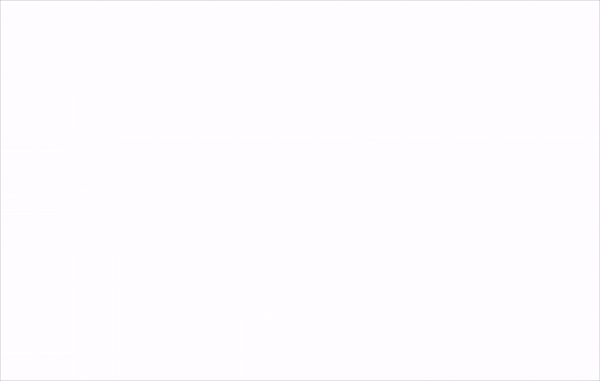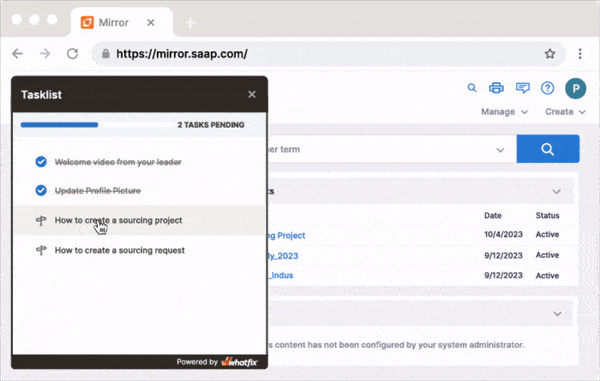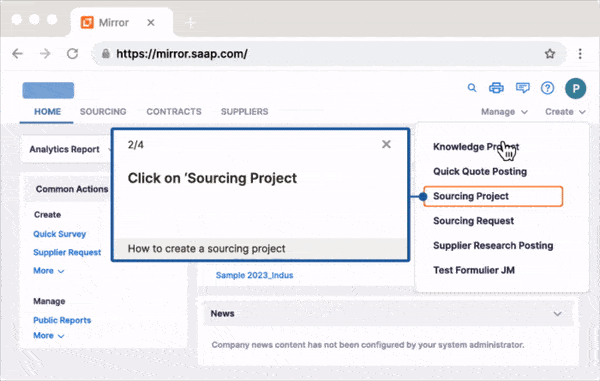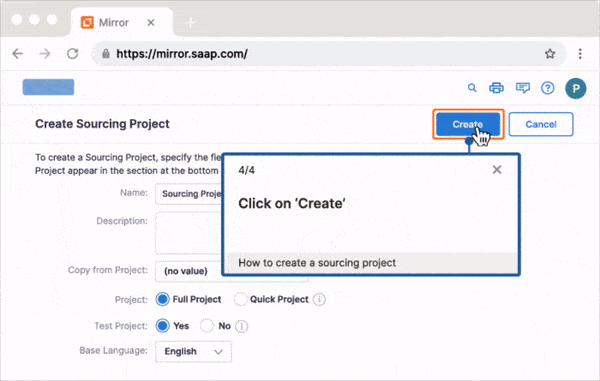As organizations build out their learning & development (L&D) program, they invest in various training methods and techniques, enabling them to create training contextual to different roles and suit different learning styles.
An innovative L&D trend that has emerged is simulation training. Immersive, simulation-based training exercises have been used in the aviation and military sectors for decades. With new eLearning technologies, this same type of hands-on training can now be applied to businesses of all types.
In this article, we’ll define simulation training, explore its benefits, share examples from different industries, and provide L&D leaders with the knowledge to build a simulation training strategy and incorporate it into their larger overall L&D strategy.
What Is Simulation Training?
Simulation training is an effective training method that involves realistic, immersive replications of real-life work processes or scenarios. This hands-on, experiential technique allows individuals to learn or practice different skills and decision-making procedures in a zero-risk environment before applying them in real life.
Benefits of Simulation Training
There are numerous benefits to simulation training for workplace learning, and different types of businesses will have contextual benefits depending on their business model, industry, and offering. However, here are some of the most obvious benefits of simulation training for employee learning and development:
1. Enhanced learning retention and contextual understanding
Many individuals learn best by doing rather than simply reading or listening to instructions. Simulation-based training allows L&D teams to provide employees with hands-on training experiences that combine several different types of instruction to maximize retention.
For example, employees completing a simulated office procedure might be able to read or hear instructions and real-time feedback as they work. This holistic way of learning improves and speeds up understanding, allowing learners to ask questions as they arise and learn from their mistakes without risk.
2. Improved decision-making abilities
While many of us would like to credit intuition for guiding us toward better choices, context and experience have more tangible positive impacts on decision-making. By allowing learners to experience various scenarios involving different circumstances, employees can better understand their responsibilities in workplace situations and make better decisions when they take that understanding into their day-to-day work lives.
It also builds adaptability for employees who often work with customers and prospects, enabling them skills to react quickly, be agile, think on their feet, and creatively solve problems.
3. Boosted confidence and competence
Another positive effect of allowing employees to gain simulated experience before encountering the real deal is the added confidence learners gain through simulation training. When learning experiences are easily accessible and engaging, employees can become proficient and get any kinks out of the way so they can feel completely secure in their abilities on the job without facing the risks involved with real business challenges.
4. Immediate feedback
In a simulation environment, employees can practice tasks and decision-making in real-time, allowing them to see the consequences of their actions instantly. This immediate feedback helps learners quickly identify areas where they excel and need improvement, fostering a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
It also allows for promptly correcting mistakes, enabling employees to adjust their approaches and develop better problem-solving skills on the spot. By reinforcing learning through immediate feedback, simulation training helps accelerate skill development and boosts confidence in performing job-related tasks.
Related Resources
What Industries Can Simulation Training Applied To?
Simulation training is widely used in fields such as healthcare, aviation, and the military. More recently, with sandbox application environments, organizations can provide hands-on training for employees to engage with replica software environments that mirror end-user tasks, workflows, and experiences without risking real-life application usage. This type of simulation training has been adopted by insurance providers to train their agents, call centers to train their service reps and other customer-facing teams. It helps bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application, enhancing both competency and confidence.
Here are a few of the industries that have already incorporated simulations into corporate learning programs:
1. Healthcare
The integration of simulation-based training has been monumental for education and career development in the healthcare industry.
It allows doctors, nurses, and other healthcare workers to practice skills like surgery, patient care, and crisis management in a risk-free environment. By simulating real-life medical situations, healthcare professionals can refine their techniques, improve teamwork, and enhance patient safety without putting actual patients at risk.
2. Aviation
In the aviation industry, simulation-based training trains pilots, flight crews, and air traffic controllers to perform their responsibilities effectively before they even set foot on a plane. From flight simulations to cabin safety, aviation industry professionals learn to handle various situations, from bad weather conditions to severe emergencies.
This training reduces time-to-proficiency and ensures aviation industry professionals are equipped to manage crises and make better decisions, ultimately minimizing risks and costs for the organizations they work for while making flying safer for airline customers and employees.
3. Military and defense
Military personnel must be ready to perform their duties at the drop of a hat. For this reason, this industry has utilized simulation-based training for decades.
Simulation training is used in the military and defense sectors to prepare service members for high-pressure scenarios, from active threats to hostage situations to strategic planning. By starting with simulated experiences, military personnel can develop skills and improve performance in high-risk decision-making situations, helping to prevent loss of life and damage to high-tech equipment or vehicles.
4. Business and management
In business and management, simulation training is used to develop leadership skills, improve decision-making, and enhance team collaboration. Business simulations can mimic market conditions, competitive scenarios, and internal organizational challenges.
Managers and employees can practice making strategic decisions, managing resources, and navigating complex business environments without the financial risks of real-life experimentation.
5. Education
Simulation training can also be used in the academic world. Students learning to perform technical or lab-based activities can do so in a simulated environment, drastically minimizing the costs of equipment, materials, and space costs. Educators can also benefit from simulation training, especially related to soft skills like conflict resolution and learning the latest educational technologies and software.
6. Call centers and customer service
Call centers and customer service teams use simulation training to enhance communication skills, problem-solving abilities, and customer interaction techniques. Simulated customer interactions allow employees to practice handling various customer scenarios, including difficult conversations, product troubleshooting, and complaint resolution. This training helps improve customer service quality, employee confidence, and the ability to manage challenging situations effectively.
PRO TIP
With Whatfix Mirror, create replica application environments of your mission-critical enterprise software to provide a no-risk environment for hands-on training. Create Task Lists, Flows, and Smart Tips that overlay your sandbox application environment and guide users through their contextual tasks and workflows. This accelerates time-to-proficiency for new users and provides hands-on learning experiences without risking live software usage.
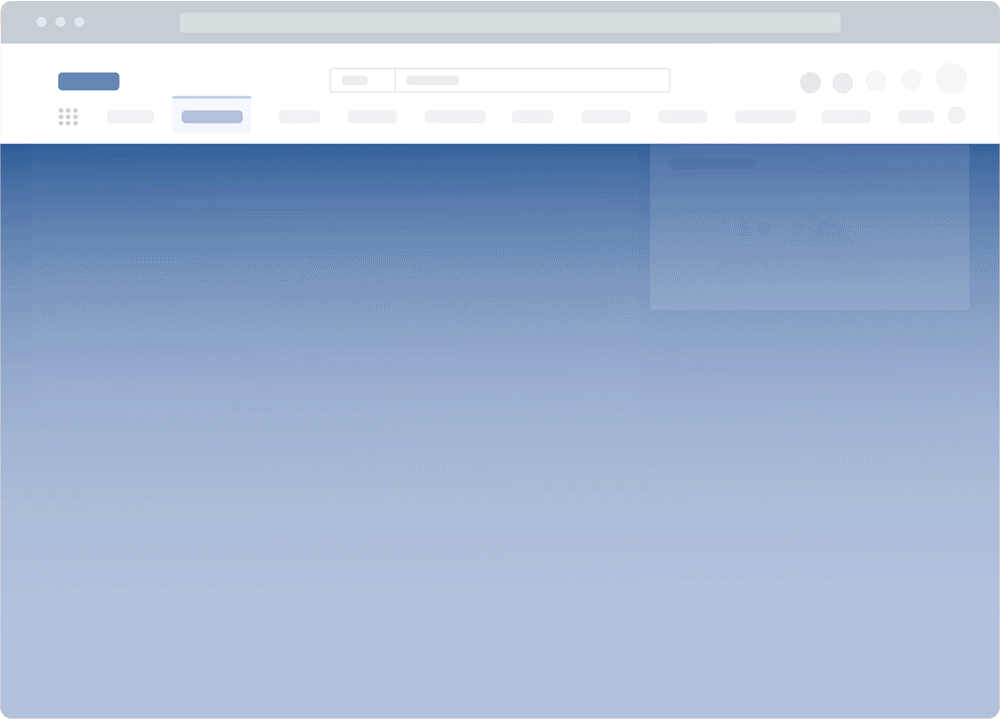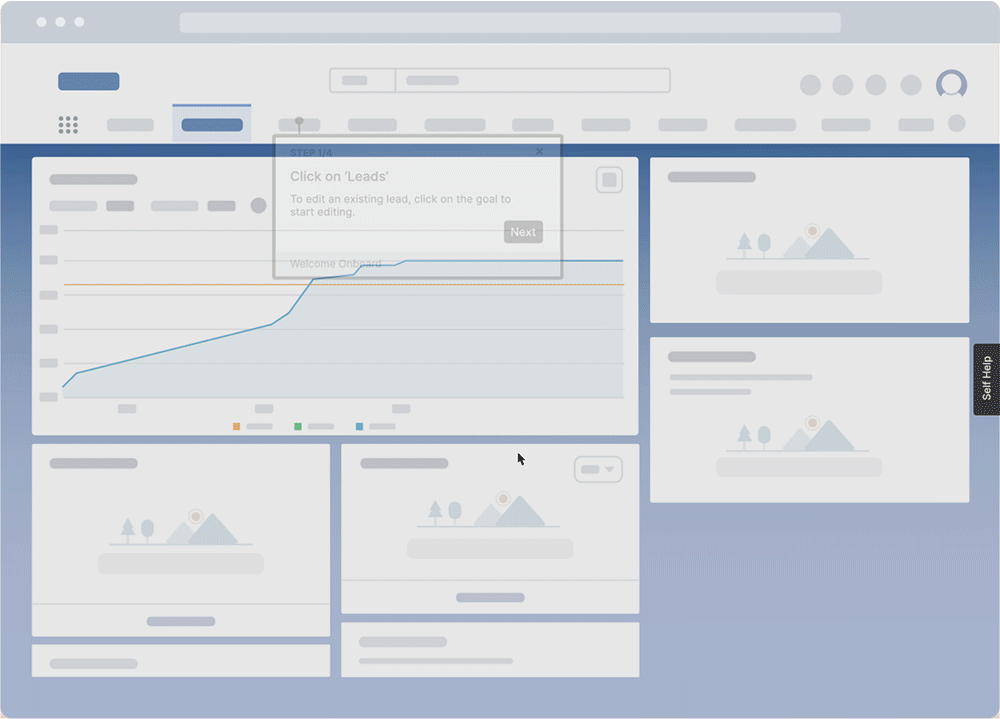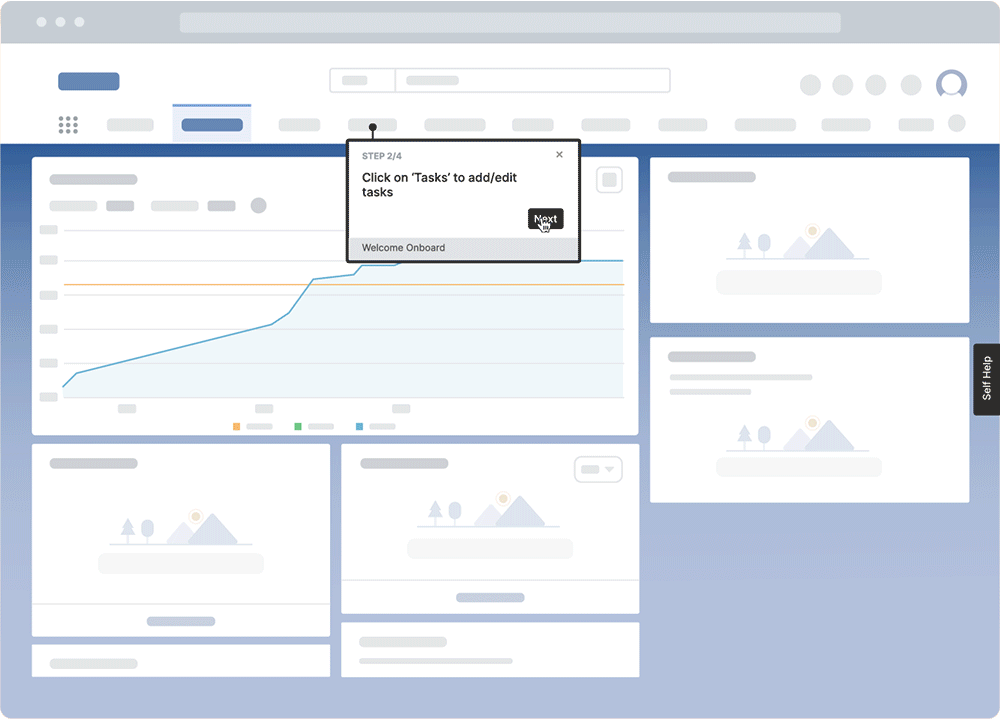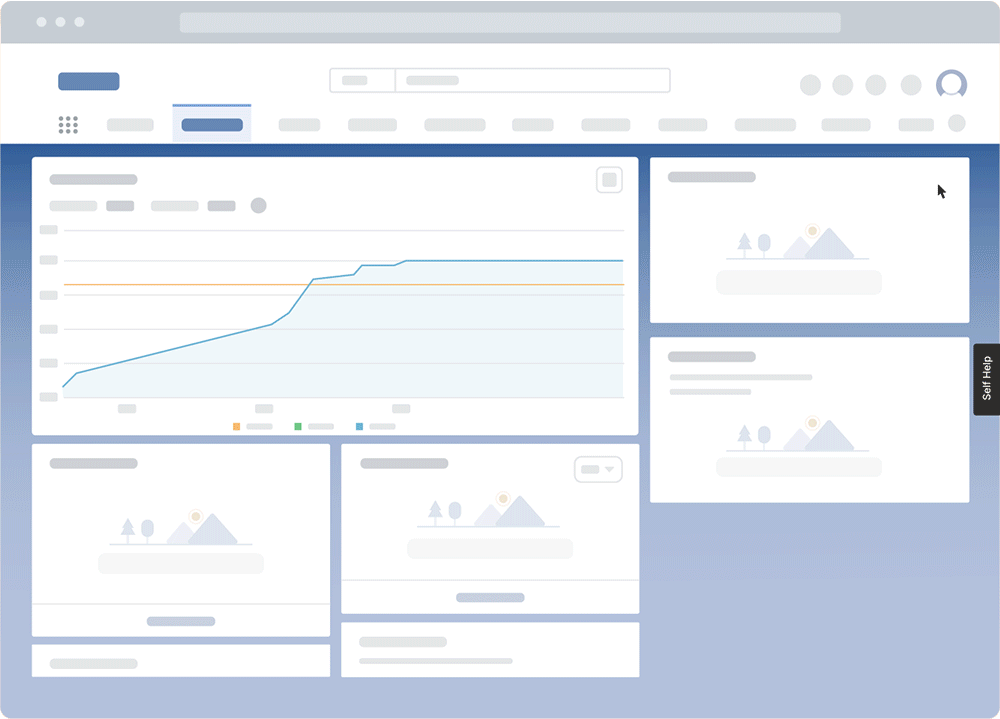
7. Construction and engineering
In construction and engineering, simulation training is employed to teach complex technical skills, safety protocols, and project management. Simulations can replicate construction sites, machinery operations, and engineering tasks, allowing workers to practice safely before working on actual projects. This training reduces the risk of accidents, improves technical proficiency, and ensures that projects are completed efficiently and to a high standard. It also allows for testing new designs and techniques in a controlled environment.
Types of Simulation Training
Here are the different types of simulations.

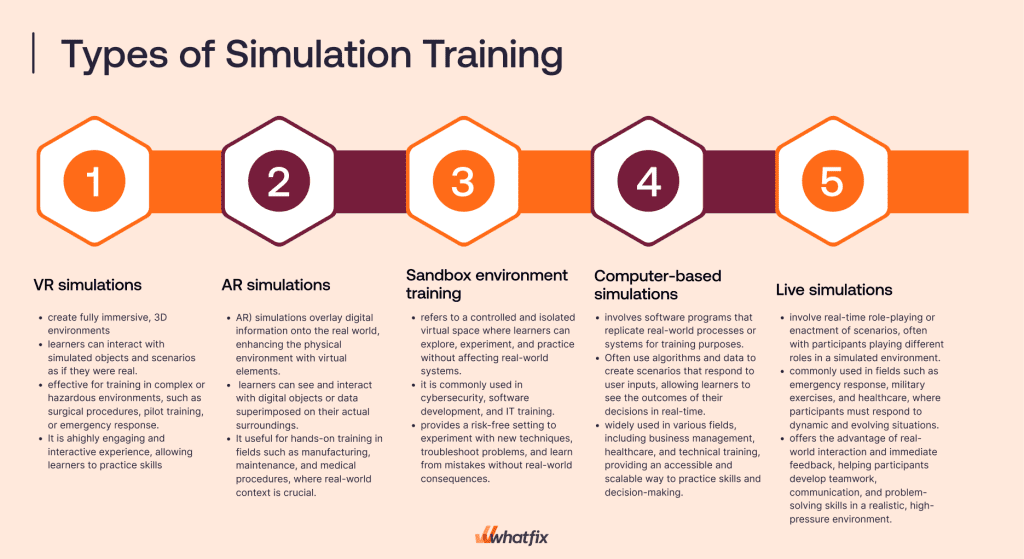
1. VR simulations
Virtual Reality (VR) simulations create fully immersive, 3D environments where learners can interact with simulated objects and scenarios as if they were real. Using VR headsets and controllers, users can move around, manipulate objects, and engage in realistic activities within a virtual space.
VR simulations are particularly effective for training in complex or hazardous environments, such as surgical procedures, pilot training, or emergency response. This simulation provides a highly engaging and interactive experience, allowing learners to practice skills and decision-making in a controlled, risk-free setting.
2. AR simulations
Augmented Reality (AR) simulations overlay digital information onto the real world, enhancing the physical environment with virtual elements. Using devices such as smartphones, tablets, or AR glasses, learners can see and interact with digital objects or data superimposed on their surroundings.
AR simulations are helpful for hands-on training in manufacturing, maintenance, and medical procedures, where real-world context is crucial. For example, AR can guide a technician through a repair process by displaying instructions and highlighting parts in the actual machinery. This type of training bridges the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application.
3. Sandbox environment training
Sandbox environment training refers to a controlled and isolated virtual space where learners can explore, experiment, and practice without affecting real-world systems. This type of simulation is commonly used in cybersecurity, software development, and IT training, allowing users to test scenarios like network breaches, coding, or system configurations safely.
The sandbox training environment provides a risk-free setting to experiment with new techniques, troubleshoot problems, and learn from mistakes without real-world consequences. It’s precious for developing technical skills and gaining hands-on experience in a secure, controlled manner.
4. Computer-based simulations
Computer-based simulations involve software programs replicating real-world processes or systems for training. These simulations range from simple models, such as business simulations that mimic market dynamics, to more complex ones, like flight simulators or engineering design software.
Computer-based simulations often use algorithms and data to create scenarios that respond to user inputs, allowing learners to see the outcomes of their decisions in real time. This type of training is widely used in various fields, including business management, healthcare, and technical training, providing an accessible and scalable way to practice skills and decision-making.
5. Live simulations
Live simulations involve real-time role-playing or enactment of scenarios, often with participants playing different roles in a simulated environment. This type of training is commonly used in fields such as emergency response, military exercises, and healthcare, where participants must respond to dynamic and evolving situations.
For example, a live simulation might involve a mock disaster in which first responders must coordinate rescue efforts or a medical simulation in which a team of healthcare providers treats a simulated patient in real time. Live simulations offer the advantage of real-world interaction and immediate feedback, helping participants develop teamwork, communication, and problem-solving skills in a realistic, high-pressure environment.
11 Steps for Incorporating Simulation Training into Your L&D Strategy
While simulation-based training solutions may vary across organizations and industries, there are common steps that should be taken across the board to effectively implement simulation training into any business’ L&D strategy:
1. Define training objectives
First things first – L&D teams should start by identifying the employee training objectives and initiatives. By pinpointing specific learning objectives built around an organization’s values and industry trends, and defining goals based on those objectives, L&D teams can design more effective training strategies to accomplish set goals.
2. Identify target audience
Once broader training objectives are set, it’s time to identify the employees or groups of employees that will engage in the simulation training programming. This will be important for determining the format of training programs as well as designing the simulation experiences themselves.
As mentioned earlier, certain business units and departments are more suited for simulation training experiences. Consider customer-facing teams like customer support, client relationship managers, business development reps, and sales teams.
3. Needs assessment
To ensure that training experiences are suitable and effective for the organization as well as the employees engaging with them, it is best to perform a formal assessment of needs before designing experiences or learning paths. Training needs assessments should incorporate industry trends and wider organizational goals in addition to employee strengths and skill gaps, as well as accommodations for remote training.
4. Choose the right simulation type
The appropriate format of simulation training can vary across industries, roles, and skill areas. Depending on the skills being trained, simulations might involve equipment or lab environments for technical skills while roleplaying, conversational simulations make the most sense for softer skills involving interpersonal interactions.
Additionally, the level of immersion can vary across training programs – from simple low- or no-tech roleplaying activities to completely immersive virtual reality training experiences.
For example, employees learning how to operate heavy machinery may benefit more from immersive VR simulation, while those learning how to use specific software to complete a task would do well with computer-based simulations.
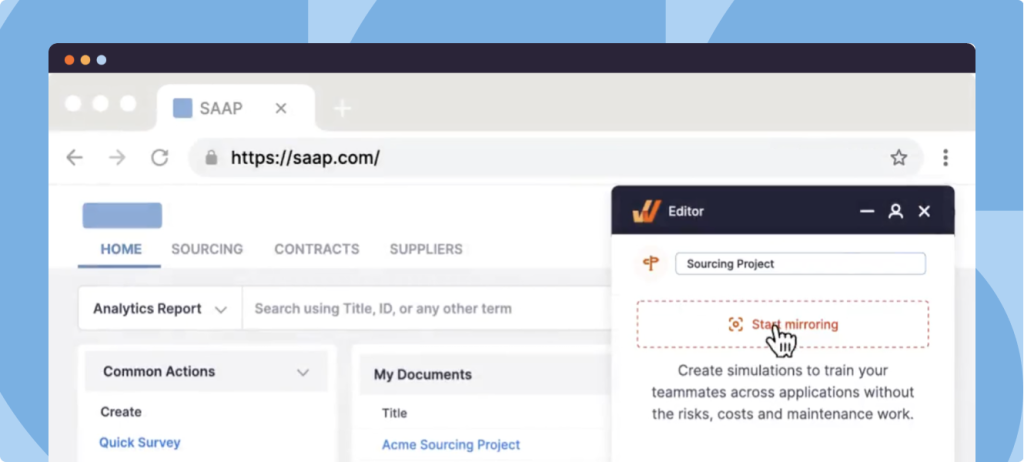
Large organizations can utilize IT virtual labs software to create replica sandbox environments of their applications to provide also provide simulated, hands-on training to their end-user employees. With a simulated training software like Whatfix Mirror, easily create sandbox IT environments of mission-critical applications and provide interactive training and onboarding experiences to your employees without risking live software use.
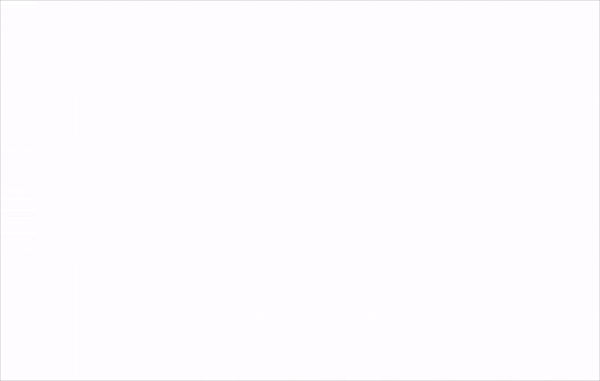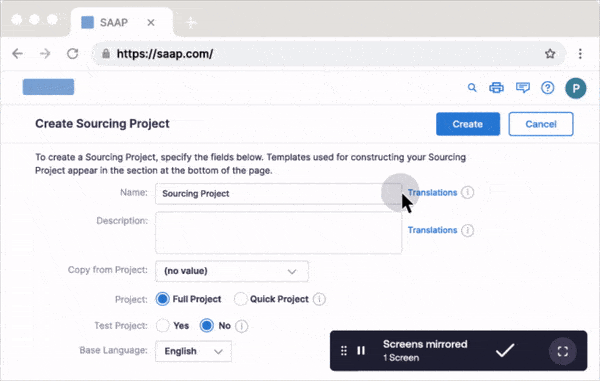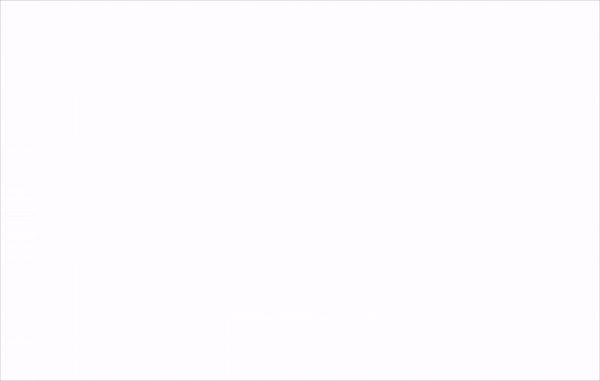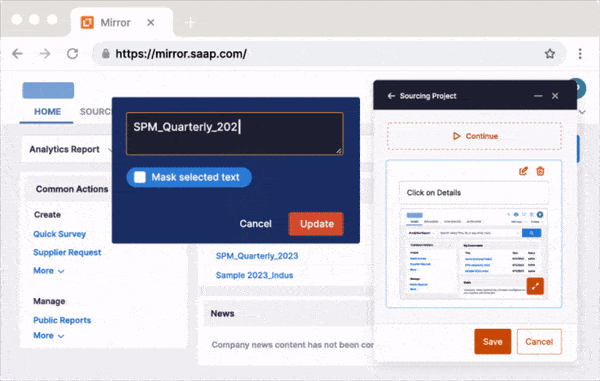
Further enable your IT end-users with in-app experiences to provide live tutorials and interactive guidance, helping users learn in replica workflows. Utilize Whatfix to create Task Lists, Flows, Tours, Smart Tips, and more – all providing real-time assistance and guidance to your users.

5. Invest in L&D software that enables simulated training scenarios
To facilitate simulation training scenarios, organizations will need to invest in the right L&D tools and employee training software to build, host, manage, and analyze these experiences.
L&D teams should invest in next-gen learning management systems (LMS), as well as interactive learning tools like digital adoption platforms (DAP) to provide in-app experiences that guide employees through complex processes or tasks and enable them with real-time support.
There are also emerging technologies, like generative AI, conversational chatbots, and AR/VR, that are making simulated training experiences even more realistic and challenging.
One of these technologies is dialogue simulation software that imitates real conversational-based tasks with realistic and unique dialoge. This is ideal for customer service reps and sellers to master customer communication skills, optimize response branching and sales processes, and to identify areas of personal need for individual employees who may need additional training – all without the risks of throwing these customer-facing employees directly into the fire, such as losing a customer or failing to close a simple deal.
6. Develop realistic scenarios
At this stage, you can begin laying out training scenarios that match the information gathered in previous steps. Build scenarios with clear narratives that cover several objectives at once to maximize learning opportunities and promote active information retrieval. Using situations and settings that closely replicate learners’ real-life working environments improves retention and triggers knowledge recall when employees take what they’ve learned into the real world.
7. Design interactive learning experiences
Once the simulated scenarios are determined, it’s time to fill in the details. Depending on the modality or type of software used for training, you can customize scenarios to include relevant challenges and decision-making opportunities.
One great way to get started with scenario development is to assemble storyboards in a flowchart-like format. Be careful not to overload learners with details, though. Keeping learning experiences easily digestible and straightforward makes for more effective learning outcomes.
8. Incorporate learner feedback and assessment
The training program should include regular progress checkpoints and opportunities for feedback. These will prompt learners to demonstrate their progress through assessments and practice exercises. Upon completion, employees should receive immediate feedback about their performance so they can improve and move forward with their learning journey.
9. Real-time monitoring
A useful feature of most simulation training software is a robust set of data analytic tools. Detailed, real-time analytics allow managers and L&D teams to monitor the progress of employees and the program’s impact on performance.
10. Offer support and resources
Real-time monitoring also enables managers, mentors, coaches, and training facilitators to step in and answer employee questions and provide clarification when needed. Organizational leaders should also be considered stakeholders in training programs and committed to allocating the necessary budget and personnel resources to ensure the success of L&D efforts.
11. Evaluate training effectiveness
Compile data from employee feedback, progress assessments, and data analytic tools regularly to evaluate the training effectiveness of simulation strategies. By continuously gathering feedback and progress data L&D teams can adjust and improve programming as needed.
By incorporating simulation training into your business’ L&D strategy, you can build a more effective and engaging employee development strategy while improving performance across the organization.
Training Clicks Better With Whatfix
Whatfix enables L&D teams and application owners to create hands-on training for end-users with Whatfix Mirror and Whatfix DAP.
With Whatfix Mirror, quickly create replica sandbox environments of your enterprise applications with a no-code platform. With Whatfix DAP, build Task Lists, Flows, and Smart Tips to guide users through their contextual application tasks and workflows to provide hands-on training experiences, all without risking live software usage.
Whatfix overlays on any mission-critical application, providing in-app performance support and guiding employees through complex processes with step-by-step instructions. It also enables employees with real-time support via Self Help, which integrates with your knowledge repositories like your SOPs, documentation, team processes, Google Drive, and more.
Whatfix enables organizations to analyze digital workflows to identify areas of application end-user friction, unused software licenses, and unproductive processes. This empowers L&D teams to accelerate digital transformation and change initiatives with in-app guidance and self-help support, all backed by end-user behavior data.
To learn more about Whatfix, schedule a free demo with us today!