Organizations generate a wealth of knowledge—from IT workflows and HR processes to customer insights and operational strategies. Yet, without a structured approach to managing this knowledge, it often becomes fragmented, inaccessible, or lost. The result? Teams duplicate efforts, opportunities slip through the cracks, and inefficiencies take root.
Knowledge management (KM) transforms this fragmented information into a cohesive resource, empowering organizations to connect departments, streamline workflows, and foster innovation. Knowledge management improves decision-making, enhances productivity, and strengthens organizational resilience by bridging IT, HR, and business operations.
However, building a successful knowledge management strategy involves more than just implementing tools. It requires breaking down silos, fostering a culture of collaboration, and addressing challenges such as resistance to change or outdated systems.
This guide explores knowledge management from all angles—its types, stages, and use cases—providing actionable insights into overcoming obstacles and unlocking the full value of organizational knowledge. Whether your focus is employee onboarding, IT workflows, or customer support, knowledge management can turn institutional information into a competitive advantage.
What Is Knowledge Management?
Knowledge management is the systematic process of capturing, organizing, storing, and sharing organizational knowledge to improve accessibility and usefulness. It transforms scattered information into a centralized, actionable resource that supports decision-making, boosts efficiency, and drives innovation.
At its core, knowledge management connects employees with the needed knowledge when needed. It ensures that explicit knowledge (documented policies), tacit knowledge (employee expertise), and implicit knowledge (procedural know-how) are readily available to those who require it.
Knowledge management’s ultimate goal is to prevent knowledge loss, minimize inefficiencies, and foster a culture of collaboration. When implemented effectively, knowledge management enables organizations to:
- Enhance operational workflows by centralizing resources.
- Equip employees to make informed, data-driven decisions.
- Strengthen organizational memory by preserving critical knowledge.
- Reduce redundancy and streamline cross-departmental communication.
Whether used for onboarding new employees, resolving customer inquiries, or optimizing IT operations, knowledge management ensures that all company knowledge is an asset that works for the organization—not against it.
Types of Knowledge Management
Organizational knowledge exists in different forms, each requiring tailored strategies for effective management and dissemination. Addressing these distinct types of knowledge enables businesses to build a more robust and adaptive knowledge management system, fostering growth and resilience.
The three primary types of knowledge are:
- Explicit Knowledge: Easily captured, documented, and shared information, such as manuals, reports, and databases. This foundational knowledge is critical for training, onboarding, and preserving organizational memory.
- Tacit Knowledge: Deeply intuitive, experience-based insights, such as leadership skills or creative problem-solving. Often challenging to articulate, tacit knowledge is best shared through collaboration, observation, and mentoring.
- Implicit Knowledge: Unwritten know-how embedded within processes and workflows. Though not yet formalized, implicit knowledge can be unlocked through careful documentation and observation.
Organizations can harness their collective expertise to drive innovation and operational efficiency by addressing explicit, tacit, and implicit knowledge.
Stages of the Knowledge Management Process
Managing organizational knowledge involves interconnected stages that transform raw information into actionable insights. These stages create a structured framework that ensures knowledge remains accessible, accurate, and impactful.
1. Documenting
This stage captures knowledge from diverse sources, such as employee expertise, processes, or customer feedback. Documentation converts tacit and implicit knowledge into explicit formats, such as written guides, video tutorials, or structured process workflows.
The key tools and processes used include:
- Knowledge capture tools, such as survey platforms or collaborative internal wikis.
- Templates for documenting workflows and creating how-to, step-by-step guides.
- Automated systems for capturing data from business activities or customer interactions.
2. Organizing and Storing
Once knowledge is documented, it must be systematically organized for easy access. This involves categorizing information, applying metadata tags, and storing it in centralized repositories.
The key tools and processes used include:
- Centralized knowledge repositories like knowledge bases or cloud-based document management systems.
- Metadata tagging and categorization frameworks.
- Secure storage solutions with version control and permission settings.
3. Sharing
Effective sharing ensures knowledge reaches the right people at the right time. Organizations use collaboration tools, intranets, or centralized knowledge repositories to distribute information and facilitate knowledge exchange. These tools streamline access to critical resources, supporting collaboration and improving operational efficiency.
The key tools and processes used include:
- Intranets and collaborative knowledge sharing platforms for easy access to shared resources.
- Centralized knowledge bases and document management repositories.
- Real-time notifications, newsletters, and updates for distributing new knowledge timeously.
4. Analyzing
Analyzing knowledge evaluates its relevance, accuracy, and effectiveness. Organizations can use analytics tools to identify knowledge gaps, track usage patterns, and refine their knowledge management strategies.
The tools and processes used include:
- Analytics dashboards within knowledge management systems.
- Usage tracking and feedback collection from employees
- Periodic audits to assess the relevance and completeness of knowledge assets.
5. Optimizing and Updating
Knowledge must remain current and valuable as organizations evolve. This stage continuously reviews and updates content to reflect new insights, processes, or technologies.
The tools and processes used include:
- Scheduled content audits and review cycles.
- Automated alerts for outdated or infrequently accessed content.
- Collaboration with subject matter experts to refresh and improve knowledge assets.
By adhering to these stages, organizations can establish a dynamic knowledge management framework that ensures information is not only accessible but also actionable. This structured process transforms knowledge into a dynamic resource supporting innovation and operational excellence.
Knowledge Management Use Cases
Knowledge management unlocks opportunities for businesses to work smarter, solve problems faster, and build stronger connections with employees and customers. Across departments, knowledge management ensures the correct information is accessible when needed so that teams can deliver better results.
Take NovaTech, a hypothetical mid-sized software company, as an example. Facing challenges like lengthy onboarding, fragmented resources, and inconsistent customer support, NovaTech adopted a knowledge management system to centralize resources and streamline processes, turning knowledge into a strategic advantage.
Let’s explore how knowledge management drives innovation and efficiency across key functions, beginning with employee onboarding.
1. Employee Onboarding
Streamlining the onboarding process is vital for setting employees up for success and ensuring they integrate quickly into their new roles. Knowledge management tools provide centralized access to policies, training resources, and role-specific guides, creating a seamless onboarding experience. For instance, NovaTech used a well-organized knowledge base and interactive resources to guide new hires through key tasks, ensuring they became productive from day one.
How it helps:
- Provides new hires with easy access to process documentation and tutorials.
- Reduces onboarding time by offering structured, self-guided resources.
- Creates a consistent employee onboarding process across departments.
2. Day-to-Day Employee Tasks
Employees regularly need access to critical information to perform their daily tasks efficiently. Knowledge management ensures that resources such as troubleshooting guides, best practices, and process documentation are easy to find and use. For example, NovaTech implemented an internal wiki with advanced search functionality. This enabled employees to quickly retrieve specific troubleshooting steps, improving efficiency across teams and providing on-demand performance support.
How it helps:
- Reduce time spent searching for information, enabling employees to focus on their tasks.
- Improve consistency in task execution by providing accurate, up-to-date guidance.
- Enhances collaboration by making shared knowledge easily accessible.
3. Organizational Communication
Open, seamless communication is imperative across the organization to ensure everyone is “on the same page.” Knowledge management breaks down silos by centralizing information and providing tools that encourage transparency and shared understanding. For instance, NovaTech used an intranet platform integrated with knowledge-sharing tools to unify team communication and ensure employees were informed about company-wide initiatives and updates.
How it helps:
- Centralizes announcements, updates, and shared resources for easy access.
- Promotes transparency by eliminating departmental (or team) silos.
- Improves employee engagement by fostering open communication.
4. IT Help Desk Agent Support
IT Support teams often handle complex technical issues that need quick access to accurate solutions. Knowledge management empowers agents with detailed troubleshooting guides, system documentation, and historical resolutions. For example, NovaTech developed a searchable knowledge repository for IT agents, enabling them to quickly find resolutions for recurring issues and significantly reducing response times.
How it helps:
- Reduces time-to-resolution by giving agents structured resources.
- Supports less experienced agents with step-by-step guidance.
- Improves customer satisfaction by enabling faster and more accurate issue resolution.
5. Customer Onboarding
Customer onboarding is a critical stage for building trust and ensuring product adoption. Knowledge management equips customers with the tools and information they need to succeed with your product or service. For instance, NovaTech offered clients a resource portal with user guides, video tutorials, and FAQs to streamline onboarding, reducing the time-to-value for their clients by 40%.
How it helps:
- Simplifies onboarding with step-by-step guides and in-app tutorials.
- Reduces reliance on support by offering customer self-service resources.
- Builds customer confidence by providing consistent and reliable information.
6. Self-Service Customer Support
Customers increasingly prefer resolving their issues independently rather than waiting for support. Knowledge management systems empower businesses to offer robust self-service options that meet these expectations. For example, NovaTech created a self-service support portal where customers could access detailed documentation and common troubleshooting steps, handling over 60% of inquiries without human intervention.
How it helps:
- Reduces support costs by deflecting common inquiries to self-service resources.
- Enhances customer satisfaction with instant access to answers.
- Scales effortlessly to support large customer bases without increasing staff.
Knowledge management drives meaningful improvements across diverse business functions by centralizing resources and improving accessibility. For companies like NovaTech, the right knowledge management strategy transforms everyday workflows into innovation, collaboration, and operational excellence opportunities.
Importance of Organizational Knowledge
Organizational knowledge management is more than just a repository of information—it’s a strategic asset that drives efficiency, collaboration, and innovation. By capturing, organizing, and sharing knowledge effectively, knowledge management empowers businesses to stay ahead of competitors, adapt swiftly to change, and foster a culture of continuous learning and growth.
Here’s why knowledge management is essential for organizational success:
1. Informed and Faster Decision Making
Access to relevant, well-organized knowledge enables leaders and teams to make decisions quickly and confidently. Knowledge management systems provide:
- Comprehensive insights, including historical data, expert knowledge, and best practices.
- Streamlined information retrieval eliminates time wasted searching for data.
- Enhanced strategic planning capabilities, driving a competitive edge.
For instance, a marketing team using a knowledge management system can instantly access customer insights and campaign performance data, enabling swift strategy adjustments to improve ROI.
2. Boosted Productivity
Centralized knowledge minimizes redundancies and streamlines workflows so that employees can focus on value-driven tasks. The result is:
- Less time is wasted searching for information or reinventing solutions.
- Simplified processes that increase task efficiency.
- A positive impact on organizational performance and employee satisfaction.
A manufacturing team, for instance, can quickly access equipment manuals and troubleshooting guides, reducing downtime and improving output.
3. Continuous Innovation and Improvement
Effective knowledge management fosters collaboration and knowledge-sharing, creating an environment ripe for innovation across teams and functions. For instance, product development teams with access to case studies, market trends, and competitor analysis can create breakthrough solutions that address modern market needs.
Key benefits include:
- Harnessing collective intelligence to refine products, services, and processes.
- Building a culture of shared insights and cross-functional learning.
- Enabling creative problem-solving through access to diverse perspectives.
4. Enhanced Organizational Learning and Adaptability
Knowledge management ensures organizations capture and apply lessons learned from past successes and mistakes, enabling agility in a constantly evolving business environment. This includes:
- Documenting and sharing insights to improve processes and outcomes.
- Preventing repeated errors by embedding institutional knowledge into workflows.
- Building resilience to market disruptions and rapid technological change.
For example, a retail chain that uses knowledge management to analyze store performance can adjust inventory strategies, improve sales, and reduce waste.
5. Knowledge Preservation During Employee Turnover
Employee turnover can lead to significant knowledge loss, especially tacit knowledge that is not easily documented. Knowledge management mitigates this by:
- Documenting expert insights and institutional knowledge in accessible formats.
- Ensuring seamless transitions during staff changes.
- Safeguarding critical know-how to maintain operational continuity.
For example, an IT department can document detailed system configurations and troubleshooting procedures, ensuring continuity despite team transitions.
6. Strengthened Collaboration and Communication
Breaking down silos is vital for organizational success. Knowledge management bridges gaps between teams and promotes open communication, resulting in:
- Transparent knowledge sharing across departments and levels.
- Improved team alignment around shared goals.
- A culture of trust and engagement that drives collaboration.
For instance, a knowledge management platform with collaboration tools can help global teams share updates in real-time, reducing delays and miscommunication.
7. Operational and Cost Efficiencies
Knowledge management transforms how organizations use information, driving cost savings and operational improvements. Key efficiencies include:
- Faster access to knowledge, minimizing workflow disruptions.
- Reduced expenses from repeated training or redundant projects.
- More efficient resource allocation through data-driven insights.
A healthcare provider, for example, can use knowledge management to standardize patient care protocols, improving care quality while reducing errors and costs.
8. Improved Data Security and Access Control
Modern Knowledge management tools ensure sensitive information is securely managed, with controlled access to maintain compliance and mitigate risks. Features include:
- Customizable permissions and secure sharing channels.
- Confidence in the integrity and reliability of organizational data.
- Compliance with data privacy and regulatory standards.
For instance, a legal firm using knowledge management securely manages client contracts, ensuring only authorized team members can access sensitive information.
Knowledge management is the catalyst for turning raw data into actionable insights, enabling organizations to innovate, collaborate, and thrive in competitive landscapes. By implementing a robust knowledge management strategy, organizations can preserve institutional knowledge, increase operational efficiencies, and position themselves as industry leaders.
RELATED ARTICLES:
Key Knowledge Management Challenges
Managing organizational knowledge is like maintaining a well-organized library. Without transparent systems to catalog, access, and share information, valuable resources can become hidden, misused, or forgotten. By addressing key challenges such as data overload, silos, and resistance to change, organizations make sure knowledge remains accessible and actionable, empowering teams to work smarter and innovate faster.
1. Data Overload
Organizations generate massive amounts of data daily, but without effective systems, this information can overwhelm employees rather than empower them.
The Challenge: Disconnected systems and unstructured data make it difficult for employees to find the necessary information, leading to inefficiencies and frustration.
The Solution:
- Use AI and analytics tools to sift through large datasets and highlight relevant insights.
- Establish governance policies for organizing, naming, and tagging data.
- Implement advanced search tools with filters to simplify information retrieval.
Impact: A streamlined approach to data management reduces time wasted searching for information, enabling employees to focus on strategic, high-value tasks.
2. Knowledge Silos
Sharing knowledge across teams is critical for collaboration and innovation, but departmental silos often create barriers to effective communication and data flow.
The Challenge: When information is confined to specific teams, collaboration suffers. Silos prevent organizations from leveraging collective knowledge, leading to redundant efforts and slower innovation.
The Solution:
- Deploy knowledge-sharing platforms like collaborative intranets or enterprise social networks.
- Encourage cross-functional collaboration through joint projects and teams.
- Reward transparency and knowledge-sharing behaviors.
Impact: Breaking down silos fosters innovation, improves collaboration, and ensures critical insights are accessible to all teams.
3. Lack of Employee Buy-In
Even the best-designed knowledge management systems can only succeed if employees are motivated to use them.
The Challenge: Employees may resist participating in knowledge management initiatives if they see them as extra work or fear their contributions could make them redundant.
The Solution:
- Highlight how knowledge management makes their work easier and supports professional growth
- Involve employees in designing and implementing knowledge management systems to increase ownership.
- Recognize and reward active participants.
Impact: With employee buy-in, knowledge management becomes integral to daily workflows, maximizing their effectiveness.
4. Lack of Leadership Support
Leadership buy-in sets the tone for organizational priorities, but when executives overlook the importance of knowledge management, adoption efforts can stall.
The Challenge: When senior leaders don’t actively champion knowledge management initiatives, employees may view them as unimportant or optional.
The Solution:
- Appoint a leadership champion to model and advocate for knowledge-sharing behaviors.
- Highlight the strategic value of knowledge management with organizational goals.
- Use leadership updates on knowledge management platforms to demonstrate their commitment.
Impact: Visible leadership support drives cultural adoption and reinforces the importance of knowledge management initiatives.
5. Absence of a Knowledge-Sharing Culture
Building a collaborative environment requires more than tools; it demands trust and transparency.
The Challenge: Without a culture that values collaboration and transparency, employees may hoard knowledge or hesitate to share it, limiting organizational innovation and efficiency.
The Solution:
- Create structured incentives and recognition programs for knowledge sharing.
- Train employees to document and share insights effectively.
- Set an example at the leadership level by promoting transparency and collaboration.
Impact: A culture of knowledge sharing unlocks innovation and increases the organization’s ability to adapt and thrive.
6. Outdated Technology
Modern knowledge management demands tools that are accessible, scalable, and intuitive, but outdated systems often fail to meet these requirements.
The Challenge: Legacy systems and disorganized tools hinder knowledge management by creating fragmented repositories and complicating access.
The Solution:
- Invest in modern, cloud-based knowledge management platforms with user-friendly interfaces.
- Regularly update systems to ensure compatibility and efficiency.
- Engage end-users in the selection process to ensure tools meet their needs.
Impact: Modern technology streamlines workflows, enhances collaboration, and improves efficiency.
7. Technology Fatigue and Low Adoption
Even the best tools can fail if employees are overwhelmed by too many platforms or poorly introduced technologies.
The Challenge: Employees often need help with using new platforms due to complexity or fatigue from constant technological changes.
The Solution:
- Consolidate tools to reduce redundancy and focus on user-friendly solutions.
- Provide in-app training and ongoing support to build confidence.
- Gradually introduce changes to minimize disruption and avoid overwhelming employees.
Impact: A thoughtful approach to technology adoption ensures KM tools are effectively used, driving productivity and engagement.
8. Resistance to Change
Change is necessary for growth; however, employees often need help transitioning from familiar processes to new workflows.
The Challenge: Employees often resist change, even when current systems are inefficient, due to a preference for familiarity.
The Solution:
- Communicate the benefits of new tools clearly and consistently.
- Involve employees in the change process to address concerns and build trust.
- Provide thorough training and support during transitions.
Impact: Proactive change management minimizes resistance, ensuring smoother transitions and higher adoption rates.
9. Difficulty Measuring ROI
Quantifying the value of KM initiatives can take time and effort, making it harder to secure ongoing support.
The Challenge: The impact of KM initiatives is often qualitative and long-term, complicating efforts to measure ROI.
The Solution:
- Use a mix of qualitative and quantitative metrics, such as reduced search times, higher reuse rates, and increased employee satisfaction.
- Set clear benchmarks and goals to measure progress.
- Leverage analytics tools to track usage and highlight value.
Impact: Demonstrating ROI builds a strong case for continued investment in KM initiatives.
10. Capturing Tacit Knowledge
Tacit knowledge, rooted in experience and intuition, is invaluable but challenging to document and preserve.
The Challenge: Tacit knowledge—experience-based insights that are difficult to document—is often lost when employees leave or change roles.
The Solution:
- Use mentoring programs and collaborative tools to capture and share tacit knowledge.
- Integrate knowledge capture into daily workflows.
- Assign knowledge managers to oversee and maintain critical insights.
Impact: Preserving tacit knowledge protects organizational memory and ensures continuity.
By addressing these challenges with proactive strategies and modern tools, organizations can unlock the true potential of their knowledge assets. Overcoming hurdles like data overload, silos, and resistance to change not only streamlines workflows but also fosters collaboration, innovation, and resilience. With a strong foundation in knowledge management, businesses can transform these hurdles into opportunities for growth and competitive advantage.
Knowledge Management Tools
The success of a knowledge management strategy depends on selecting the right tools to capture, store, and share information effectively. Modern organizations can leverage various technologies to centralize resources, encourage collaboration, and boost productivity.
Below are key tools that form the foundation of a robust knowledge management system:
1. Knowledge Base Software
A knowledge base is a centralized repository for critical information such as policies, FAQs, user guides, and more. It ensures employees and customers have on-demand access to accurate and up-to-date resources, reducing repetitive inquiries and expediting issue resolution. Knowledge base software enables organizations with a tool to create, manage, and organize this knowledge base.
Use Case: A global IT support team can document troubleshooting guides for common technical issues in a knowledge base, enabling employees to resolve problems independently and decreasing the volume of incoming support tickets.
2. FAQs
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) are a simple yet effective way to address common queries. These sections can be incorporated into websites, intranets, or customer portals to provide quick answers, minimizing the need for direct support.
Use Case: An HR department can create an FAQ section to address common questions about employee benefits, leave policies, and payroll, freeing up HR staff to focus on more complex issues.
3. Internal Wiki
An internal wiki enables employees to create, edit, and share knowledge collaboratively. These platforms are user-friendly and adaptable, making them ideal for documenting evolving processes, team workflows, and organizational best practices.
Use Case: A marketing team might use an internal wiki to maintain campaign templates, branding guidelines, and content strategies, ensuring consistency across projects.
4. Company Drive
Cloud-based company drives (like Google Drive and OneDrive) provide a centralized space for storing and sharing documents securely. They simplify version control and ensure team-wide access to the latest documents.
Use Case: A cross-departmental project team can use a company drive to store shared resources like meeting notes, project timelines, and deliverables, ensuring all team members have access to the latest updates.
5. AI Chatbots
AI-powered chatbots enhance access to knowledge by delivering instant responses to queries. Using natural language processing (NLP), these tools provide accurate, context-aware answers by retrieving data from integrated knowledge bases.

Use Case: A customer service chatbot can address routine inquiries about product setup or account troubleshooting, allowing human support agents to focus on more complex cases, reducing response times, and improving customer satisfaction.
By leveraging these tools, organizations can create an effective knowledge management infrastructure tailored to their specific needs. From reducing response times with chatbots to maintaining consistency with knowledge bases, thse technologies ensure knowledge remains accessible, relevant, and actionable—ultimately driving efficiency and collaboration across the enterprise.
How to Build a Knowlege Management Strategy
A robust knowledge management strategy ensures your organization captures, organizes, and shares information effectively. A well-crafted strategy identifies the knowledge your organization needs to manage and provides a roadmap to keep the initiative on track and aligned with business goals.
Follow these steps to build a knowledge management strategy that transforms information into a strategic advantage.
1. Build Your Knowledge Management Team
Start by assembling a team of individuals who understand the importance of managing organizational knowledge and can champion its implementation. This team will serve as champions for the initiative, driving adoption, and ensuring the system meets organizational needs.
Key considerations:
- Include representatives from key departments to incorporate a range of perspectives.
- Choose individuals who can inspire their peers and direct reports to embrace the system.
- Assign clear roles, such as project lead and support specialists, to streamline responsibilities and maintain accountability.
2. Identify Your Knowledge Goals
Define specific, measurable goals for your knowledge management strategy, ensuring they align with your organization’s broader objectives. This clarity not only provides a roadmap for implementation but also helps secure leadership buy-in
Key considerations:
- Link knowledge management goals to tangible outcomes, like faster onboarding times or improved customer service resolution rates.
- Align knowledge goals with strategic initiatives like improving employee retention or boosting operational efficiency.
For instance, if your business aims to increase profits by 5% in Q4, your knowledge management goal might focus on equipping sales teams with instant access to training and product resources to close deals faster.
3. Conduct a Knowledge Audit
A knowledge audit assesses the current state of your organization’s information assets and identifies gaps or inefficiencies. Unlike a content audit, which reviews specific materials, a knowledge audit evaluates where the information resides, who has access to it, and how effectively it supports organizational needs.
Steps to conduct a knowledge audit include:
- Map existing information repositories and tools used to store and share knowledge.
- Identify bottlenecks or barriers to accessing or sharing information.
- Highlight outdated, incomplete, or hard to find resources.
These insights will form the foundation for streamlining and improving your KM approach.
4. Choose Your KM Technology
Select tools that align with your organization’s requirements, digital maturity, and KM objectives. The right technology is the backbone of your knowledge management system, enabling seamless storage, retrieval, and collaboration. Create a checklist of essential features—such as advanced search capabilities, user permissions, and integration options—to evaluate potential solutions before buying.
Popular knowledge management tools include:
- Digital adoption platforms (DAPs) like Whatfix provide real-time guidance and integrate self-help resources directly into your applications..
- Knowledge base software centralizes resources like FAQs, troubleshooting guides, and manuals.
- Internal wikis allow teams to create and share knowledge collaboratively.
- Learning management systems (LMS) deliver structured training programs and track progress.
5. Create a Communication Plan
An effective communication plan ensures employees understand the purpose and benefits of the knowledge management system, fostering engagement and participation.
Key elements to include:
- Messaging that highlights how the knowledge management system will simplify workflows and add value to employees’ roles.
- Channels for communication, such as email updates, team meetings, and intranet announcements.
- Opportunities for employees to provide feedback and ask questions during the rollout.
6. Establish Milestones
Milestones help keep the knowledge management strategy on track by breaking the project into manageable steps. Setting clear, measurable goals ensures accountability and provides a sense of progress.
Examples of effective milestones include:
- “Complete the knowledge audit by March 15.”
- “Select and implement a knowledge base platform by April 30.”
- “Train all employees on the KM system by June 1.”
Setting specific, time-bound goals ensures accountability and keeps the project on track.
7. Build a Knowledge Roadmap
Once the foundational elements are in place, construct an implementation roadmap that outlines your knowledge management strategy’s stages, objectives, and timelines. A detailed roadmap ensures alignment among stakeholders and provides a clear path forward.
What to include in your roadmap:
- Defined objectives for each stage of the implementation.
- Milestones to track progress and measure success.
- Timelines for delivering tools, training, and system optimizations.
For instance, a roadmap for deploying a new knowledge base might include phases like content migration, employee training, and ongoing system updates.
By following these steps, your organization can create a knowledge management strategy that fosters collaboration, enhances efficiency, and delivers measurable value. When executed effectively, a knowledge management strategy transforms knowledge into a powerful asset that drives innovation and organizational growth.
Knowledge Sharing Clicks Better With Whatfix
Just as a well-organized library helps readers find exactly what they need, knowledge management solutions should guide employees to the right information effortlessly. Whatfix’s digital adoption platform (DAP) goes beyond traditional knowledge delivery by providing real-time, contextual guidance tailored to employees’ specific requirements. This approach reduces skill gaps and cultivates a culture of continuous learning and development.
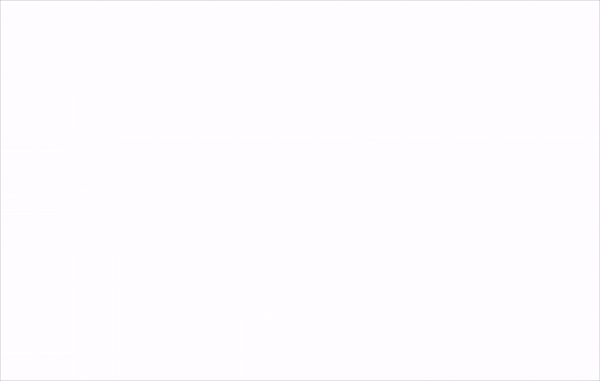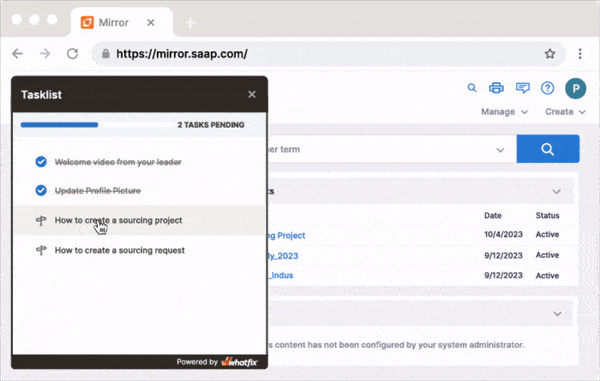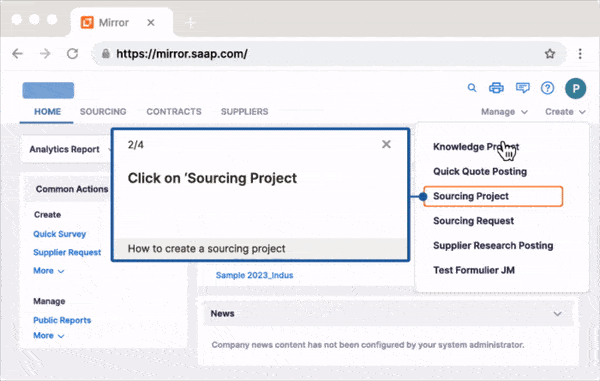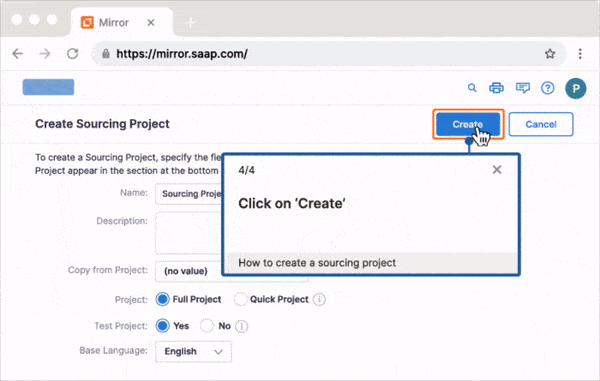
With Whatfix, employees gain immediate access to the information and tools they need to succeed, delivered directly within the applications they use daily. Whatfix ensures your workforce is fully equipped to meet their goals by eliminating adoption barriers, streamlining processes, and enabling self-sufficiency. Additionally, robust analytics capabilities allow you to monitor engagement, identify areas for improvement, and refine your knowledge management strategies to maximize impact.