply knowledge in real time.
In-app guidance and walkthroughs
Whatfix enables organizations to design step-by-step interactive walkthroughs inside their applications. These guides lead employees through complex processes in real time, ensuring they learn by doing rather than memorizing from a manual. New hires can follow onboarding flows tailored to their role, while experienced employees benefit from refresher guidance on infrequently used tasks. The result is reduced errors, greater confidence, and faster proficiency without disrupting productivity.
Sandbox practice with Whatfix Mirror
For high-stakes workflows, employees need a safe space to practice before applying new skills in live environments. Whatfix Mirror creates a fully interactive simulation of enterprise applications, replicating real workflows without the risk of impacting production data. Employees can experiment, make mistakes, and repeat steps until they are comfortable. This not only shortens ramp-up time for new tools and processes but also minimizes costly errors once employees move into live systems.
Personalized task lists and smart tips
Whatfix allows managers and L&D teams to create task lists customized to job roles, guiding employees through the most critical workflows they need to master. These lists act as structured checklists embedded within the application, ensuring training aligns with business priorities. Smart tips can be placed on specific fields or steps to remind users of compliance requirements, data entry rules, or process updates. This proactive guidance reinforces best practices exactly when employees need it, strengthening adherence and reducing rework.
Contextual self-help
Employees often encounter friction mid-task like a missing step, an unfamiliar feature, or a forgotten policy. With Whatfix Self Help, answers are available directly in the application, tailored to the user’s context. Employees can access articles, SOPs, videos, or microlearning modules without leaving their workflow. By empowering users to solve problems independently, Self Help reduces dependency on managers or IT support, lowers ticket volumes, and ensures employees stay productive.
Analytics to measure training impact
Training programs often fail because they lack visibility into what works and what doesn’t. Whatfix’s Guidance Analytics provide detailed insights into how employees interact with training flows, where they drop off, and which processes cause the most friction. L&D leaders can use this data to refine content, prioritize support for high-impact workflows, and demonstrate ROI by tying training interventions to measurable improvements such as reduced errors, faster task completion, and increased adoption of digital tools.
On the Job Training FAQs
Is on-the-job training effective?
Yes. OJT is highly effective because it allows employees to apply new skills immediately in their actual work environment. This hands-on approach improves retention, reduces ramp-up time, and helps employees build confidence faster compared to classroom-only training.
What are the disadvantages of on-the-job training?
Disadvantages can include inconsistent delivery across trainers, potential errors during live practice, and limited tracking of outcomes without supporting technology. These risks can be minimized with structured programs and digital tools.
How does on-the-job training improve employee engagement?
OJT shows employees that the organization invests in their growth by providing practical, relevant learning. This builds confidence, reduces frustration, and creates higher engagement, which contributes to better retention.
How is on-the-job training different from coaching or mentoring?
Coaching and mentoring are forms of support often used in OJT, but OJT also includes structured activities like shadowing, rotation, or simulations. Coaching focuses on performance improvement, mentoring on career development, while OJT covers both immediate and long-term skill building.
How can technology improve on-the-job training?
Tools such as learning management systems (LMS), knowledge management platforms, and digital adoption platforms (DAPs) help structure, track, and deliver OJT. DAPs, in particular, embed in-app guidance, walkthroughs, and self-help resources, making training continuous and measurable.
How do you measure the effectiveness of on-the-job training?
Effectiveness can be tracked using pre- and post-training assessments, performance KPIs (such as time-to-proficiency, error rates, and task completion times), employee feedback, and analytics from LMS or DAP tools.
Upskilling Clicks Better With Whatfix
On-the-job training is a powerful method for developing employee skills directly within the work environment, leading to immediate application and improved retention of knowledge. However, effectively implementing and managing OJT can be challenging, particularly when balancing productivity, ensuring consistency, and addressing individual learning curves.
This is where Whatfix can make a significant difference. Whatfix’s digital adoption platform enables seamless on-the-job training by providing in-app guidance, personalized learning experiences, and real-time support embedded directly within the application or software. With Whatfix, organizations can empower their employees to learn as they work, ensuring that training is both efficient and effective, ultimately leading to enhanced performance and better business outcomes.
To learn more about Whatfix, schedule a free demo with us today!