Digital Transformation & Tech Adoption by Sector (2024)
Explore digital transformation across the largest business sectors to find how new technology is evolving the way industries operate, enable employees, and provide better customer experiences. See which industries are adopting new digital technologies faster, and which are falling behind.
- Published:
- Updated: July 2, 2024
-
 Levi Olmstead
Levi Olmstead
What industries are leading digital transformation and tech adoption?
McKinsey Research recently found that the US economy is only operating at 18% of its digital potential – an estimated $2 trillion hit to the economy. Research also shows that this isn’t because of a reluctance to invest in new digital technologies; instead, its because of a gap in digital literacy and usage, with causes including the need for digital upskilling, poor end-user enablement, and lack of contextual support – among a range of other factors.
But which sectors are driving digitalization spend and tech adoption at the fastest pace? This depends on how you define digital transformation – and what factors you look at.
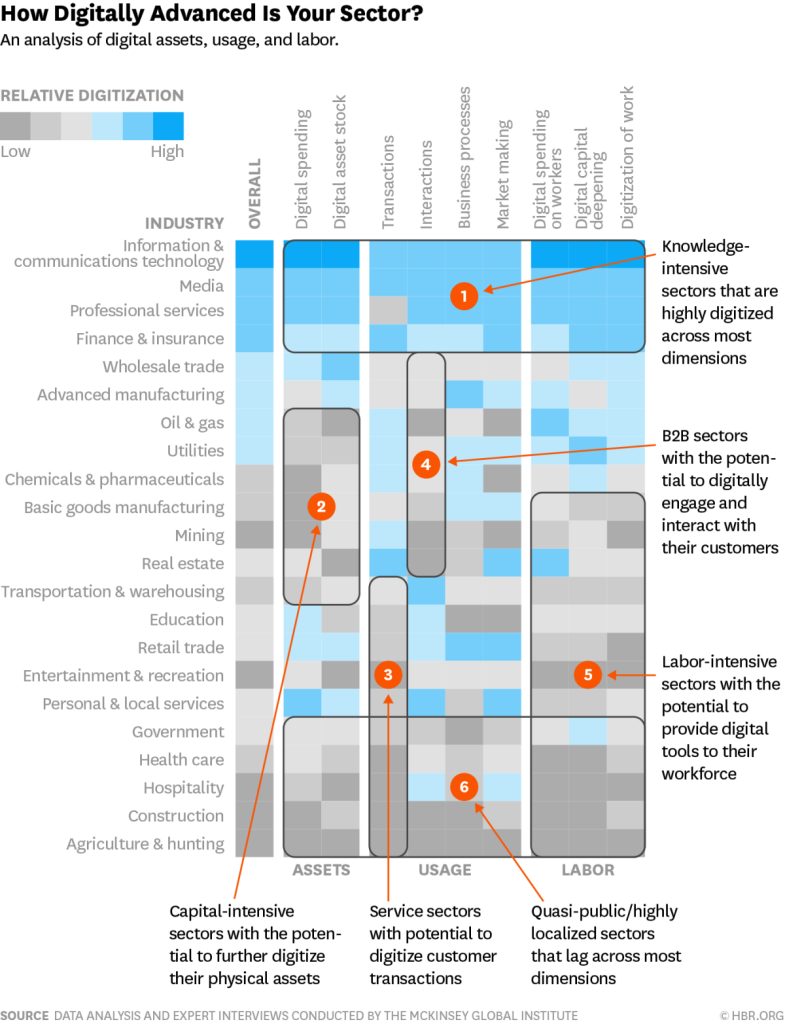
Research from McKinsey and HBR conducted a thorough digital maturity analysis across 22 sectors, looking at nine factors such as digital spending, business processes, digitalization of work, customer interactions, target buyer personas, transactions, and more – across three broad categories including digital assets, digital usage, and labor.
| Category | Factors |
| Assets |
|
| Usage |
|
| Labor |
|
Below you can see a graphic on how digitally advanced each sector is across multiple factors and considerations:
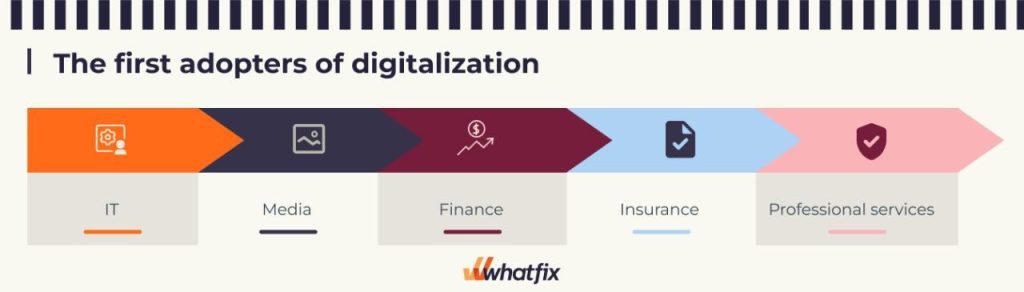
What sectors are the first adopters for digitalization?
The research found that the IT technology sector leads all industries, following by media, finance and insurance, and professional services. These four sectors have developed a culture of digital enablement that drives end-user adoption and usage, widened their offerings, enabled self-service, and more.
IT, media, and insurance and finance all outpaced the average rate of digitalization across every factor. Professional services outpaced the digitalization average in all but one factor (transactions).
What sectors are technology adoption laggards?
The research also found that the government and public sector, healthcare, hospitality, construction, and agriculture were the five industries most behind on digital adoption efforts and digital adoption programs.
These five sectors are known to be less innovative and slower to respond to market changes than its counterparts. Government for example relies on public funding and isn’t granted the ability to be as lean and experimental in its operations, while healthcare and agriculture both are heavily regulated. An older workforce also plays a role here, as well as overall less digital spending and resources.
In fact, the only factor that these five sectors outpaced the average rate of digitalization was government and the public sector for digital capital deepening.
There is also a growing gap between organizations in the same industry, with the most digital companies in outpacing their legacy counterparts. It found that individual companies within laggard sectors could still be digitally mature and a case study for other companies to model their digital efforts.
Video Source: McKinsey’s ‘How Digitalized is the United States?’

Explore digital transformation and adoption by sector
Agriculture
Digital transformation of agriculture refers to how farmers and agriculture-centric companies utilize new technologies to improve operations, become more sustainable, and build better food systems and supply chains. Examples of agriculture digitalization include remote sensing, GPS technologies, AI-powered systems, SPS systems, and more.
By the numbers:
- According to the McKinsey and HBR report, agriculture and hunting is the least digitalized sector, scoring a 1 (the worst) across every category and factor.
- Adoption of automated guidance has increased sharply in the past 20 years, with application on well over 50% of the acreage planted to corn, cotton, rice, sorghum, soybeans, and winter wheat
- As of 2020, the market value of smart agriculture worldwide will reach nearly $20B.
- 85% of farmers have implemented at least one precision agriculture technique, such as GPS technology or remote sensing.
Automotive
Digital transformation of the automotive industry refers to how car manufacturers and dealerships are innovating with digital technologies. Examples of automotive digitalization include self-driving cars, dealer management systems, AR/VR showroom experiences, and more.
By the numbers:
- The automotive revenue pool will significantly increase and diversify toward on-demand mobility and data-driven services. This could create up to $1.5T in additional revenue potential in 2030, compared with about $5.2T from traditional car sales and aftermarket products and services in 2015.
Banking
Digital transformation in banking is essential, but research shows that only 30% of banks have successfully implemented their digital strategy. Examples of new technologies driving digitalization in banking include online banking portals, predictive analytics, self-service banking, etc.
By the numbers:
- According to the McKinsey and HBR report, the banking, finance, and insurance is one of the most digitalized sectors, outscoring the average digitalization score in every factor and scoring a digitalization score of 4.5 (average: 3.025).
- The global digital banking platform market size is expected to grow from $8.2B in 2021 to $13.9B in 2026 at a CAGR of 11.3%.
- As for the customers using digital banking, a study by Statista predicts that 2.5B individuals will utilize online banking services by 2024.
- However, only 30% of banks that have undergone a digital transformation report successfully implementing their digital strategy
Casino & Gambling
Digital transformation in the casino and gambling industry refers to technology improvements across casino property operations and gamer experience. Examples of casino transformation include customer loyalty apps, online and mobile gambing, improved security and verification, and more.
By the numbers:
- The total market size for the online gambling sector grow is around $63.53B and is expected to double over the next few years.
Construction
Digital transformation in construction refers to new technology investments across construction job sites and construction-based organizations. Examples include building information modeling (BIM) systems, construction management software, aerial drones, automation, and more.
By the numbers:
- According to the McKinsey and HBR report, construction is the second least digitalized sector, scoring an average of 1.375 across sectors (average: 3.025).
- The construction sector is one of the least digital industries, yet employees 7% of the world’s working-age population.
- Digitalization of the construction sector can result in productivity gains of 15% and cost reductions of 6%.
Energy & Utilities
Digital transformation in energy and utilities refers to how new technologies are enabling better reliability, improved operations, sustainability, better customer experiences, and grid resiliency. Examples include self-service customer portals, data analytics to optimize employee productivity, automated maintenance, predictive analytics, and more.
By the numbers:
- Surprisingly, energy and utilities outpaces the average rate of digitalization across 7 of 9 factors – scoring a digitalization score of 3.5 (average: 3.025).
- By 2025, 40% of energy and utility companies will face a 50% increase in capital demands triggered by resource scarcity and soaring demands.
Engineering & Architecture
Digital transformation in the engineering and architecture sector refers to how new technologies are changing the way architecture and engineering firms operate more efficiently, reduce costs, and provide better customer service. Examples include project management software, CAD software, enterprise architecture (EA) tools, APIs, self-service customer experiences, and more.
By the numbers:
- Only 13% of architecture firm executives say that they’re getting the business value they expected from their IT and technology spending.
- According to research firm Gartner, the enterprise architecture sector is experiencing annual revenue growth up to 30% with more direct control of IT departments and into more democratized technology environments.
Fashion
Digital transformation in the fashion sector refers to how digital tech is improving fashion enterprises operations, improving supply chains, and provide more personalized self-serve customer experiences. Examples of digitalization of fashion include e-commerce marketing automation platforms, using data for personalized shopping experiences, mobile app shopping, supply chain management systems, AI-powered customer support, and more.
By the numbers:
- Digital investments from fashion brands into new technologies are expected to rise to 3.5% of their revenue in 2022, up from 1.7% in 2021.
- The global market for online fashion is expected to grow from $498.7 million in 2021 to $4.8 billion by 2031 at a CAGR of 26.4%.
Financial Services & Wealth Management
Digital transformation in financial services refers to integrating emerging technologies into financial institutions. It changes how financial service companies operate, service customers, and empower employees. Examples of digital transformation in wealth management and financial services include robotic process automation (RPA), brokerage trading platforms, financial advisor CRMs, wealth management apps, and more.
By the numbers:
- According to the McKinsey and HBR report, the banking, finance, and insurance is one of the most digitalized sectors, outscoring the average digitalization score in every factor and scoring a digitalization score of 4.5 (average: 3.025).
- IT spend in the financial services sector exceeded $500B globally 2021, up from $440B in 2018.
- 56% of financial services leaders reported a decrease in costs, while 51% said revenues had risen and 42% said profits had grown – all as a result of next-gen technologies and transformation efforts.
Government & Public Sector
Digital transformation in the public sector refers to how technology improves government operations, citizen experience, spend transparency, and more. Examples of digital adoption in the public sector include self-service portals for citizens and businesses, open-data platforms, electronic document management, and more.
By the numbers:
- According to the McKinsey and HBR report, the public sector lags behind more digital sectors, with an average digitalization score of 2.5 (average: 3.025).
- 91% of government agency leaders called 2022 a success for their modernization efforts, yet 71% said there is still work to be done.
- 46% of public sector CIOs are actively trying to improve legacy systems with digital transformation efforts.
Healthcare
Digital transformation in healthcare refers to the impact of emerging technologies on healthcare operations, patient experience, and overall quality of care. Examples of healthcare digital transformation include electronic healthcare record (EHR) systems, patient portals, virtual visits, predictive analytics in diagnostics, and more.
By the numbers:
- According to the McKinsey and HBR report, even with COVID-19 advancing digital transformation, healthcare is still one of the least digitalized sectors, with an average digitalization score of 1.875 (average: 3.025).
- 96% of hospitals had adopted an EHR by 2021, up from 28% in 2021, while office-based physican adopting EHRs grew from 34% to 78% in the same period.
- The top desired outcome from digital transformation (92%) for healthcare providers is achieving a better patient experience.
Higher Education
Digital transformation in higher education refers to the impact of new software and technology on higher-education institution operations, student experience, campus management, and more. Examples of higher education transformation include student portals, online student recruitment, student information systems (SIS), classroom management systems, and more.
By the numbers:
- According to the McKinsey and HBR report, higher education is slightly behind the average digitalization pace, with a score of 2.375 (average: 3.025).
- 69% of higher education institution leaders cite digital transformation as their biggest challenge.
- 89% of higher-ed leaders said their institution needs to be more digital.
Hospitality
Digital transformation in the hospitality sector refers to the impact of emerging technologies like big data and cloud computing on hotel operations, guest experience, and enabling hospitality employees. Examples of hospitality transformation include hotel operations software, guest experience apps, hospitality CRMs, hotel property management systems, and more.
By the numbers:
- According to the McKinsey and HBR report, the hospitality industry is a tech laggard with an average digitalization pace, with a score of 1.875 (average: 3.025).
- Only 7% of operators say their current tech systems are fully integrated.
- The same report found that while 60% of hospitality operators have a dedicated role for digital transformation and strategy, 80% lack a set digital budget and 63% feel like they haven’t invested enough resources.
Insurance
Digital transformation in insurance refers to how insurance technology improves all aspects of P&C insurance including insurance operations, claims management, policyholder experience, and more. Examples include claims management software, fraud detection systems, insurance analytics in pricing, policyholder portals, and more.
By the numbers:
- According to the McKinsey and HBR report, the banking, finance, and insurance is one of the most digitalized sectors, outscoring the average digitalization score in every factor and scoring a digitalization score of 4.5 (average: 3.025).
- 96% of insurance CEOs accelerated their digitalization efforts after COVID, primarily focusing on customer-centric experiences like self-service and online portals.
- 75% of insurance c-suite leaders report a positive ROI from digital investments and strategy.
K-12 Education
Digital transformation in K-12 education refers to how digitalization and new technologies impact the classroom on student learning experiences, administration operations, and classroom management. Examples of K-12 digitalization include student information systems (SIS), digital learning platforms, generative AI in the classroom, and more.
By the numbers:
- According to the McKinsey and HBR report, K-12 education is slightly behind the average digitalization pace, with a score of 2.375 (average: 3.025).
- 34% of educators and K-12 administration use data to inform learning strategy implementation, 33% use tech to track student behavior objectives and progress, and 28% use tech to reinforce positive classroom behavior.
- 30% of K-12 education leaders said that digital transformation and tech adoption was the biggest challenge facing their district in 2023.
Law Firms & Legal
Digital transformation in the legal sector refers to how law firms are going digital by adoption new technologies to improve their operations, reduce costs, and provide better experiences and representation to their customers. Examples include contract management software, eDiscovery platforms, client portals, enterprise legal management (ELM) software, predictive analytics, online advertising personalization, and more.
By the numbers:
- While over half of the world’s top law firms increased their IT and technology spend in 2022, all 100 top law firms are considered digital laggards compared to enterprises in other industries.
- 80% of people surveyed are more likely to do business with organizations that provide a personalized content experience, and only 3% of the law firms tested show signs of personalization on their websites.
Logistics, Shipping, & Transportation
Digital transformation in logistics, shipping, and transportation refer to how using emerging digital technologies like big data, automation, and cloud computing to improve operations, provide better customer experiences, make better decisions, reduce risks, and innovate. Examples include using big data to predict sales data and understand trade lane information, customer-facing self-service experiences, using AI to improve the supply chain, CRMs, supply chain management software, and more.
By the numbers:
- According to the McKinsey and HBR report, the transportation sector is average in its digitalization with a score of 2.875 (average: 3.025)
- 72% of leaders from enterprise logistic companies said there is not only an ignorance of digitalization, but also a lack of roadmap in terms of what needs to be done
- In the same report, 76% of leaders from enterprise logistic companies any freight and logistics company not focusing on building digital capabilities will seriously endanger their business
- In the same report, 75% of logistics leaders said they still have a large percentage of analog, manual office administration processes, including processing jobs, warehouse operations and accounting.
Manufacturing
Digital transformation in manufacturing refers to how technology is changing on manufacturing companies operate, automate administrative processes, provide better customer experiences, and improve overall efficiency. Examples of manufacturing digitalization include robotic process automation (RPA), 3D printing, automation of knowledge work, predictive analytics for forecasting, mobile apps for frontline workforce management, ERPs, RFID tracking, and more.
By the numbers:
- According to the McKinsey and HBR report, advanced manufacturing outpaces the average rate of digital adoption with a digitalization score of 3.75 (average: 3.025).
- Gartner research reported that 80% of manufacturing company CEOs increased digital tech investments to counter economic pressures in 2023 like inflation, supply chain issues, and the talent shortage.
- Forrester Consulting research found that 90% of manufacturing leaders believe a digital transformation strategy is critical for their company’s success.
- Foundry’s Digital Business Study reported that 89% of all manufacturing companies have adopted a digital-first business model or have a plan to implement digital transformation initiatives in the near future.
Media & Entertainment
Digital transformation in the media and entertainment industry refers to how new technologies and software are reshaping business models, improving business processes, providing better customer experiences, etc. Examples of digitalization in media include personalized customer experiences, streaming services, automation of manual tasks and processes, online subscriptions, content management systems, AR/VR, and more.
By the numbers:
- According to the McKinsey and HBR report, media is the second best tech adopter with a digitalization score of 5 (average: 3.025).
- A report from MediaSense found that 40% of media-based businesses are now at least 70% of the way through the transformation of their media model.
- According to the same MediaSense research, most media businesses (73%) say “driving performance” is the most important reason behind their media transformation, followed by “agility” (53%) and “cost savings” (47%).
Nonprofits
Digital transformation of nonprofit organizations refers to using technology to improve operations, streamline processes, provide better donor experiences, and make data-driven decisions. Examples of nonprofit digitalization include nonprofit CRMs, donor management systems, online events, big data for effective and targeted campaigns, and more.
Oil & Gas
Digital transformation of the oil and gas sector refers to the integration of technologies like cloud computing, automation, and big data to streamline operations, provide better customer experiences, optimize production, reduce risk, and improve modeling accuracy. Examples of oil and gas industry digitalization include AI-powered safety management, predictive maintenance, oil product software, exploration software, manufacturing execution systems (MES), and more.
By the numbers:
- According to the McKinsey and HBR report, the oil and gas sector is average in its digitalization with a score of 2.875 (average: 3.025)
- 58% of oil and gas leaders said COVID-19 made investing in digital technology more urgent, with a majority planning to invest a great deal (29%) or a moderate amount (51%) relative to their total budget.
- The same report found that across 200 leading oil and gas companies, only 7% called themselves a “digital champion”, showing the lack of digital maturity in the sector.
Pharma
Digital transformation in pharma refers to how pharmaceutical companies are updating legacy systems and manual processes with new technologies to improve operations, provide better patient experiences, and revolutionize drug development. Examples of big pharma digitalization include quality management systems (QMS), regulatory information management (RIM) systems, e-clinical platforms, patient portals, digital pills, and more.
By the numbers:
- According to the McKinsey and HBR report, the pharmaceutical sector slightly outpaces normal digitalization with a score of 3.125 (average: 3.025)
- 55% of pharma firm leaders report implementing new digital transformation projects to some degree.
- Certain digital technologies like cloud computing (49%), AI (38%), data lakes (33%), and wearables (33%) have been adopted in day-to-day pharma operations.
- 70% of pharma leaders say their organization views digital innovation as a major competitive differentiator.
Professional Services
Digital transformation in professional services refers to how professional services firms are implementing emerging technologies to automate manual processes, improve internal operational, provide better client and customer services, and innovate their business models. Examples of professional services digitalization include billing management systems, client portals, CRMs, resource management systems, and more.
By the numbers:
- According to the McKinsey and HBR report, professional services is the third faster tech adopter with a digitalization score of 4.625 (average: 3.025).
- Only 29% of professional services leaders reported being confident in their organizations digital transformation roadmap.
- Salesforce reports that 1/3rd of professional services firms expect 75% or more of their revenue will come from digital over the next three years, tripling their expectations from 2019.
- PwC found that 56% of professional service firm CFOs believe tech investments made during COVID left their company better off in the long run.
Property Management
Digital transformation in property management refers to how modern technology is changing how property management companies operate and provide tenant experiences. Examples of property management digitalization include self-service tenant portals, property management software, document management systems, online listing platforms, and more.
By the numbers:
- 80% of property management companies plan to increase their technology budgets despite experiencing operational challenges related to new tech.
- 62% of property managers say technology helps to creatively solve problems.
- 72% of property management companies have adopted some form of PropTech in their operations, an increase from just 48% in 2020.
Real Estate
Digital transformation in real estate and real estate tech adoption refers to how the real estate sector is integrate new technology to modernize its operations, automate manual processes, enable home buyers and sellers with better experiences, use big data, and more. Examples of real estate digitalization include real estate CRMs, online self-service lending, MLS databases, AI-powered appraisals, and more.
By the numbers:
- 69% of commercial real estate leaders say that technology as a strategic agenda is a high priority.
- 61% of commercial real estate companies admit their firms’ core technology infrastructures still rely on legacy systems, but 50% are trying to modernize.
- 58% of real estate companies say they already have a digital strategy.
Retail
Digital transformation in retail refers to implementing new software and emerging technologies into business workflows to improve customer experiences, optimize operations, automate manual processes, and build more agile, future-proof business models. Examples of retail digitalization include implementing POS systems, personalized shopping experiences, supply chain managemgent software, dropshipping, self-service checkout, branding mobile apps, and more.
By the numbers:
- According to the McKinsey and HBR report, retail slightly outpaces traditional sector digitalization with a score of 3.125 (average: 3.025)
- Gartner found that 57% of retail companies plan to spend more on software and new tech in 2024 and they will prioritize marketing and IT investments.
- The same report found that 49% of retailers regret at least one software purchase made over the last year.
- The same report found that the biggest reasons for digital tech failure is difficulty training and onboarding end-users (36%) and lack of tech support (31%).
Staffing
Digital transformation in staffing refers to how software and emerging technologies are empowering staffing companies to improve operations, automate manual processes, improve customer and client experience, and rethink business models. Examples of staffing digitalization includes application tracking systems (ATS), AI-powered resume screenings, client portals, and more.
By the numbers:
Telecommunications
Digital transformation in the telecommunications sector refers to how the integration of software and new technologies are improving customer experiences, optimizing operations, automating processes, and innovating product lines. Examples of telcom digitalization includes virtual assistants, robotic process automation (RPA), CRMs, 5G, IoT, edge computing, predictive analytics for maintenance, and more.
By the numbers:
- BCG found that only 22% of telcos have successfully delivered a digital transformation.
- The same report shows that 62% of telecom providers had created value from digital transformation efforts but had not met their total target or achieved long-term outcomes.
- IDC found that telecom provider leaders believe AI and 5G are the two most promising digital technologies but also rated them the two most difficult to implement.
What leaders need to know about digital adoption
Whatfix DAP Features
Across these DAP use cases, we referred to various Whatfix features. Here, learn more about each of these DAP features to understand how organizations are enabled to create frictionless in-app experiences.
Flows
Flows (commonly known as interactive walkthroughs) enable end-users with step-by-step guidance on their contextual digital processes and workflows.

Pop-Ups
Pop-Ups overlay on the entire application screen and require the end-user to engage with the Pop-Up to close it. Pop-Ups can welcome new end-users to an application, announce company or team news, alert end-users to a process change or new feature, and more. With Pop-Ups, organizations can embed a video, link a third-party resource, or prompt an in-app guided experience.
Self Help
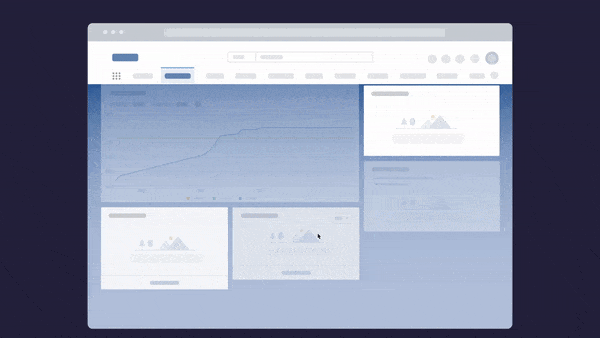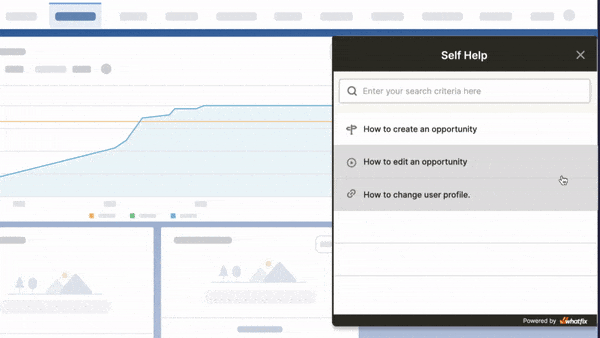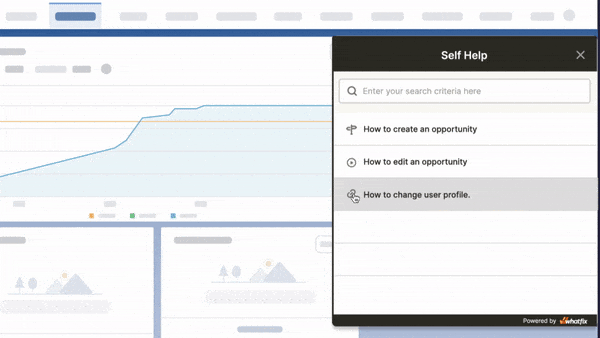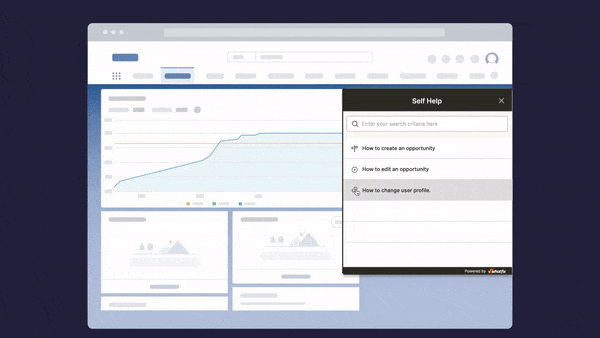
Smart Tips
Smart Tips provide additional context and information to end-users with in-app tooltips. Smart Tips appear as pop-ups over on application modules or elements and can include links to additional information (like SOPs or best practices) and can prompt in-app guidance.
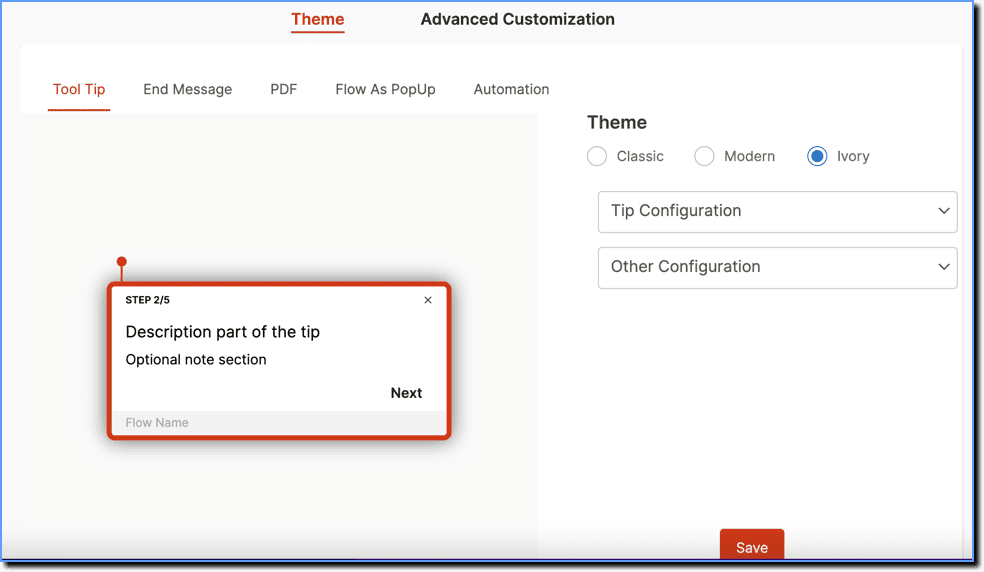
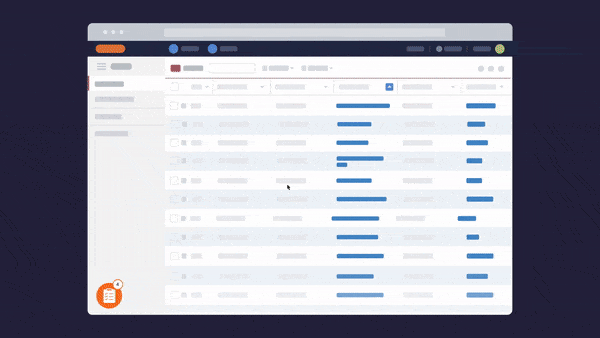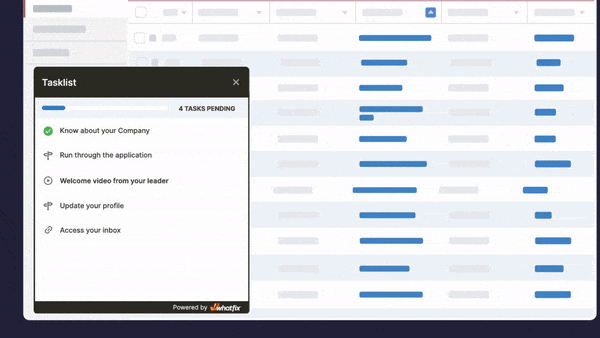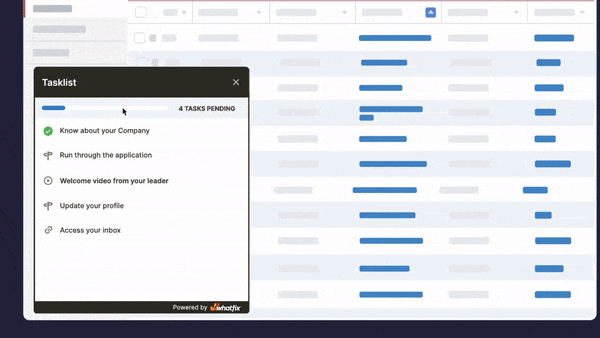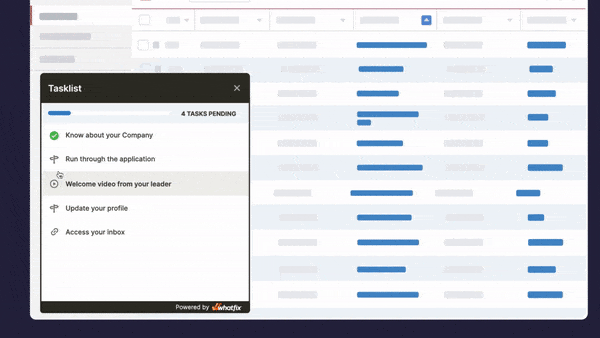
Task Lists
Task Lists are end-user checklists used during application onboarding and times of change, providing end-users with a list of mandatory or recommended first action items to complete in an application, such as setting up an account, engaging with the product tour, completing a first task, or using a specific feature. Task Lists help reduce time-to-proficiency for new users and guide them to their “aha!” moment.
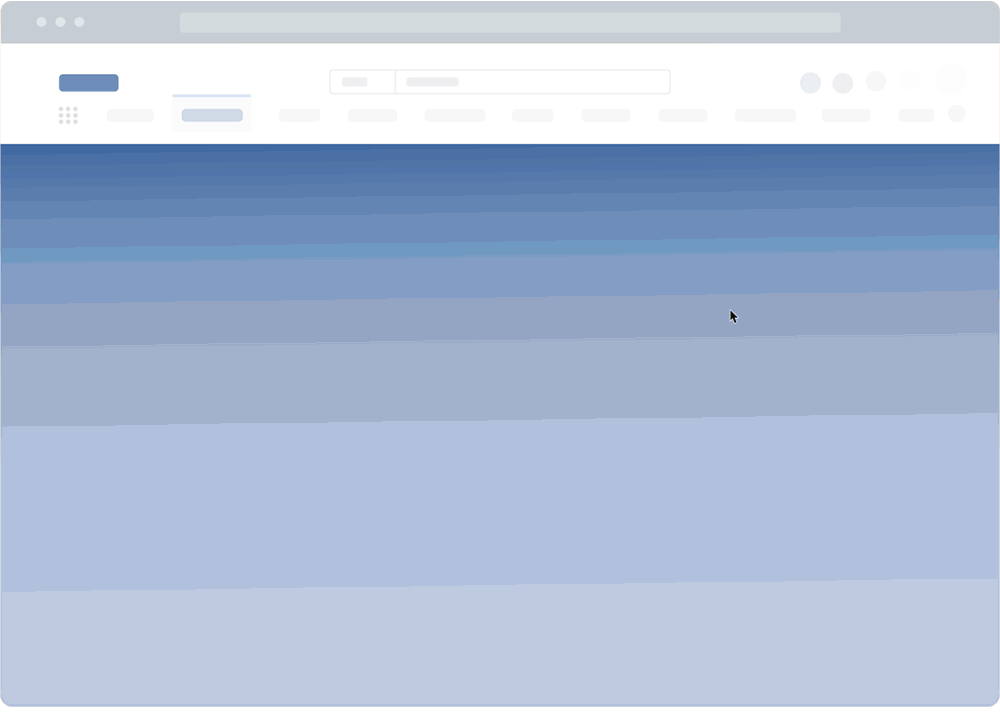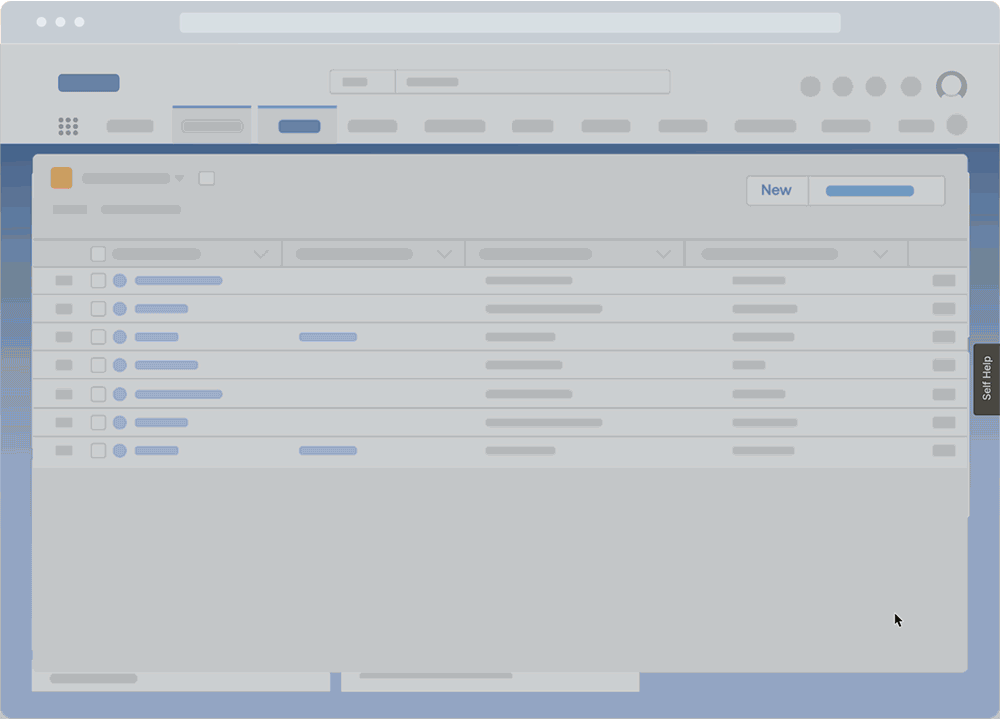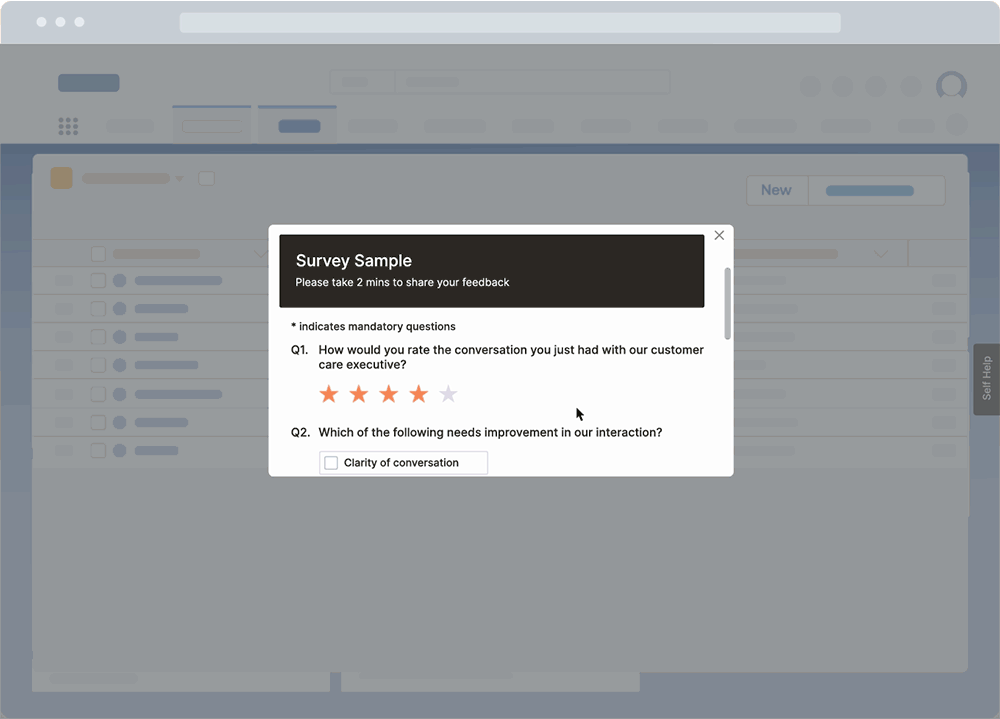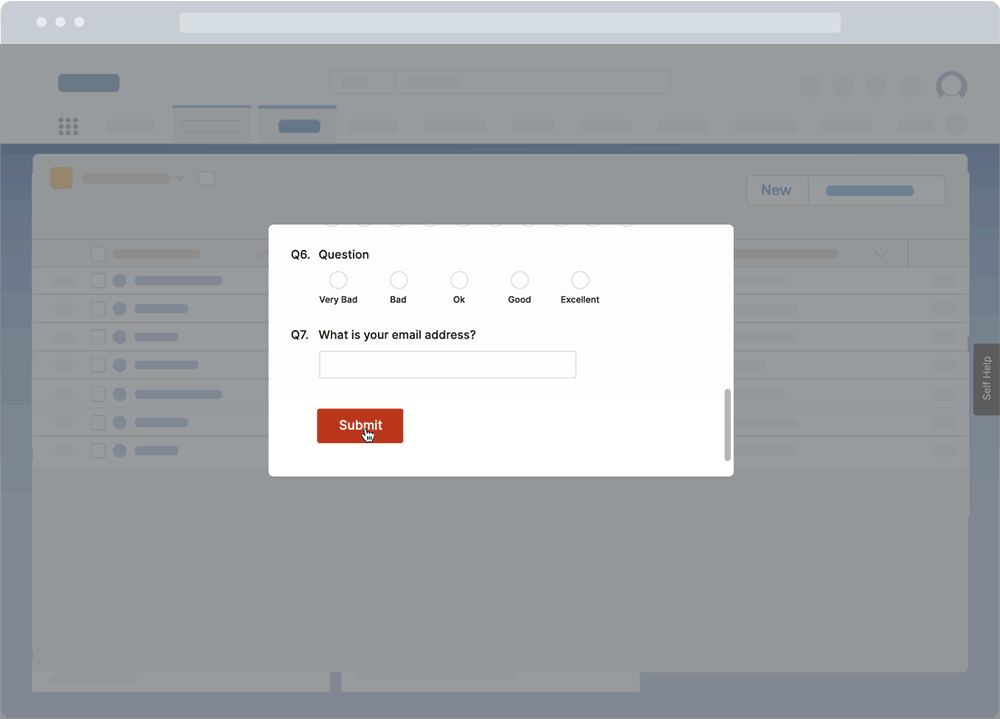
Surveys
Whatfix Surveys provides a no-code solution to creating and launching on-brand in-app surveys to collect end-user feedback. Surveys can be simple eNPS/NPS surveys, gather feedback on recent changes, run post-training and onboarding surveys, and more.
Analytics
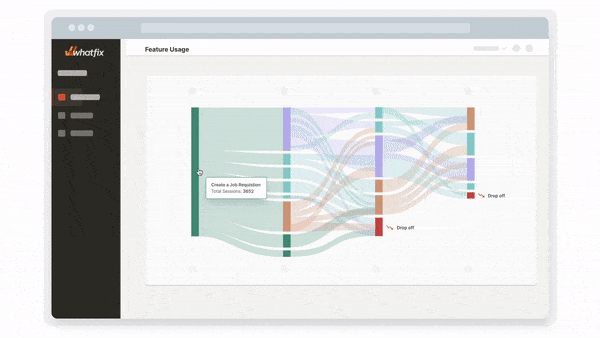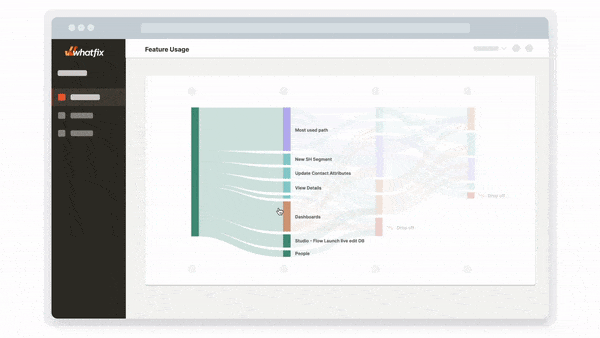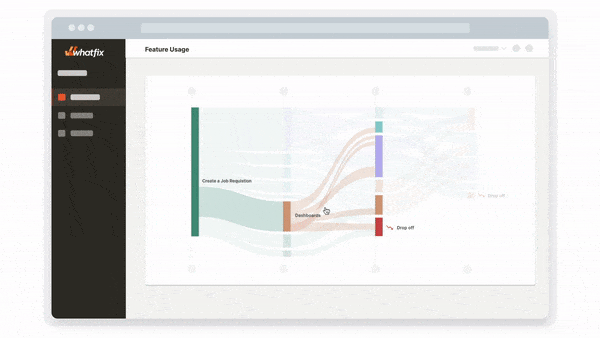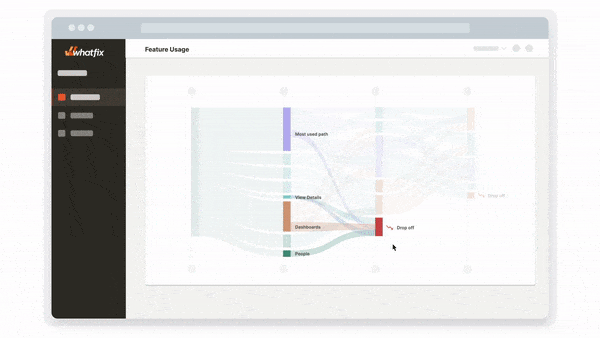
Whatfix Analytics provides a no-code event tracking solution to monitor and analyze end-user behavior across your software and digital processes. Track in-app clicks, page visits, mouse interactions, and more to identify areas of end-user friction, optimize digital processes, gain an understanding of feature and workflow adoption, and use data to make software and technology-related decisions.
Enterprise Insights
Enterprise Insights enables organizations with the ability to track, visualize, and analyze applications, workflows and processes across your application stack, as well as adoption rates and engagement data across your enterprise and its department units. This data enables IT and business leaders to gain visibility into software license utilization and adoption, as well as end-user engagement metrics, of all business-critical enterprise applications and processes. This empowers enterprises to remove productivity blockers, create frictionless digital workflows, and drive overall efficiency in your organization.
Thank you for subscribing!