The workplace is relentlessly evolving—new technologies, shifting market demands, evolving job roles. The ability to adapt to organizational change isn’t just an advantage—it’s a necessity. But what separates employees who thrive in uncertainty from those who struggle to keep up? Learning agility.
Contrary to what many believe, learning agility isn’t just about your potential to learn—it’s about how quickly and effectively you can apply new knowledge in real-world situations. It determines whether an employee stagnates in the face of change or transforms challenges into opportunities. High-learning agility professionals don’t just absorb information; they adjust, innovate, and drive results, making them indispensable for modern organizations.
In this article, we explore the concept of learning agility and its five key dimensions—mental, people, change, results, and self-awareness. We’ll discuss how to measure learning agility, why it’s a critical predictor of workplace effectiveness, and how to cultivate it at every level of your organization.
What Is Learning Agility?
Learning agility is the ability to quickly learn, unlearn, and apply new knowledge in unfamiliar situations. It refers to an individual’s or organization’s capacity to adapt, think critically, and solve problems in evolving environments. Learning agility emphasizes flexibility, curiosity, and the ability to transfer past experiences to new challenges.
Organizations that foster learning agility stay ahead of industry shifts, drive innovation, and build a workforce capable of navigating uncertainty. Employees with high learning agility are more resilient, adaptable, and effective in leadership roles, making it a crucial skill for long-term career and business success.
The Five Dimensions of Learning Agility
Learning agility is a multi-faceted skill that enables individuals to adapt, grow, and thrive in changing environments. It is built on five key dimensions that determine how effectively someone can absorb new information, apply insights, and navigate uncertainty.
Mental Agility
Mental agility is the ability to think critically, analyze complex problems, and approach challenges with an open mind. Individuals with high mental agility can quickly process information, see patterns, and connect ideas across different domains. Here are some characteristics of individuals with mental agility:
- Embraces complexity and enjoys solving tough challenges.
- Comfortable with ambiguity and thinking outside the box.
- Quickly adapts strategies when faced with new problems.
People Agility
People agility is the ability to work well with diverse teams, communicate effectively, and build strong relationships. Those with high people agility adapt their approach based on different personalities, work styles, and cultural dynamics. Here are some characteristics of individuals with people agility:
- Open to different perspectives and feedback.
- Excels in team collaboration and conflict resolution.
- Builds strong professional networks and relationships.
Change Agility
Change agility refers to a person’s ability to embrace and drive change rather than resist it. Here are some characteristics of individuals with change agility:
- Thrives in new, uncertain, or disruptive environments.
- Seeks out new challenges and enjoys experimenting with different approaches.
- Stays positive and resilient when facing unexpected shifts.
Results Agility
Results agility is the ability to deliver high performance in challenging situations, even when working outside one’s comfort zone. It reflects a person’s drive to succeed, problem-solving skills, and ability to stay focused under pressure. Here are some characteristics of individuals with results agility:
- Stays composed and resourceful in high-stress situations.
- Balances risk-taking with a strong focus on achieving goals.
- Adapts strategies to maximize performance in new environments.
Self-Awareness
Self-awareness is the foundation of learning agility, as it helps individuals understand their strengths, weaknesses, and learning preferences. People with high self-awareness actively seek feedback and adjust their approach to maximize personal and professional growth. Here are some characteristics of individuals with self-awareness agility:
- Recognizes areas for improvement and seeks continuous development.
- Actively solicits feedback and uses it constructively.
- Maintains emotional intelligence and understands personal impact on others.
Related articles:
The Importance of Learning Agility in Leadership
In times of change, leaders need to be more agile than ever. Navigating shifting business strategies, collaborating across diverse cultures, managing remote teams, and handling new responsibilities all demand leaders to be flexible and agile.
Learning agility in leadership is the ability of leaders to adapt, learn from experiences, and apply new knowledge in unfamiliar or rapidly changing situations. It is a critical trait that allows leaders to navigate uncertainty and make informed decisions.
Unlike traditional leadership skills that rely on past experiences, learning-agile leaders continuously evolve, embracing new challenges, feedback, and perspectives. They are open to rethinking strategies, unlearning outdated methods, and developing new approaches to tackle business complexities.
Key traits of learning-agile leaders include:
- Mental Agility: They think critically, analyze complex problems, and adapt to changing environments.
- People Agility: They communicate effectively, build strong relationships, and inspire diverse teams.
- Change Agility: They embrace transformation, take calculated risks, and see change as an opportunity.
- Results Agility: They maintain focus and deliver strong outcomes, even in uncertain conditions.
- Self-Awareness: They actively seek feedback, reflect on their performance, and continuously improve.
The Benefits of Learning Agility
Let’s discuss some of the most significant benefits of learning agility both for businesses and individuals.
Benefits of Learning Agility for Businesses
- Faster adaptation to market changes: Organizations with learning-agile employees can quickly adjust to industry shifts, technological advancements, and economic disruptions, maintaining a competitive edge.
- Increased innovation and problem-solving: A culture of learning agility encourages experimentation and creativity, enabling teams to find new solutions to evolving challenges.
- Stronger leadership and decision-making: Learning agile leaders navigate uncertainty with confidence, make data-driven decisions, and inspire teams to embrace change.
- Higher employee engagement and retention: Employees who continuously learn and develop feel more valued, motivated, and committed, reducing turnover and improving workplace satisfaction.
- Future-proofing against disruptions: Organizations that prioritize learning agility can upskill their workforce, stay ahead of automation trends, and thrive in unpredictable business environments.
Benefits of Learning Agility for Individuals
- Career growth and job security: Professionals who continuously acquire new skills and adapt to industry trends stay relevant and unlock more career opportunities.
- Better problem-solving and critical thinking: Learning agility enhances analytical thinking, adaptability, and the ability to solve complex problems efficiently.
- Higher resilience and ability to handle uncertainty: Those with strong learning agility embrace change, recover quickly from setbacks, and turn challenges into opportunities.
- Stronger collaboration and adaptability in teams: Adaptable individuals work well in diverse teams, communicate effectively, and adjust to different work cultures.
- Lifelong learning and personal fulfillment: A mindset of continuous learning leads to personal growth, intellectual curiosity, and a greater sense of purpose in both professional and personal life.
How to Measure and Assess Learning Agility in the Workplace
Measuring learning agility requires a structured approach that evaluates how well individuals and organizations adapt, learn, and apply new knowledge in dynamic environments. Below are key methods to assess learning agility effectively.
Define key indicators
Before measurement, organizations must identify key behaviors that reflect learning agility. These indicators include:
- Openness to new experiences – Willingness to embrace unfamiliar challenges.
- Speed of learning and adaptability – Ability to acquire and apply new knowledge quickly.
- Problem-solving and innovation – Thinking critically and creatively to find solutions.
- Resilience and comfort with uncertainty – Ability to recover from setbacks and navigate change.
- Feedback responsiveness – Seeking and applying constructive criticism.
- Interpersonal responsiveness: Ability to foster positive relationships, and function effectively in diverse teams.
Implement methods for measuring learning agility
Here are some of the methods for measuring learning agility in the workplace.
Learning agility assessments and psychometric tests
Organizations can use the following structured assessments to evaluate an individual’s adaptability, decision-making, and problem-solving abilities.
- Korn Ferry assessment – This assessment evaluates an individual’s ability to learn, adapt, and perform in new and changing environments. It measures agility across five dimensions: Mental, People, Change, Results, and Self-Awareness. This assessment is widely used in leadership development and talent identification.
- Lominger agility model – This model focuses on identifying high-potential employees based on their ability to learn from experiences, adapt to new challenges, and apply knowledge effectively. It assesses how individuals seek feedback, embrace change, solve problems, and handle complex situations, making it a useful tool for succession planning, leadership development, and talent management.
- Hogan agility assessment – Measures adaptability, curiosity, and ability to handle complexity. It evaluates traits such as openness to new experiences, willingness to take risks, and problem-solving capabilities to determine how well someone can navigate uncertainty and learn from different situations. This assessment is commonly used for leadership hiring, executive coaching, and high-performance team development.
Behavioral interviews and situational judgment tests
Behavioral interviews and situational judgment tests (SJTs) provide insight into how candidates respond to new challenges, adapt to change, and apply past experiences to solve unfamiliar problems.
Behavioral Interviews – Use open-ended, experience-based questions to assess how a person has handled challenges in the past. The assumption is that past behavior is a strong predictor of future performance. Candidates are asked to describe specific experiences where they had to learn, adapt, or navigate uncertainty.
Example questions:
- “Explain a time when you had to learn something new quickly—how did you manage?” → This assesses the candidate’s ability to upskill rapidly, problem-solve, and seek knowledge proactively.
- “Describe a situation where you had to lead a project outside your expertise. What did you do?” → This evaluates how well the candidate handles ambiguity, collaborates with others, and acquires new knowledge on the go.
Situational Judgment Tests – Present candidates with hypothetical work-related scenarios and assess their ability to analyze situations, make decisions, and adapt to change. These are commonly used in leadership hiring, talent development, and high-potential employee identification.
Candidates are given realistic workplace scenarios and must choose the best response from multiple options. For instance: “You’ve just been assigned to lead a project in an area you’re unfamiliar with. Your team looks to you for guidance, but you lack technical expertise. What do you do?”
- Try to learn everything yourself before making any decisions.
- Collaborate with team members who have relevant experience and seek their input.
- Stick to what you know and delegate technical parts without involvement.
- Request to be reassigned to another project.
The best response is B. Collaborate with team members who have relevant experience and seek their input. This demonstrates learning agility, teamwork, and adaptability—critical traits for high-performance employees.
Both behavioral interviews and SJTs provide organizations with data-driven insights into a candidate’s ability to handle unfamiliar situations, continuously learn, and thrive in dynamic environments.
Performance reviews and 360-degree feedback
Performance reviews and 360-degree feedback provide a comprehensive, real-time assessment of an individual’s learning agility, offering insights from managers, peers, and direct reports.
In formal performance reviews, managers assess how well employees embrace feedback, develop new skills, and adjust to evolving job demands. 360-degree feedback, on the other hand, expands this evaluation by gathering insights from colleagues, subordinates, and external stakeholders, ensuring a well-rounded perspective on an individual’s adaptability, collaboration, and resilience.
Real-world learning challenges and simulations
Real-world learning challenges and simulation training test employees’ ability to adapt, problem-solve, and apply knowledge in unfamiliar situations. By placing employees in new environments, stretch assignments, or cross-functional roles, organizations can observe how well they learn on the job, handle uncertainty, and navigate complex challenges.
Business simulations, hackathons, and project-based learning exercises further help assess critical thinking, collaboration, and agility under pressure. For leadership and high-potential employees, temporary role rotations or crisis management scenarios provide insights into decision-making, adaptability, and resilience—key traits of learning agility.
Tracking learning engagement and upskilling efforts
Monitoring an employee’s participation in L&D programs, self-directed learning, and upskilling initiatives provides insights into their commitment to continuous learning and adaptability. Metrics such as course completion rates, certifications earned, engagement with training content, and participation in mentorship programs help gauge learning agility.
With a digital adoption platform like Whatfix DAP, organizations can provide hands-on learning and support employees in the flow of work to reinforce training and govern processes.
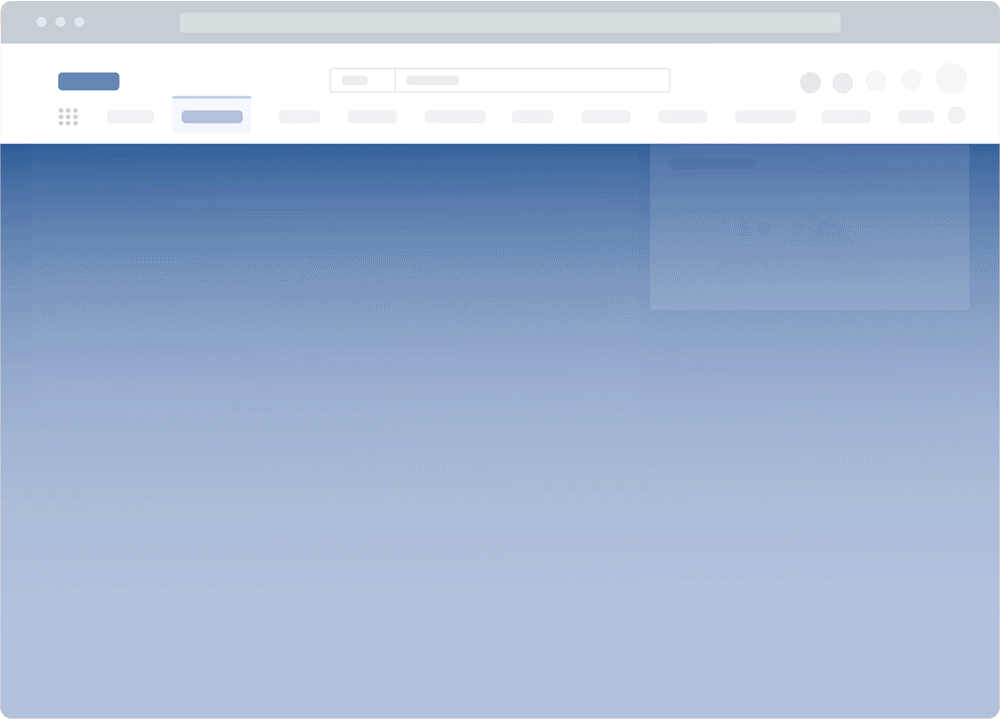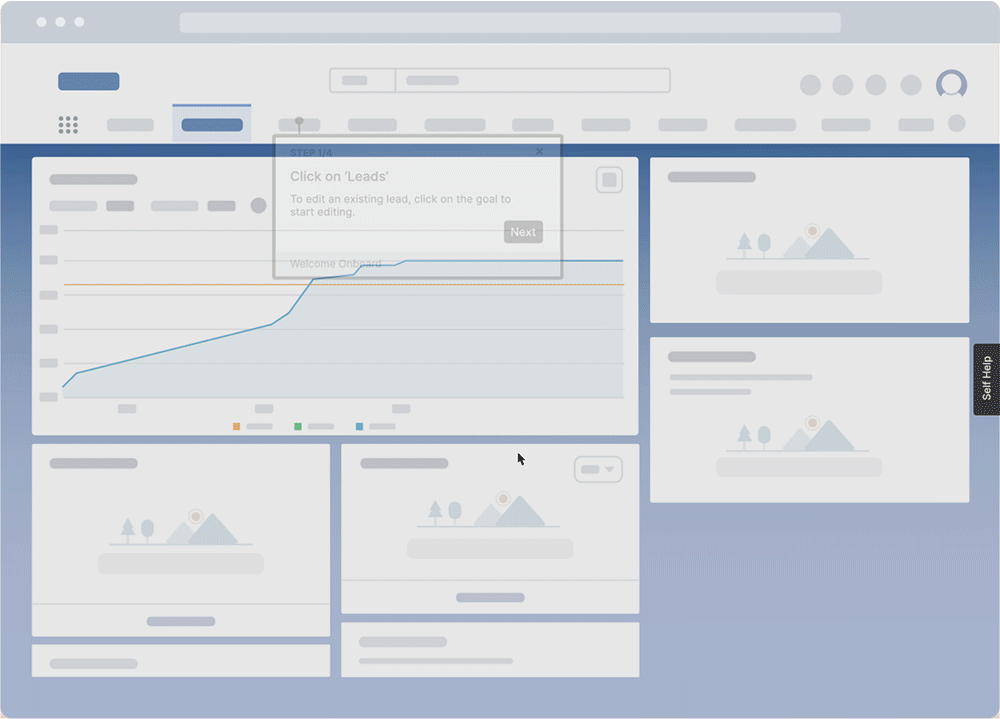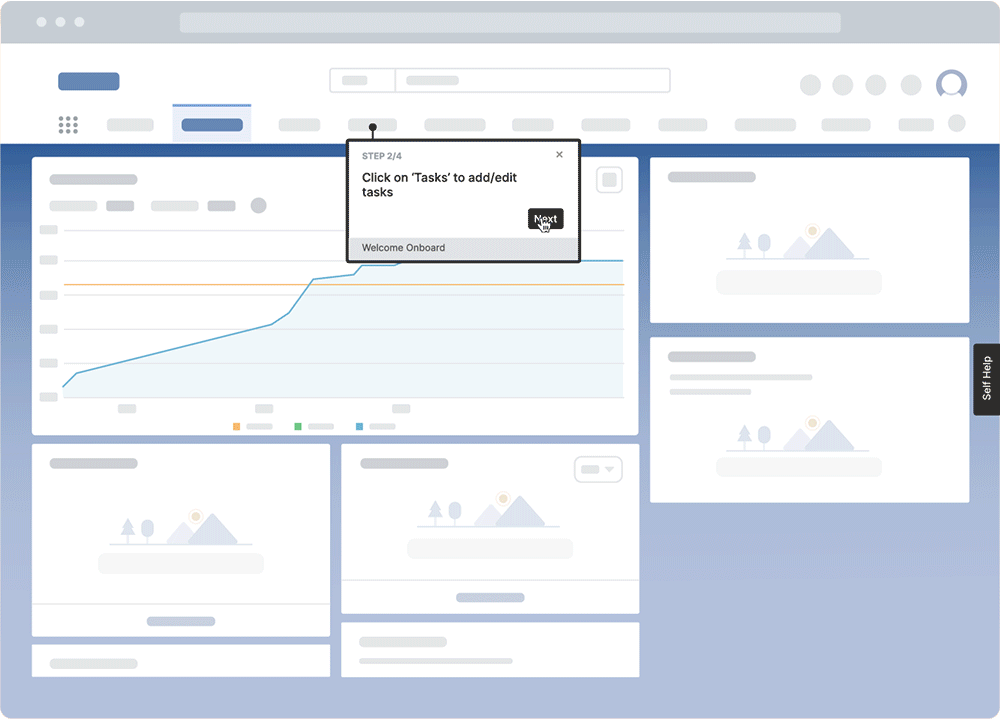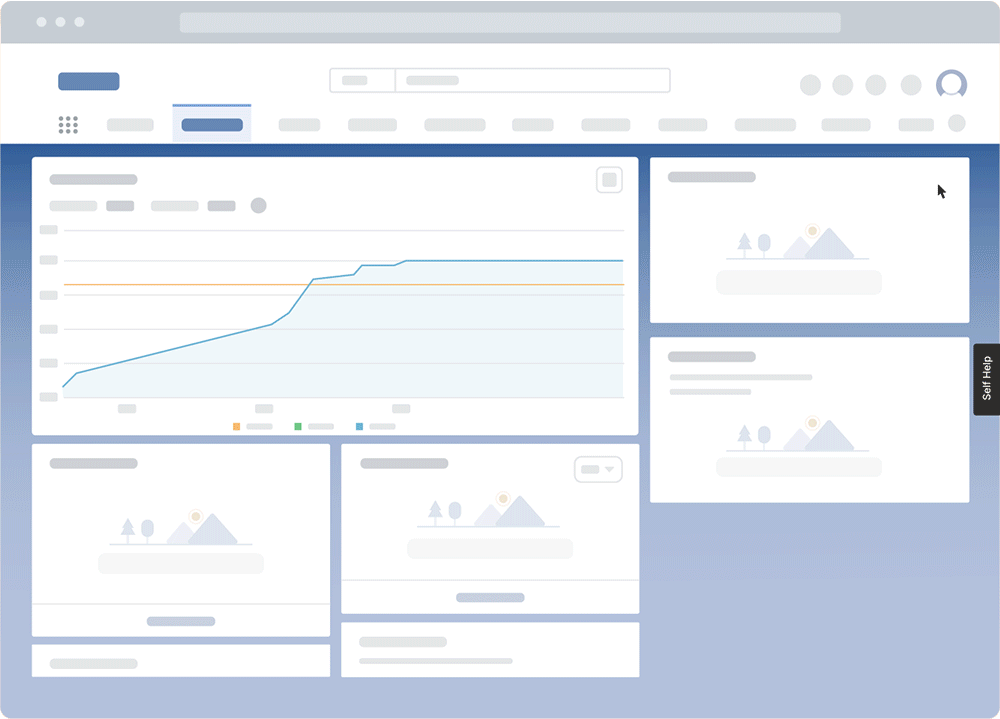
With Whatfix, create in-app guided experiences to assist employees in their day-to-day tasks. Track learning engagement with Guidance Analytics which provides real-time insights into how employees interact with training content embedded within your applications. The analytics dashboard tracks walkthrough completion rates, user interactions, time spent on guided flows, and drop-off points, helping L&D teams assess engagement levels and identify knowledge gaps. With user-level and behavioral analytics, organizations can measure the effectiveness of in-app training, track self-paced learning adoption, and optimize content based on data-driven insights.
Assess learning agility at an organizational level
Here’s how learning agility can be assessed at an organizational level.
Measure company-wide adaptability
- Conduct employee pulse surveys to assess how well teams handle change.
- Analyze adoption rates of new technologies and processes.
- Measure the effectiveness of change management initiatives.
Evaluate leadership agility
- Track how leadership teams respond to market shifts and crises.
- Assess whether leaders encourage innovation and continuous learning within teams.
- Monitor decision-making effectiveness in fast-changing environments.
Use data-driven insights to improve learning agility
- Leverage HR analytics and AI tools to track skill development and agility trends.
- Identify high-potential employees based on their adaptability and upskilling efforts.
- Use predictive analytics to anticipate training needs and future skill gaps.
How to Develop Learning Agility in the Workplace
Building a workplace that embraces continuous learning, adaptability, and resilience requires fostering learning agility at all levels. Organizations that develop learning agility see faster adaptation to change, higher innovation, and a workforce ready for future challenges. Below are key strategies to cultivate learning agility in the workplace.
Foster a growth mindset
A growth mindset is the foundation of learning agility. Employees with this mindset see challenges as opportunities, embrace feedback, and believe they can develop new skills through effort and learning.
Here’s how to encourage a growth mindset:
- Train employees to view mistakes as learning experiences rather than failures.
- Provide ongoing development opportunities to reinforce a culture of improvement.
- Encourage managers to recognize and reward effort and persistence, not just success.
- Use real-world case studies and storytelling to showcase employees who have overcome challenges through learning.
Encourage cross-functional collaboration
Working across different teams exposes employees to new ideas, perspectives, and problem-solving approaches, enhancing learning agility.
Here’s how to implement cross-functional collaboration in the workplace:
- Implement job rotations and shadowing programs so employees learn about different functions.
- Create cross-functional project teams to solve company-wide challenges.
- Encourage employees to participate in company-wide brainstorming sessions.
- Build a knowledge-sharing culture where departments exchange insights and best practices.
Invest in continuous L&D
Employees must have access to ongoing upskilling opportunities to enhance their ability to learn, adapt, and take on new challenges.
To strengthen your L&D initiatives,
- Offer personalized learning paths tailored to employees’ skill levels and career goals.
- Provide microlearning modules that focus on bite-sized, easily digestible knowledge.
- Encourage employees to attend conferences, workshops, and industry events.
- Implement mentorship and coaching programs for leadership and employee development.
Promote a feedback-driven environment
Feedback is essential for employees to reflect, adapt, and improve. A culture of constructive feedback builds learning agility by encouraging employees to iterate and refine their skills.
To build a feedback-driven workplace,
- Implement real-time feedback tools for instant learning and improvement.
- Train managers to provide actionable, constructive feedback rather than just evaluations.
- Encourage peer-to-peer feedback to foster a collaborative learning culture.
- Use 360-degree performance reviews to ensure well-rounded feedback from multiple sources.
Build a safe space for experimentation and risk-taking
Employees must feel safe to take risks, test new ideas, and learn from failures. Without fear of repercussions, they can develop resilience, adaptability, and problem-solving skills.
To foster experimentation,
- Celebrate “learning moments” from failures rather than penalizing mistakes.
- Encourage employees to test new approaches through pilot projects.
- Hold innovation challenges and hackathons to spark creativity.
- Create safe-to-fail environments where employees can test and refine ideas before implementation.
Motivate employees to step out of their comfort zone
Employees grow when they take on new challenges beyond their usual responsibilities. Encouraging them to explore different roles, projects, and skill sets builds adaptability.
To push employees beyond their comfort zone,
- Offer stretch assignments that challenge employees to develop new skills.
- Encourage participation in cross-departmental initiatives.
- Provide opportunities for employees to speak at industry events, lead training sessions, or mentor others.
- Recognize and reward employees who take on new and unfamiliar challenges.
Use technology to enhance learning agility
Technology plays a crucial role in making learning more accessible, engaging, and scalable. Here are some of the technologies that enable learning agility in the workplace.
Digital Adoption Platforms (DAPs)
Digital Adoption Platforms enable learning agility by providing real-time, in-app guidance, allowing employees to learn while performing tasks rather than relying on traditional training methods. Tools like WhatfixDAP embed interactive walkthroughs, tooltips, and self-help widgets directly into enterprise software, ensuring employees grasp new processes quickly, adapt to software changes effortlessly, and reduce dependency on IT support. By delivering personalized, on-demand training, DAPs help organizations create a continuous learning culture, ensuring employees stay agile, upskill rapidly, and remain productive in an evolving digital environment.
Learning Management Systems (LMS)
Learning Management Systems act as centralized platforms for organizing, delivering, and tracking learning activities. LMS platforms provide structured courses, on-demand learning, and analytics-driven insights to measure employee progress. Some of the best LMS platforms include:
- SAP SuccessFactors – A powerful corporate LMS that integrates HR and talent development, offering AI-driven course recommendations and performance tracking.
- Cornerstone OnDemand – Ideal for personalized learning experiences, enabling companies to build tailored learning paths based on employee needs.
- Docebo – An AI-powered LMS that automates content recommendations and provides interactive learning experiences.
- LinkedIn Learning – Offers thousands of industry-specific courses with AI-driven suggestions based on employees’ skill gaps.
Sandbox environments
A sandbox environment is a risk-free, simulated space where employees can experiment with new technologies, test scenarios, and practice problem-solving without real-world consequences. These environments are widely used in cybersecurity, software development, and corporate training to help employees build confidence and adaptability before applying their skills in a live setting.
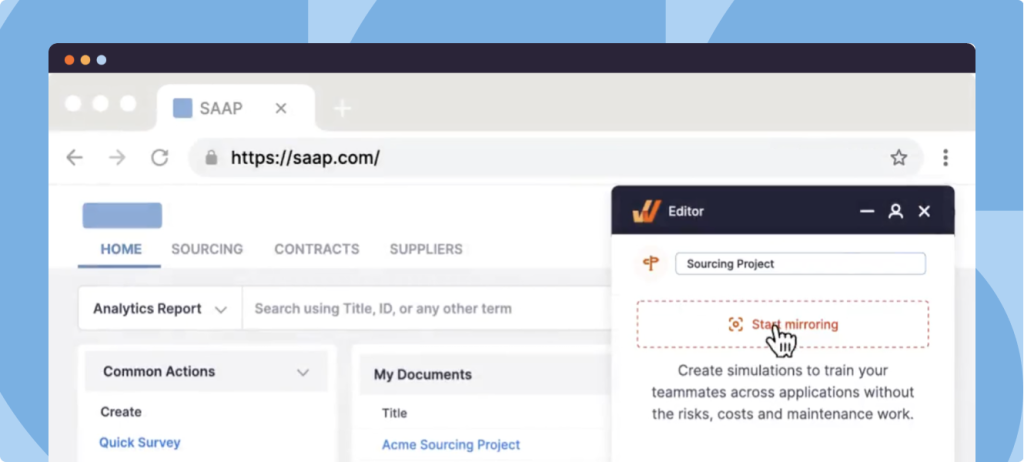
With Whatfix Mirror, IT teams and application owners can quickly create replica sandbox environments of web applications and enterprise software without technical dependencies. They can also create in-app guided experiences like Tours, Flows, Smart Tips, and Task Lists to guide new users through the simulated application and provide hands-on user training without risking live application usage.
AI & Analytics
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and analytics are revolutionizing how companies assess, personalize, and optimize employee learning. AI-driven learning platforms analyze skill gaps, track learning progress, and suggest tailored training modules based on an employee’s job role and career goals.
Develop leadership that models learning agility
Leaders must demonstrate adaptability, curiosity, and a commitment to continuous learning for employees to follow suit.
To develop learning-agile leaders,
- Train leaders to embrace change, take risks, and lead with flexibility.
- Encourage mentorship and reverse mentoring programs.
- Promote self-awareness and feedback-driven leadership.
- Expose leaders to cross-functional responsibilities to develop adaptability.
Training Clicks Better With Whatfix
Developing learning agility requires a shift toward continuous, adaptable, and personalized learning experiences—and that’s exactly where Whatfix transforms the game. Traditional training methods often lead to information overload and slow adoption, but with Whatfix’s Digital Adoption Platform (DAP), employees learn in the flow of work through interactive walkthroughs, in-app guidance, and real-time support. This ensures that learning isn’t just an event—it’s an ongoing, intuitive experience. By embedding training directly into the tools employees use daily, Whatfix empowers organizations to foster agility, accelerate skill development, and drive long-term business success. With Whatfix, training isn’t just effective—it clicks.
To learn more about Whatfix, schedule a free demo with us today!