Digital transformation has changed organizations’ operations, accelerated employee productivity, and automated manual processes.
As technology is adopted faster than workforces can adapt, employees need new skills to meet the requirements of their current responsibilities and roles, improve their performance, and advance in their careers.
A Microsoft report found that 65% of hiring managers report difficulty finding qualified talent due to a lack of digital skills.
The digital skills gap is real and prevents organizations from maximizing digital transformation and achieving business outcomes. Organizations must maintain a highly digital-literate workforce to stay ahead of the curve, which can be accomplished through employee training programs that provide digital upskilling and reskilling.
In this article, we’ll explore the importance of upskilling and reskilling programs, highlight their differences, share best practices, and examine examples of effective corporate upskilling programs.
What Is Upskilling?
Upskilling refers to improving or expanding an individual’s existing skill set to enhance their performance in their current role. It involves learning additional skills or enhancing current abilities to keep pace with technological advancements and changing job requirements within the same area of work.
Upskilling is typically focused on progression rather than change, aiming to make employees more proficient, efficient, and valuable in their current position.
Examples of upskill training include:
- An IT professional learning advanced cybersecurity techniques to handle emerging security challenges.
- A digital marketer gaining expertise in new social media tools and analytics software to enhance marketing campaigns.
- Training a manufacturing worker on newer, more sophisticated machinery that has been integrated into the production line.
Upskilling benefits for employees
- Enhanced career prospects, promotion opportunities, and job security: Upskilling enables employees to acquire new skills and expand knowledge in desirable areas, making them more competitive and valuable in the job market. This increased competence can open doors to promotions, higher-paying roles, and more challenging positions within their current organization or elsewhere. As employees expand their skill sets, they also widen their career options and enhance their visibility and attractiveness to potential employers.
- Increased job satisfaction: Learning new skills can rejuvenate interest in a role and make daily tasks more engaging. As employees become more proficient and can handle more complex challenges, they often experience a greater sense of accomplishment and confidence. Moreover, companies investing in upskilling value their employees highly, contributing to a positive work environment where employees feel appreciated and valued.
- Greater independence: With advanced skills, employees can operate more autonomously and take on additional responsibilities. They become less dependent on others for solving routine problems and can innovate more freely. This level of independence enhances their effectiveness and positions them as leaders and go-to experts within their teams. It empowers them to drive projects, make decisions, and lead initiatives, which can further their career and personal development.
- Personal growth: Beyond professional development, upskilling contributes to personal growth. Learning is a fulfilling activity that stimulates the mind and boosts mental health. Employees who engage in continuous learning often enjoy acquiring new knowledge and skills, which keeps them mentally active and personally fulfilled. This ongoing development can lead to discovering new passions or deepening existing ones, enriching their personal lives alongside their professional ones.
Upskilling benefits for organizations
- Improved productivity: Upskilling often involves introducing employees to new tools and methods that automate routine tasks, allowing them to focus on more complex aspects of their jobs that require critical thinking and decision-making. This not only speeds up work processes but also reduces the likelihood of errors, resulting in a smoother, more efficient operation overall. As employees become more competent, they can take on additional responsibilities, reducing bottlenecks and improving work flow across departments.
- Innovation: Employees trained in the latest technologies and methodologies are more likely to identify opportunities for improvement and innovation within the organization. Upskilled employees bring fresh perspectives and ideas that can lead to developing new products, services, or processes that drive business growth. Furthermore, employees encouraged to learn and experiment are often more engaged and motivated, which is conducive to creative problem-solving and innovation. This continuous influx of new ideas and approaches helps keep the company at the cutting edge of its industry.
- Higher retention rate: Ensuring high levels of employee satisfaction across your business is crucial for maintaining high employee performance and low turnover rates. According to a study by Willis Towers Watson, 70% of “high-retention-risk” employees want to leave because they see no future advancement in their current job.” To ensure high employee satisfaction, organizations must make employees feel valued. Upskilling is a great way to show your employees that you care about their progression and make them feel there’s something ‘in it for them,’ which, in turn, boosts employee productivity, satisfaction, and retention rates within an organization.
- Adaptability: By continuously updating employees’ skills, employers ensure that their workforce can handle new challenges, technologies, and shifts in the business landscape. This readiness to adapt helps the organization navigate disruptions more effectively and enables it to seize new opportunities more swiftly than competitors. An adaptable workforce can more easily adjust to internal changes, such as restructurings or shifts in strategic direction, minimizing downtime and maintaining productivity.
What Is Reskilling?
Reskilling is a process where employees learn new skills to move into a different job role within the organization or to meet the new demands of a current role. It typically occurs when an employee’s previous tasks or responsibilities become irrelevant, often due to technological advances or skill gaps.
It is often driven by automation, downsizing, or considerable industry shifts that make specific skills or roles obsolete. Reskilling is about transition and transformation, enabling individuals to adapt to new job environments or roles that are starkly different from their previous ones.
Examples of reskill training include:
- An assembly line worker whose job has been automated learns software programming to move into a tech-based role within the company.
- A retail sales associate moving into a customer service role in an e-commerce setting, requiring new skills in digital communication and order management software.
- A financial analyst shifting to a data science career requiring extensive training in big data analytics, programming, and machine learning.
Reskilling benefits for employees
- Job security: Reskilling provides employees with a greater sense of job security as it increases their value within the company. It showcases their willingness to learn new skills and adapt to their company’s needs.
- Reskilling opens the door for new career opportunities: Reskilling helps employees who want to change career paths independently reach these goals. As “work” changes and digital transformation continues unabated, automation and AI will eliminate many roles. Reskilling enables employees to open new opportunities as their previous skills become obsolete and automated.
- Internal mobility: Reskilling offers employees a better chance of staying with the company. The more skills an employee obtains, the more eligible they are for versatile or elevated roles within the company. Apart from maintaining their place within the company, reskilling gives employees a jump start to expand their skills and gain higher positions later.
Reskilling benefits for organizations
- Reduced recruiting, hiring, and onboarding costs: Recruiting and hiring are costly. Employee onboarding and new hire training require dedicated resources to train new hires on their role, company processes, software, and protocol, which current employees are already well aware of. When current employees are reskilled to work in different roles across the organization, you can save money on onboarding and overall employee training costs.
- Identify and retain resilient talent: Reskilling allows organizations to identify employees willing to adapt to change and learn new skills to support a company’s evolution and growth. It also showcases that you believe in their future at the company and are willing to invest in them for the long haul, improving employee retention and engagement.
- Develops your employees: Reskilling training programs allow employees to improve on both personal and professional levels. It provides a baseline for an employee development plan that provides reskill training to keep up with the fast-paced technological changes and future-proof their careers.
- More versatile workforce: As employees expand their skill set through reskilling, they become more adaptable, gaining a way to elevate their positions within the organization. Reskilling enables the internal mobility of employees within the company. Internal mobility offers considerable benefits, including reduced time and money spent on hiring, improved employee retention rates, and greater diversity and innovation in the workplace.
- Meets future demand: Targeting the development of crucial skills in your existing workforce prepares you to meet future demand. This prepares your employees for challenges they will inevitably face and provides your team members with the skills they need to be agile and adaptive in the workplace.
- Improves company reputation: Today’s top talent looks for employers committed to investing in their employees. The right reskilling strategy makes your organization more attractive in the eyes of both your current workforce and potential hires.
Upskilling vs. Reskilling
Upskilling refers to employees expanding and elevating their current skill sets to improve their performance in their current role or enable career growth. Reskilling, on the other hand, refers to employees learning entirely new concepts and skill sets to help them adapt to a changing role, widen the scope of their current role, or move to an entirely new role.
Here are the core ways upskilling and reskilling differ:
| Upskilling | Reskilling | |
| Purpose and focus | Enhances and adds to existing skills to improve performance and productivity in the current role. | Equips individuals with new skills for a different role, often in response to changing job demands or industry restructuring. |
| Driven by | The need to stay current with industry trends, technological advancements, and increasing job complexity within the same field is driven by the need to stay current. | Driven by fundamental changes in the job market, organizational restructuring, or the need to pivot to new career opportunities due to job obsolescence. |
| Outcome | Employees become more competent and can take on more complex or a greater variety of tasks within their current roles. | Employees transition to different roles or career paths, often within new departments or industries. |
| Organizational benefits | Helps improve the quality of work and productivity without significant changes to workforce composition. | Helps retain valued employees by transitioning them into emerging roles or sectors, thus adapting to industry changes without the need for extensive new hires. |
Why Is Upskilling & Reskilling Important?
In the digital age, several factors drive the need for reskilling and upskilling, influencing the organization’s ability to achieve business outcomes and support employees in their career aspirations. Here are the main causes driving the need for upskilling training programs:
1. Rapid technological advancements
According to a report by PwC, technological changes will disrupt one in three jobs in the next decade. Digital transformation had led to a sharp rise in the development of new systems and software, reducing the shelf-life of current technical skills and creating a demand for new skill sets.
The pace at which new technologies are implemented within organizations is accelerating significantly, transforming the landscape of all industries. Once considered emergent, technologies such as cloud computing, big data, AI, and blockchain are now essential for businesses to remain competitive and operate.
The skill sets required to utilize technologies will also change as technologies evolve. Organizations and individuals must commit to continual learning to enable employees with the skills to use the latest tools and technologies. This ensures businesses can leverage new technologies to drive innovation, streamline operations, and enhance service offerings and allows employees to meet the requirements of their career trajectory aspirations.
2. Automation and AI
Digital transformation has increased the demand for digital skills such as AI and machine learning, as they drive productivity, automate processes, and perform complex computational tasks quickly. Organizations must invest in their workforce reskilling to adapt to these changing conditions. Otherwise, they will lose their market position and fade into their competition.
Upskilling in areas such as AI management, oversight, and application in business processes is crucial for employees to complement these technologies rather than be replaced by them. This helps individuals enhance their career longevity and enables organizations to harness the full potential of AI and automation technologies.
3. Job market competitiveness
Employers seek candidates with the latest technical competencies and soft skills such as adaptability, critical thinking, and advanced communication. Existing employees must invest time into upskilling to meet these demands.
Upskilling and reskilling become a key differentiator in career progression, with proactive learners more likely to seize growth opportunities and secure leadership positions. Additionally, organizations emphasizing upskilling attract top talent and are better positioned to retain high-performing employees.
4. Closing the skill gap
There is a noticeable gap between job seekers’ skills and the capabilities employers need, particularly in sectors experiencing rapid technological changes. This skills gap hinders organizational growth and innovation as companies need help finding candidates with the required competencies.
By investing in continuous upskilling initiatives, organizations can work on closing this gap, ensuring their workforce is proficient in the latest industry-relevant skills. Such initiatives prepare businesses to tackle current challenges more effectively and future-proof their workforce against upcoming industry shifts.
Best Practices for Upskilling & Reskilling Employees
Anticipating the right skills for the future, developing effective training programs, and building a culture of continuous learning and development with the right learning technologies enable organizations to upskill their workforce successfully for the digital era.
Here are a few steps to help you plan effective upskilling training for your workforce:
1. Conduct a skills gap analysis to identify needs and employees with transferable skills
Once you identify the critical skills needed, look for adjacent abilities or skills closely matched to those in demand to make the reskilling process more manageable. Employees with related competencies may already know or can quickly learn what they need for a new role.
An updated skills inventory of what your employees have to offer helps reveal their secondary and tertiary skills. Use it to identify skills gaps and select employees easily transitioning to new job roles.
A skills gap analysis is an assessment conducted by HR teams to determine whether or not their workforce’s current skills meet the overall needs of the company. A skill gap analysis, as an output, gives you a list of skills employees already have, need to improve, and need to develop.
From there, you can fill in the skill gap using online courses and training programs to upskill your workforce and build a team of skilled workers who are able to meet your overall company’s objectives.
To help you conduct a skill gap analysis, you can download our free template below:
2. Build upskilling into your employee development plans
According to the World Economic Forum, 6 in 10 workers will require training before 2027, but only half of workers are seen to have access to adequate training opportunities today.
To provide training and upskilling opportunities for employees, organizations can align their training programs with individual employee’s career aspirations and development plans to acquire the skills, as well as those that support the overall company’s objectives.
Upskilling training plans empower employees to acquire the knowledge and skills necessary to be proficient and productive in their roles. They prepare them for the future by identifying employee development areas and then equipping them with the skills to fill these gaps.
Remember, any goals you set for employees should be specific, obtainable yet challenging, and time-bound. For instance, a goal could be: every employee in the sales department becomes proficient in two critical future skills within a period of 6 months.
3. Utilize a variety of training methods
In a recent Econsultancy report, 63% of employees critiqued their corporate learning experience and wished they received a broader mix of training methods.

Employees benefit from a mixed-method approach to training, as it better engages them with learning materials in various formats and mediums, reinforcing learning and accommodating learner preferences.
The 70-20-10 rule of learning echoes this by stating that 70% of learning comes from real-life experiences, 20% from social interactions, and 10% from traditional training methods.
Organizations should use this framework to build a multi-format training program designed to enable skill acquisition and task mastery. Examples of training programs to facilitate each bucket of learning include:
- 70%: Hands-on training enables employees to “learn by doing”. This can include providing software training in sandbox application environments, simulated scenario training, integrating microlearning into day-to-day workflows, and providing on-demand performance support.
- 20%: Social learning is a more ambiguous form of training from everyday peer interaction. Examples include job shadowing, onboarding buddy programs, conducting lunch and learn sessions, having team discussions, and chatting through Slack.
- 10%: Traditional training includes face-to-face learning, instructor-led training, certificate programs, and online courses.
To find the best training delivery methods and tactics that work for your employees, L&D teams must understand employee learning styles and consider other factors such as their training objectives, goals, cost, and timeline.
4. Set reskilling and upskilling goals
Once you identify the skills required for specific departments, the next step is to set clear and tangible outcomes to structure your upskilling program, set clear reskilling objectives, and allows you to measure training effectiveness and the program’s impact on skill acquisition.
One approach that can prove beneficial is to set SMART goals. The SMART in SMART goals stands for specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound. Defining these parameters ensures that the objectives are attainable within a particular time frame.
An example of a SMART goal for reskilling is – “increase the number of IT staff enrolled in cybersecurity training programs by 10% over the next three months.”
To get employees on board with upskilling and reskilling, you may consider incentives to reward those willing to expand their abilities or build specific skills into an employee’s annual goals and learning objectives.
4. Utilize technology
Leverage employee training software to deliver effective upskilling programs. These software tools allow you to create engaging training modules, ensure compliance and security, track employee engagement, analyze performance, and gather feedback.
Organizations should invest in the following learning technologies to facilitate upskill training and enable employees to learn in the flow of work:
- Learning Management System (LMS): A corporate LMS handles all aspects of employee training – from creating, delivering, organizing, and tracking L&D programs. With an LMS, an organization can deliver online courses, automate tracking, manage enrollment, and delivery integrated training programs.
- Digital Adoption Platform (DAP): A DAP enables organizations to create in-app guidance and on-demand performance support that overlays the digital workplace. With a DAP, employees learn in the flow of work via interactive walkthroughs, tooltips, task lists, and other contextual in-app experiences that guide employees step-by-step through contextual business processes, tasks, and software applications. Using a DAP integrates upskilling into your employees’ day-to-day activities without disrupting their workflow or productivity
- Knowledge Management Systems: Knowledge management systems provide an online, self-service center for employees to search for answers to any question on company policy, benefits, or processes. They act as internal wikis for companies and save time by decreasing HR questions and support tickets.
5. Enable employees to learn in the flow of work
As previously mentioned, learning in the flow of work provides an integrated, microlearning approach to upskilling that supports employees in their day-to-day tasks.
A “learn by doing” method allows for immediate application of new skills, which enhances retention and relevance. By delivering learning in the work context, this strategy minimizes disruption and removes the need for employees to step away from their workstations to participate in traditional learning environments. It offers a seamless, just-in-time learning experience that is both efficient and highly relevant to the tasks at hand.
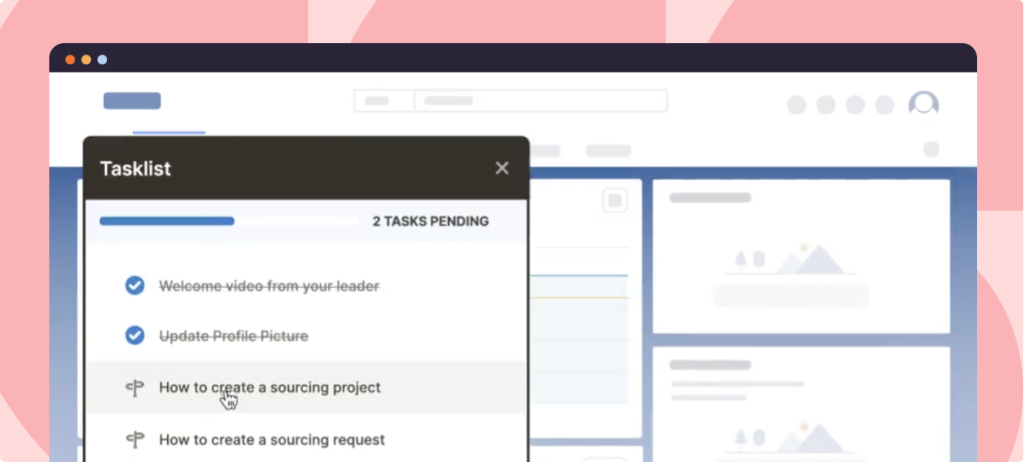
Invest in a digital adoption platform (DAP) like Whatfix to deliver in-app guided learning in the flow of work. Whatfix provides contextual, in-app guidance and support that helps users navigate complex software without leaving their workflow, with in-app content like Tours, Flows, Task Lists, Field Validations, Smart Tips, Self Help, and more, all enabling employees with contextual guidance and support inside their workflows.
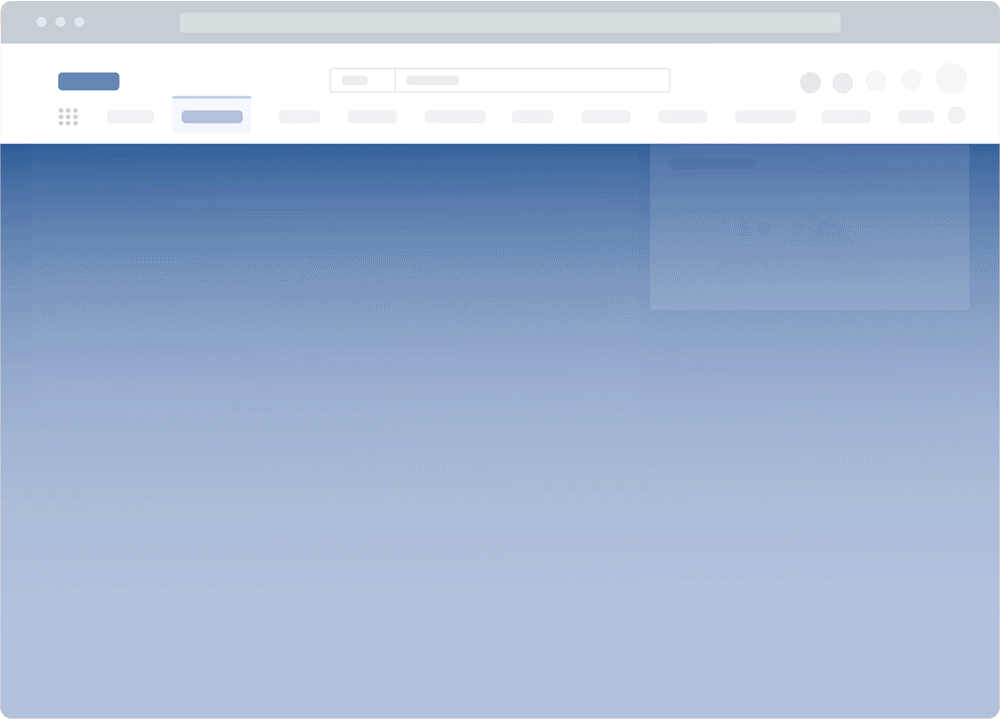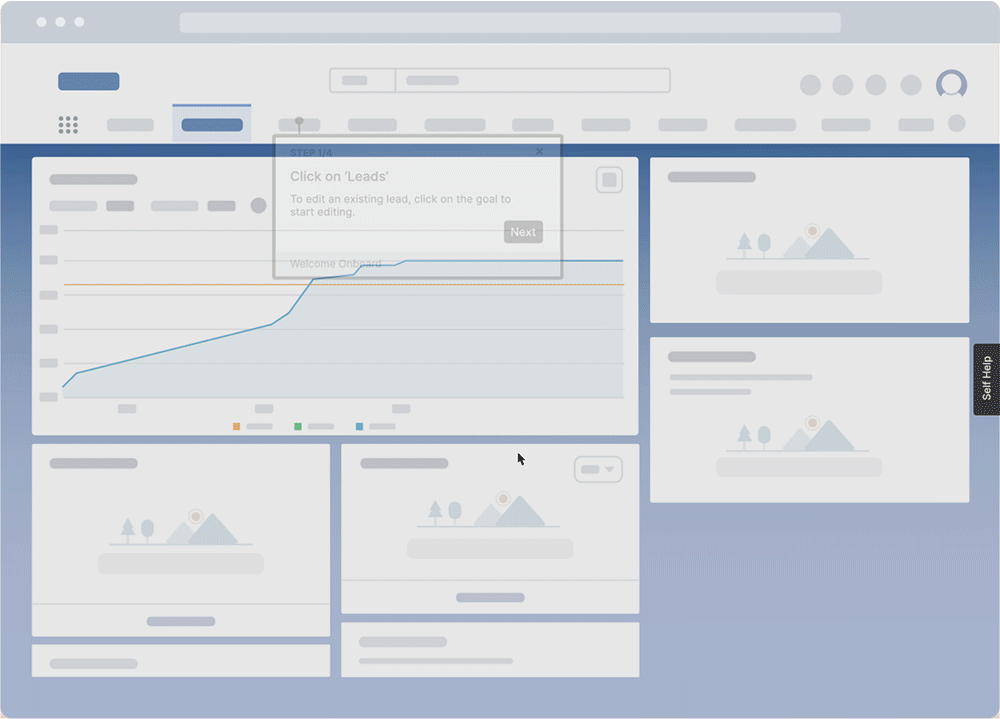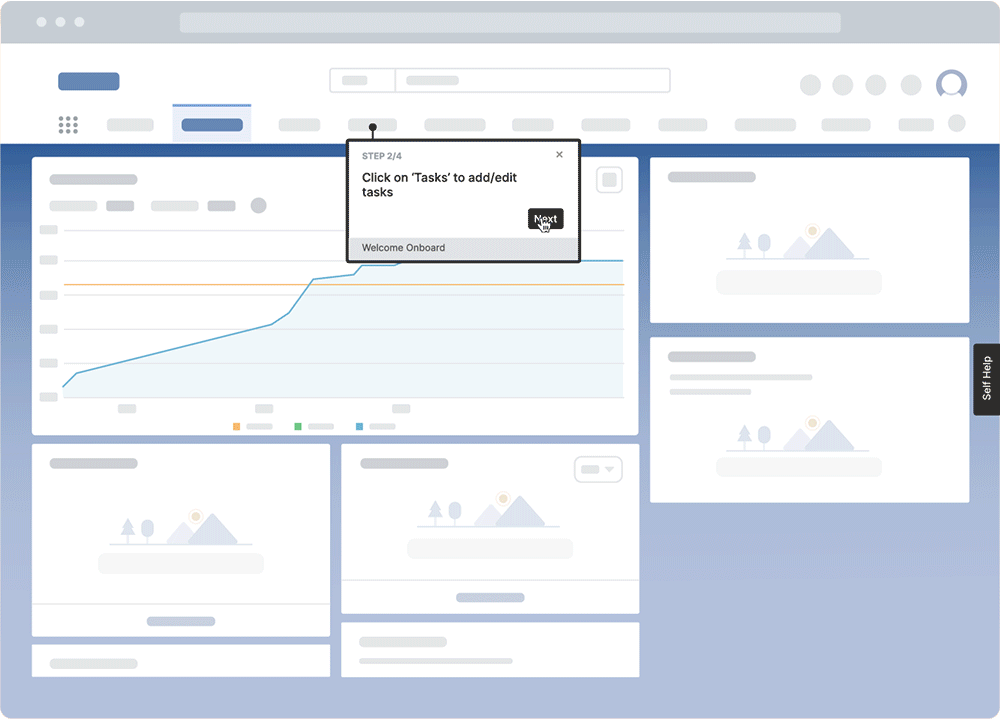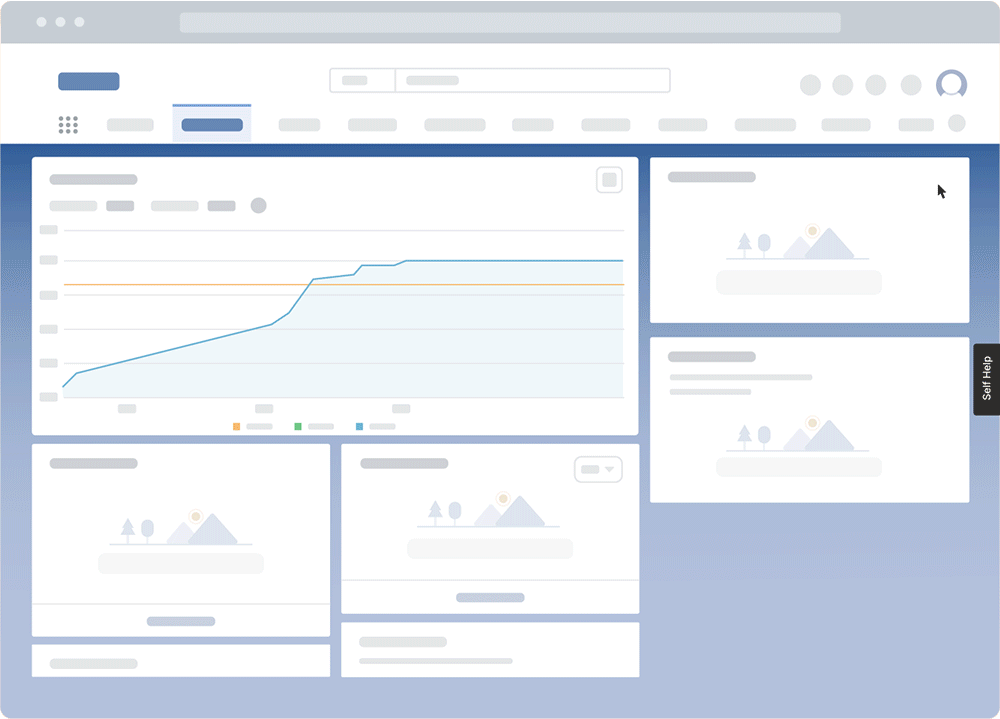
Whatfix is designed to accelerate proficiency with new software and systems, and support employees at the moment of need. Whatfix offers a powerful solution to deliver personalized, step-by-step guidance that is embedded directly into the daily workflows, ensuring that employees not only learn but also apply new skills effortlessly as part of their regular activities.
6. Measuring upskill training effectiveness
The last step is to evaluate the entire upskilling program to determine if it was successful and met its objectives.
As mentioned earlier, employee training software allows you to measure the effectiveness of your training and development programs. Monitoring KPIs such as course completion rates, training progression rates, assessment scores, lowering skill gap analysis, improving proficiency or productivity, etc. helps determine training effectiveness and knowledge or skill acquisition by the end of your upskilling program.
Consider using the following metrics to measure your training effectiveness:
- Employee feedback: Post-training employee feedback helps determine whether or not the training helped your employees learn new skills.
- Assessments: Tests, quizzes or demonstrations help evaluate the skills, knowledge, and learnings gained by employees after the upskilling training programs.
- Post-training job proficiency: Observe your employees to figure out whether or not they’re using the newly gained skills in their day-to-day tasks.

7 Training Methods to Upskill Employees
There are various ways to reskill and upskill your workforce. You can choose the most appropriate one depending on your organization’s and individual employee’s needs:
1. Cross-training
Allow employees to cross-train in other roles that require skillsets similar to their current job. Cross-training allows your employees to learn on the job and refine their skills, laying the groundwork for future mobility into evolving roles.
For instance, an account manager who demonstrates customer interaction skills could cross-train as a customer success manager. The role calls on similar skills but takes them to the next level. Then, that employee can bring enhanced customer success skills back to benefit their team and can also look for an opportunity to switch in the future.
2. In-app guidance
In-app guidance enables end-users with interactive, contextual assistance and support through a combination of in-app elements. It may include interactive walkthroughs, tooltips, checklists, self-help wikis, and other UX elements that help to educate users on product functionality, drive engagement, provide contextual assistance, and achieve product adoption.
Whatfix is one such solution that specializes in helping businesses drive digital adoption and create a seamless training experience for users. It provides step-by-step instructions for key workflows. Users see these instructions as they follow the steps of a guided tour, learning about processes as they work.

3. Hands-on simulated training
Hands-on training is a proven method that effectiveness upskills employees, particularly in complex or technical fields.
A simulated training approach involves creating realistic work scenarios that closely mimic actual job conditions. This allows employees to gain practical experience in a controlled, risk-free environment. Simulations enable employees to interact with the systems and tools they will use in their roles without the pressure of real-world consequences.
Additionally, hands-on simulated training enhances engagement by involving learners actively, which improves retention rates and helps employees gain confidence in their skills.
Whatfix Mirror enables L&D teams to easily create sandbox environments for hands-on simulated training quickly. It allows employees to navigate the real systems they will use but in a controlled setting that eliminates any risk to actual data or operations. This is particularly beneficial for complex software applications where navigating the interface can be challenging. Whatfix further supports these environments with contextual guidance and interactive walkthroughs integrated directly into the sandbox. This means that employees not only practice in an environment that mirrors their actual work scenarios but also receive real-time, step-by-step guidance tailored to their specific interactions and learning needs.
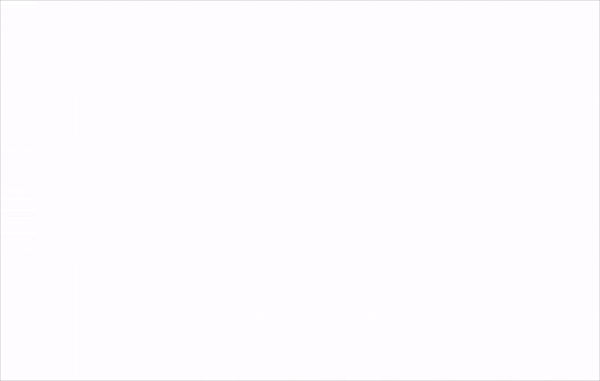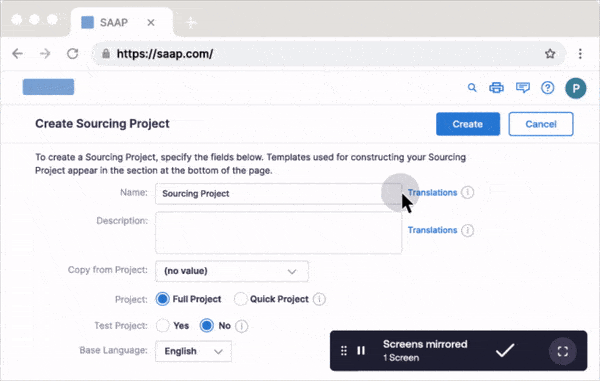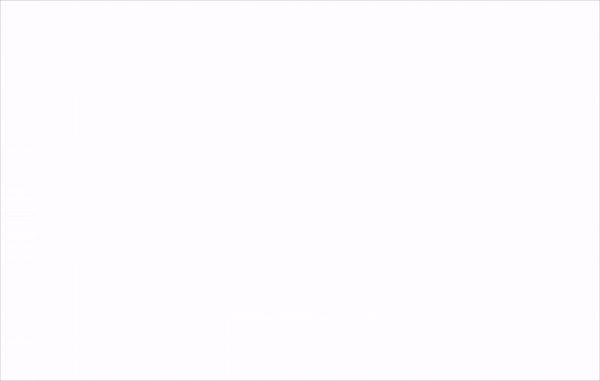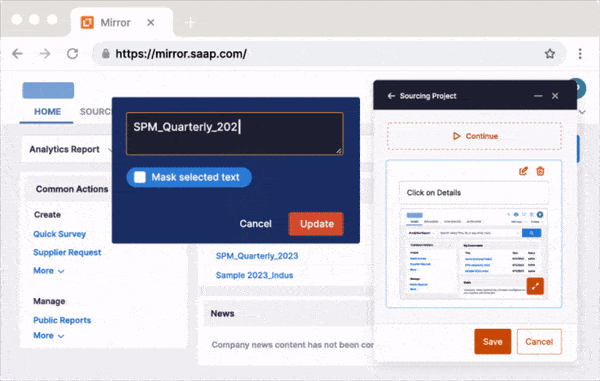
4. Job rotation
Job rotation involves moving employees through a series of job assignments in different departments or areas of the company. This strategy is particularly beneficial for broadening the skills and experiences of employees, exposing them to different facets of the business, and enhancing their understanding of the organization as a whole. By rotating through various roles, employees not only acquire a diverse set of skills but also gain valuable insights into how different units operate, how roles interconnect, and how their work impacts other parts of the business.
This method serves several upskilling objectives: it helps employees develop new technical skills specific to different roles, enhances their problem-solving and decision-making abilities by exposing them to new challenges, and improves adaptability by requiring them to adjust to various work environments and team dynamics.
Furthermore, job rotation fosters a more flexible workforce that can effectively manage broader responsibilities and fill in gaps as needed, which is especially valuable in times of organizational change or employee absences.
5. Peer-to-peer learning
Peer-to-peer learning is a collaborative method where employees partner to share knowledge, skills, and experiences to mutually enhance their professional development. This approach leverages the existing talents within the organization, creating a supportive learning environment that fosters continuous growth and development.
In peer coaching, colleagues work together through regular interactions, such as discussions, feedback sessions, and shared problem-solving experiences, enabling them to learn from each other’s strengths and insights.
The peer coaching method is particularly effective because it promotes a deeper, more personal learning experience. Coaches and learners are often on similar professional levels, which can reduce the intimidation and hierarchy that sometimes accompany traditional mentoring relationships. This setting encourages open communication, honest feedback, and mutual respect, making it easier for individuals to discuss challenges and explore solutions candidly.
6. Outsourcing
Outsourcing is a strategic approach to training when an organization lacks the in-house resources or expertise necessary to develop and deliver effective learning. By contracting with external providers, companies can access specialized training that is both high-quality and tailored to the specific needs of their workforce.
This method is particularly beneficial for organizations needing to quickly implement advanced or niche skills that are not within the realm of their current capabilities. Furthermore, outsourcing training allows organizations to focus on their core business operations without the burden of developing and managing complex training programs.
7. Self-training
Self-learning represents a highly flexible and individualized approach, allowing employees to take charge of their own professional development. This method enables individuals to learn new skills at their own pace and according to their own specific career needs. By engaging in self-learning, employees can explore a vast array of resources such as online courses, tutorials, webinars, and ebooks that are readily available on numerous platforms.
For organizations, encouraging self-learning among employees fosters a culture of continuous improvement and lifelong learning. Additionally, self-learning can be a cost-effective solution for businesses, minimizing the need for extensive in-house training resources while maximizing the potential for employee development.
Examples of Corporate Upskill Training Programs
The most recognizable enterprises have built their organization by investing in their workforce. Here are a few examples of successful corporate upskill training initiatives:
1. AlphaSights
AlphaSights, a leading global provider of on-demand knowledge services, experienced rapid growth and needed to expand its training capabilities accordingly. The company realized that its traditional upskilling strategy of conducting in-person, presentation-based training, led solely by the L&D team, lacked relevance. As a result, employees lacked the motivation to complete training courses and the L&D team also didn’t have a way to track progress or measure the effectiveness of their material.
To overcome these challenges, AlphaSights employed a bold upskilling strategy and turned to the experts who knew their training needs best—their employees—and brought them into the course creation process with the help of 360Learning. With an easy-to-use authoring tool, SMEs from different departments like engineering or commercial, turned their knowledge into eLearning courses. The training content instantly became more role-specific, relevant, and engaging.
Ultimately, the company mobilized more than 300 employees—27% of their workforce—to become course authors and share their knowledge. Their course completion rate soared to 95%, with improved engagement and productivity. Using 360Learning, they can now consistently monitor progress and training results, which helps them prioritize training initiatives that best serve their business needs.
2. Amazon
In September 2021, Amazon committed $1.2 billion to provide 300,000 employees with access to education and skills training programs through 2025 as part of Amazon’s Upskilling 2025 pledge.
Through the Upskilling 2025 program, Amazon is focused on creating pathways to careers in future growing areas. Amazon continues to launch new training opportunities and expand on existing programs for employees across the U.S., including
- AWS Grow Our Own Talent: on-the-job training and job placement opportunities to Amazon employees and entry-level candidates with non-traditional backgrounds.
- Surge2IT: help entry-level IT employees across Amazon’s operations network pursue careers in higher-paying technical roles through self-paced learning resources.
- The UXDR Apprenticeship program: combines instructor-led training and real-world experience to offer employees the opportunity to learn and develop skills in research and design.
- Mechatronics and Robotics Apprenticeship Program: learn skills and technical knowledge to fulfill technical maintenance roles.
3. SupportWorks
Supportworks, a home services company, prioritized leadership development to enhance employee skills and cultivate a new generation of management. This initiative not only broadened their pool of potential future leaders but also fostered a company culture centered around employee growth.
In response to the challenges posed by the pandemic, including managing a hybrid workforce and integrating new technologies, Supportworks recognized the necessity of a hybrid learning strategy that catered to their employees.
To achieve this, the company adopted a blended learning approach for their ManagementU program, combining live, instructor-led sessions with self-paced online learning. This program was developed through the collaborative efforts of in-house experts, company leaders, and the L&D team. The curriculum covered a variety of topics, from recruitment and onboarding to communication strategies.
As a result, participants with different experiences and backgrounds get a baseline level of knowledge that they are more likely to retain and use. So, when the same learners attend in-person upskilling programs, they already have basic leadership skills and can pursue a new career path.
4. IBM
IBM made a global plan to provide 30 million people of all ages with new skills needed for the jobs of tomorrow by 2030. To achieve this goal, IBM announced a clear roadmap with more than 170 academic and industry partnerships. The plan relies on a broad combination of programs, and includes collaborations with universities, key government entities, and NGOs. In general, IBM’s efforts mobilize the private sector across the globe to open and expand opportunity pathways for underrepresented and historically disadvantaged communities.
5. McDonald’s Hamburger University
McDonald’s established “Hamburger University” at its global headquarters to train and upskill its employees. At Hamburger University, employees can develop skills and knowledge on the restaurant’s operational procedures in real-life scenarios and simulated restaurant environment.
6. Mastercard
In order to remain competitive, Mastercard wanted to create a learning culture that would encourage its employees to build new skills. They decided to use Degreed as a platform that offers personalized learning experiences, creates career pathways, and helps employees connect to the content relevant to them. There’s a breadth of content available on Degreed, including ‘bite-sized’ learning in the form of short articles, videos, and podcasts. This makes it easy for employees to engage with learning on the go.
7. ManpowerGroup
ManpowerGroup is a global leader in recruiting and staffing, connecting organizations with top talent to fill workforce gaps and skill needs.
Bullhorn ATS is “mission-critical” for ManpowerGroup to manage applicants, sift through incoming applications, communicate with its talent pool and customers, and connect companies with the right employees.
This means that employees must be proficient in Bullhorn ATS to be effective. To upskill and support its recruiters and talent reps, ManpowerGroup uses Whatfix to provide contextual in-app training and performance support in the flow of work.
With Whatfix, ManpowerGroup’s L&D team provided in-app guidance and support to its employees with:
- 100+ Flows that guided employees through Bullhorn ATS tasks and essential processes with step-by-step interactive walkthroughs, like how to merge duplicate applicant profiles or how to schedule an interview.
- Smart Tips that provided contextual information and additional knowledge at critical moments when employees hovered over in-app tips and fields. This increased data entry accuracy and improved ATS process governance.
- Pop-Ups to alert employees to ATS process changes, new hiring regulations, mandatory training programs, and company news.
- Searchable Self Help that overlays its ATS. Self Help is integrated with ManpowerGroup’s LMS, internal wiki, ATS user training, and ther knowledge repositories, allowing users to search for any ATS process or technical-related issue, without leaving Bullhorn or asking a colleague for help. Self Help surfaced personalized content through custom API based on the user’s needs. For example, system admins would see different Self Help entries compared to recruiters.
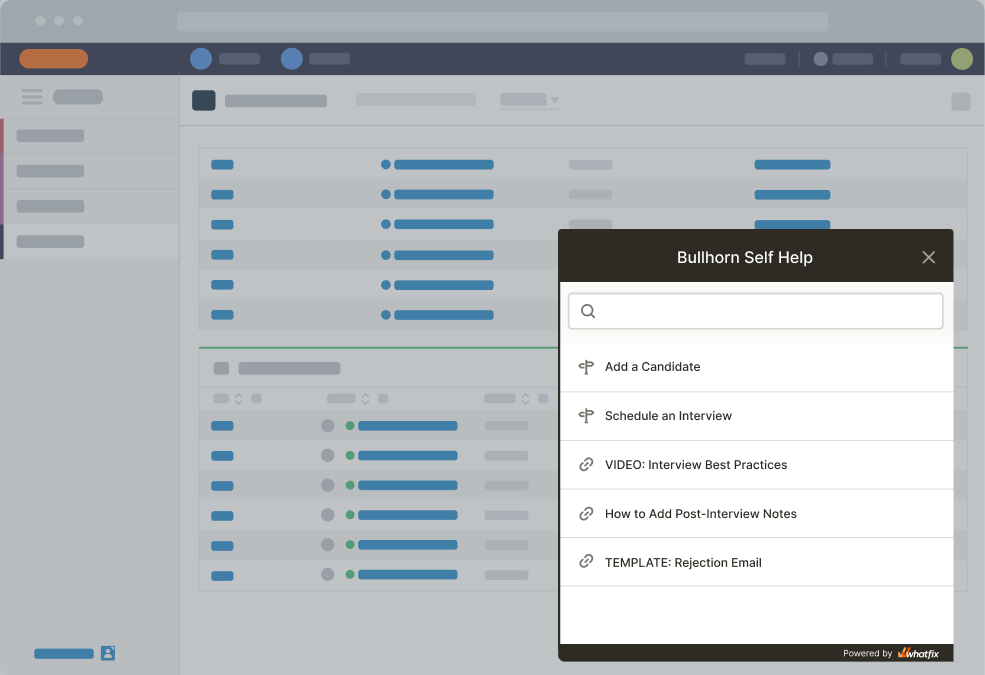
With Whatfix, ManpowerGroup kept team members productive while also upskilling them to master ATS-related tasks, which helped the company maximize its ATS ROI and achieve its business outcomes.
Jill Busch, Director of L&D at ManpowerGroup, said, “The in-system training is a game changer. Whatfix helped us move toward using more current and innovative training solutions. We strongly value innovation as an organization, including innovating how we learn.”
Reception to Whatfix was so positive that ManpowerGroup’s global leaders view Whatfix’s DAP as an effective employee training solution across its various business units and teams – providing additional in-app support and communication to employees for deadline reminders and new training alerts with Smart Tips and Pop-Ups.
Upskilling Clicks Better With Whatfix
Companies invest in new technologies to improve business processes and save time and money. However, if your employees are wasting too much time learning about those new technologies, you might get a very low return on your investment. Employees are also resistant to new technology when you’ve not created a culture of constant learning and innovation.
Whatfix integrates with your new technologies to show employees how to use technology to its full potential and produce better business results. DAPs break the resistance barriers by training your employees with interactive walkthroughs, giving them better access to information through Self Help, and guiding them through processes when they need help.
Ready to get started? Request a demo today!